EXPLANATIONS
Objective Questions
10. (c) The structural formula of pentane C H
5
12 is
1. (c) Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of carbon
H
H
H
H
H
dioxide gas (CO )
2
in air (only 0.03%). Carbon also occurs in
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
the earth’s crust in the form of minerals like carbonates. It also
H⎯C⎯
C⎯
C⎯
C⎯
C⎯H
occurs in the form of fossil fuels, organic compounds, wood,
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
cotton and wool, etc.
H
H
H
H
H
2. (b) Oxygen atom has six (6) valence electrons. Thus, to
It contains 16 covalent bonds.
complete its octet, it forms double bond with another oxygen
11. (a) C H
3
8 isanalkanebecauseitresembleswiththegeneral
atom to get O2 molecule as
formula of alkane, i.e. C H
n
6
6 isbenzenewhichisa
cyclic ring having double bonds in alternate carbon atoms
C H
2
2 resembleswiththegeneralformulaofalkyneand
O
O
or O==O
C H
4
8 isanalkenebecausenumberofH-atomsaredoubleof
that of carbon atoms.
Shared electrons
12. (a) ‘Eth’ represents 2 carbon atoms and ‘yne’ shows presence
(covalent bond
of a triple bond. Thus, ethyne has the structural formula as
formation)
H⎯C ≡≡ C⎯ H. It is also known as acetylene.
3. (d) Electronic configuration of N (atomic number 7) isKL .
13. (c) Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bond in
2
5
their structure. Both (ii) and (iv) have double carbon-carbon
Therefore, it needs three more electrons to complete its
bonds in their structures.
octet. Each nitrogen atom shares three electrons to form a
14. (c) Benzene molecule contains alternate single and double
molecule of N2 as
bonds. Its formula is C H
6
6.
In structure (a), double bonds are not at alternate positions.
N
N
In structure (b), the formula is C6H
and in structure (d),
12
the formula is C H
6
8.
15. (a) Structure (i) is n-butane.
4. (c) Carbon has 4 electron in its valence shell, while hydrogen
Structure (iii) is iso-butane.
has one electron in its valence shell.
Since, molecular formula is same, only structures are
To complete their octet and duplet respectively, they form
different. So, (i) and (iii) are isomers while structure (ii) and
covalent bonds. Carbon utilises its 4 valence electron and
(iv) have molecular formula C H
4
8.
forms 4 covalent bonds with 4 hydrogen atoms, using one
16. (a)BothA and Rare true and Risthe correct explanationofA.
valence electron with each hydrogen atom.
Covalent compounds consist of molecules and not ions
5. (a) A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has only single bonds and
which can transfer charge.
these are covalent bonds.
17. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation
Lone pair
of A.
Diamond is not good conductor of electricity because of the
H×
N
× H or H — N — H
|
absence of free electrons.
×
H
H
18. (a)BothA and Rare true and Risthe correct explanationofA.
A graphite crystal consists of various layers of carbon atoms
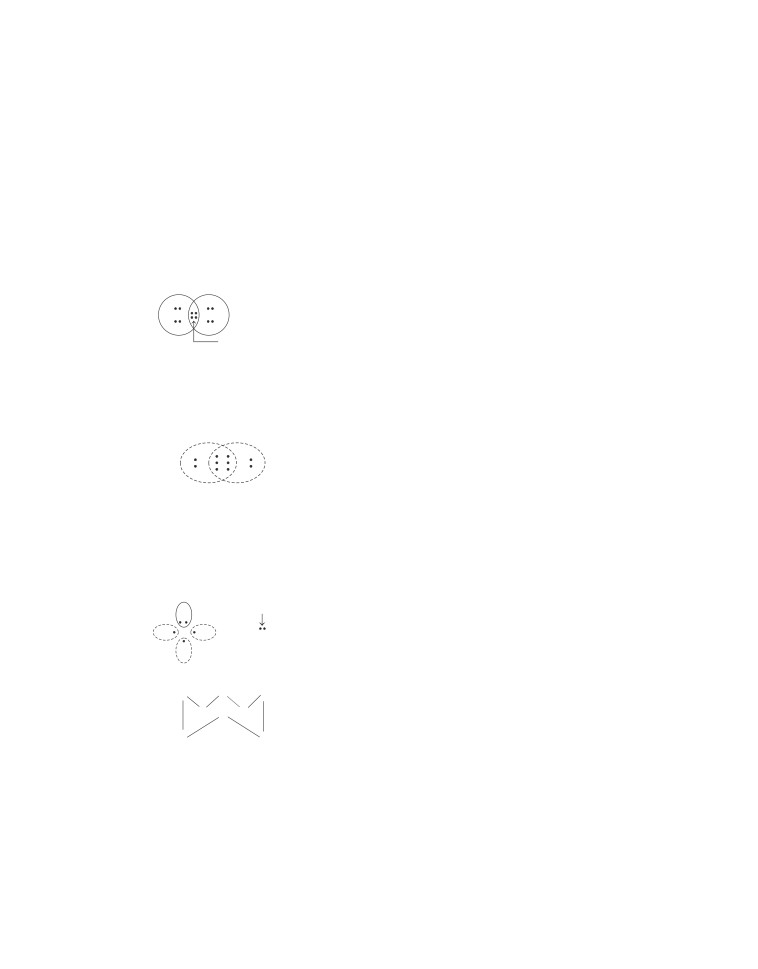
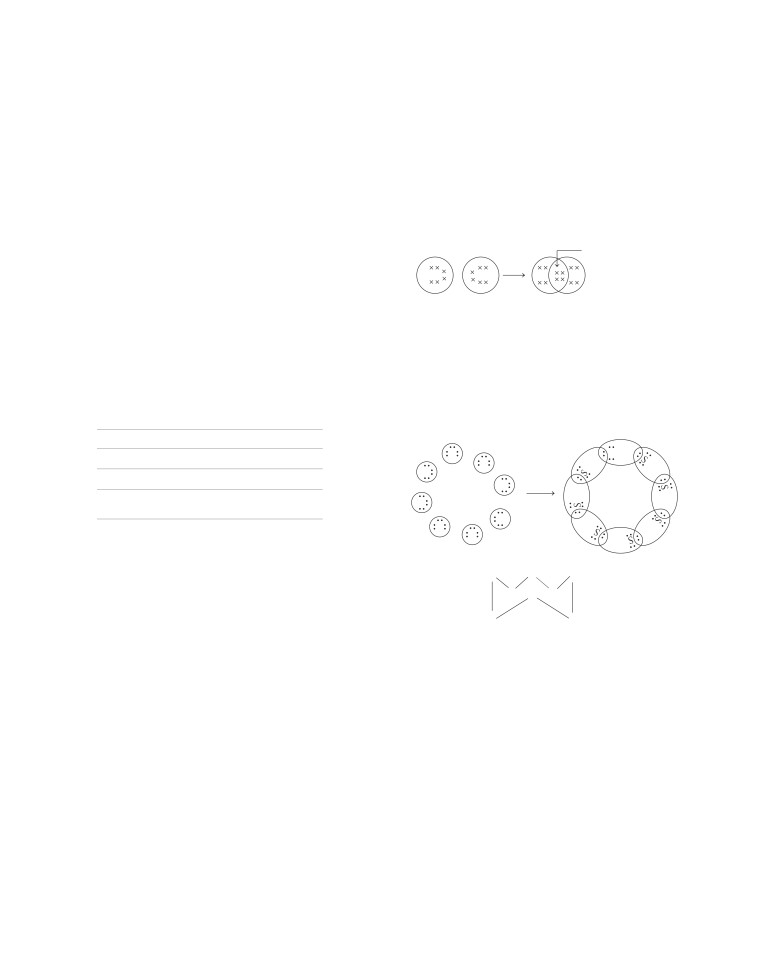
6. (b) 8 covalent bonds are formed in S molecule.
in which each carbon atom is joined to three other atoms by
S
S
S
strong covalent bonds. The various layers of carbon atoms in
S
S
graphite are held together by weak van der Waals’ forces
S
making it slippery to touch.
19. (a)BothA and Rare true and Risthe correct explanationofA.
S
S
Catenation is the bonding of atoms of the same element into
Crown shaped (S 8) molecule
a series, called as chain.
7. (d) Graphite can not be used for making insulated plates, as
Catenation occurs more readily with carbon, which forms
it is a good conductor of electricity.
strong covalent bond with other C-atoms to form long chains
8. (d) C, Si and Gebelongs to group 14 and their valency is 4.
and structures.
But oxygen has electronic configuration 2, 6. So, its valency
20. (a)BothA and Rare true and Risthe correct explanationofA.
is 2. Hence, it does not show tetravalency.
The alchohols have general formula of C H
n
2n + 1
OH. So, the
9. (b) Friedrich Wohler accidently prepared urea from
alcohols have the series of formula from the different
ammonium cyanate and the synthesis of urea discarded the
compounds with different between the succeeding and
vital force theory.
preceding molecules being a — CH2 — unit.
21.
(i)
(b)The structuresofthe following givencompoundsare:
(II) is the structure of diamond and (III) is the structure
I. SO2
II. N2
of Buckminster fullerene as their structure resembles
with geodesic domes.
O== S== O
N≡≡ N
(iv)
(b) In graphite, only three valence electrons are used
III. HCl
IV. NH3
for bond formation and hence fourth electron is free to
••
H⎯Cl
H⎯ N⎯ H
move which makes it a good conductor of electricity.
⏐
(v)
(d) Coke is an example of amorphous form of carbon
H
which is obtained as a residue in destructive distillation
∴ I, III and IV do not contain a triple bond. Hence,
of coal.
option (b) is correct.
Subjective Questions
(ii)
(a) O2 contains a double bond between it’s atoms.
1. Carbon shares it’s valence electrons with other atoms of
The structures of the given compounds are :
carbon or with atoms of other elements in order to complete
(a) O2 ⇒O == O
it’s octet. These shared electrons belong to the outermost
shells of both atoms and in this way, both atoms attain the
(b) N2 ⇒ N ≡≡ N
nearest noble gas configuration. This type of bonding is
H
called covalent bonding.
⏐
(c) CH4 ⇒ H ⎯ C ⎯H
2. The bonds that are formed by sharing electrons are known
⏐
as covalent bond. In covalent bonding, both atoms share the
H
valence electrons, i.e. the shared electrons belong to the
valence shells of both the atoms. CH Cl
3
is called
O
chloromethane, which contains 1 carbon atom, 3 hydrogen
(d) H O
⇒
2
atoms and 1 chlorine atom.
H H
K L
(iii)
(c) In chlorine molecule, both chlorine atoms
Electronic configuration of carbon, 6 = 2,
4
contribute one electron and thus share single electron
K
pair to form single covalent bond. As electrons are
Electronic configuration of hydrogen, 1 = 1
shared by both atoms, they acquire inert gas
K L M
configuration of argon atom in valence shell.
Electronic configuration of chlorine,17= 2
,
8
,
7
Carbon atom has four outermost electrons, each hydrogen
Sharing of
atom has one electron and chlorine has seven outermost
Cl Cl
Cl Cl
or Cl Cl or Cl — Cl
electrons
electrons. Carbon shares its four outermost electrons with
3 hydrogen atoms and 1 chlorine atom to form CH Cl
as
One shared electron pair
3
follows
(iv)
(c) The number of electrons shared between two atoms
to complete their octet is known as the covalency of
H
H
that atom. Therefore, the covalency of nitrogen is
three because it needs three electrons to complete it’s
3H + C + Cl
H
C
Cl
or H—C—Cl
octet.
H
(v)
(a) The shared pair of electrons constitute a single bond
H
between the two H-atoms, which is represented by a
single line between two H-atoms.
3. Atomic number of C = 6
K L
Electronic configuration =
,
2
4
H
×
× H
or H—H
Atomic number of O = 8
K L
Electronic configuration =
,
Single bond showing H molecule
2
2
6
To attain the stable electronic configuration, carbon needs
22.
(i)
(c) Each atom is covalently bonded to four other atoms,
4 electrons, while oxygen needs 2 electrons. So, in CO2, each
which in turn, are bonded to four more atoms. Thus, X
oxygen atom share two electrons from carbon. Thus, oxygen
is a giant molecule and has a structure similar to that of
diamond. Substance X is not a compound as it consists
and carbon both complete their octet.
of only one type of atoms.
Before
After
(ii)
(a) In the structure of diamond, carbon atoms are held
combination
combination Shared electrons
together by single covalent bonds as this is a rigid
three-dimensional network structure because each
O
C O
O C O
carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms.
(iii)
(d) (I) is the structure of graphite crystal which
or
O==C==O
consists of layers of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon
Carbon dioxide (CO )
2
molecule
atoms.
4. (i) The formation of calcium chloride with the help of
6. Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points
electron dot structure.
due to small intermolecular forces of attraction between the
Element
Atomic
Electronic
atoms.
number
configuration
7.
(i) Valency of each carbon atom in an alkane is four.
Calcium (Ca)
20
2, 8, 8, 2
(ii) Valency of each carbon atom in an alkyne is four.
8. Covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity
Chlorine (Cl)
17
2, 8, 7
because covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electrons
Cl
between atoms.
-
Ca2+
So, they don’t have a free electron that is required for
Ca
+
Cl
2
electricity transfer (electricity is the flow of free electrons).
Cl
Thus, they are bad conductors.
2+
Ca
+2Cl− ⎯→
CaCl
2
9. In the structure of diamond, all the four valence electrons of
carbon are involved in the formation of covalent bonds.
Two valence electrons of calcium attack the valency of
Thus, no free electrons are available.
two chlorine to attain the noble gas configuration.
Whereas, in the structure of graphite, three electrons in the
(ii)
Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state
valence shell of carbon are involved in covalent bond
but conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state
formation and the fourth electron is free to move.
because in solid state, there is no free ion to move and
Therefore, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
pass electricity. Whereas in the molten and aqueous
state, there is free ions to move and pass electricity.
10. Diamond has a giant structure that consists of carbon atoms
in which each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon
K L
5.
(i)
Electronic configuration of carbon, C(6) is 2,
4
atoms forming a rigid three-dimensional network structure,
which is responsible for it’s hardness.
K L M
Electronic configuration of chlorine, Cl(17
)
is 2,
8,
7
So, a lot of energy is required to break the network
of strong covalent bonds. That’s why it has high melting
To attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble
point.
gas,carbonneeds4electronand chlorine needs 1electron.
11. The main factors that enables carbon to form large number
So, with chlorine, carbon forms carbon tetrachloride.
of compounds are
Electron dot structure and structural formula ofCCl4 is as
follows
(i) Catenation The tendency of carbon to form chains of
identical atoms is known as catenation. Carbon forms
Cl
long chains by combining with other carbon atoms
Cl
through covalent bonds.
orCl—C—Cl
(ii) Tetravalency It has 4 valence electrons, so it can form
Cl
C
Cl
4 covalent bonds with four different atoms, or two
double bonds or a single and a triple bond with other
Cl
Cl
atoms. This tendency helps carbon to form a large
number of compounds.
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl
)
4
(iii) Tetravalency Carbon forms strong bonds with most of
K L
(ii)
Electronic configuration of oxygen, O(8) is 2,
6
other elements like H, O, N, S, Cl etc., due to it’s
small size which helps it to attract more number of
With oxygen, carbon forms carbon dioxide. To attain the
electrons.
electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas, carbon
12. The hydrocarbons in which all the carbon atoms are
needs 4 electrons and oxygen needs 2 electrons.
connected by only single bonds are called saturated
Therefore, in CO2, each oxygen atom shares 2 electrons
hydrocarbons or alkanes or paraffins. The general formula of
with carbon. Electronic configuration of carbon (6) is
these compounds is C H
n
2n+ 2 .
K L
where, n = number of carbon atoms in one molecule of a
2,
4
hydrocarbon.
The electron dot structure and structural formula of CO2
Amongst, the given compounds, only C4
10
H
and C6
14
H
is as follows:
belongs to the formula of C H
n
4
10 and
6
C H
14 aresaturatedhydrocarbons.
orOCO
13. General formula of cycloalkane = C H
n
2n
O
C
O
In cyclopentane, n = 5
∴ Formula of cyclopentane, C H
=
CH
5
5 ×2
5
10
Carbon dioxide (CO )
2
Electron dot structure of cyclopentane
The structures of possible isomers of butane (C H
)
4
10
are
H
H
×
×
H H
H
H
H
H
H H
H
H
H
×
C
×
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
C
H⎯C⎯C⎯C⎯C⎯H
H⎯C⎯C⎯C⎯H
C
C
H
H
×
×H
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
H
C
C
or
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
⏐
H
H
×
C
C
C
n-
butane
H⎯C⎯H
H
C
×H
H
(I)
⏐
×
×
H H H
H
H
H
Iso-butane
(II)
14.
(i)
Carbon is a versatile element because of its properties.
It shows the property of catenation due to which it
The first three members of alkane series are:
forms a large number of compounds. Carbon is
(i) CH4 (methane)
tetravalent. Due to this, it forms covalent compounds
(ii) C H
(ethane)
2
6
only.
(iii) C H
(propane)
3
8
(ii)
Saturated hydrocarbons contain carbon-carbon single
In the above members of alkane series, it is not possible to
bonds. e.g. Methane (CH )
4 ,
ethane (C H )
2
6 .
have different arrangements of carbon atoms, because
Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain atleast one
branching is not possible from either first or last carbon.
carbon-carbon double or triple bond. e.g. Propene
Thus, we cannot have isomers of first three members of
(C H )
3
4
6 .
alkane series.
(iii)
Functional group is an atom or group of atoms joined in
17. There are four isomers possible for the molecular formula
a specific manner which is responsible for the
C H O
3
6
. These are as follows:
characteristics chemical properties of the organic
H
H
H H
compounds.
•
••
••
••
•
•
•
3
(i) CH CH CHO
2
or CH CH
3
2
—C
⏐ →H••
•
•
C
•
C ••O
•
Examples are alcohols ( ⎯OH), aldehyde group
••
••
⏐⏐
(⎯CHO), carboxylic group (⎯COOH) , ketone (⎯CO)
H H
O
etc.
H
H
15.
(i)
Molecular formula of ethane is C H
Its electron dot
••
••
2
6.
•
•
(ii) CH
3
⎯
C⎯
CH
3
→ H••C
•
C
•
C
•
• H
structure is
••
••
••
⏐⏐
H
•
H H
O
•
••O H
••
H C C
H
H
H
••
••
••
•
H H
(iii) CH
CH ==CH ⎯OH
→ H••C
C •••C •O
• H
3⎯
•
•
••
••
••
H H
(ii)
Molecular formula of ethene is C H
2
4.
Its electron dot
structure is
H
••
••
• •
•
(iv) CH
2
==
CH⎯CH ⎯OH
2
→ H••C
•
•
C ••C
•
O
•
• H
H H
••
••
••
••
H H H
18. An atom or a group of atoms present in a molecule which
C C
largely determines it’s chemical properties is called functional
group.
H H
Compound Structural formula Functional group
(i) Ethanol
H
H
⎯OH
(iii)
Molecular formula of ethyne is C H
2
2.
Its electron dot
(C H OH)
⏐
⏐
(Alcoholic)
structure is
2
5
H⎯C
⎯C
⎯OH
⏐
⏐
H
C
C
H
H
H
(ii) Ethanoic acid
H O
O
(CH COOH)
⏐
⏐⏐
⏐⏐
3
H⎯C⎯C⎯OH
⎯C ⎯OH
16. Isomers are those molecules which have same molecular
⏐
(Carboxylic acid)
formula but different structural formula, i.e. show different
H
properties.
19. Application of homologous series are as follows
shell. So, it requires 2 electrons to complete it’s octet for
● All members of homologous series shows similar chemical
attaining noble gas configuration. Hence, it shares two
electrons with another atom of oxygen to make a molecule of
properties and generally prepared through one common
oxygen.
method, e.g. all alkenes are prepared by dehydration of
By doing so, both the atoms of oxygen get 8 electrons in their
corresponding alcohols.
outermost shell. Thus, a double bond is formed between two
● The physical properties of the members change gradually,
oxygen atoms which consists of four electrons.
i.e. show gradation in properties as the number of carbon
Before
After
atom per molecule increased.
combination
combination
20. A homologous series is the family of organic compounds
Shared electrons
having the same functional group, similar chemical
properties but the successive (adjacent) members of the
O
+
O
O
O or O
⎯
O
series are differ by a CH2 unit or 14 mass units.
Consecutive members of the homologous series of alcohols
Oxygen atoms
Oxygen molecule
are
CH OH⎤
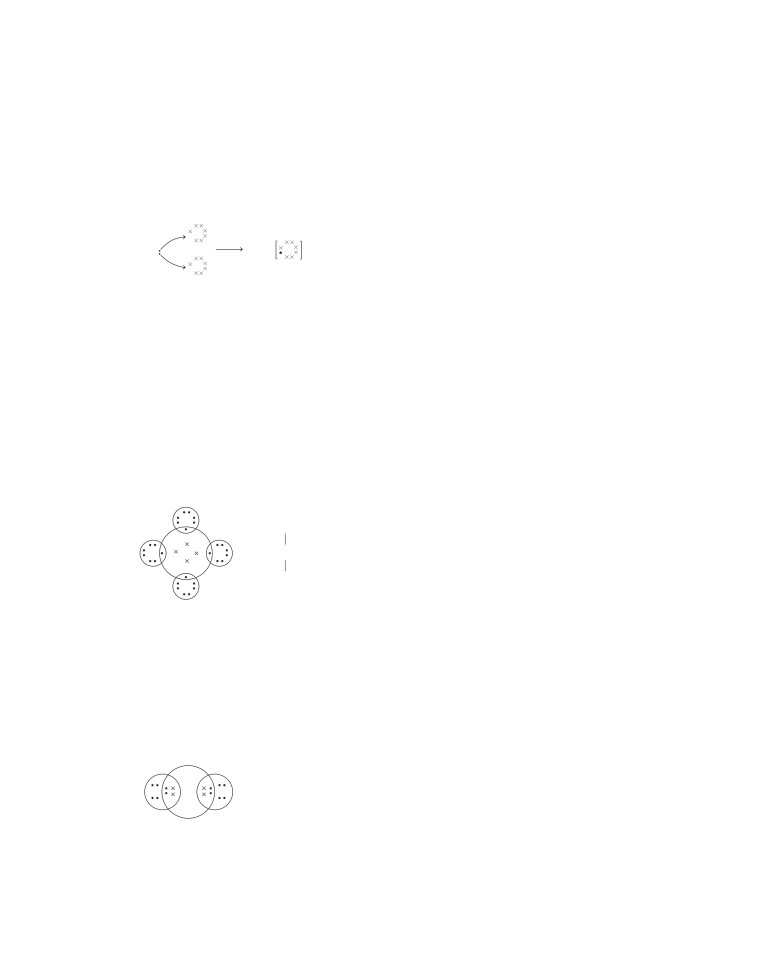
Formation of Sulphur Molecule (S )
3
8
⎥Theydifferby⎯CH2 unit.
2
C H OH5
⎦
The atomic number of sulphur is 16 and electronic
configuration is 2, 8, 6. It also has 6 electrons in it’s outermost
The physical properties are determined by alkyl group/
hydrocarbon part/part other than the functional group.
shell and requires 2 electrons to complete it’s octet state.
So, each sulphur atom shares two electrons, 1 with each
The chemical properties are determined by functional
group such as ⎯OH group.
adjoining sulphur atom by single covalent bonds and thus,
complete it’s octet.
21. Add —CH2 group to each compound to obtain next
homologous.
Before
After
combination
combination
Compounds
Homologue compounds
S
+
S
CH2 O
C H O,C H O,C H O
+
2
4
3
6
4
8
S
S
+
2
C H
2
3
C H
4
5
8...
+
S
2
5
C H COOH
3
7
C H COOH
4
9
,C H COOH,
S
+
5
11
C H COOH
+
S
S
+
+
22. Atomic number of carbon is six. This means that it has four
S
electrons in its outermost shell and it needs four more
electrons to attain noble gas electronic configuration. It
8 covalent bonds are formed
does not form C4+ cation, as the removal of four valence
electrons will require a huge amount of energy.
S
S
S
S
S
The cation formed will have six protons and two electrons.
S
This makes it highly unstable. Carbon is unable to form
C4−anion as its nucleus with six protons will not be able to
S
S
hold ten electrons due to its small size. Thus, carbon
Crown shaped (S 8) molecule
achieves noble gas electronic configuration by sharing its
Eight sulphur atoms form a puckered ring or crown structure
four electrons either with same or different other atoms,
to form an eight atom molecule.
i.e. it forms covalent compounds.
24. Covalent compounds are those compounds which are formed
(i) Covalent compounds does not have free ions, due to
by sharing of valence electrons between the atoms. e.g.
this they are bad conductors of electricity in solid,
Hydrogen molecule is formed by mutual sharing of electrons
molten or aqueous state.
between two hydrogen atoms.
(ii) Covalent compounds are formed by covalent bonds and
They are different from ionic compounds as ionic compounds
it has been found that the intermolecular force of
are formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one
attraction in covalent compounds are weak.
atom to another, e.g. NaCl is formed when one valence
Thus, low amount of energy is required to break these
electron of sodiu m gets completely transferred to outer shell
force of attraction. Hence, their melting and boiling
of chlorine atom. The characteristic properties of covalent
points are quite low.
compounds are
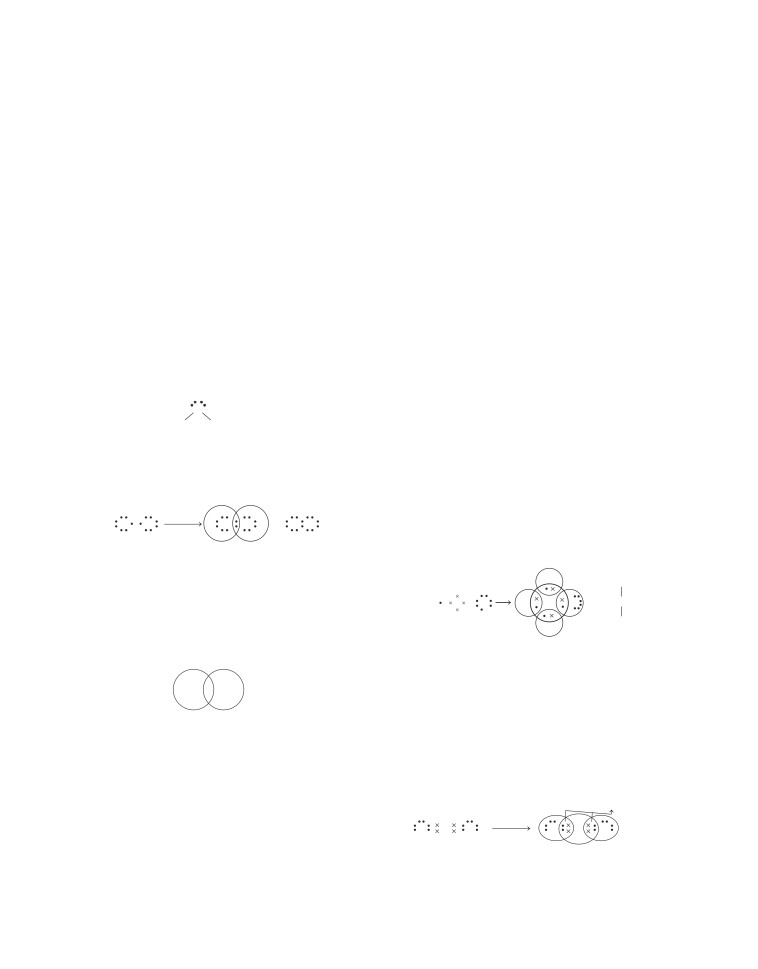
23. Formation of Oxygen Molecule (O )
2
(i) They are generally insoluble or less soluble in water but
The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and electronic
soluble in organic solvents.
configuration is 2, 6, i.e. has 6 electrons in it’s outermost
(ii) They have low melting and boiling points.
(iii) They do not conduct electricity as they do not contain
H
H O
H
ions.
⏐
⏐
⏐⏐
⏐
(v)
H⎯C⎯C⎯ ⎯C⎯H
(iv) They are volatile in nature.
⏐
⏐
⏐
25. Organic compounds are called as hydrocarbons because
H
H
H
O
they are made up of only the elements-carbon (C) and
⏐⏐
hydrogen (H).
This compound contains ⎯
C
⎯
functional group
General formula for the homologous series of alkanes is
which belongs to ketone.
C H
n
2n + 2 whichareclassifiedassaturatedhydrocarbonsor
27.
(i)
Compound B has molecular formula as C H
5
10 and
alkanes. First member of the alkane family is “methane”.
H
contains five number of carbon atoms, i.e. n = 5.
⏐
It resembles with the general formula of alkene which
H⎯ C⎯ H
is C H2
n n.
⏐
So, the name of this compound is pent + ene = pentene.
H
When five number of carbon atoms are present, it is
General formula for the homologous series of alkenes is
named as “pent”.
n
CH
2n.whichareclassifiedinthecategoryofunsaturated
hydrocarbons. They are known as alkenes or olefins. First
Saturated
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
(ii)
member of the alkene family is “ethene”.
hydrocarbons
H
!
H
These hydrocarbons
These hydrocarbons contains at
"C
==C
!
"
H
H
are linked by only
least one double or triple bond
General formula for the homologous series of alkynes is
single covalent
along with single bonds.
bond.
They are divided into two
n
C H
2n − 2
and they are also in the category of unsaturated
hydrocarbons. First member of the alkyne family is “ethyne”.
categories
H⎯C≡≡ C⎯ H
→ Alkenes or Olefins
→ Alkynes.
26. The functional group present in the following compounds are
General formula of
General formula of alkene is
H O
these compounds is
CH2
n n andgeneralformulaof
⏐
⏐⏐
CH2
n n+ 2.
alkyne is C H
n
2n − 2 .
(i) H
⎯
C
⎯
C
⎯
OH
⏐
(iii)
The minimum number of carbon atoms present in an
H
O
unsaturated compound is two because formation of
⏐⏐
double or triple bonds is possible only between two
This compound contains ⎯
C
⎯
OH functional group
carbon atoms.
which is the formula of carboxylic acid.
(iv)
The molecular formula of compound A is C H
3
8
, i.e.
H
H
H
contains three number of carbon atoms and resembles
⏐
⏐
⏐
with the general formula of alkanes which is C H
n
2n + 2 .
(ii) H
⎯ ⎯C
⎯C⎯H
So, A is saturated hydrocarbon.
⏐
⏐
⏐
H
OH
H
While the molecular formula of compounds B and C is
In this compound, ⎯OH functional group is present
CH5
10
and C H
4
6 whichresembleswiththegeneral
formula of alkene and alkyne. So, B and C are
which is the formula of alcohol.
unsaturated hydrocarbon.
H
(v)
The molecular formula of compound C is C H
⏐
4
6 which
(iii) H
⎯
C⎯CHO
resembles with alkyne because there is four number of
⏐
carbon atoms and 6H-atoms, i.e. number of H-atoms
H
are only increased by 2. So, the general formula of
This compound contains ⎯CHO functional group
alkyne is C H
n
2n−2 .
which belongs to the formula of aldehyde.
28.
(i)
Butane and iso-butane are the compounds that
H
H
have same molecular formula but different structural
formula.
⏐
⏐
(iv) H⎯C⎯C⎯Br
CH CH CH CH
CH CH CH
3
2
2
3
3
3
⏐
⏐
Butane
⏐
H
H
CH3
This compound contains halo (bromo) functional group
Iso
- butane
as ⎯Br.
(ii) Due to catenation property of carbon, it forms long,
(v) Minimum four carbon atoms are required to show
straight or branched chains and rings of different sizes.
isomerism because branching is not possible with
(iii) Pentane (C H
carbon-1, 2 and 3.
5
12 )hasthreestructuralisomers:
i.e.
C—C—C
C
—C
(3 -carbon atoms)
CH ⎯CH ⎯CH ⎯CH ⎯CH
3
2
2
2
3
|
n-pentane
1444 2444
3
3
CH ⎯CH⎯CH ⎯CH
2
3
Same
⏐
CH3
C—C—C—C C—C—C
(4 -carbon atoms)
Iso
-pentane
|
CH
3
1444
4 4444
4
Isomers
⏐
3
CH ⎯C⎯CH
3
29.
(i) P and T are the compounds that belongs to same
⏐
homologous series. Both these compounds are alkynes
CH3
and differ by ⎯CH2 unit in their molecular formula.
-pentane
Neo
(ii) The functional group of compounds (R) is ⎯OH which
(iv) Cyclohexane (C H
6
6
6)aretwo
is the formula of alcohol.
compounds that contain six carbon atoms and have
(iii)
(T) is an alkyne having general formula of C H2
n n−2.
cyclic structure.
H
H
H H
H
⏐
⏐
H
H
(iv) Compound (S), i.e. H⎯C⎯C⎯Hbelongs to an alkane
H
C
H
C
C
C
C
C
⏐
⏐
H
H
H
H
H
H
C
C
C
C
series having general formula of C H
n
2n + 2 .
H
H
C
H
C
H
H
H
(v) Compound (U), i.e.
C==C is unsaturated
H H
H
H
H
C6H12
hydrocarbon becuase it contain double bond, i.e.
C6H6
(Cyclohexane)
belongs to alkene.
(Benzene)