Chapter
Practice
PART 1
8.
Which of the following elements does not show
tetravalency?
Objective Questions
(a) Ge
(b) Si
(c) C
(d) O
9.
......... is the first synthesised organic compound.
●
(a) Alcohol
(b) Urea
Multiple Choice Questions
(c) Vinegar
(d) Benzene
1.
Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
(a) only carbon monoxide
(NCERT Exemplar)
10.
Pentane has the molecular formula C H
5
12 .
It has
(NCERT Exemplar)
(b) carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) only carbon dioxide
(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(d) coal
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
11.
Match the following :
2.
Which of the following will contain covalent double
bond between its atoms?
Column I
Column II
(a) H2
(b) O2
A. C3H
8
(i) Cyclic compound
(c) NaCl
(d) Cl2
B. C6H
(ii) Alkyne
3.
Which of the following is the correct representation
6
of electron dot structure of nitrogen? (NCERT Exemplar)
C. C2H
(iii) Alkene
2
••
••
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
(a) •N
•
N
•
(b) •N
•
•
N
•
D. C4H
8
(iv) Alkane
••
•
•
••
•
•
(c) •
N
•
N
•
(d) •N
N
•
Codes
•
•
••
A B C D
4.
Carbon can use four hydrogen atoms to form
(a)
(iv)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
methane (CH4
)
, because
(b)
(iii)
(iv)
(i)
(ii)
(a) valency of carbon is four
(c)
(ii)
(i)
(iv)
(iii)
(b) valency of hydrogen is one
(d)
(ii)
(iii)
(i)
(iv)
(c) Both (a) and (b)
12.
Structural formula of ethyne is
(NCERT Exemplar)
(d) carbon gets noble gas configuration by making four
covalent bonds with hydrogen
(a) H⎯C ≡≡ C ⎯ H
(b) H C⎯C3
≡≡
C⎯H
H
H
H
H
5.
A molecule of ammonia (NH )
3
has
(NCERT Exemplar)
"
!
"
!
(c)
C==C
(d) H⎯C⎯C⎯H
(a) only single bonds
! "
! "
(b) only double bonds
H
H
H
H
(c) only triple bonds
13.
Which among the following are unsaturated
(d) two double bonds and one single bond
hydrocarbons?
6.
The structure of S8 molecule is
shaped.
(i) CH
3
⎯
2
CH ⎯CH
3
(ii) CH
3
⎯
CH== CH⎯CH
3
(a) ring
(b) crown
CH
3
(c) circle
(d) rectangle
⏐
7.
Which of the following is not the use of graphite?
(iii) CH
⎯C⎯
CH
(iv) CH
⎯C==
CH
3
3
3
2
(a) It is used as lubricant
⏐
⏐
(b) It is used in manufacturing of lead-pencils
CH3
CH3
(c) It is used in manufacturing of artificial diamond
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii) (NCERT Exemplar)
(d) It is used for making insulated plates
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
14.
Structural formula of benzene is
(NCERT Exemplar)
18. Assertion Graphite is slippery to touch.
Reason The various layers of carbon atoms in
H H
graphite are held together by weak van der Waals’
C
C
forces.
H
H
H—C
C—H
C
C
H
H
19. Assertion Carbon shows maximum catenation
(a)
H
(b)
H
H
property in the periodic table.
C
C—H
C
C
H
H
H
Reason Carbon has small size and thus, forms
C
C
strong C⎯ C bond.
H H
H
20. Assertion Following are the members of a
H
H
homologous series:
C
C
CH OH3
3
,CH CH OH
2
3
,CH CH CH OH
2
2
H
H—C
C—H
H—C
C
Reason A series of compounds with same
H
(c)
(d)
functional group but differing by ⎯ CH
2
⎯
unit is
H—C
C—H
H—C
C H
called a homologous series.
(CBSE 2020)
H
C
C
● Case Based MCQs
H
H
21.
Read the following and answer the questions from
15.
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of
(i) to (v) given below
butane?
The bonds which are formed by the sharing of an
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
electron pair between the atoms (either same or
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
different atoms) are known as covalent bonds.
H⎯C⎯C⎯C⎯H
(i) H⎯C⎯C⎯C⎯C⎯H
(ii)
⏐
As neutral atom carbon has electronic configuration
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
H
C
KL. To gain inert gas configuration carbon can
H
H
H
H
2
4
H H
either donate 4 valence electrons (helium gas
H
H
H
H
H
configuration) or gain 4 electrons (neon gas
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
configuration), but it cannot do so. To acquire inert
(iii) H⎯C⎯⎯C⎯⎯C⎯H
(iv) H⎯C
⎯C
⎯H
gas configuration carbon can only share its 4 valence
⏐
⏐
⏐
|
|
electrons with other atoms forming covalent bonds.
H
H⎯C
⎯C
⎯H
H⎯C⎯HH
The concept of covalent bonds was given by
|
|
⏐
Langmuir and Lewis to explain bonding in non-ionic
H
H
H
compounds. The covalent bonds are of three types. If
(NCERT Exemplar)
each atom contributes one electron, the covalent
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
bond formed is called a single covalent bond and is
represented by a single line (—) and if each atom
● Assertion-Reasoning MCQs
contributes two electrons, the covalent bond formed
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-20) Each of these questions
is called a double bond and is represented by a double
contains two statements Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
line (==) and if each atom contributes three electrons,
Each of these questions also has four alternative choices,
the covalent bond formed is called a triple bond and is
any one of which is the correct answer. You have to select
represented by a triple line (≡≡
)
one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
The electrons in a covalent bond are simultaneously
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
attracted by the two atomic nuclei. A covalent bond
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct
forms when the difference between the
explanation of A.
electronegativities of two atoms is too small for an
(c) A is true, but R is false.
electron transfer to occur to form ions.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
(i) Which of the following do not contain a triple
16. Assertion Covalent compounds are poor conductor of
bond?
electricity.
I. SO2
II. N2
III. HCl
IV. NH3
Reason The electrons are shared between atoms and no
(a) I and II
charged particles are present.
(b) I, III and IV
17. Assertion Diamond does not conduct electricity.
(c) III and IV
Reason Diamond has high refractive index.
(d) I and IV
(ii) Which of the following contains a double bond?
Which statements about substance X are correct?
(a) O2
(b) N2
I. It is a covalent compound.
II. It has a giant molecular structure.
(c) CH4
(d) H O
2
III. It has the same structure as graphite.
(iii) Chlorine forms a diatomic molecule, Cl2. The
IV. It has the same structure as diamond.
electron dot structure for this molecule is
(a) I and III
(b) II and III
(c) II and IV
(d) I, II and IV
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
(ii)
Which of the following is correct about the structure
(a)
(b)
of diamond?
(a) Carbon atoms are held together by single covalent
bonds
(b) Electrons move freely through the structure
(c)
Cl
Cl
(d)
Cl
Cl
(c) Layers of atoms slide easily over each other
(d) Carbon atoms conduct electricity in the molten state
(iv) What is the covalency of nitrogen?
(iii)
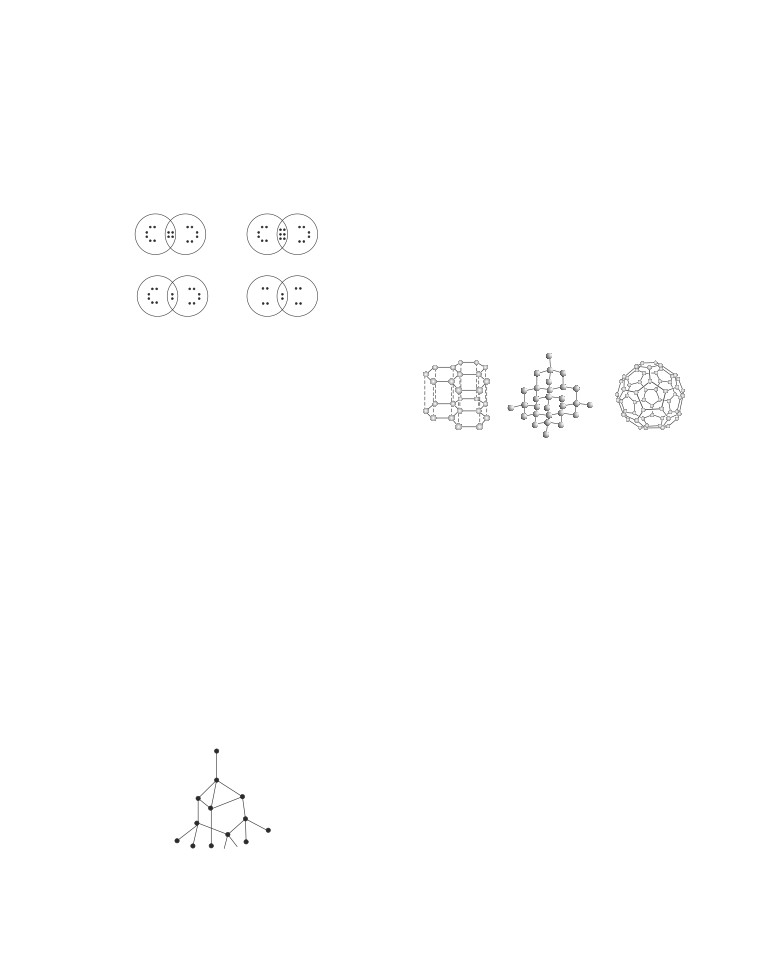
Which three allotropes of carbon, do the given figures
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
represents?
(v) The shared pair of electrons is said to constitute a
……… bond between two hydrogen atoms.
(a) single
(b) double
(c) triple
(d) ionic
22.
Read the following and answer the questions from (i)
to (v) given below
Allotropy is the property by virtue of which an
(I)
(II)
(III)
element exists in more than one form and these
I
II
III
different forms of an element are called allotropes.
(a) Diamond Graphite
Buckminster fullerene
Allotropes have similar chemical properties but they
(b) Graphite Buckminster
Diamond
differ in their physical properties. Carbon exists in
fullerene
crystalline and amorphous forms.
(c) Diamond Buckminster
Graphite
In crystalline form, it occur as diamond, graphite and
fullerene
fullerenes. Diamond is a colourless, transparent
(d) Graphite Diamond
Buckminster fullerene
substance having extraordinary brilliance. It is the
hardest natural substance known. It is used for cutting
(iv)
Identify the incorrect statement(s).
marble, granite and glass. Graphite is a greyish-black
I. Diamond is the hardest substance known while
opaque substance. It is lighter than diamond, i.e., it
graphite is smooth and slippery.
has lower density. It has sheet like structure having
II. Diamond is made up of billions of carbon atoms.
hexagonal layers.
Each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon
One layer slides over the other layer which makes it
atoms in a tetrahedral manner to form a giant
soft to touch. It is the reason that graphite is used as a
lattice. All carbon atoms are bonded by strong
lubricant. The amorphous form of carbon is also
covalent bonds.
known as micro-crystalline form which consists of
III. Graphite is a poor conductor of electricity unlike
coal, lampblack and charcoal.
other non-metals.
(i) Substance X is a moderate conductor of electricity.
IV. Graphite has a giant covalent structure that is
Substance X has the structure shown below :
made up of layers of carbon atoms. In each layer,
each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon
atoms to form hexagonal rings of carbon atoms.
(a) I and III
(b) Only III
(c) II and IV
(d) I, II and IV
(v) Which of the following is an example of amorphous
form of carbon ?
(a) Wood
(b) Oil
(c) Chalk
(d) Coke
15.
Write the molecular formula of the following
PART 2
compounds and draw their electron dot structures
(i) Ethane
(ii) Ethene
(iii) Ethyne
Subjective Questions
16.
What is meant by isomers? Draw the structures of two
isomers of butane, C H
● Short Answer Type Questions
4
10 .Explain,whywecannot
have isomers of first three members of alkane series?
1.
What do you mean by covalent bonding?
17.
Draw the possible isomers of the compound with
2.
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the
molecular formula C H O
3
6
and also give their
bond formation in CH Cl
(NCERT)
3
electron dot structures.
(NCERT Exemplar)
3.
What would be the electron dot structure of carbon
18.
What is meant by functional group in carbon
dioxide which has molecular formula CO2 ?
(NCERT)
compounds? Write in tabular form the structural
4.
(i) Explain the formation of calcium chloride with the
formula and the functional group present in the
help of electron dot structure.
following compounds:
(Atomic numbers of Ca = 20; Cl =17)
(i) Ethanol
(ii) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Why do ionic compounds not conduct electricity in
19.
Describe the applications of homologous series.
solid state but conduct electricity in molten and
aqueous state?
20.
Why is homologous series of carbon compounds so
called? Write the chemical formula of two
5.
Carbon a group (14) element in the periodic
consecutive members of any homologous series and
table, is known to form compounds with many
state the part of these compounds that determines
elements. Write an example of a compound formed
their (i) physical and (ii) chemical properties.
with
(i) chlorine (group 17 of periodic table)
21.
Write the next higher order homologous of CH O,
2
(ii) oxygen (group 16 of periodic table)(NCERT Exemplar)
C H
2
2
5
6.
Why covalent compounds are volatile in nature with
● Long Answer Type Questions
low boiling and low melting point?
7.
State the valency of each carbon atom in
22. State the reason why carbon can neither form C4+
cations nor C4− anions, but forms covalent
(i) an alkane and
(ii) an alkyne
compound. Also state reasons to explain why
8.
Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors
covalent compounds
of electricity. Why?
(CBSE 2020)
(i) Are bad conductors of electricity?
9.
Diamond is a poor conductor of electricity while
(ii) Have low melting and boiling point?
graphite is a good conductor. Assign reason.
23. Explain the formation of oxygen (O
)molecule and
2
10.
Why diamond has high melting point?
sulphur (S8 ) molecule.
11.
What are the main factors that enables carbon to
24. What are covalent compounds? Why are they
form large number of compounds?
different from ionic compounds? List their three
12.
Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following:
characteristics properties.
C H
C H
C H
C H
C H
25. Why organic compounds are called as hydrocarbons?
3
6;
5
10;
4
10;
2
4;
6
14
Write the general formula for homologous series of
13.
What will be the formula and electron dot structure
alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the
of cyclopentane?
(NCERT)
structure of the first member of each series.
14.
Answer the following
26. Identify the functional group present in the
(i) Carbon is a versatile element. Give reason.
following compounds
(ii) Explain the structural difference between saturated
H O
H
H
H
and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples
⏐
⏐⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
each.
(i) H⎯C⎯C⎯OH
(ii) H⎯C ⎯
C
⎯C⎯H
(iii) What is a functional group? Write examples of four
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
different functional groups.
H
H
OH H
H
H
H
any reference to space, the phenomenon is called
⏐
⏐
⏐
structural isomerism. In other words, structural
(iii) H⎯C ⎯CHO
(iv) H⎯C⎯C⎯Br
isomers are compounds that have the same molecular
⏐
⏐
⏐
formula but different structural formulas, i.e. they are
H
H
H
different in the order in which different atoms are
H
H O
H
linked or they have different connectivities depending
⏐
⏐
⏐⏐
⏐
upon the order they are put together. In these
(v) H⎯C⎯C⎯ ⎯C⎯H
compounds, carbon atoms can be linked together in the
⏐
⏐
⏐
form of straight chains, branched chains or even rings.
H
H
H
(i) Name any set of compound that have same molecular
formula but different structural formula.
● Case Based Questions
(ii) Which property of carbon leads to formation of
27.
Read the following and answer the questions from (i)
branched chains?
to (v) given below
(iii) How many isomers of pentane are possible?
Compounds which contain only carbon and
(iv) Name two compounds that contains six carbon atoms
hydrogen are called hydrocarbon. Among these, the
and have cyclic structure.
compounds containing all single covalent bonds are
(v) What is the minimum number of carbon atoms
called saturated hydrocarbons while the compounds
required to form an isomer?
containing atleast one double or triple bond are
29.
Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to
called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(v) given below
Saturated hydrocarbons after combustion give a
Hydrocarbons are the simplest organic compounds and
clean flame while unsaturated hydrocarbons given a
are regarded as parent organic compounds. All other
yellow sooty flame. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are
compounds are considered to be derived from them by
more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons.
the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by
Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the
other atoms or group of atoms.
presence of catalysts such as palladium or nickel to
Functional groups is an atom or group of atoms which
give saturated hydrocarbons.
makes a carbon compound (or organic compound)
Study the table related to three hydrocarbons
reactive and decide it’s properties. A series of organic
A,B,Cand answer the questions that follows
compounds having same functional group with similar
or almost identical chemical characteristics in which
Organic compound Molecular formula
all the members can be represented by the same
A
C H3
8
general formula and two consecutive members of series
B
CH
differ by ⎯CH2 group in their molecular formula is
5
10
called a homologous series.
C
C H4
6
H
H
H
H
(i) What is the name of compound B?
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
(ii) Write two differences between saturated and
H⎯C≡≡C⎯C⎯H,H⎯C⎯Br,H⎯C⎯C⎯OH,
unsaturated hydrocarbons.
⏐
⏐
⏐
⏐
H
H
H
H
(iii) In unsaturated compounds, what is the minimum
(P)
(Q)
(R)
number of carbon atoms and why?
H
H
(iv) Among compounds A, B and C, which of the
⏐
⏐
following is saturated hydrocarbon?
H
!
H
H⎯C⎯C⎯H,H⎯C≡≡C⎯ H,
"C==C
(v) Compound C belongs to which category of
!
"
(T)
H
H
⏐
⏐
hydrocarbon and what is it’s general formula ?
(U)
H
H
(S)
28. Read the following and answer the questions from (i)
to (v) given below
(i) Which compounds belongs to same homologous series?
(ii) What is the functional group of compound R ?
Organic compounds with same molecular formula
(iii) Compound T belongs to which homologous series ?
but different chemical and physical properties are
(iv) Among the P,S,T and U compounds which belongs to
called isomers. This phenomenon is called isomerism.
alkane series?
When the isomerism is due to difference in the
(v) With respect to Q,R,S and U compounds which one is
arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without
an unsaturated hydrocarbon?