CBSE Class 12 Physical Education Important Questions Sports Medicine
1 Mark Questions
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION –
(1 MARK EACH)
Q.1 What is sports medicine?
Ans. Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness, treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise.
Q.2 What is sports injury?
Ans. “Sports injuries” are the type of injuries that occur during participating in sports/competition, training sessions or sports activities.
Q.3 How to classify sports injury?
Ans. 1. Soft tissue injuries:- The injury of muscles, tendons, ligaments.
2. Hard tissue injury:- The injury of bones & joints.
Q.4. What is soft tissue injury?
Ans. A soft tissue injury is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body.
Q.5 Write types of soft tissue injury.
Ans. Types of soft tissue injuries include:
·Bruises (haematoma)
·Sprains (ligaments)
·Strains (tendons)
·Lacerations (skin)
·Dislocations (joints)
·Tendonitis (tendons)
Q.6 What is R.I.C.E.R. ?
Ans. The most effective, initial treatment for soft tissue injuries is the R.I.C.E.R.. (R) rest, (I) ice, (C) compression, (E) elevation and obtaining a (R) referral for appropriate medical treatment.
Q.7 Define sprain?
Ans. Sprain is a sudden stretching of ligaments of a joints & associated with the pain & de-coloration into tissues. For example:-ankle, elbow, knee
Q.8 What is abrasion?
Ans. Abrasions is injury of skin or mucous membrane due to scrapping or rubbing. This injury to caused to fell on a hard rough surface.
Q.9 What is Laceration?
Ans. Laceration is a more severe injuries of tearing or ripping of the layers of skin and the fatty tissues and muscles below the wound.
Q.10 Define dislocation?
Ans. A dislocation is an injury to a joint — a place where two or more of your bones come together — in which the ends of your bones are forced from their normal positions.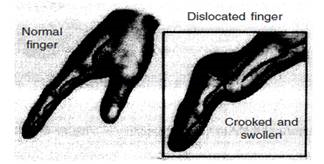
Q.11 What do you mean by fracture?
Ans. A fracture is a broken bone. It can range from a thin crack to a complete break. Fracture caused by a direct blow to the bone either in a fall or a kick.
Q.12 What is FISM?
Ans. The International Federation of Sports Medicine.
3 Mark Questions
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION (80 TO 90 WORDS) –
(3 MARKS EACH)
Q.1 What is the concept of sports medicine?
Ans. The modern concept of sports medicine are:-
1. The psychological aspect of performance
2. Exercise in cardio-vascular disease prevention & rehabilitation.
3. Bio-mechanics related to sports
4. Cardiac-respiratory function in relation to performance.
5. Nutrition & metabolism in relation to competitive performance.
6. Effect of altitude on endurance performance
7. Recommendations of FISM at world level.
Q.2 What are the Aims of sports medicine?
Ans. The Aims of sports medicine are:-
1. To prevent to damage to the human system caused mostly by inactivity due to sedentary habits and lack of physical exercise.
2. To concentrate on the causes of injury
3. To recover from the injury and regain maximum body functioning after an accident.
4. Advance preparation to protect athlete from physical injury occurred during play, practice or competition in a match.
Q.3 What are the most common causes of fracture?
Ans. 1. High impact sports injuries
2. Traumatic, forceful and unnatural movements
3. Overuse – prolonged long-distance walking or running
4. Falls
5. Accidents
6. Osteoporosis
Q.4 What are the differences between intrinsic and extrinsic factors of Injury?
Ans.
| Intrinsic Factors of Injury | Extrinsic Factors of Injury |
| Factors present in the athlete’s body Like-lack of physical and physiological Parameter. | Factors present surrounding the atheletes, like-climate, playing surfaces ,equipment and facilities. |
| This factors may be heredity. | This factors may be natural o r man made. |
| This factor may be prevented by the proper training and conditioning of the body. | This factor may be prevented by providing good environment & preventive measures. |
5 Marks Questions
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION (150 TO 200 WORDS) –
(5 MARKS EACH)
Q.1 Write down types of bone fracture?
Ans. Simple – the bone is broken in one place.
Closed – the skin over the broken bone has not been pieced.
Comminuted – the broken bone has three or more bone fragments.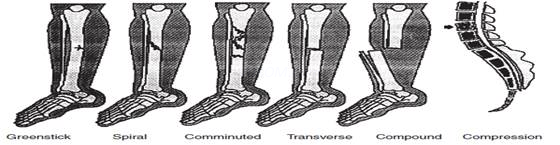
Open or compound – the skin over the fracture has been pierced and the broken bone is exposed.
Undisplaced – the broken bone pieces are aligned
Displaced – the broken bone pieces are not aligned
Transverse fracture – the fracture is at a right angle to the long axis of the bone.
Greenstick fracture – the fracture is on one side of the bone, causing a bend on the other side of the bone.
Q.2. How you can avoid sports injuries?
Ans. 1. Proper coaching
2. Proper use of equipment
3. Proper conditioning
4. Proper warming up and cooling down
5. Protective sports equipment and gear
6. Avoid dehydration
7. Balanced diet
8. Use of right techniques
9. Proper knowledge of sports skills
10. Avoid overdoing training
11. Avoid working when muscle is weak because of fatigue
12. Appropriate sports environment
13. Injury management
Q.3 What are the types of injury and its possible causes?
Ans.
| Type of Injury | Structure | Possible Cause |
| Soft Tissue | ||
| Sprain | Ligament | Excessive movement force the joint past its maximum range of motion, or external violence such As a side push on the knee during a football kick. |
| Strain | Muscle or Tendon | Overstretching of muscles or tendon generally during sudden acceleration or deceleration. |
| Contusion(bruise or Haematoma) or a Cork Open wound-cut, Abrasion, laceration | Muscle, Tendon Or Skin Skin | Direct blow from a collision with A player or piece of equipment, orfrom a heavy fall. Direct blow from a collision with a player or piece of equipment. |
| Hare Tissue | ||
| Fracture Dislocation/ Subluxation | Bone Joint | Direct trauma such as a blow: Indirect trauma such as falling on an outstretched hand Excessive movement of the Joint. |
Q.4 What are the symptoms and treatment of dislocation? What are the preventive measures for dislocation?
Ans. Signs and symptoms of dislocation:
·Discoloured
·Swollen
·Mis-happen
·Limited in mobility
·Intensely Painful
·Incapable of bearing weight
FIRST AID of dislocation:-
·Call 1099 or your local emergency assistance number.
·Splint the joint in its current position to give support. Attempting to reposition the joint could cause additional damage.
ICE & REST
·Ease swelling with ice.
·Rinse the wound gently if the skin is cut.
·Elevate the injured part of body
·Rest & relax the patient
·Elevate the injured part
·Support the injured part with supporting material
·Tie and cover the injured part
Preventive measures for dislocation
1. Awareness: Players should be well rested and alert. The ability to recognize and avoid hazards on the field, whether from an opponent or a stationary obstacle, is critical.
2. Equipment : Gear should fit properly. Shoes should be comfortable and supportive. Helmets should never block vision. Uniforms should fit well and not restrict movement.
3. Protective gear : Pads and helmets are a must. Protective gear buffers the force of any impact.
4. Proper warming up and cooling down:-
5. Avoid Irregular surfaces
Rehabilitation – Refer to qualified doctors for treatment.
·Normal Movement
1. Treatment
2. Physiotherapy
3. Massage
·Fitness for Sports participations
·Measurement of Injured parts fitness component.
Q5. Explain the meaning & need of Sports Medicine in detail.
Ans. Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness, treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise.
Sports medicine is the area which creates a positive environment, so an athlete converts his all genetic potentialities into phenotypic realities.
Need of sports medicine:-
·Identification of proper sports talent with the help of medical tests.
·Selection and rejection of team members on the basis of sports medical problems.
·Helping in the preparation of training schedule
·Prescribing the balance and special diet for people and sports men.
·Suggesting coaches and trainers for modifying their training programme.
·Educating the athlete regarding first aid of some common sports medical problems.
·Educating the athlete regarding use and abuse of drugs and other medicines.
Q6. Give description of intrinsic & extrinsic factors in sports injury?
Ans. EXTRINSIC RISK FACTOR
Inappropriate coaching
This is given by a coach who doesn’t have up to date knowledge of the current sporting rules and are not implying these rules in training situations.
Incorrect technique
This is where the participant slips from the correct technique taught by their coach. Bad technique can then adapt into bad habits leading to injuries.
Environmental conditions
These create a risk if the sports hall is slippery or it is raining outside stopping the participant in doing attacking or defensive work making them more likely to slip and cause injury.
Other sports players
Getting injured in a contact game from tackles, e.g rugby, in non contact sport getting injured from accidental collision or foul tackles.
Equipment and clothing
This could cause someone to get injured, and there is these to help certain sports. In football they have shin pads.
INTRINSIC RISK FACTOR
Inadequate warm up
This prepares the body mentally and physically before a game. It also gets the blood moving around the body.
Poor preparation
This is due to the ability of the sport, if someone is not very fit they cannot go in and play a 90 minute football match. It is also affected by the weather conditions, for example a marathon runner in England and Africa.
Postural defects
Most people are born with this and can affect their running technique by putting more strain on a part of the body compared to the other.
Poor technique
If a athlete has been taught not using the correct method then they can allow injury due to muscles and bones moving in the wrong direction.
Risk factor – age
This varies the type of injury to the level of competition. On one end of the scale one they can fall over lots whereas the other end the injury tends to be more overused
Physical Education Class 12 Important Questions Sports Medicine
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Define sports medicine. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of injuries related to participation in sports and /or exercise.
Question 2.
What are acute injuries?
Answer:
Acute injuries are the injuries that occur due to sudden trauma to the tissue. The symptoms of acute injuries present themselves almost immediately. For example sprains, fractures etc.
Question 3.
What are the important objectives of sports medicine?
Answer:
The three important objectives of sports medicine are
- Scientific promotion of sports.
- Developing preventive healthcare.
- Providing sports medical extension services.
Question 4.
What do you mean by first aid?
Answer:
First aid is the assistance given to any person; suffering a sudden illness or injury with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening and/or promote recovery.
Question 5.
What kind of sports injury can be termed as Abrasion? (All India 2016)
Answer:
In dermatology, an abrasion is a wound caused by superficial damage to the skin, no deeper than the epidermis. Mild abrasion is known as grazes or scrapes, a more traumatic abrasion that removes all layers of skin is known as avulsion.
Question 6.
What do you mean by RICER?
Answer:
RICER is one of the standard treatment procedures for sports injuries. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation and Referral.
Question 7.
What is incision? (All India 2017)
Answer:
An incision of skin and subcutaneous tissue is a surgical procedure performed in order to drain an abscess. An incision is a cut or a wound produced by cutting with a scalpel.
3 Marks Questions
Question 8.
Explain briefly the concept of sports medicine.
Answer:
Sports medicine deals with injuries related to participation in sports or in exercise. It is not a single field of speciality. It is an area that involves., healthcare professionals, researchers and educators from a wide variety of disciplines. Also, sports medicine requires the ‘combination of medical knowledge ’ with knowledge of a .particular sport. It is not only curative and rehabilitative but also preventive.
Question 9.
Discuss the need for sports medicine in brief.
Answer:
Sports medicine is one Of the very important fields in professional sports. Sports injuries have great impact on the physiology and psychology of athletes. Also there is social and financial harm associated with them. Therefore sports medicine is needed to ensure overall development and growth of air athlete.
Question 10.
What is scope of sports medicine?
Answer:
The scope of sports medicine is very wide. Other than the prevention and treatment of sports-related injuries, sports medicine also looks at a diverse area. The scope of sports medicine involves issues related to women’s participation in sports. Algo athletic nutrition, fitness and psychological aspects of sports performance are areas of concern for sports medicine.
Apart from these, sports medicine also deals with ageing and sports performance, an illness caused by environmental, physiological and psychological disturbances. Adaptive physical training, conditioning exercises and use and abuse of drugs are also fields of study for sports medicine.
Question 11.
What are the main objectives of first aid?
Answer:
The main objectives of first aid are as follows Preserving life by carrying out emergency first aid procedure. It also includes first aider’s life. Preventing the casualty’s condition from deteriorating any further. Promoting recovery by arranging prompt emergency medical help.
Question 12.
Explain briefly strain and sprain.
Answer:
Strain and sprain are two common soft tissue injuries. Strain is caused due to tearing of muscle fibres with pain, swelling and loss of muscle strength. On the other hand, sprain is a partial or complete tear of a ligament with symptoms of pain, swelling, bruising, loss of function, and often an audible ‘popping sound.
Question 13.
How are sports injuries classified?
Answer:
Sports injuries are classified in various ways. The classification can be based on the time taken for the tissues to become injured, the tissue type affected and severity of the injury.
These are detailed below
- Classification based on time taken for the tissue to become injured
- Acute injuries
- Overuse injuries
- Classification based on tissue type affected
- Soft tissue injuries
- Hard tissue injuries
- Special tissue injuries
- Classification based on severity
- Mild injuries
- Moderate injuries
- Severe injuries
Question 14.
A famous cricket star Phillip Hughes was struck behind the ear by a ball while batting and died two days after the injury. He was wearing a helmet but the possible reason mentioned was that even when using a helmet, possible a significant part of the neck remained exposed and the ball hit him there. And now most of the top cricketers across the world use deeper protection.
(i) Do you feel protective gears are important? Lay stress on your view.
(ii) What first aid should be provided during injury at the superficial layer of the skin? (All India 2017)
Answer:
(i) Yes, protective gears are very important in sports as they serve an integral role in maintaining the safety of the players and in preventing injuries. In contact sports like football, handball and in sports where prop is used like hockey sticks, players have a greater chance of injury. Therefore protective gears are important.
(ii) Injury at the superficial layer of the skin also called abrasion is a soft tissue injury. The RICER technique should be used as first aid in soft tissue injuries.
5 Marks Questions
Question 15.
What are the objectives of first aid?
Answer:
Objectives of first aid are as follows
1. Preserve Life Main aim of first aid is to preserve life by carrying out emergency first aid procedures. For example, opening a casualty’s airway or performing Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CCR). Preserving life should always be the overall aim of all first aiders. This includes first aider’s own life. We should never put ourselves or others in danger.
This is why the first stage in assessing a casualty is to conduct a risk assessment and check for any dangers. If a situation is too dangerous to approach, we should stay back and call for professional help.
2. Prevent Deterioration The second aim of first aid is to prevent the casualty’s condition from deteriorating any further. For example, asking a casualty with a broken limb to stay still and padding around the injury will prevent the fracture from moving and causing further injury or pain.
In addition, this aim includes preventing further injuries. We should attempt to make the area as safe as possible and removing any dangers. If removing danger is not possible, we should attempt to remove the patient from the danger or call for specialist help.
3. Promote Recovery Finally we can promote recovery by arranging prompt emergency medical help. In addition, simple first aid can significantly affect the long-term recovery of an injury. For example, quickly cooling a burn will reduce the risk of long-term scarring and will encourage early healing.
Question 16.
Classify sports injuries. Explain RICER procedure as a treatment of soft tissue injuries. (All India 2017)
Answer:
Sports injuries are classified in various ways. The classification can be based on the time taken for the tissues to become injured, the tissue type affected and severity of the injury. These are detailed below
- Classification based on time taken for the tissue to become injured
- Acute injuries
- Overuse injuries
- Classification based on tissue type affected
- Soft tissue injuries
- Hard tissue injuries
- Special tissue injuries
- Classification based on severity
- Mild injuries
- Moderate injuries
- Severe injuries
RICER stands for Rest Ice Compression, Elevation and Referral. RICER is used to manage soft tissue injury to reduce scarring and pain for faster recovery. This is a technique to be used as a first aid technique immediately after an injury ‘ occurs.
Question17.
What are the aims and scope of sports medicine?
Answer:
The major aim of sports medicine is maintaining physical fitness of sportspersons. It also aims at treating and preventing sports-related injuries and rapid recovery of patients. There are three specific aims of sports medicine.
- Scientific Promotion of Sports and Games
- Developing Preventive Healthcare
- Sports Medical Extention Services
The scope of sports medicine is very wide. It is not a single area of speciality. It is an area that involves healthcare professionals, researchers and educators from a wide variety of disciplines. Other than the prevention and treatment of sports-related injuries sports medicine also looks after a diverse area.
Question 18.
Explain following sports injuries briefly.
(a) Fracture
(b) Dislocation
(c) Green stick
(d) Stress fracture
(e) Concussion
Answer:
(a) Fracture is a crack or full break in a bone or bones. It can be closed or open. It has symptoms of intense pain, loss of function, swelling, bruising and possible deformity.
(b) Dislocation means partial or total separation of a joint. It most commonly affects ball and socket joints.
(c) Its symptoms include pain, bruising, swelling, loss of function and deformity. young, soft bone. In green stick the bone bends and’ breaks.
(d) Stress Fracture Stress fracture is a microfracture in bones. It occurs usually in the tibia. It leads to localised pain and tenderness.
(e) A concussion is a head injury with a temporary loss of brain function. Concussion can cause a variety of physical, cognitive and emotional symptoms.
in athletes.
Question 19.
Write in detail about the’dislocation and fractures among the bones and joint injuries. (All India 2016)
Answer:
The musculoskeletal systeih comprises over half the body mass. The most common musculoskeletal dysfunctions are joint stiffness, joint swelling and joint pains.
Bones, being no yielding structures, are damaged when excessive force is applied directly or indirectly. The nature of the damage depends on the direction of the applied force on the bones and the manner in which these bones are attached to other structures. The principal acute skeletal injuries are sprains, strains? subluxation, fractures and dislocations.
Many fractures and disldcatibn complications siich as nerve and vessel’injury bccur not from the trauma itself but from poor first-aid which does
not provide adequate Splinting prior to movement. Traumatic bone injury rarely occurs without significant soft-tissue damage. Fractures are classified as open and closed.
An open fracture is one in which there is a break in the skin that is contiguous with the fracture. The bone is either protruding from the wound or exposed through a channel, which can be produced by an arrow, javelin, bullet or other ways.
Question 20.
What are the causes of sports injuries?
Answer:
To effectively diagnose, rehabilitate and ultimately prevent subsequent injuries, a sport therapist should know the causes or mechanism of injury. Some common causes of sports injuries are
- Anatomical Factors These are related to make up of the body. Leg length differences and body misalignment can lead to unequal forces being transferred to the tissues. It can cause injuries to ankle, hip and back.
- Age-Related Causes As the body ages, it changes. It is less able to produce force, recovers slower and soft tissues lose the ability to stretch. Therefore it is more prone to injury.
- Training Related Causes Excessive repetitive loading of the tissues is needed for successive adaptation. However without suitable recovery, tissues never have the chance to adapt and can fail.
- Equipment Selection Factors These are related to the suitability of equipment. An instance is incorrect footwear, which will not protect the foot and ankle adequately. It also will not distribute forces effectively. Thus it increases the risk of injury.
- Impact and Contact Causes Impact or contact can be with objects, surfaces or other people. These injuries are common in contact sports like football, rugby, hockey etc. Also they are common in more dangerous sports like motor racing, boxing and skiing.
Question 21.
Discuss five techniques used to avoid sports injuries.
Answer:
One of the important objectives of sports medicine is preventing injuries. It also prevents other physical, mental, social and financial harm accompanying sports injuries. General techniques that can prevent sports injuries are
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down A well-structured warm-up and cool-down is necessary to increase blood and nutrient flow and concentration. Also it helps in relaxation, improved flexibility and recovery of muscles.
- Planning a Session Careful planning of training and rehabilitation sessions allows gradual specific adaptations. It reduces the damage to the tissues as a result of training.
- Using Protective Equipment The use of protective equipment like proper footwear, helmets, goggles, gum shield, shin pads and gloves prevents many sports injuries.
- Adherence to the Rules If all performers are aware of and adhere to the rules and laws of the particular sport, then injuries can be reduced to a great extent.
- Psychological Training Some form of mental skills training and practice could reduce injuries by reducing anxiety and improving concentration.
Question 22.
Write about standard techniques for minor sports injury management.
Answer:
The standard techniques for sports injury management are TOTAPS, RICER and No-HARM techniques.
These techniques are generally helpful for treating minor and non-serious injuries to soft tissues and to bones and joints. These techniques are essential for accurate assessment and quick recovery from injuries.
TOTAPS stands for Talk, Observe, Touch, Active movement, Passive movement and Skill test. It is helpful in assessing all non-serious injuries.
RICER is used to manage soft tissue injuries to reduce scarring and pain for faster recovery. RICER stands for Rest Ice Compression, Elevation and Referral. It should be used as a first-aid technique.
No-HARM or Avoid harm technique stands for No-Heat, No-Alcohol, No-Running and No-Massage. These are important precautions that any injured athlete must take for the first 72 hours after an injury occurs.
Question 23.
Define sports injuries. Write classification, prevention of sports injuries. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Sports injuries are injuries that occur in sports-related activities. They can result from acute trauma, or from overuse of a particular body part.
Classification Sports injuries can be classified in various ways. Classification can be based on the time taken for the tissues to become injured, tissue type affected and the severity of the injury.
Acute and Overuse Injuries It is based on the time taken for the tissues to become injured. Acute injuries occur due to sudden trauma to the tissue. Common acute injuries are sprains, fractures and dislocations. Overuse injuries are not so pervasive and represent a greater challenge for the sports therapist in diagnosis and management.
Overuse injuries occur over a period of time. These are usually caused due to repetitive loading of a particular tissue or tissues. Symptoms of such injuries show themselves gradually. The common example of overuse injuries are tennis elbow, achilles tendinitis, iliotibial band syndrome, swimmer’s shoulder etc.
Injuries Based on Tissue-Type Injured Sports injuries can be classified according to which tissue has been damaged. This allows sports therapists to identify soft, hard and special tissue injuries. The injuries to muscle, ligament, tendon and skin are soft tissue injuries.
The injuries to bones, joints and particular cartilage are hard tissue injuries. On the other hand, the injuries to brain, peripheral nerves, eyes, nose, sinuses, organs, teeth and blood vessels are special tissue injuries.
Injuries Based on Severity Most sports injuries require sportspersons to reduce participation or cease it altogether. Therefore sports injuries can also be classified relating to how long the symptoms present themselves.
Thus, injuries can be classified as
- Mild injuries, which usually last for 1-7 days.
- Moderate injuries, which usually last for I 8-20 days.
- Severe injuries, which usually last for 21 days and may also lead to permanent damage.
Prevention of General preventive measures that can prevent sports injuries are
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down A well- structured warm-up and cool-down is necessary to either prepare the individual 1 physically and mentally or aid recover from sport/exercise.
- Planning a Session Any training or rehabilitation programme should be carefully planned considering frequency, intensity, duration and type of training method. If programmes are carefully arranged, it allows a gradual specific adaptation to the imposed demands and reduces damage to the tissues as a result of training.
- Using Protective Equipment The use of protective equipment is to prevent , harmful movements, reduce or disperse shock and force, and act as a shield to block force. Key pieces of protective equipment are footwear, helmet, goggles, gum shield, shin pads, glove etc.
- Adherence to the Rules If all performers are aware of and adhere to the rules and laws of the game, then injuries can be reduced.
- Regular Fitness Testing Individuals must be fit enough to train or compete, otherwise their tissues can fail. Regular fitness testing will ensure individuals have the basic fitness to participate safely and effectively.
- Psychological Training Some form of mental skills training and practice could reduce injury by reducing anxiety, improving attention and allowing athletes to achieve optimal arousal for their sport.
- Meeting Nutritional Requirements Active individuals have increased nutritional requirements to meet extra energy, hydration and recover needs. Increasing carbohydrate, fluid and protein intake can play an important role in injury prevention by delaying fatigue and promoting recovery.
Value-Based Question
Question 24.
Read the following paragraph and give the answer
Ram was playing cricket with his friends in the summer of June. Time was around 10:00 am, suddenly his teammate Rohan fall down and was unconscious. His body was very hot, skin was hot red and dry and having rapid pulse rate. These were the signs of heat stroke. Ram told Pradeep to call ambulance and carried Rohan near cooler to reduce heat, removed his clothing and also tried to bring dpyvn his temperature with cold sponge, Pradeep tried to give him water but Ram immediately stopped him. After some time ambulance came and took Rohan to hospital. All friends were looking at Ram proudly because his awareness saved’Rohan’s life.
(i) What happened to Rohan, when he was playing cricket?
(ii) How did Pradeep come to know that it was heat stroke?
(iii) What was the first step Ram took?
(iv) What first aid Ram gave to Rohan?
(v) What values were shown by Ram?
Answer:
(i) He fell down and was unconscious.
(ii) Pradeep came to know that it was heat stroke because body of Rohan was very hot, skin was hot red and dry and pulse rate was also rapid which are the signs of heat stroke.
(iii) Ram told Pradeep to call ambulance and carried Rohan near cooler to reduce heat.
(iv) Ram removed his clothing and also tried to bring down his temperature with cold sponge.
(v) Values shown by Ram were helpful, awareness and intelligency.
1 Mark Questions
Question.1. Define sports medicine.
Answer. Sports medicine is a branch of healthcare. It deals with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of injuries related to participation in sports and /or exercise.
Question.2. What are acute injuries?
Answer. Acute injuries are the injuries that occur due to sudden trauma to the tissue. The symptoms of acute injuries present themselves almost immediately. For example sprains, fracture etc.
Question.3. What is/are the important objectives of sports medicine?
Answer. The three important objectives of sports medicine are:
- Scientific promotion of sports.
- Developing preventive healthcare.
- Providing sports medical extension services.
Question.4. What do you mean by RICER?
Answer. RICER is one of the standard treatment procedures for sports injuries. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation and Referral.
Question.5. Distinguish between natural surface and artificial surface used in sports.
Answer.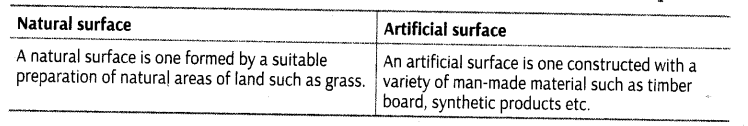
3 Marks Questions
Question.6. Explain briefly strain and sprain.
Answer. Strain and sprain are two common soft tissue injuries. Strain is caused due to tearing of muscle fibres with pain, swelling and loss of muscle strength. On the other hand, sprain is a partial or complete tear of a ligament with symptoms of pain, swelling, bruising, loss of function, and often an audible ‘popping sound.’
Question.7. How are sports injuries classified?
Answer. Sports injuries are classified in various ways. The classification can be based on the time taken for the tissues to become injured, the tissue type affected and severity of the injury.
These are detailed below:
- Classification based on time taken for the tissue to become injured
(a) Acute injuries (b) Overuse injuries - Classification based on tissue type
(a) Soft tissue injuries
(b) Hard tissue injuries
(c) Special tissue injuries - Classification based on severity affected
(a) Mild injuries
(b) Moderate injuries
(c) Severe injuries
Question.8. Explain briefly the concept of sports medicine.
Answer. Sports medicine deals with injuries related to participation in sports or in exercise. It is not a single field of speciality. It is an area that involves healthcare professionals, researchers and educators from a wide variety of disciplines. Also, sports medicine requires the combination of medical knowledge with knowledge of a particular sport. It is not only curative and rehabilitative, but also preventive.
Question.9. Discuss the need for sports medicine in brief.
Answer. Sports medicine is one of the very important fields in professional sports. Sports injuries have great impact on the physiology and psychology of athletes. Also there is social and financial harm associated with them. Therefore sports medicine is needed to ensure overall development and growth of an athlete.
Question.10. What do you mean by environment in the context of sports?
Answer. Environment in the context of sports may be any indoor or outdoor condition that potentially impacts on performance. The environment in sports will include prevailing weather conditions as well as physical nature of the venue such as topography, altitude etc. Also it will include man-made factors such as pollution and traffic, which can impact cycling, or noise such as stadium noise.
Question.11. What is scope of sports medicine?
Answer. The scope of sports medicine is very wide. Other than the prevention and treatment of sports related injuries, sports medicine also looks at a diverse area. The scope of sports medicine involves issues related to women’s participation in sports. Also athletic nutrition, fitness and psychological aspects of sports performance are areas of concern for sports medicine.
Apart from these, sports medicine also deals with ageing and sports performance, illness caused by environmental, physiological and psychological disturbances. Adaptive physical training, conditioning exercises and use and abuse of drugs are also fields of study for sports medicine.
5 Marks Questions
Question.12. Discuss five techniques used to avoid sports injuries.
Answer. One of the important objectives of sports medicine is preventing injuries. It also prevents other physical, mental, social and financial harm accompanying sports injuries. General techniques that can prevent sports injuries are:
- Warm-up and Cool-down A well structured warm-up and cool-down is necessary to increase blood and nutrient flow and concentration. Also it helps in relaxation, improved flexibility and recovery of muscles.
- Planning a Session Careful planning of training and rehabilitation sessions allows gradual specific adaptations. It reduces the damage to the tissues as a result of training.
- Using Protective Equipment The use of protective equipment like proper footwear, helmets, goggles, gum shield, shin pads and gloves prevents many sports injuries.
- Psychological training Some form of mental skills training and practice could reduce injuries by reducing anxiety and improving concentration.
- Adherence to the rules If all performers are aware of and adhere to the rules and laws of the particular sport, then injuries can be reduced to great extent.
Question.13. Write about standard techniques for minor sports injury management.
Answer. The standard techniques for sports injury management are TOTAPS, RICER and No-HARM techniques. These techniques are generally helpful for treating minor and non-serious injuries to soft tissues and to bones and joints. These techniques are essential for accurate assessment and quick recovery from injuries.
TOTAPS stand for Talk, Observe, Touch, Active movement, Passive movement and Skill test. It is helpful in assessing all non-serious injuries.
RICER is used to manage soft tissue injuries to reduce scarring and pain for faster recovery. RICER stands for Rest, ICE, Compression, Elevation and Referral. It should be used as a first aid technique. No-HARM or Avoid HARM technique stands for No-Heat, No-Alcohol, No-Running and No-Massage. These are important precautions that any injured athlete must take for the first 72 hours after an injury occurs.
Question.14. Distinguish between natural surface and artificial surface in sports and how they impact the performance of athletes.
Answer. There are two types of surfaces used in any indoor or outdoor games. These are natural and artificial surfaces. Natural surfaces are the surfaces that are prepared through proper combination of natural elements like soil and grass. On the other hand, artificial surfaces are more like carpets which are made from artificial components like rubber, synthetic fibre etc.
These surfaces impact performance of athletes differently. .In many contact games like football, cricket, running and Kabaddi natural surfaces are preferred because they provide more familiarity, grip and avoid severe injuries.
On the other hand, artificial surfaces provide more opportunities for practice because their use need not be stopped for maintenance. Also, with innovation in technology, artificial surfaces are becoming more user friendly. Risks of injuries are reducing in artificial surfaces also nowadays.
Question.15. What are the environmental factors that impact athletes? Explain any three.
Answer. Environmental factors in sports will include any indoor or outdoor conditions that potentially impact performance. Common environmental factors that influence performance of athletes are:
- Warm Weather Warm weather is often accompanied by high humidity. It is the most common adverse environmental factor encountered by athletes. Warm weather impacts hydration of body. Heat and humidity will increase the body’s production of sweat.
- High altitude High altitude is technically any altitude where oxygen is less than sea level. At higher altitudes the body is forced to produce more red blood cells to carry oxygen, which is available in less quantity. It affects peak performance of athletes.
- Crowd noise Crowd noise is the most important man-made factor which affects athlete performance. Because of high noise, athletes cannot concentrate and also teams cannot hear their own signals.
Question.16. Explain following sports injuries briefly.
1. Fracture 2. Dislocation
3.Green stick 4. Stress fracture
5. Concussion
Answer.
- Fracture Fracture is a crack or full break in a bone or bones. It can be closed or open It has symptoms of intense pain, loss of function, swelling, bruising and possible deformity.
- Dislocation Dislocation means partial or total separation of a joint. It most commonly affects ball and socket joints. It’s symptoms include pain, bruising, swelling, loss of function and deformity.
- Green Stick Green stick is a fracture in a young, soft bone. In green stick the bone bends and breaks. This fracture is very difficult to detect.
- Stress Fracture Stress fracture is a micro fracture in bones. It occurs usually in the tibia. It leads to localised pain and tenderness.
- Concussion Concussion is a head injury with a temporary loss of brain function. Concussion can cause a variety of physical, cognitive and emotional symptoms in athletes.
Question.17. What are the causes of sports injuries?
Answer. To effectively diagnose, rehabilitate and ultimately prevent subsequent injuries, a sport therapist should know the causes or mechanism of injury. Some common causes of sports injuries are
- Anatomical Factors These are related to make up of the body. Leg length differences and
body misalignment can lead to unequal forces being transferred to the tissues. It can cause injuries to ankle, hip and back. - Age related causes As the body ages, it changes. It is less able to produce force, recovers slower and soft tissues lose the ability to stretch. Therefore it is more prone to injury.
- Training related causes Excessive repetitive loading of the tissues is needed for successive adaptation. However without suitable recovery, tissues never have the chance to adapt and can fail.
- Equipment selection factors These are related to the suitability of equipment. An instance is incorrect footwear,-which will not protect the foot and ankle adequately. It also will not distribute forces effectively. Thus it increases the risk of injury.
- Impact and contact causes Impact or contact can be with objects, surfaces or other people. These injuries are common in contact sports like football, rugby, hockey etc. Also they are common in more dangerous sports like motor racing, boxing and skiing.
