Question
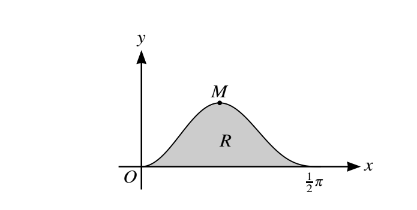
The diagram shows the curve\( y = 5sin^{2}xcox^{3}x \) for\( 0 ≤ x ≤\frac{1}{2}\pi \)
, and its maximum point M. The shaded region R is bounded by the curve and the x-axis.
(i) Find the x-coordinate of M, giving your answer correct to 3 decimal places. [5]
(ii) Using the substitution u = sin x and showing all necessary working, find the exact area of R. [4]
Answer/Explanation
(i) Use product rule
Obtain correct derivative in any form Equate derivative to zero and obtain an equation in a single trig function
Obtain a correct equation, e.g.
Obtain answer x = 0.685
(ii) Use the given substitution and reach\( a\int (u^{2}-u^{4})du\) Obtain correct integral with a = 5 and limits 0 and 1
Use correct limits in an integral of the form \(a\left ( \frac{1}{3} u^{3}-\frac{1}{5}u^{5}\right )\)
Obtain answer \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question
(i) By first expanding cos(2x + x), show that \(cos 3x \equiv 4cos^{3}x-3cosx\)
(ii) Hence solve the equation cos 3x + 3 cos x + 1 = 0, for 0 ≤ x ≤ \Pi.
(iii) Find the exact value of \(\int _{\frac{1}{6}\Pi }^{\frac{1}{3}\Pi }cos^{3}x dx\)
Answer/Explanation
(i) Use cos(A +B) formula to express cos3x in terms of trig functions of 2x and x Use double angle formulae and Pythagoras to obtain an expression in terms of cos x
only
Obtain a correct expression in terms of cos x in any form
Obtain \(cos3x= 4cos^{3}x-3cosx\)
(ii) Use identity and solve cubic \(4cos^{3}x=-1\) for x
Obtain answer 2.25 and no other in the interval
(iii) Obtain indefinite integral \(\frac{1}{12}sin3x+\frac{3}{4}sinx\)
Substitute limits in an indefinite integral of the form a xb x sin 3 sin + , where ab ≠ 0
Obtain answer \(\frac{1}{24}(\sqrt[9]{3-11})\) , or exact equivalent
Alternative method for question (iii)
\(\int cosx(1-sin^{2}x)dx=sinx-\frac{1}{3}sin^{3}x(+C)\)
Substitute limits in an indefinite integral of the form\( asinx+bsin^{3}x \)where ab ≠ 0
Obtain answer \( \frac{1}{24}(\sqrt[9]{3}-11)\) , or exact equivalent
Question
Let \(fx =\frac{x^{2}+x+6}{x^{2}(x+2)}\)
(i) Express fx in partial fractions.
(ii) Hence, showing full working, show that the exact value of \(\int _{1}^{4f(x)dx is \frac{9}{4}}\)
Answer/Explanation
(i) State or imply the form \(\frac{A}{x}+\frac{B}){x^{2}}+\frac{c}{x+2}\ Use a correct method for finding a constant
Obtain one of A = – 1, B = 3, C = 2
Obtain a second value
Obtain the third value
(ii) Integrate and obtain terms In \( x-\frac{3}{x}+2 In(x+2)\) Substitute limits correctly in an integral with terms a In x\( \frac{b}{x}\) and c x ln 2 ( + ) , where abc
≠ 0
Obtain\( \frac{9}{4}\) following full and exact working
Question
(i) By differentiating \(\frac{cosx}{sinx}\) show that if y = cot x then \(\frac{dy}{dx}=-cosec^{2}x\)
(ii) Show that\( \int_{\frac{1}{4\pi }}^{\frac{1}{2\pi }}xcosec^{2}xdx=\frac{1}{4}(\pi +In4).
Answer/Explanation
(i) Use correct quotient rule Obtain \(\frac{dy}{dx}=-cosec^{2}x\) correctly
(ii) Integrate by parts and reach \( axcotx+b\int cotxdx\) Obtain\( -xcotx+\int cotx dx\)
State ±ln sinx as integral of cotx Obtain complete integral −x cotx ln sin x Use correct limits correctly
Obtain \(\frac{1}{4}(\pi +In4)\)following full and exact working
Question
(i) By first expanding sin(2x + x), show that sin \(3x\equiv 4sin^{3}x\)
(ii) Hence, showing all necessary working, find the exact value of \(\int_{0}^{\frac{1}{3\Pi }}sin^{x}dx\)
Answer/Explanation
(i) State correct expansion of sin (2x+x)
Use trig formulae and Pythagoras to express sin 3x in terms of sin x Obtain a correct expression in any form Obtain sin3 x \(3sin^{3} \)4sinx ≡ −x x correctly
(ii) Use identity, integrate and obtain
Use limits correctly in an integral of the form
a cosx + b cos 3x, where ab≠0 Obtain answer 5\24
Question
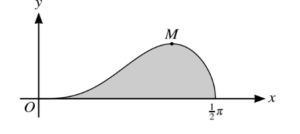
The diagram shows the curve \(y=sin^{3}x\sqrt{(cos)}\)for for\( 0 ≤ x ≤\frac{1}{2}\pi\) and its maximum point M.
(i) Using the substitution u = cos x, find by integration the exact area of the shaded region bounded
by the curve and the x-axis.
(ii) Showing all your working, find the x-coordinate of M, giving your answer correct to 3 decimal
places.
Answer/Explanation
(i) State or imply du = – sin xdx
Using Pythagoras express the integral in terms of u
Obtain integrand\(\pm \sqrt{u}(1-u^{2})\)
Integrate and obtain\(-\frac{2}{3}u^{\frac{3}{2}}+\frac{2}{7}u^{\frac{7}{2}}\), or equivalent
Change limits correctly and substitute correctly in an integral of the form \(au^{\frac{3}{2}}+bu^{\frac{7}{2}}\)
Obtain answer\(\frac{8}{21}\)
(ii) Use product rule and chain rule at least once
Obtain correct derivative in any form
Equate derivative to zero and obtain a horizontal equation in integral powers of sin x and cos x
Use correct methods to obtain an equation in one trig function
obtain \(tan^{2}x=6,7cos^{2}x=1 or 7sin^{2}x=6\),or equivqlent,and obtain answer 1.183
Question
Use the substitution u = 1 + 3 tan x to find the exact value of
\(\int_{0}^{\frac{1}{4}\pi } \frac{\sqrt{(1+3tanx)}}{cos^{2}}dx\)
Answer/Explanation
State\( \frac{du}{dx}=3sec^{2}x \) or equivalent
Express integral in terms of and (accept unsimplified and without limits)
Obtain \(\int \frac{1}{3}u^{\frac{1}{2}}\) du
Integrate \(Cu^{\frac{1}{2}} to obtain \frac{2C}{3}u^{\frac{3}{2}}\)
Obtain\( \frac{14}{9}\)
Question
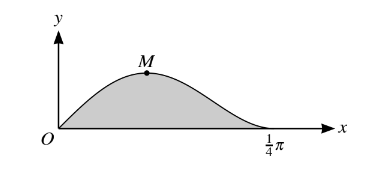
The diagram shows the curve y = \(sin x cos^{2}\) 2x for 0 ≤ x ≤\(\frac{1}{4}\) 0 and its maximum point M.
(i) Using the substitution u = cos x, find by integration the exact area of the shaded region bounded by the curve and the x-axis.
(ii) Find the x-coordinate of M. Give your answer correct to 2 decimal places
Answer/Explanation
.
10(i) State or imply du=-sinxdx
Using correct double angle formula, express the integral in terms of u and du
Obtain integrand \(\pm (2u^{2}-1)^{2}\)
Change limits and obtain correct integral \(\int_{\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}^{1}(2u^{2}-1)^{2}du\)
Substitute limits in an integral of the form \(au^{5}+bu^{3}+cu\)
Obtain answer \(\frac{1}{15}(7-4\sqrt{2}) \)or exact simplified equivalent
10(ii) Use product rule and chain rule at least once
Obtain correct derivative in any form
Equate derivative to zero and use trig formulae to obtain an equation in
cosx and sin x
Use correct methods to obtain an equation in cos x or sin x only
Obtain \(10cos^{2}x\) =9 or
\(10sin^{2}\) =1 , or equivalent
Obtain answer 0.32
Question
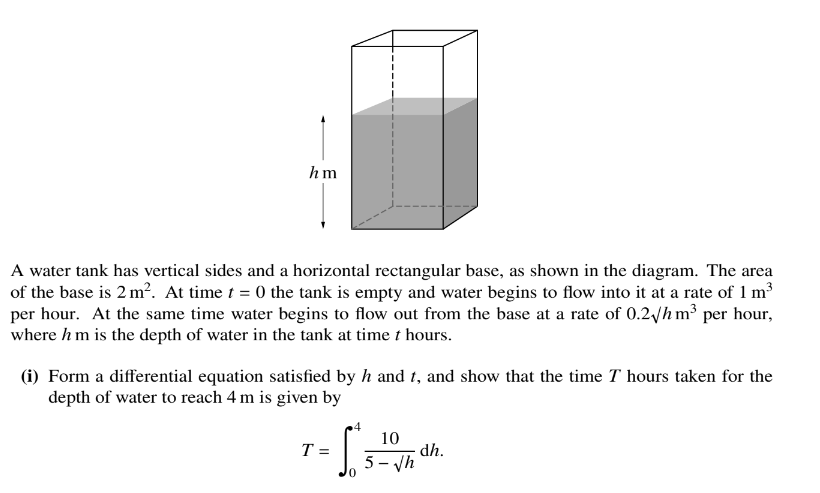
(ii) Using the substitution u= 5 −h, find the value of T.
Answer/Explanation

Question
The equation of a curve is \(y=x^{-\frac{2}{3}}\) ln x for x > 0. The curve has one stationary point.
(a) Find the exact coordinates of the stationary point. [5]
(b) Show that \(\int_{1}^{8}ydx=18ln2-9\) [5]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) Use correct product rule or correct quotient rule
Obtain correct derivative in any form
Equate 2 term derivative to zero and solve for x
Obtain answer \(x=e^{\frac{3}{2}}\)
Obtain answer \(y=\frac{3}{2e}\
(b) Commence integration and reach \(ax^{\frac{1}{3}}ln\ x+b\int x^{\frac{1}{3}}\frac{1}{x}dx\)
Obtain \(3x^{\frac{1}{3}}ln \ x-3\int x^{\frac{1}{3}}\frac{1}{x}dx\)
Complete the integration and obtain \(3x^{\frac{1}{3}}ln \ x-9x^{\frac{1}{3}}\)
Use limits correctly in an expression of the form \(px^{\frac{1}{3}}ln\ x+qx^{\frac{1}{3}} (pq\neq 0)\)
Obtain 18ln 2 9 − from full and correct working
Question
Using the substitution u = \(\sqrt{x}\) , find the exact value of
\(\int_{3}^{\infty } \frac{1}{\left ( x + 1 \right )\sqrt{x}}dx.\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
State that \(\frac{du}{dx} = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}} or du = \frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}dx\)
Substitute throughout for x and dx
Obtain a correct integral with integrand \(\frac{2}{u^{2}+1}\)
Integrate and obtain term of the form k tan−1 u
Use limits \(\sqrt{3} and \infty \) for u or equivalent and evaluate trig.
Obtain answer \(\frac{1}{3}\pi \)
Question

The diagram shows the curve \(y=sin 2x cos^2\) for \(0≤x≤\frac{1}{2}\pi\), and its maximum point M.
(a) Using the substitution u = sin x, find the exact area of the region bounded by the curve and the x-axis.
(b) Find the exact x-coordinate of M.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
- State or imply du =cos x dx
Using double angle formula for sin 2x and Pythagoras, express integral in terms of u and du.
Obtain integral \(\int 2(u-u^3)du\)
Use limits u = 0 and u = 1 in an integral of the form \(au^2+bu^4\), where ab≠0
Obtain answer \(\frac{a}{2}\) - Use product rule
Obtain correct derivative in any form
Equate derivative to zero and use a double angle formula
Obtain an equation in one trig variable
Obtain \(4x^2=1, 4cos^2x=3\) or \(3tan^2x=1\)
Obtain answer \(x=\frac{1}{6}\pi\)
Question
Let \(f(x) = \frac{5a}{(2x-a)(3a-x)}\), where a is a positive constant.
(a) Express f(x) in partial fractions.
(b) Hence show that \(\int_{a}^{2a}f(x)dx=In6\).
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
- Carry out a relevant method to determine constants A and B such that
\(\frac{5a}{(2x-a)(3a-x)}=\frac{A}{2x-a}+\frac{B}{3a-x}\)
Obtain A=2
Obtain B=1 - Integrate and obtain terms In(2x-a)-In(3a-x)
Substitute limits correctly in a solution containing terms of the form bIn(2x-a) and cIn(3a-x), where bc≠0
Obtain the given answer showing full and correct working
Question
The diagram shows the curve y = sin x cos 2x for 0 ≤ x ≤ \(\frac{1}{2}\) π, and its maximum point M.
(a)Find the x-coordinate of M, giving your answer correct to 3 significant figures.
(b)Using the substitution u = cos x, find the area of the shaded region enclosed by the curve and the x-axis in the first quadrant, giving your answer in a simplified exact form.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)Use correct product rule or chain rule
Use correct product rule or chain rule
Equate derivative to zero and use a correct double angle formula
Obtain an equation in one trigonometric variable
Obtain 6sin2 x= 1, 6cos2 x= 5 or 5tan2 x=1
Obtain final answer x = 0.421
(b)
State or imply du =−sin x dx
Using double angle formula, express integral in terms of u and du
Integrate and obtain ± \(\left ( u – \frac{2}{3} u^{3}\right )\)
Use limits u = 1, u = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\) in an integral of the form au + bu3 , where ab ≠ 0
Obtain \(\frac{1}{3}\left ( \sqrt{2} -1\right )or \frac{1}{3}\sqrt{2}\frac{1}{3} or \frac{2}{3}\left ( \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right )\frac{1}{3}\) or simplified equivalent
Question
Let f(x) = \(\frac{3x^{3}+6x-8}{x\left ( x^{^{2}}+2 \right )}\) .
(i) Express f(x) in the form \(A+\frac{B}{x}+\frac{Cx+D}{x^{2}+2}\) .[5]
(ii) Show that \(\int_{1}^{2}f\left ( x \right )dx = 3 – ln 4\) .[5]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(i) State or obtain A = 3
Use a relevant method to find a constant
Obtain one of B = −4, C = 4 and D = 0
Obtain a second value
Obtain the third value
(ii) Integrate and obtain 3x – 4ln x
Integrate and obtain term of the form k ln(x2 +2)
Obtain term 2ln(x2 +2)
Substitute limits in an integral of the form ax + b ln x + c ln(x2 + 2) , where abc ≠ 0
Obtain given answer 3 − ln 4 after full and correct working
Question
Let \(I=\int_{0}^{1}\frac{9}{\left ( 3+x^{2} \right )^{2}}dx.\)
(i) Using the substitution x = (√3) tan θ, show that \(I=\int_{0}^{\frac{1}{6}\pi } cos^{2}θdθ\) .[3]
(ii) Hence find the exact value I.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(i) State or imply dx = √3 sec2 θ dθ
Substitute for x and dx throughout
Obtain the given answer correctly
(ii) Replace integrand by \(\frac{1}{2} cos 2 θ +\frac{1}{2}\)
Obtain integral \(\frac{1}{4} sin 2 θ +\frac{1}{2}θ\)
Substitute limits correctly in an integral of the form c sin 2θ +bθ , where cb ≠ 0
Obtain answer \(\frac{1}{12}\sqrt{3\pi }+\frac{3}{8}\) , or exact equivalent
[The f.t. is on integrands of the form a cos 2θ + b, where ab ≠ 0.]
