Chapter Practice
PART 1
(a) directly above the wire
(b) directly below the wire
Objective Questions
(c) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the
North side of the wire
(d) at a point located in the plane of the paper, on the
● Multiple Choice Questions
South side of the wire
1.
Which of the following is the property of magnetic
5.
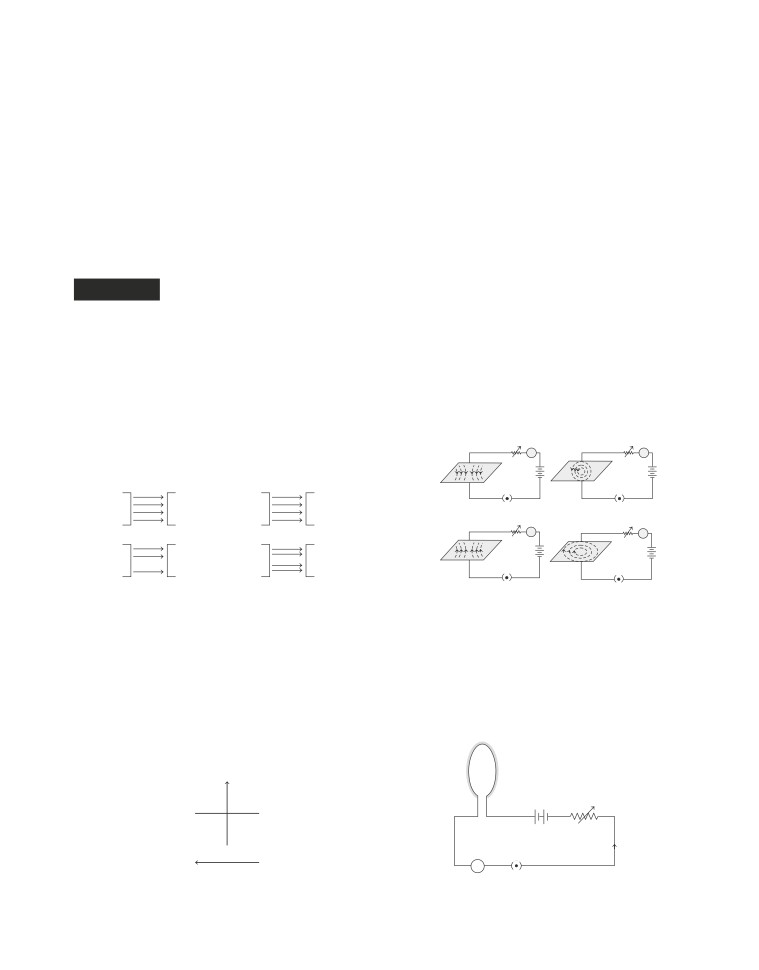
Four students A, B, C and D plotted the sketch of
field lines ?
the patterns of magnetic field lines representing the
(a) Magnetic field lines are closed and continuous curves
magnetic field around a current carrying straight
(b) Magnetic field lines never intersect with each other
wire as shown. Whose sketch is correctly
(c) Magnetic field lines are crowded near the poles
represented?
(d) All of the above
-
-
A+
A+
2.
Which of the following is the correct representation
-
-
of uniform magnetic field?
(a)
N
S
(b)
S
N
K
K
Student A
Student B
-
-
A+
A+
N
-
-
(c)
N
(d)
N
S
K
K
3.
Which of the following correctly describes the
Student C
Student D
magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(NCERT)
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the
6.
A circular loop placed in a plane perpendicular to the
wire
plane of paper carries a current when the key is ON.
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire
The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the
of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anti-clockwise
wire
and clockwise, respectively.
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the
wire
The magnetic field lines point from B to A.
The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face
4.
A constant current flows in a horizontal wire in the
close to
(NCERT Exemplar)
plane of the paper from East to West as shown in
figure. The direction of the magnetic field at a point
will be North to South
A
B
N
Variable
resistance
-
W
E
S
+
-
W
E
(NCERT)
A
K
(a) B
(a) forces both pointing into the plane of paper
(b) A
(b) forces both pointing out of the plane of paper
(c) A, if the current is small and B, if the current is large
(c) forces pointing into the plane of paper and out of the
(d) B, if the current is small and A, if the current is large
plane of paper, respectively
(d) force pointing opposite and along the direction of
7.
Which of the following properties of a proton can
the uniform magnetic field, respectively
change when it moves freely in a magnetic field?
12.
A rectangular loop carrying a current i is situated
(a) Mass
(b) Speed
(NCERT)
near a long straight wire such that the wire is
(c) Velocity
(d) Momentum
parallel to one of the sides of the loop and is in
8.
A positively charged particle (α-particle) projected
the plane of the loop. If a steady current i is
towards West is deflected towards North by a
created in wire as shown in figure below, then
magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is
the loop will
(NCERT)
i
(a) towards South
(b) towards East
(c) downwards
(d) upwards
i
9.
The strength of magnetic field inside a long current
carrying straight solenoid is
(a) rotate about an axis parallel to the wire
(a) more at the ends than at the centre
(b) move towards the wire
(b) minimum in the middle
(c) move away from the wire or towards right
(c) same at all point
(d) remain stationary
(d) found to increase from one end to the other
13.
The direction of the induced electric current in a
10.
Match the items in Column I with the items in
conductor, when placed in a varying magnetic
Column II and choose the correct codes given below.
field can be assessed by
(CBSE 2020)
Column I
Column II
(a) Maxwell’s right hand-thumb rule
A. SI unit of magnetic field
(i) Small bar magnet that rotates
(b) Ohm’s law
(c) Fleming’s left hand rule
B. Magnetic field inside
(ii) Tesla
(d) Fleming’s right hand rule
solenoid
C. Compass needle
(iii) Temporary magnet
14.
In the arrangement shown in figure below, there
are two coils wound on a non-conducting
D. Solenoid
(iv) Uniform value
cylindrical rod. Initially, the key is not inserted.
Codes
Then, the key is inserted and later removed.
A B C D
Then,
(NCERT Exemplar)
(a)
(ii)
(iv)
(i)
(iii)
Coil I
Coil II
(b) (iii)
(ii)
(iv)
(i)
(c)
(i)
(iii)
(ii)
(iv)
(d) (iv)
(i)
(iii)
(ii)
11.
A uniform magnetic field exists in the plane of paper
+
-
pointing from left to right as shown in the figure. In
e
the field, an electron and a proton move as
(a) The deflection in the galvanometer remains zero
shown in the figure. The electron and the proton
throughout.
experience
(NCERT Exemplar)
(b) There is a momentary deflection in the
Proton
galvanometer only when the key is removed.
(c) There are momentary galvanometer deflections that
Uniform
die out shortly; the deflections are in the same
magnetic
field
direction.
(d) The galvanometer shows momentary deflections in
opposite directions.
Electron
15. Match the terms of Column I with Column II and
19. Assertion The magnetic field produced by a current
choose the correct option from the codes given below.
carrying solenoid is independent of its length and
cross-sectional area.
Column I
Column II
Reason The magnetic field inside the solenoid has
A. Direction of force
(i)
Direction of magnetic
force on a North pole
variable value.
B. Direction of induced
(ii) Fleming’s left hand rule
20. Assertion Production of an electric current in a
current
closed circuit by a changing electric field is called
C. Direction of magnetic
(iii) Maxwell’s right hand
an induced current.
field produced by
thumb rule
Reason The direction of induced current is given
straight current
carrying conductor
by Fleming’s right hand rule.
D. Direction of magnetic
(iv) Fleming’s right hand
● Case Based MCQs
field lines at a point in
rule
a magnet
21.
Read the following and answer the questions from
(i) to (v) given below
Codes
A B C D
A solenoid is a long helical coil of wire through
(a)
(ii)
(iv)
(iii)
(i)
which a current is running in order to create a
(b)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
magnetic field.
(c)
(ii)
(iii)
(i)
(iv)
The magnetic field of a solenoid is the superposition
(d)
(i)
(iii)
(ii)
(iv)
of the fields due to the current through each coil. It
is nearly uniform inside the solenoid and close to
● Assertion-Reasoning MCQs
zero outside and is similar to the field of a bar
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-20) For given questions two
magnet.
statements are given-one labelled Assertion (A) and the
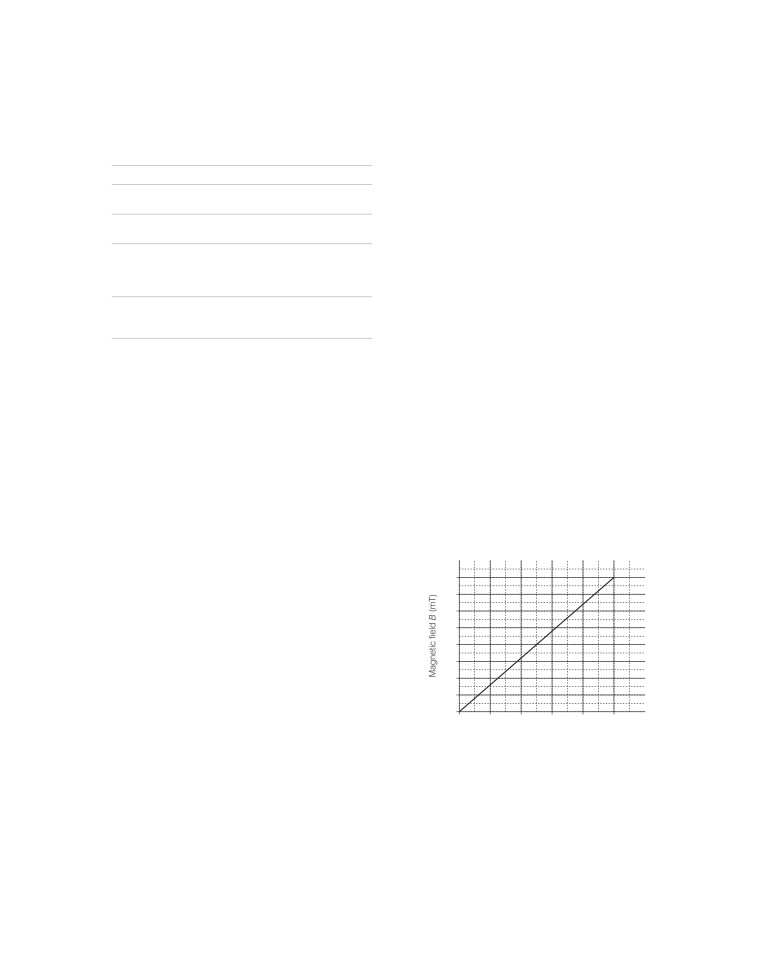
The following graph is obtained by a researcher,
other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to
while doing an experiment to see the variation of the
these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as
magnetic field with respect to the current in the
given below.
solenoid. The unit of magnetic field as given in the
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct
graph attached is in (mT) and the current is given
explanation of A.
in (A).
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct
18
explanation of A.
16
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
14
12
16. Assertion The magnetic field is stronger at a point
which is nearer to the conductor and goes
10
on decreasing on moving away from the conductor.
8
Reason The magnetic field B produced by a straight
6
current carrying wire is inversely proportional to
4
the distance from the wire.
2
17. Assertion A current carrying conductor experiences
0
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
a force in a magnetic field.
Current (A)
Reason The force acting on a current carrying
(CBSE Sample Paper)
conductor in a magnetic field is due to interaction
between magnetic field produced by the conductor
(i) What type of energy conversion is observed in a
and external magnetic field.
linear solenoid?
(a) Mechanical to magnetic
18. Assertion If an electron, moving vertically from outer
(b) Electrical to magnetic
space, enters the earth’s magnetic field, then it gets
deflected towards West.
(c) Electrical to mechanical
(d) Magnetic to mechanical
Reason Electron has negative charge.
(ii) What will happen, if a soft iron bar is placed inside the
(i)
The direction of rotation of the coil, when viewed
solenoid?
from the front by the student is
(a) A high amount of electric charge flows in the bar
(a) clockwise
resulting in short-circuit.
(b) anti clockwise
(b) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current
(c) First half clockwise and other half anti-clockwise
in the circuit
(d) First half anti-clockwise and other half clockwise
(c) The bar will be magnetised permanently
(ii)
The student is still testing on the feasibility of using
(d) The bar will not be affected by any means
metal strips in the model. His observations are given
(iii) The magnetic field lines produced inside the solenoid
below.
are similar to that of
I. As the current reverses in the coil for every half
(a) a bar magnet
turn, the coil rotates in one direction.
II. The speed of rotation of the motor is increased, if
(b) a straight current carrying conductor
the value of current is increased.
(c) a circular current carrying loop
III. The direction of force, acting on the coil is given by
(d) electromagnet of any shape
Fleming’s left hand rule.
(iv) After analysing the graph, a student writes the following
IV. The coil continues its rotation in magnetic field
statements.
even if there is no current in circuit.
I. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is
The correct observations made by him are
inversely proportional to the current.
(a) I, II and IV
(b) II, III and IV
II. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is
(c) I, II and III
(d) II and III
directly proportional to the current.
(iii)
Commercial electric motors do not use
III. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is
(a) an electromagnet to rotate the armature.
directly proportional to square of the current.
(b) effectively large number of turns of conducing
IV. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is
wire in the current carrying coil
independent of the current.
(c) a permanent magnet to rotate the armature
Which of the following would be the correct statement(s).
(d) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound
(a) Only IV
(b) I, III and IV
(iv)
Which one of the following is true about electric
(c) Both I and II
(d) Only II
motor?
(v) From the graph, deduce which of the following
(a) It converts electrical energy into mechanical
statements is correct?
energy
(a) For a current of 0.8 A, the magnetic field is 13 mT.
(b) It converts mechanical energy into electrical
(b) For larger currents, the magnetic field increases
energy
non-linearly.
(c) It converts magnetic energy into electric energy
(c) For a current of 0.8 A, the magnetic field is 1.3 mT.
(d) It converts electric energy into magnetic energy
(d) There is not enough information to find the magnetic
(v)
The direction of magnetic field at a place is coming
field corresponding to 0.8 A current.
out of the paper. A wire whose direction of current
22.
Read the following and answer the questions from (i)
flow is as shown in the figure is placed there. In
to (v) given below
which direction is the force due to the magnetic
A student wants to study the working of electric motor.
field experienced by the wire?
He used a model of DC motor for electromagnetism as
N
shown in figure.
i
45°
S
N
45°
Metal
strips
W
E
O
Rheostat
S
-
+
K
(a) North-West direction
He fixed the two ends of the coil to a pair of curved
(b) North direction
elastic metal strips. The metal strips are connected to
(c) South-West direction
the power supply with a rheostat.
(d) South-East direction
(i) Vertically in North-South plane and an observer
PART 2
looking it from East sees the current to flow in
anti-clockwise direction.
Subjective Questions
(ii) Vertically in East-West plane and an observer looking it
from South sees the current to flow in anti-clockwise
●
direction.
Short Answer Type Questions
(iii) Horizontally and an observer looking at it from below
1.
List the properties of magnetic lines of force. Why
sees current to flow in clockwise direction.
do two magnetic lines of force not intersect with
8. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can
each other?
(NCERT)
you determine the North and South poles of a
2.
The adjoining diagram shows two
current carrying solenoid using a bar magnet?
parallel straight conductors carrying
Explain.
(NCERT)
same current. Copy the diagram and draw
9. Give reasons for the following
the pattern of the magnetic field lines
(i) There is either a convergence or a divergence of
around them showing their directions.
X
magnetic field lines near the ends of a current
What is the magnitude of magnetic field at
carrying straight solenoid.
a point X which is equidistant from the
(ii) The current carrying solenoid when suspended freely
conductors? Give justification for your
rests along a particular direction.
answer.
(CBSE 2019)
(iii) The strength of magnetic field is uniform inside a
solenoid.
(CBSE 2020)
3.
How will the strength of the magnetic field change
when the point where magnetic field is to be
10.
When is the force experienced by a current
determined is moved away from the straight wire
carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field
carrying constant current? Justify your answer.
largest? Which rule determines the direction of
(CBSE 2019)
force on current carrying conductor?
4.
AB is a current carrying conductor in the plane of
11.
A magnetic field is non-uniform but its direction is
the paper as shown in figure. What are the
constant (East to West) is set-up in a chamber. A
directions of magnetic fields produced by it at
charged particle enters the chamber and travels
points P and Q?
undeflected along a straight path with constant
A
P
speed.
r1
What do you say about the initial velocity of the
particle?
I
12.
An α-particle (positive charge) enters, a uniform
r2
magnetic field at right angles to it as shown below.
Q
B
Given r1 > r2 , where will the strength of the
α-particle
Magnetic
magnetic field be larger?
(NCERT Exemplar)
field
5.
A horizontal power line carries a current from East
to West direction. What is the direction of the
magnetic field due to the current in the power
In which direction α-particle moves, if the direction
line at a point above and at a point below the power
of magnetic field gets reversed?
line?
13.
State whether an α-particle will experience any
6.
A circular loop carrying a current is placed on a
force in a magnetic field, if (α-particles are
horizontal surface (current is in the clockwise
positively charged particles).
direction).
(i) It is placed in the field at rest.
What is the direction of its magnetic field at
(ii) It moves in the magnetic field parallel to field
the centre? What is the direction of the
lines.
magnetic field at a point outside the surface of the
(iii) It moves in the magnetic field perpendicular to
loop?
field lines.
7.
Find the direction of magnetic field due to a
Justify your answer in each case.
current carrying circular coil held
14.
The electron enters in uniform magnetic field with
What are the two observations that can be noted
three different ways as shown below.
from the galvanometer reading?
e
20.
(i) A coil of insulated wire is connected to a
B
e-
galvanometer. What would be observed if a
B
B
strong bar magnet with its south pole towards
e-
one face of the coil is
(a) moved quickly towards it?
(a)
(b)
(c)
(b) moved quickly away from it?
Identify the case in which the force on electron will
(c) held stationary near it?
be maximum and minimum, respectively. Give
(ii) Name the phenomenon involved.
reasons for your answer. Find the direction of
(CBSE 2020, NCERT)
maximum force acting on electron.
● Long Answer Type Questions
15.
The figure shows the split ring commutator and
21. Why does a magnetic compass needle pointing
the two carbon brushes in their respective positions.
North and South in the absence of a nearby
magnet get deflected when a bar magnet or a
Carbon brush
current carrying loop is brought near it? Describe
some salient features of magnetic lines of field
concept.
(NCERT Exemplar)
Split ring
22. PQ is a current carrying conductor in the plane of
commutator
+
-
the paper as shown in the figure below.
P
What can you say about carbon brush and split ring
commutator?
R
r1
16.
Sketch the schematic diagram of electric motor. What
is the role of split rings in an electric motor?
(NCERT)
S
17.
(i) In what ways the speed to rotation of an electric
r2
motor is increased?
Q
(ii) Name some devices in which electric motors are
used.
(NCERT)
(i) Find the directions of the magnetic fields
produced by it at points R and S.
18.
A circular metallic loop is kept above the wire AB as
shown below.
(ii) Given r
1
>
r
2
, where will the strength of the
magnetic field be larger? Give reasons.
(iii) If the polarity of the battery connected to the
wire is reversed, how would the direction of the
A
B
magnetic field be changed?
What is the direction of induced current produced in
(iv) Explain the rule that is used to find the direction
the loop, if the current flowing in the straight wire
of the magnetic field for a straight current
(i) is steady, i.e. does not vary?
carrying conductor.
(CBSE Sample Paper)
(ii) is increasing in magnitude?
23. What is solenoid? Draw the pattern of magnetic
Justify your answer in each case.
field lines of (i) a current carrying solenoid and
19.
In the arrangement shown in figure there are two
(ii) a bar magnet.
coils wound on a non-conducting cylindrical rod.
List two distinguishing features between the two
Initially the key is not inserted in the circuit. Later
fields.
(CBSE Delhi, 2019)
the key is inserted and then removed shortly after.
24. (i) State Fleming’s left hand rule.
Coil I
Coil II
(ii) Write the principle of working of an electric
motor.
(iii) Explain the function of the following parts of
an electric motor.
K
(a) Armature
(b) Brushes
G
(c) Split ring
(CBSE 2018, NCERT)
25.
(i) What is meant by electromagnetic induction? Name
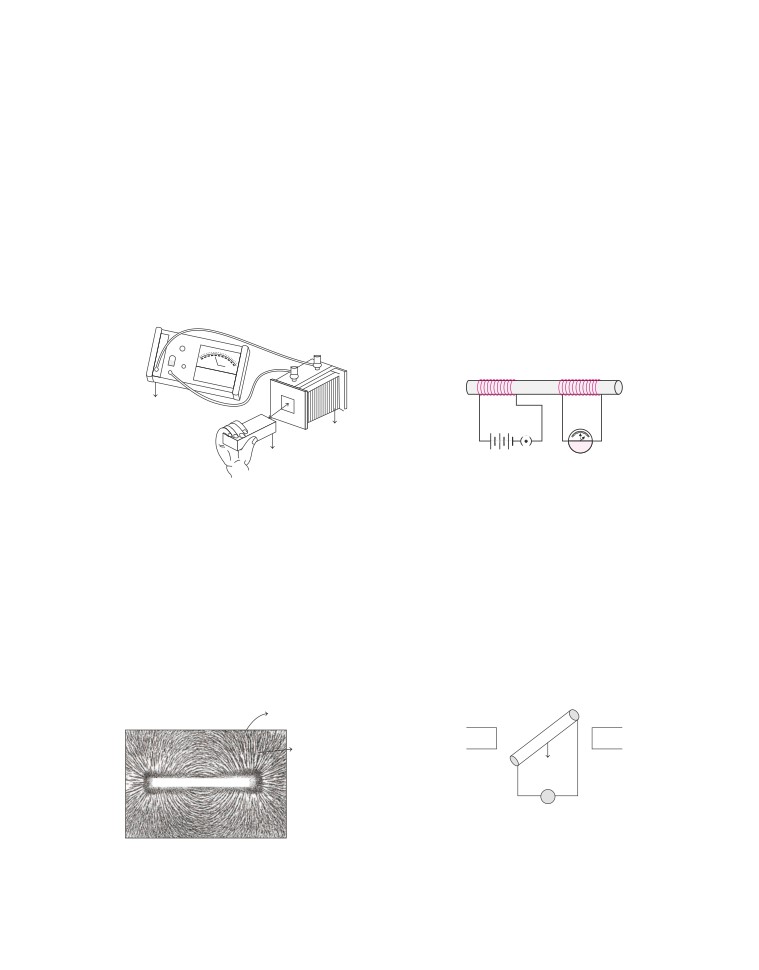
(i) What type of material is placed on white paper?
one device which works on the principle of
(ii) Why do the iron fillings arrange in such a
electromagnetic induction.
pattern?
(ii) Describe three different ways to produce induced
(iii) What should we call to the region in which
current in a coil of wire.
magnetic force can be detected?
(iv) What do the lines on pattern demonstrate?
● Case Based Questions
(v) Does degree of closeness of the field lines relate
26. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to
something?
(v) given below
28.
Read the following and answer the questions
A bar magnet is moved in and out of a coil, i.e.
from (i) to (v) given below
connected to a sensitive centre zero meter as shown in
Jay performs an experiment by using two
the figure given below.
different coils of copper wire having different
number of turns.
He inserted them over a non conducting
cylindrical roll as shown.
Coil 1
Coil 2
Sensitive
centre zero
N
meter
Coil
+
-
G
Bar magnet
K
Setup of two stationary coils
Then he connects the coil-1, having large
The meter needle swings to the left when the magnet is
number of turns in series with a battery and plug
moving towards the coil.
key and other coil-2 with galvanometer. As, he
(i) How the needle behaves when the bar magnet is at rest?
plug the key, he observes some deflection in
galvanometer.
(ii) How the needle behaves when the bar magnet is at rest
and the coil is moving away from the magnet?
(i) Why there is deflection in the galvanometer
when a key is inserted in the circuit ?
(iii) In which condition, the meter needle swings to the left?
(ii) When there is flow of induced current through a
(iv) Which phenomenon is involved in this?
coil ?
(v) Give two applications based on the given phenomenon.
(iii) Jay disconnected coil-1 from the battery and
27. Read the following and answer the questions from (i) to
noted the following observation.
(v) given below
‘‘The needle momentarily moves but to the
A child performs an activity with a special material. He
opposite direction’’. Justify the statement.
fixes a sheet of white paper on a drawing board using
(iv) When will the induced current is found to be
some adhesive material and places that material in the
highest?
centre of it.
(v)
Y
White paper
N
S
Iron fillings
V
X
Material
G
A conducting rod XY moves across two magnets
as shown and the needle in galvanometer gets
deflected momentarily. What is the name of this
Then he sprinkles some iron fillings uniformly around it
physical phenomenon?
with a salt-sprinkler and taps the board gently.