The Chain Rule
If \(y=f\left ( u \right )\) and \(u=g\left ( x \right )\) are both differentiable functions, then \(y=f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )\) is differentiable and
\(\frac{dy}{dx}\cdot \frac{dy}{du}\cdot \frac{du}{dx}\)
or, equivalently,
\(\frac{d}{dx}\left [ f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right ) \right ]={f}’\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right ){g}’\left ( x \right ).\)
The Power Chain Rule
If n is any real number and \(u=g\left ( x \right )\) is differentiable, then
\(\frac{d}{dx}\left ( u^{n} \right )=nu^{n-1}\frac{du}{dx}\)
or, equivalently,
\(\frac{d}{dx}\left [ g\left ( x \right ) \right ]^{n}=n\left [ g\left ( x \right ) \right ]^{n-1}\cdot {g}’\left ( x \right ).\)
Example 1
- Find \(\frac{dy}{dx}\) for \(y=\sqrt{x^{4}-2x+5}.\)
Answer/Explanation
Solution
\(\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{2}\left ( x^{4}-2x+5 \right )^{1/2}\frac{d}{dx}\left ( x^{4}-2x+5 \right )\) Power Chain Rule
\(=\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x^{4}-2x+5}}\cdot \left ( 4x^{3}-2 \right )\)
\(=\frac{2x^{3}-1}{\sqrt{x^{4}-2x+5}}\)
Example 2
- Find \({h}”\left ( x \right )\) if \(h\left ( x \right )=f\left ( x^{3} \right ).\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution
\({h}’\left ( x \right )={f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )\frac{d}{dx}\left ( x^{3} \right )\) Chain Rule
\(={f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )\cdot \left ( 3x^{2} \right )\)
\({h}”\left ( x \right )={f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )\frac{d}{dx}\left ( 3x^{2} \right )+\left ( 3x^{2} \right )\frac{d}{dx}{f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )\) Product Rule
\(={f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )\left ( 6x \right )+\left ( 3x^{2} \right ){f}”\left ( x^{3} \right )\frac{d}{dx}\left ( x^{3} \right )\) Chain Rule
\(={f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )\left ( 6x \right )+\left ( 3x^{2} \right ){f}”\left ( x^{3} \right )\left (3 x^{2} \right )\)
\(=6x{f}’\left ( x^{3} \right )+9x^{4}{f}”\left ( x^{3} \right )\)
Exercises – The Chain Rule and the Composite Functions
Multiple Choice Questions
- If \(f\left ( x \right )=\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}\), then \({f}’\left ( x \right )=\)
(A) \(\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}}\) (B) \(\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{2\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}}\) (C) \(\frac{2\sqrt{x}}{4\sqrt{x+\sqrt{x}}}\) (D) \(\frac{2\sqrt{x}+1}{4\sqrt{x^{2}+x\sqrt{x}}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1. D
2. If \(f\left ( x \right )=\left ( x^{2}-3x \right )^{3/2}\), then \({f}’\left ( 4 \right )=\)
(A) \(\frac{15}{2}\) (B) 9 (C) \(\frac{21}{2}\) (D) 15
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2. D
3. If f , g , and h are functions that is everywhere differentiable, then the derivative of \(\frac{f}{g\cdot h}\) is
(A) \(\frac{g h {f}’-f {g}’ {h}’}{g h}\)
(B) \(\frac{gh{f}’-fg{h}’-fh{g}’}{gh}\)
(C) \(\frac{gh{f}’-fg{h}’-f{g}’h}{g^{2}h^{2}}\)
(D) \(\frac{gh{f}’-fg{h}’+fh{g}’}{g^{2}h^{2}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3. C
4. If \(f\left ( x \right )=\left ( 3-\sqrt{x} \right )^{-1}\), then \({f}”\left ( 4 \right )=\)
(A) \(\frac{3}{32}\) (B) \(\frac{3}{16}\) (C) \(\frac{3}{4}\) (D) \(\frac{9}{4}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
4. A
Free Response Questions
Questions 5-9 refer to the following table.
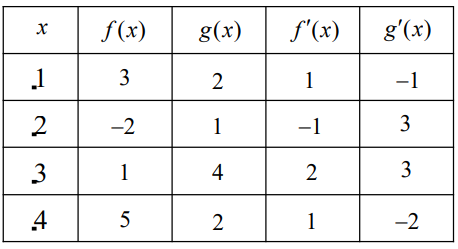
The table above gives values of f , f ′ , g , and g′ at selected values of x .
5. Find \({h}’\left ( 1 \right ), if h\left ( x \right )=f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right ).\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
5. 1
6. Find \({h}’\left ( 2 \right )\), if \(h\left ( x \right )=xf\left ( x^{2} \right ).\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
6. 13
7. Find \({h}’\left ( 3 \right )\), if \(h\left ( x \right )=\frac{f\left ( x \right )}{\sqrt{g\left ( x \right )}}.\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
7. \(\frac{13}{16}\)
8. Find \({h}’\left ( 2 \right )\), if \(h\left ( x \right )=\left [ f\left ( 2x \right ) \right ]^{2}.\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
8. 20
9. Find \({h}’\left ( 1 \right )\), if \(h\left ( x \right )=\left ( x^{9}+f\left ( x \right ) \right )^{-2}.\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
9. \(-\frac{5}{16}\)
10. Let f and g be differentiable functions such that \(f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )=2x\) and \({f}’\left ( x \right )=1+\left [ f\left ( x \right ) \right ]^{2}.\)
(a) Show that \({g}’\left ( x \right )=\frac{2}{{f}’\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )}.\)
(b) Show that \({g}’\left ( x \right )=\frac{2}{1+4x^{2}}.\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
10. (a) \(f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )=2x,\frac{d}{dx}\left [ f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right ) \right ]=\frac{d}{dx}\left [ 2x \right ]\Rightarrow {f}’\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )\cdot {g}’\left ( x \right )=2\Rightarrow {g}’\left ( x \right )=\frac{2}{{f}’\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )}\)
10. (b) \({f}’\left ( x \right )=1+\left [ f\left ( x \right ) \right ]^{2}\Rightarrow {f}’\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )=1+\left [ f\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right ) \right ]^{2}=1+\left [ 2x \right ]^{2}=1+4x^{2}\)
Therefore, \({g}’\left ( x \right )=\frac{2}{{f}’\left ( g\left ( x \right ) \right )}=\frac{2}{1+4x^{2}}.\)
