Question
As the angle of incidence for a ray of light passing from glass to air increases, the critical angle of incidence for the glass
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) increases and then decreases
(D) remains the same
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(D)
The critical angle is set by the ratio of the indices of refraction.
Question
Which of the following can produce polarized light? Select two answers.
(A) A liquid crystal display (LCD)
(B) Reflection
(C) Refraction
(D) Fluorescent bulbs
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(A) and ( B )
LCD by nature of the long-chain molecules involved emit polarized light. Reflected light can be partially or completely polarized depending on the angle.
Question
A ray of light is incident from a slower medium (smaller than the critical angle) to one that is faster. The refracted ray will
(A) not refract at all
(B) refract toward the normal
(C) refract away from the normal
(D) “refract” at 90 degrees such that it does not actually enter the faster medium
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(C)
Rays going from slow to fast mediums refract away from the normal up until the critical angle, at which point no more refraction occurs.
Question
Light of wavelength λ in a vacuum has what wavelength in a material with index of refraction n?
(A) \(nλ\)
(B) \(\frac{ n}{ λ}\)
(C) \(\frac{ λ}{ n}\)
(D) \(\frac{ n}{c λ}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: (C)
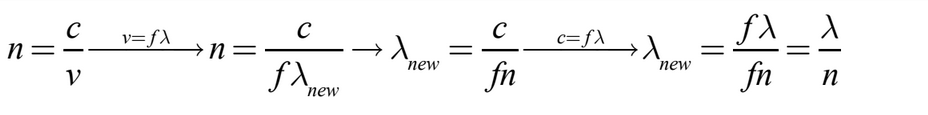
Question
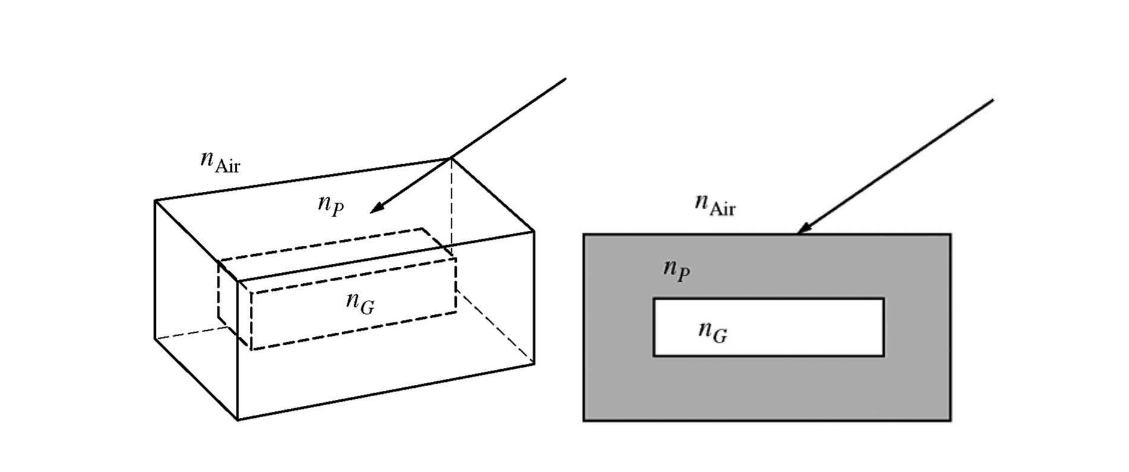
Students in a lab group are given a plastic block with a hollow space in the middle, as shown in the figures above. The index of refraction\(n_p\) of the plastic is known. Th e hollow space is filled with a gas, and the students are asked to collect the data needed to find the index of refraction \(n_g\) of the gas. e arrow represents a light beam that they shine into the plastic. They take the following set of measurements:

The three measurements are shared with a second lab group. Can the second group determine a value of \(n_g\) from only this data?
(A) Yes, because they have information about the beam in air and in the plastic above the gas.
(B) Yes, because they have information about the beam on both sides of the gas.
(C) No, because they need additional information to determine the angle of the beam in the gas.
(D) No, because they do not have multiple data points to analyze.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
