Question
A comet moves in an elliptical orbit around the Sun. Which of the following is at a maximum when the comet is at its farthest distance from the Sun?
(A) Kinetic energy of the comet
(B) Speed of the comet
(C) Acceleration of the comet
(D) Gravitational potential energy of the Sun- comet system
(E) Total energy of the Sun-comet system
Answer/Explanation
Questions (a)-(c)
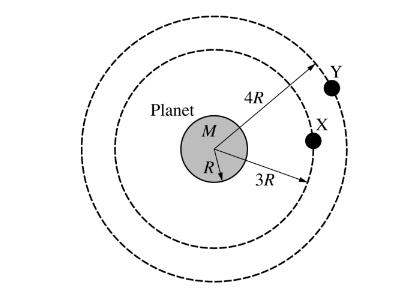
Identical satellites X and Y of mass m are in circular orbits around a planet of mass M. The radius of the planet is R. Satellite X has an orbital radius of 3R, and satellite Y has an orbital radius of 4R. The kinetic energy of satellite X is\( K_X\) .
In terms of \(K_X\) , the gravitational potential energy of the planet-satellite X system is
(A) \(−2K_X\)
(B) \(−K_X\)
(C) \(− K_X /2\)
(D) \(K_X /2\)
(E) \(2K_X\)
Answer/Explanation
Question(b)
The kinetic energy of satellite X is\( K_X\) . The kinetic energy of satellite Y is \(K_Y \). The ratio \(K _X /K_ Y\) is
(A) 1 /4
(B) 3 /4
(C) 1 /1
(D) 4/ 3
(E) 4 /1
Answer/Explanation
Question(c)
Satellite X is moved to the same orbit as satellite Y by a force doing work on the satellite. In terms of\( K_X\) , the work done on satellite X by the force is
(A) \(−K_X/ 2\)
(B) \(−K_X/ 4\)
(C) 0
(D) \(+K_X/ 4\)
(E) \(+K_X/ 2\)
Answer/Explanation
Question
A satellite is in a circular orbit such that itstays directly over the same point on Earth’s equator. Which of the following must be true for the satellite?
I. It must have a specific mass.
II. It must have a specific altitude.
III. It must have a specific angular velocity.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(E)I, II, and III
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Setting the centripetal force on the satellite equal to the gravitational force between the satellite and Earth and substituting\( F_C=F_g\)
\( \frac{mv^2}{r}=G\frac{Mm}{r^2}\)
\ (\omega ^2=G \frac{M}{r^3}\)
