NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force and Pressure:
Section Name | Topic Name |
11 | Force and Pressure |
11.1 | Force – A Push or a Pull |
11.2 | Forces are due to an Interaction |
11.3 | Exploring Forces |
11.4 | A Force can Change the State of Motion |
11.5 | Force can Change the Shape of an Object |
11.6 | Contact Forces Muscular Force |
11.7 | Non-contact Forces Magnetic Force |
11.8 | Pressure |
11.9 | Pressure Exerted by Liquids and Gases |
11.10 | Atmospheric Pressure |
Force and Pressure Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions
Question 1.
Give two examples each of the situations in which you push or pull to change the state of motion of objects.
Answer:
(i) Push: We close drawer by pushing.
We move a wooden box by pushing.
(ii) Pull: We draw water from a well by pulling the rope.
A horse pulls a cart.
Question 2.
Give two examples of situations in which applied force causes a change in the shape of an object.
Answer:
When we apply force on a rubber band to stretch it and on clay to change its shape.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements.
(a) To draw water from a well we have to ______ at the rope.
(b) A charged body ______ an uncharged body towards it.
(c) To move a loaded trolley we have to ______ it.
(d) The north pole of a magnet _______ the north pole of another magnet.
Answer:
(a) pull
(b) attracts
(c) push
(d) repels
Question 4.
An archer stretches her bow while taking aim at the target. She then releases the arrow, which begins to move towards the target. Based on this information fill up the gaps in the following statements using the following terms:
muscular, contact, non-contact, gravity, friction, shape, attraction
(a) To stretch the bow, the archer applies a force that causes a change in its ______
(b) The force applied by the archer to stretch the bow is an example of ______ force.
(c) The type of force responsible for a change in the state of motion of the arrow is an example of a ______ force.
(d) While the arrow moves towards its target, the forces acting on it are due to _______ and that due to _____ of air.
Answer:
(a) shape
(b) muscular
(c) contact
(d) gravity, friction
Question 5.
In the following situations identify the agent exerting the force and the object on which it acts. State the effect of the force in each case.
(a) Squeezing a piece of lemon between the fingers to extract its juice.
(b) Taking out paste from a toothpaste tube.
(c) A load suspended from a spring while its other end is on a hook fixed to a wall.
(d) An athlete making a high jump to clear the bar at a certain height.
Answer:
(a) Agents are fingers, object is lemon, effect of force changes the shape of lemon.
(b) Agents are fingers of the person squeezing the tube, object is toothpaste tube and effect of the force can be observed as the paste coming out of the tube (change in shape).
(c) Agent is the load suspended, object is the spring and effort can be seen in the form of elongation of spring on suspension of load (change in shape).
(d) Agent is muscles of athlete, object is athlete himself and effect of the force changes the state of motion of the athlete.
Question 6.
A blacksmith hammers a hot piece of iron while making a tool. How does the force due to hammering affect the piece of iron?
Answer:
The force due to hammering causes the change in the shape of the iron and iron can be moulded in the shape of the required tool.
Question 7.
An inflated balloon was pressed against a wall after it has been rubbed with a piece of synthetic cloth. It was found that the balloon sticks to the wall. What force might be responsible for the attraction between the balloon and the wall?
Answer:
Electrostatic force.
Question 8.
Name the forces acting on a plastic bucket containing water held above ground level in your hand. Discuss why the forces acting on the bucket do not bring a change in its state of motion.
Answer:
Forces acting on bucket are as follows:
(i) Muscular force of arms acting upward.
(ii) Force of gravity acting downward.
Both the forces do not bring any change in the state of motion because both of them are acting in equal and opposite directions and thus they cancel each other’s effect.
Question 9.
A rocket has been fired upwards to launch a satellite in its orbit. Name the two forces acting on the rocket immediately after leaving the launching pad.
Answer:
The forces that act when a rocket leaves launching pad are as follows:
(i) Gravitational force of the earth (downward)
(ii) Frictional force of air (in opposite direction)
Question 10.
When we press the bulb of a dropper with its nozzle kept in water, air in the dropper is seen to escape in the form of bubbles. Once we release the pressure on the bulb, water gets filled in the dropper. The rise of water in the dropper is due to
(a) pressure of water
(b) gravity of the earth
(c) shape of rubber bulb
(d) atmospheric pressure
Answer:
(d) atmospheric pressure
Force and Pressure Class 8 Science NCERT Intext Activities Solved
Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 128)
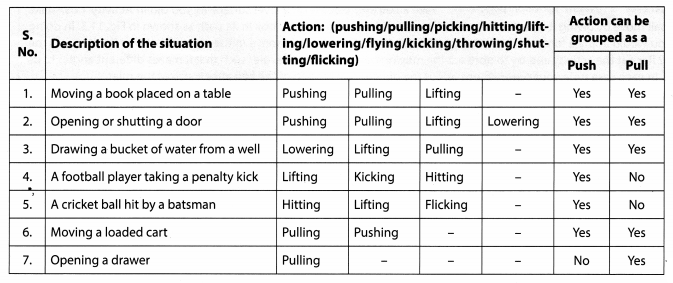
Table 11.1 gives some examples of familiar situations involving the motion of objects. You can add more such situations or replace those given here. Try to identify action involved in each case as a push and/or a pull and record your observations. One example has been given to help you.
Identifying Actions as Push or Pull
Activity 2 (NCERT Textbook, Page 130)
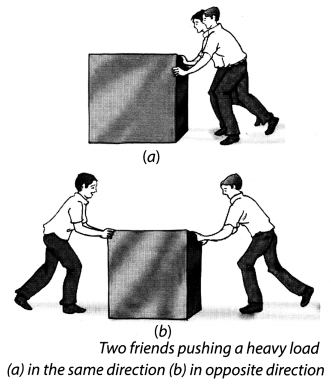
Choose a heavy object like a table or a box, which you can move only by pushing hard. Try to push it all by yourself. Can you move it? Now ask one of your friends to help you in pushing it in the same direction [Fig. 11.1(a)]. Is it easier to move it now? Can you explain why? Now push the same object, but ask your friend to push it from the op¬posite side [Fig. 11.1 (b)]. Does the object move? If it does, note the direction in which it moves. Can you guess which one of you is applying a larger force?
Solution:
(i) The box moves with difficulty when we push alone but moves easily if helped by our friend. Thus, force applied on an object in the same direction add to one another.
(ii) When the object is pushed from the opposite side, it does not move. Thus, if two forces acting in the opposite direction on an object the net force acting on it is the difference between the two forces.
Activity 3 (NCERT Textbook, Page 131)
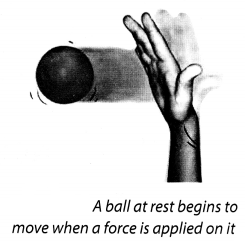
Jake a rubber ball and place it on a level surface such as a tabletop or a concrete floor. Now, gently push the ball along the level surface (Fig. 11.2). Does the ball begin to move? Push the ball again while it is still moving. Is there any change in its speed? Does it increase or decrease?
Next, place your palm in front of the moving ball. Remove your palm as soon as the moving ball touches it. Does your palm apply a force on the ball? What happens to the speed of the ball now? Does it increase or decrease? What would happen if you let your palm hold the moving ball?
Solution:
When we push the ball along the level surface, the ball begin to move. When we push the ball again while it is still moving, increases its speed.
When we place our palm in front of the moving ball, decreases its speed. Hence, force can change the state of motion.
Activity 4 (NCERT Textbook, Page 132)
Take a ball and place it on a level surface as you did in Activity 11.3. Make the ball move by giving it a push. Now place the ruler from your geometry box in its path as shown in Fig. 11.3. In doing so, you would apply a force on the moving ball. Does the ball continue to move in the same direction after it strikes the ruler? Repeat the activity and try to obstruct the moving ball by placing the ruler such that it makes different angles to its path. In each case note your observations about the direction of motion of the ball after it strikes the ruler.
Solution:
Ball changes direction after it strikes the ruler. Thus, a force can change direction of motion of a moving object.
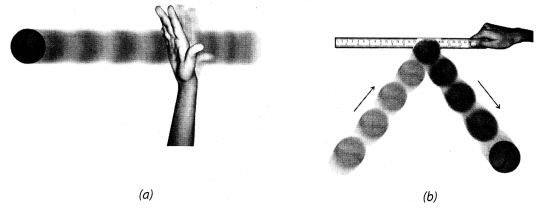
(a) A ball set in motion by pushing it along a level surface and
(b) the direction of motion of the ball after it strikes the ruler placed in its path
Activity 5 (NCERT Textbook, Page 133)
Some situations have been given in Column 1 of Table 11.2 in which objects are not free to move. Column 2 of the Table suggests the manner in which a force can be applied to each object while Column 3 shows a diagram of the action. Try to observe the effect of the force in as many situations as possible. You can also add similar situations using available material from your environment. Note your observations in Columns 4 and 5 of the table.
Studying the Effect of Force on Objects
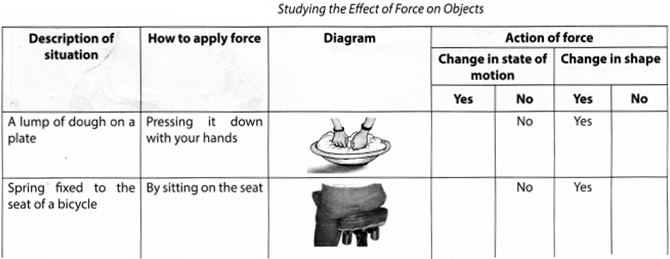
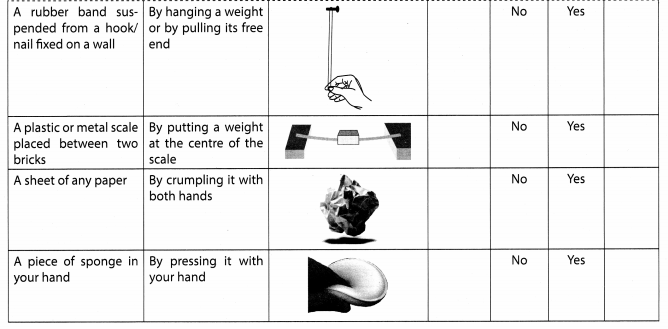
Solution:
From the above actions, we can conclude that force can change the shape of an object.
Activity 6 (NCERT Textbook, Page 135)
Take a pair of bar magnets. Place the longer side of one of the magnets over three round shaped pencils or wooden rollers as shown in Fig. 11.4. Now bring one end of the other magnet near the end of the magnet placed on the rollers. Make sure that the two magnets do not touch each other. Observe what happens. Next, bring the other end of the magnet near the same end of the magnet placed on the rollers (Fig. 11.4). Note what happens to the magnet placed on the rollers every time another magnet is brought near it.
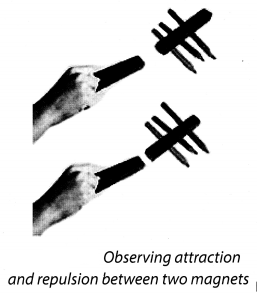
Solution:
When unlike poles of the magnet are brought near the other magnet, they attract each other and moves in the direction of another magnet. When like poles of a magnet are brought near to the other magnet, they repel each other and moves in the direction away from the other magnet.
Thus, the force exerted by a magnet on another magnet is a type of non-contact force.
Activity 7 (NCERT Textbook, Page 136)
Take a plastic straw and cut it into nearly two equal pieces. Suspend one of the pieces from the edge of a table with the help of a piece of thread (Fig. 11.5). Now hold the other piece of straw in your hand and rub its free end with a sheet of paper. Bring the rubbed end of the straw near the suspended straw. Make sure that the two pieces do not touch each other. What do you observe?
Next, rub the free end of the suspended piece of straw with a sheet of paper. Again, bring the piece of straw that was rubbed earlier with paper near the free end of the suspended straw. What do you observe now?
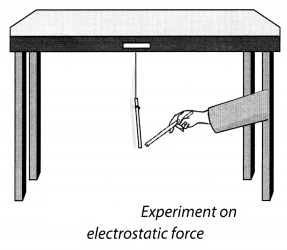
Solution:
A straw rubbed with paper attracts another straw but repels it if it has also been rubbed with a sheet of paper.The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body is known as electrostatic force.
Activity 8 (NCERT Textbook, Page 138)
Take a transparent glass tube or a plastic pipe. The length of the pipe/tube should be about 15 cm and its diameter should be 5-7.5 cm. Also take a piece of thin sheet of a good quality rubber, say, a rubber balloon. Stretch the rubber sheet tightly over one end of the pipe. Hold the pipe at the middle, keeping it in a vertical position (Fig. 11.6). Ask one of your friends to pour some water in the pipe. Does the rubber sheet bulge out? Note also the height of the water column in the pipe. Pour some more water. Observe again the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe. Repeat this process a few more times. Can you see any relation between the amount of the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe?
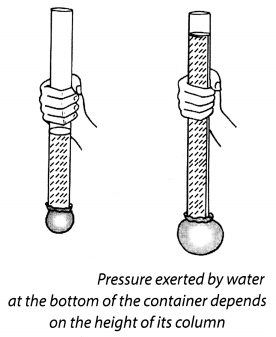
Solution:
The amount of bulge in the rubber sheet increases with the height of the water column in the pipe. Thus, the pressure exerted by water at the bottom of the container depends upon the height of its column.
Activity 9 (NCERT Textbook, Page 138)
Take a plastic bottle. You can take a discarded water or soft drink bottle. Fix a cylindrical glass tube, a few cm long near its bottom as shown in Fig. 11.7. You can do so by slightly heating one end of the glass tube and then quickly inserting it near the bottom of the bottle. Make sure that the water does not leak from the joint. If there is any leakage, seal it with molten wax. Cover the mouth of the glass tube with a thin rubber sheet as you did in Activity 11.8. Now fill the bottle upto half with water. What do you observe? Why does the rubber sheet fixed to the glass tube bulge this time? Pour some more water in the bottle. Is there any change in the bulge’of the rubber sheet?
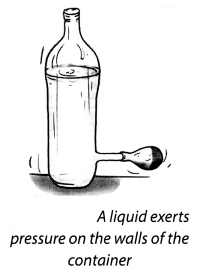
Solution:
Yes, the rubber tube bulge out and the bulging increases with the amount of water in the bottle. Thus, liquid exert pressure on the walls of the container.
Activity 10 (NCERT Textbook, Page 139)
Take an empty plastic bottle or a cylindrical container. You can take a used tin of talcum powder or a plastic bottle. Drill four holes all around near the bottom of the bottle. Make sure that the holes are at the same height from the bottom (Fig. 11.8). Now fill the bottle with water. What do you observe?
Do the different streams of water coming out of the holes fall at the same distance from the bottle? What does this indicate?
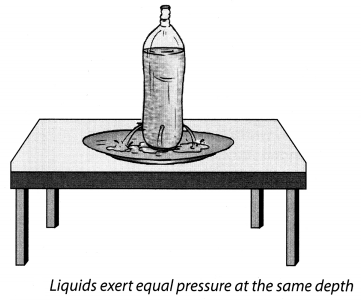
Solution:
We observed that different streams of a waterfall at the same distance from the bottle. Thus, it indicates that liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth.
Activity 11 (NCERT Textbook, page 140)
Take a good quality rubber sucker. It looks like a small rubber cup (Fig. 11.9). Press it hard on a smooth plane surface. Does it stick to the surface? Now try to pull it off the surface. Can you do it?

Solution:
when we press the sucker, most of the air between its cup and the surface escapes out. The sucker sticks to the surface because the pressure of the atmosphere acts on it. To pull the sucker off the surface, the applied force should be large enough to overcome the atmospheric pressure. Thus, this activity gives us an idea about the magnitude of atmospheric pressure.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 – 1 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
When we press the bulb of a dropper with its nozzle kept in water, air in the dropper seems to escape in the form of bubbles. Once we release the pressure on the bulb, water gets filled in the dropper. The rise of water in the dropper is due to [NCERT]
· pressure of water
· gravity of the earth.
· shape of rubber bulb.
· atmospheric pressure.
Answer:
atmospheric pressure
Question 2.
An inflated balloon was pressed against a wall after it has been rubbed with a piece of synthetic cloth. It was found that the balloon sticks to the wall. What force might be responsible for the attraction between the balloon and the wall ? [NCERT]
Answer:
Electrostatic force.
Class 8: Force and Pressure
B. V. Short types: |
