Practice Paper 1
(Solved)
General Instructions
Time : 2 Hours
Max. Marks : 40
1. There are 11 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2.
, Question no. 1 to 3 is a Case Based Questions, which has four MCQs/Questions. Each question carries one mark.
Section A
3.
, Question no. 4 to 8 are Short Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 2/3 marks.
Section B
4.
, Question no. 9-11 are Long Answer Type Questions. Each question carries 5 marks.
Section C
5. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. Students have to attempt
only one of the alternatives in such questions.
As exact Blue-print and Pattern for CBSE Term II exams is not released yet. So the pattern of this
*
paper is designed by the author on the basis of trend of past CBSE Papers. Students are advised
not to consider the pattern of this paper as official, it is just for practice purpose.
Section A
1. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to (iv) given below
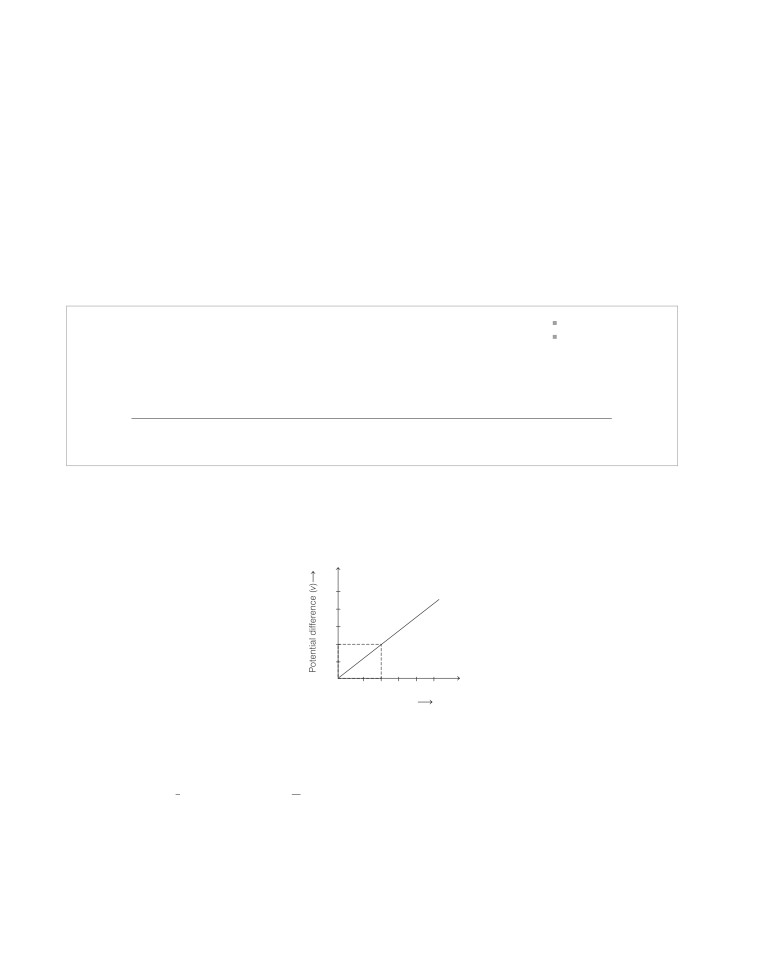
A student wants to study the dependence of potential difference (V)on current (I)flowing across a resistor.
He plotted a graph by taking I along X-axis and V along Y-axis of all his observations.
Y
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
X
0.2
0.4
0.6 0.8 1.0
Current (I)
(i) The value of resistance used in the circuit is
(a) 1 Ω
(b) 2 Ω
(c) 4 Ω
(d) 0.5 Ω
(ii) The inverse of the slope of V-Icurve gives
(a) resistance
(b) conductance
(c) reactance
(d) resistivity
(iii) The correct representation of Ohm’s law is
1
(a) V
∝1
(b) I ∝
(c) V ∝ I
(d) I ∝ V
I
V
(iv) His friend noticed some observations from this demonstration as follows
1. The slope of the line gives the resistance of a conductor.
2. Motion of electrons through a conductor is retarded by its resistance.
3. All conductors do not obey Ohm’s law.
Which of the following observation(s) is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Or
3.
Read the following and answer the questions from
What is the use of the variable resistor in the circuit in
(i) to (iv) given below
the Ohm’s law experiment shown below?
Sex-determination is the method by which
distinction between males and females is
established in a species. The sex of an individual is
A
determined by specific chromosomes. In human
beings, it is determined as follows
Sperms
Egg
V
and
X
Y
X
I. To change the voltage across the fixed resistor.
X X
X Y
II. To change the resistance across the fixed resistor.
III. To change the current flowing through the fixed
(i)
In XX-XY type of sex-determination,
resistor.
(a) females produce two different types of gametes
(a) Only I
(b) Only III
(b) males produce two different types of gametes
(c) I and III only
(d) I, II and III
(c) female produces gametes with Y-chromosome
(d) male produces gametes with X-chromosome only
2.
Read the following and answer the questions from
(i) to (iv) given below
(ii)
A couple has six daughters. What is the possibility
of them having a girl child next time?
In modern periodic table, some properties show a
(a) 10%
(b) 90%
(c) 100%
(d) 50%
regular trend when we move along a period from
left to right or in a group from top to bottom.
(iii)
Number of chromosome present in the egg cell of a
human female is
Atomic size refers to the radius of an atom. It may
(a) 23 pairs
(b) 23
be visualised as the distance between the centre of
(c) 22
(d) 22 pairs
the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated
atom. It is measured in picometres.
(iv)
Choose the incorrect statement from the following
set of statements.
About 75% of all elements in one periodic table are
metals. The most common metal found in the
I. XX-XY type of sex-determination is the example of
male heterogamety.
Earth’s crust is aluminium. The non-metals also are
some of the most abundant elements in the
II. XX-XY type of sex-determination is the example of
universe including the Earth’s crust, the
female heterogamety.
atmosphere and the human body.
III. There are always 50% chances of having a baby girl
The position of three elements A, B and C in the
child.
periodic table are shown below
IV. Changes in the non-reproductive tissues can be
passed on to the DNA of the germ cells.
Group 16
Group 17
Codes
—
—
(a) I and III
(b) II and IV
—
A
(c) III and IV
(d) I and III
—
—
Or
Sex of human child is determined by
B
C
(a) size of the egg
(b) size of the sperm
(i) State whether A is a metal or non-metal.
(c) type of the sperm
(d) type of the egg
(ii) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive
than A.
Section B
(iii) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B?
4. Choose the kind of chemical bonding (ionic bond,
(iv) Which type of ion- cation or anion, will be formed
covalent bond, both ionic and covalent bonds)
by A?
present in the following compounds. Potassium
Or
chloride, magnesium oxide, sulphuric acid,
ammonium hydroxide, zinc sulphide, phosphorus
What are metalloids? Give examples.
trichloride (PCl
)
[2 M]
3
Or
Section C
Write the name and structure of a saturated
compound in which the carbon atoms are
9.
(i) Which is the better way to connect lights and other
arranged in a ring. Give the number of single
appliances in domestic circuit, series connection or
bonds present in this compound.
[2 M]
parallel connection? Justify your answer.
(ii) An electrician has made electric circuit of a house in
5.
Differentiate between pollen tube and style.
[2 M]
such a way that, if a lamp gets fused in a room of the
6.
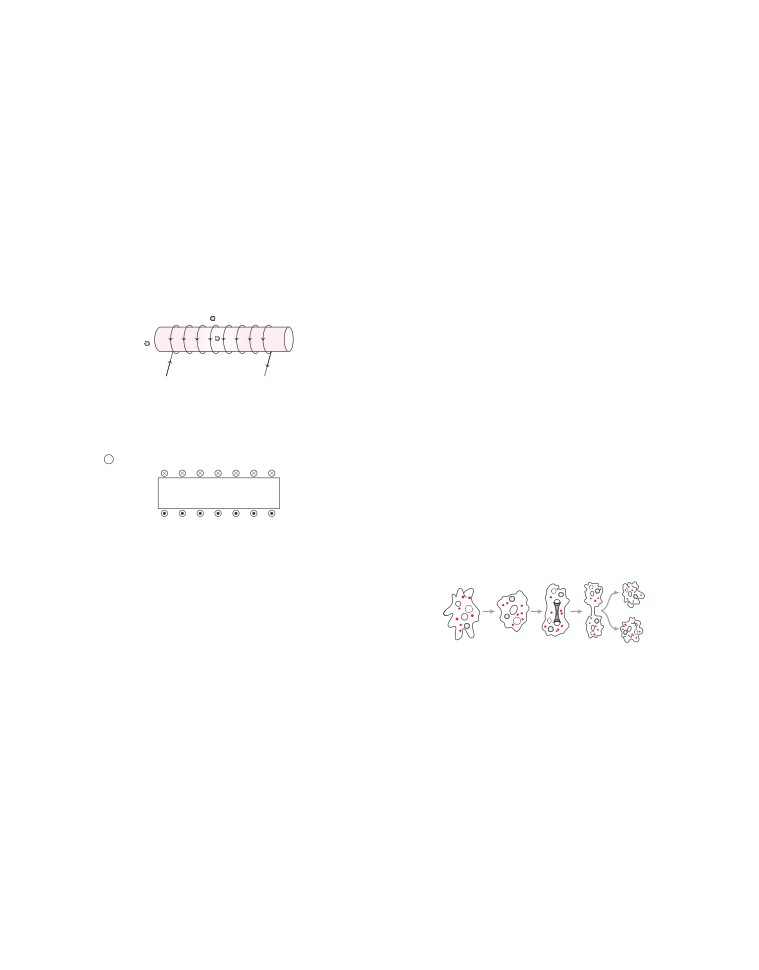
For the current carrying solenoid as shown below,
house, then all the lamps in other rooms of the
draw magnetic field lines and give reason to
house stop working. What is the defect in this type
explain that out of the three points A, B and C at
of circuit wiring? Give reason.
which point, the field strength is maximum and at
Or
which point, it is minimum.
Three incandescent bulbs of 100 W each are
B
connected in series in an electric circuit. In another
set of three bulbs of the same wattage are connected
A
in parallel to the source.
C
(i) Will the bulb in the two circuits glow with the same
I
I
[3 M]
brightness? Justify your answer.
Or
(ii) Now, let one bulb in both the circuits get fused. Will
Diagram shows the lengthwise section of a current
the rest of the bulbs continue to glow in each circuit?
carrying solenoid.
Give reason.
⊗ Indicates current entering into the page,
10.
Differentiate between monohybrid and dihybrid
crosses with the help of an example.
• Indicates current emerging out of the page.
Or
A
B
Explain the term ‘regeneration’ as used in relation to
reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how
regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms
Decide which end of the solenoid A or B, will
like Hydra?
behave as North pole. Give reason for your
11.
(i) How can pregnancy be prevented surgically?
answer. Also, draw field lines inside the
solenoid.
[3 M]
(ii) Study the diagram given below
7.
Give an example of each of the following
(i) A carbon compound containing two double
bonds.
(ii) A molecule in which central atom is linked to
three other atoms.
(a) Identify the process.
(iii) A compound containing both ionic and covalent
bonds.
[3 M]
(b) Which organism uses the above method for
reproduction?
Or
(c) How is the above method different from the
Define homologous series. Examine it with an
process of fragmentation?
example. Will there be any change in their physical
properties? Give reason for your answer.
[3 M]
Or
(i) Why should biodegradable and non-biodegradable
wastes be discarded in two separate dustbins?
8. Give any three points of differentiation between
(ii) Why do we exemplify crop fields as artificial
acquired and inherited characters with one
ecosystem?
example each.
[3 M]
Explanations
1.
(i)
(a) The slope of V-I graph gives resistance.
(ii)
(d) When a sperm having an X-chromosome fuses with
the egg, the zygote formed will develop into a female
0.4
−
0
0.4
∴ Resistance =
=
= 1Ω
baby whereas when a sperm having Y-chromosome
0.4
−
0
0.4
fuses with the egg, the zygote formed will develop into
(ii)
(b) The inverse of the slope of V-I curve gives
a male baby. Thus, there are always 50% chances of
conductance. i.e.
having a girl child by the couple.
1
1
(iii)
(d) Gametes are haploid in nature, i.e they contain half
=
= Conductance (σ)
Slope Resistance(R)
the number of chromosomes as compared to other
somatic cells. Human beings have 23 pairs of
(iii)
(d) The correct representation of Ohm’s law is I ∝ V. It
chromosomes. Therefore, the egg cell (gamete) contains
states that current flowing through the conductor is
23 chromosomes only.
directly proportional to the potential difference
(iv)
(b) Statements II and IV are incorrect and can be
applied across the conductor.
corrected as
(iv)
(d) All the observations are correct. The slope of the
● XX-XY type of sex-determination shows male
line in V-I graph gives the resistance of a conductor
heterogamety and female homogamety.
whereas motion of electrons through a conductor is
● Changes in the non-reproductive tissues cannot be
retarded by its resistance.
passed on to the DNA of the germ cells.
All conductors do not obey Ohm’s law i.e., Ohm’s
Or (c) Sex of a human child is determined by the type of sperm
law is not universal.
(X or Y) that fuses with egg during fertilisation.
Or
(c)
Ohm’s law states that the resistance (ratio of the voltage
A sperm with an X-chromosome will produce a baby girl and
across the fixed resistor to the current flowing through
that with Y-chromosome will produce a baby boy on
it) is constant. The aim of Ohm’s law experiment is to
fertilisation.
find the resistance of a fixed resistor. By adjusting the
4.
variable resistor.
Covalent
Both ionic and
• the voltage across the variable resistor and fixed
Ionic bond
bond
covalent bond
resistor will change.
(i) Potassium chloride
Phosphorus
Sulphuric acid
• the total resistance in the circuit will change
trichloride
Ammonium
leading to a change in current flowing through the
(ii) Magnesium oxide
hydroxide
fixed resistor.
(iii) Zinc sulphide
2.
(i)
Since, A belongs to group 17 and has 7 valence
Or Cyclopropane
electrons so it is a non-metal because it will gain one
electron to complete its octet.
H
H
C
(ii)
C lies below A and belong to the same group. As we
H
H
move down a group, the size increases and
C C
H
H
electronegative character decreases. With the decrease
in electronegative character, the electron accepting
Cyclopropane contains three C⎯C single bond and six C⎯H
tendency and hence the reactivity of non-metals
single bond.
decreases, so C is less reactive than A.
Total 9 single bonds are present in cyclopropane.
(iii)
C and B both belongs to the same period therefore, C is
5. Differences between pollen tube and style are as follows
smaller than B in size because as we move left to right
in a period, atomic size decreases due to increased
Pollen Tube
Style
effective nuclear charge.
A tube growing out of pollen The middle elongated
(iv)
As discussed in that element A has a tendency to gain
grain when it reaches stigma. part of the carpel, i.e.
electron to complete its octet. It needs to take up one
female part of a flower.
electron, so it will form anion (A−).
It transports male gametes
The attachment of stigma
Or These are some elements which exhibit the properties
from pollen grains to ovules.
to the ovary.
of both metals and non-metals. These are called
metalloids. In modern periodic table, a zig-zag line
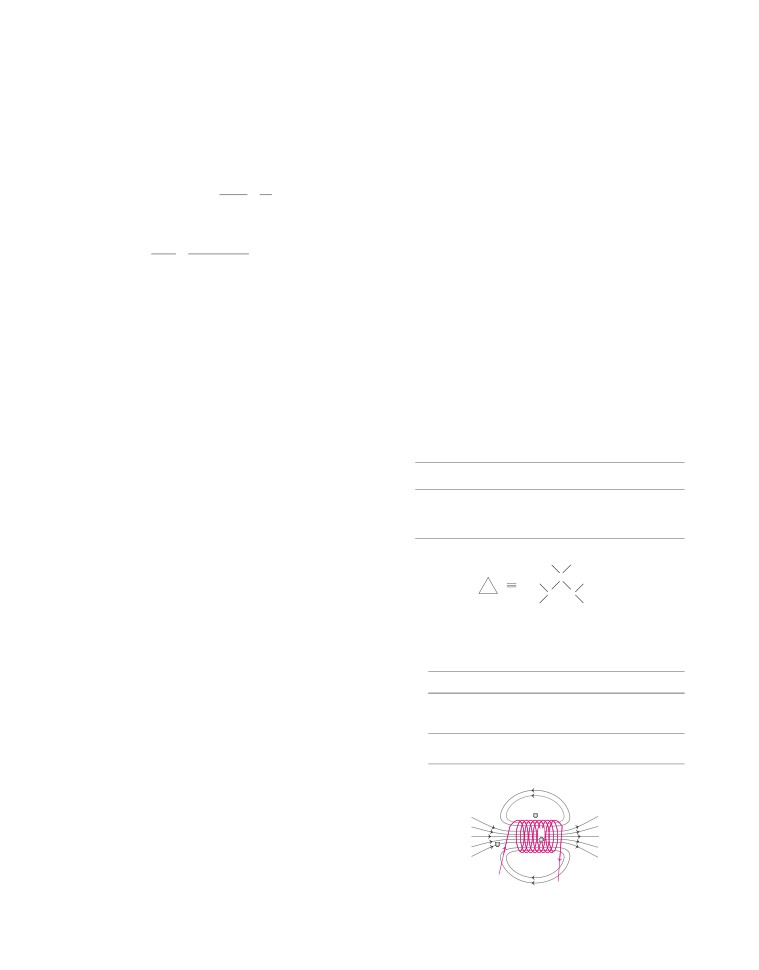
6. Magnetic field lines due to a solenoid
separates metals from non-metals.
The border line elements—boron, silicon, antimony are
B
intermediate in properties, so they are called mtalloids
or semi-metals.
A
3.
(i)
(b) In XX-XY type of sex-determination (human’s sex-
C
determination), the males produce two different types
of gametes, one contains X-chromosome whereas the
I
I
other contains Y-chromosome.
In case of an ideal solenoid, magnetic field strength is
9.
(i) Parallel connection is a better way to connect lights and
maximum at point A and is minimum or zero at point B. This
other appliances in domestic circuit.
is because the magnetic field is strong, where magnetic field
It is because
lines are crowded and is weak, where magnetic field lines
(a) when we connect a number of devices in parallel
are far apart. At the point C, the density of the field lines is
combination, each device gets the same potential
less than that of point A but greater than that of point B. So,
as provided by the battery and it keeps on
the order of magnetic field at points A, B and C is
working even, if other devices stop working.
B <B <B
B
C
A
(b) parallel connection is helpful when each device
Or From diagram, we can see that current is entering from A
has different resistances and requires different
and emerging out from B.
current for its operation as in this case the
current divides itself through different devices
unlike series connection.
A
B
(ii) Electrician has made series connection of all the lamps
in electric circuit of house because of which, if one
lamp gets fused, all the other lamps stop working.
This is due to the fact that when devices are connected
in series, then if one device fails, the circuit gets broken
Thus, using right hand thumb rule, direction of magnetic
and all the devices in that circuit stop working.
field lines is from B to A. We know that, magnetic field lines
Or
(i) Let us assume that the resistance of each bulb be R.
move from North to South direction. Thus, B represents
The circuit diagram in two cases may be drawn as given
North pole or A represents South pole.
below
B1
7.
(i) Carbon dioxide (CO2)
••
A1
(ii) Ammonia molecule (NH3) H — N— H
A
B2
B1
B2
B3
⏐
A2
H
B3
+
-
K
A3
(iii) Ammonium chloride (NH Cl)contains both ionic and
4
K
covalent bonds.
V
+
+
-
⎡
H
⎤
⎢
|
⎥
Equivalent resistance in series combination
−
⎢H⎯N⎯H⎥ Cl
RS =R+R+R =3R
, voltage = V
⎢
|
⎥
⎢
H
⎥
Let current through each bulb in series combination be I1.
V
Or A series of similarly constituted compounds in which the
By Ohm’s law, V = I
×3R
⇒ I
=
1
1
members present have the same functional group and
3R
similar chemical properties and any two successive members
∴Power consumption of each bulb in series combination,
2
2
in a particular series differ in their molecular formula by
V
⎞
P =I2(3R)
=⎜
⎟
×3R = V
×
3R
= V2
...(i)
(⎯
CH )unit, is called a homologous series, e.g. alkane
1
1
2
2
⎝ 3R⎠
9R
3R
series C H
n
2n+ 2 .
For parallel circuit, the resistance of each bulb = R
CH4
Methane
C H2
6
Ethane
Voltage across each bulb = V
C H
3
8
Propane
C H
4
10
Butane
[Q same voltage in parallel combination]
∴ Power consumption of each bulb in parallel combination
5
C H
12
Pentane
is given by
With increase in the molecular mass, a gradual change in
their physical properties is seen. e.g. The melting and
P2 = V2
…(ii)
R
boiling points increase with increasing molecular mass.
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
8. Differences between acquired and inherited traits are as
P
2
V2/R)
follows
= (
P
1
(
V2/3R)
Acquired Characters
Inherited Characters
2
R
3
⇒ V
×
=
3
⇒ P =3P
2
1
R V2
They develop in the organism They are received by the
during their lifetime.
organisms from their parents.
Therefore, each bulb in parallel combination glows 3 times
brighter than that of each bulb in series combination.
They do not bring any change They bring about certain changes
(ii) When one bulb gets fused then in series combination, the
in the genes of organisms.
in the genes of the organisms.
circuit gets broken and current stops flowing, whereas in
They are lost with the death of They are transferred to the next
parallel combination, same voltage continues to act on the
the individual, e.g. intelligence. generation, e.g. free and fused
remaining bulbs and hence other bulbs continues to glow
earlobes.
with same brightness.
10. Differences between monohybrid and dihybrid crosses are
Or
as follows
Regeneration is used in relation to reproduction because
Monohybrid cross between homozygous tall plant and
reproduction is the process by which a living organism is able
homozygous short plant is shown below
to produce new individuals of its own kind likewise
regeneration is the ability of some organisms to give rise to
Monohybrid cross A hybridisation cross in which
new organisms when the individual is cut or broken up into
inheritance of only one pair of
many pieces.
contrasting characters is studied.
It is seen in Hydra and Planaria.
Dihybrid cross
A cross in which inheritance of two
Regeneration in Multicellular Organism like Hydra
pairs of contrasting characters is
(i)
It is carried out by specialised cells.
simultaneously studied.
(ii)
When Hydra is cut or broken up into many pieces, these
specialised cells proliferate and make large number of
cells.
(iii)
From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes
to become various cell types and tissues.
(iv)
These changes take place in an organised sequence
referred to as development thereby making each piece
to grow into a separate individual.
Tall
Short
All tall offsprings
11.
(i)
When vas deferens in males are blocked surgically,
(TT)
× (tt)
(Tt)
sperm transfer is be prevented. Similarly, when
P×P
F1
Fallopian tubes are blocked in females the egg will
not be able to reach the uterus therby preventing
pregnancy.
(ii)
(a) The process in the figure depicts binary fission in
Amoeba, a method of asexual reproduction.
(b) Binary fission also occurs in Euglena and Paramecium,
etc.
(c) Differences between fission and fragmentation are as
Tall
Tall
Tall
Tall
Tall
Short
F1
F2
follows
(Tt)
×
(Tt)
(TT)
(Tt)
(Tt)
(tt)
Fission
Fragmentation
Dihybrid cross between pure breed of plants having Round
and Green seed and Wrinkled and Yellow seeds is shown
It is the division of parent
It is the division of
below
body into two identical
parent body into two
daughter cells.
or more small fragments.
Parents
RRyy
×
rrYY
(Round green)
(Wrinkled yellow)
It occurs in unicellular
It occurs only in
↓
↓
organisms or multicellular
multicellular organisms
Gametes
Ry
rY
organisms with simple body
with complex cellular
organisation.
organisations.
F1-generation
RrYy
e.g. Amoeba, Plasmodium
e.g. Spirogyra (algae)
(Round yellow)
(protozoan)
×
F1
F1
Or
(i)
Biodegradable materials are broken down by
microorganisms in nature into simple harmless
RY
Ry
rY
ry
F
substances. Non-biodegradable materials need a
2
RY
different treatment like heat and temperature for
disposal and hence, both should be discarded in two
RRYY
RRYy
RrYY
RrYy
different dustbins.
Ry
(ii)
Artificial ecosystems are those ecosystems which are
RRYy
RRyy
RrYy
Rryy
modified and managed by human beings.
rY
Crop fields are man-made. Here plants do not grow
RrYY
RrYy
rrYY
rrYy
naturally rather most of the plants are grown by humans
ry
according to the season, type of soil, etc.
RrYy
Rryy
rrYy
rryy
In crop fields, the land is managed, soil is prepared
Ratio
for sowing seeds, then irrigated and further
F2
-generation
315 round yellow
9
progress is also kept under observation for getting good
108 round green
3
yield.
101 wrinkled yellow
3
32 wrinkled green
1
This is why, crop fields are known as artificial ecosystem.
556 seeds
16