Question
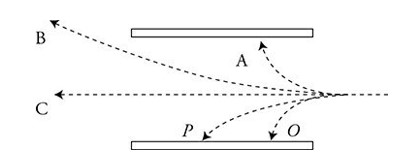
A beam of various particles is launched into the space between two oppositely charged parallel plates as shown in the figure. It is known that the particles are all traveling at the same initial velocity as they enter the region, and that particle P is a proton. What else can be inferred?
(A) Particle A could be a -particle.
(B) Particle B could be an a-particle.
(C) Particle Chas too much mass to be affected by the external force field.
(D) Particle D could be an electron.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A—Particle A bends in the opposite direction with a tighter radius, indicating that it is negative with a smaller mass. A §-particle would satisfy these requirements. Particle B must be negative and have a larger mass. All charges would be affected in some way by the electric field; thus particle C must have no charge. Particle D must be positive and have a smaller mass than a proton. Perhaps it is a positron?
Question
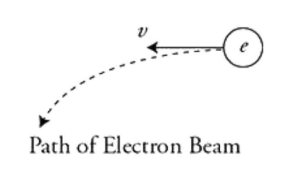
In an experiment, a scientist sends an electron beam through a cloud chamber and observes that the electron accelerates in a downward direction at a constant rate as shown in the figure. Which of the following could the scientist conclude?
(A) Earth’s gravitational field is causing the beam to change direction.
(B) A uniform electric field is causing the beam to change direction.
(C) A uniform magnetic field is causing the beam to change direction.
(D) The electron beam collided with another particle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Since the acceleration is constant in direction, this cannot be a collision or a force from a magnetic field. The electron mass is very small, so any gravitational acceleration on the election will be too small to see in a cloud chamber. However, a uniform electric field could easily produce this parabolic trajectory effect.
Question
Two identical, uncharged, nonconducting spheres hang vertically from insulating strings and are a distance of 10 cm apart, as shown in the figure above. The spheres are then each given a net charge; sphere A gets\( -10 \mu C\) and sphere B gets \(-20 \mu C\). The spheres are allowed to come to rest in a new equilibrium configuration.
Consider a position P located halfway between the charged spheres in their new equilibrium configuration. Which of the following correctly indicates whether the electric potential at this position is positive, negative, or zero and explains why?
(A) Zero, because without a charge at position P no electric potential can exist there.
(B) Zero, because both spheres are located the same distance from position P, so the contributions from each charge cancel each other out.
(C) Positive, because both negatively charged spheres contribute a negative electric potential, and these negatives multiplied together produce a net positive electric potential.
(D) Negative, because both negatively charged spheres contribute a negative electric potential to the total.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
