NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science. Here we have given. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
1. Answer the following questions.
Question 1(1).
What is agriculture?
Answer:
Agriculture is the primary activity which includes growing of crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and the rearing of livestock.
Question 1(2).
Name the factors influencing agriculture?
Answer:
Factors influencing agriculture:
- Favourable Topography
- Soil
- Climate
- Irrigation
Question 1(3).
What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?
Answer:
Shifting cultivation is the form of agriculture in which a plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmers move to a different place. It is disadvantageous because it involves deforestation and the burning of trees. Thus it is not good for the environment.
Question 1(4).
What is plantation agriculture?
Answer:
- Plantation agriculture is a type of commercial agriculture:
- It is a single crop farming which resembles factory production,
- Large amount of labour and capital is required.
- The produce may be processed on the farm itself or in factories.
- Crops like banana, rubber, tea, coffee etc. are grown on plantations.
Question 1(5).
Name the fiber crops and name the climatic conditions required for their growth.
Answer:
The two fibre crops are cotton and jute. The conditions required for their cultivation
| Cotton | Jute |
| It requires high temperature. | High temperature required. |
| Light rainfall, 210 frost free days, bright sunshine for its growth. | Heavy rainfall. |
| Grows well in black and alluvial soil. | Grows well in alluvial soils. |
| Area of cultivation: China, USA India, Pakistan, Brazil and Egypt. | Areas of prod: India and Bangladesh. |
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(1) Horticulture means
(a) growing of fruits and vegetables
(b) primitive farming
(c) growing of wheat
(2) Golden fiber refers to
(a) tea
(b) cotton
(c) jute
(3) Leading producers of coffee
(a) Brazil
(b) India
(c) Russia
Question 3(1).
Give reasons.
In India, agriculture is a primary activity.
Answer:
- In India agriculture is a primary activity because:
- Of its tropical climate and topography which is suitable for cultivation.
- More than 60% of the population is dependent on it.
- Needs food security for feeding millions.
Question 3(2).
Different crops are grown in different regions because of the following reasons:
Answer:
The growth of crops depends on a lot of factors. Climate, rainfall, humidity, etc are important factors. In absence of certain conditions, it may not be possible to grow a certain crop. So, different crops are grown in different regions.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the following.
(1) Primary activities and tertiary activities.
(2) Subsistence farming and intensive farming.
Answer:
(1) Distinction between Primary Activities and Tertiary Activities.
| Primary Activities | Tertiary Activities |
| 1. Primary activities are those activities in which natural resources are obtained. 2. Examples: Extraction, hunting, mining, gathering, agriculture, fishing and rearing of livestocks. | 1. Tertiary activities are those activities which provide support to primary and secondary sectors. 2. Examples: Transport, communication, trade, banking, insurance, and advertising. |
(2) Distinction between Subsistence and Intensive Farming.
Intensive farming is a part of subsistence farming. So both have a little difference. Still, some differences are:
Answer:
| Subsistence Fanning | Intensive Farming |
| 1. Subsistence farming is the type of farming practice in which the farmer raises agriculture crops for himself and his family. 2. Household labour is used. 3. Subsistence farming is done on a traditional basis by traditional tools and implements. 4. Production is meant for their own family only. | 1. Intensive farming is an agricultural practice in which efforts are made to increase production with added units of labour and capital and raise two to three crops in a year. 2. Outside labour is hired. 3. Extra tools may be hired. 4. Production is primarily meant for domestic consumption. Excess is sold in the market. |
5. Activity
Question 5 (1).
Collect seeds of wheat, rice, jowar, bajra, ragi, maize, oilseeds, and pulses available in the market. Bring them to the class and find out which type of soil they grow.
Answer:
Collect the seeds of wheat, rice, jowar, bajra, ragi, maize, oilseeds, and pulses available in the market yourself and bring them to the class
Question 5(2).
Find out the differences between the lifestyle of farmers in the USA and India on the basis of pictures collected from magazines, books, newspapers, and the internet.
Answer:
| Criteria | Farm in India | Farm in the USA |
| Average size | 1.5 Hectares. | 250 Hectares. |
| Land tenure | Tenancy, sharecropping fragmentation due to hereditary. | Freehold ownership. |
| Environment issues | Use of fertilizers, HYV seeds and irrigation. | Physical factors are less important. |
| Soil | Generally fertile gives two to three crops a year, use traditional knowledge. | Regular soil testing for nutrient deficiency. |
| Crops | Mainly food Crops along with other related activities. Wheat, rice, millets etc. | Specialized farming like com, soya bean, wheat, cotton etc. |
| Operations | Lack of use of scientific technology, machines, more of manual power. | Use of latest technical knowledge and satellite for information. |
| Economic conditions | Lack of good transport, communication or even storage facilities, poor farmers. | Better facilities and prosperous farmers. |
| Human factors | Work as farm labour, many dependent on this activity. | Work as a business person, not as a farmer. |
Question 6.
For Fun
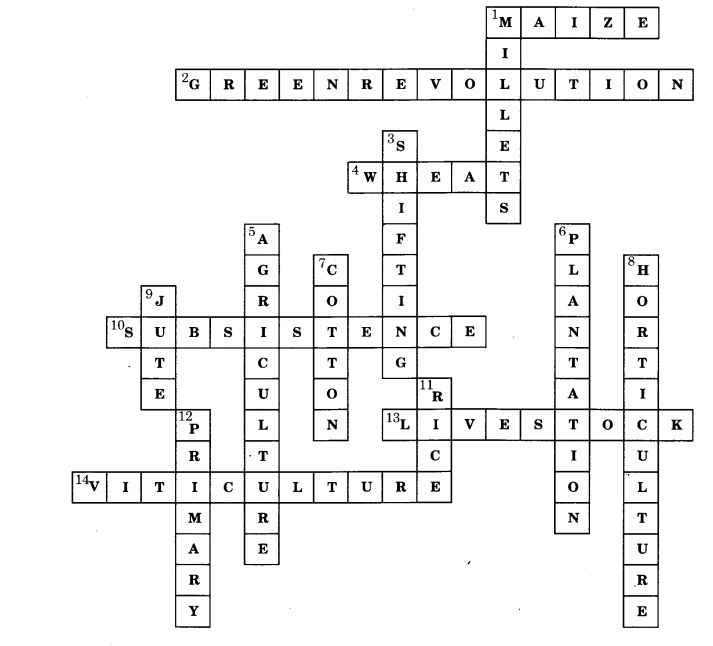
Solve the crossword puzzle with the help of given clues.
| Across | Down |
| 1. Crop that needs well-drained fertile soils, moderate temperatures and lots of sunshine (5) 2. Increasing production through use of HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers and pesticides (5, 10) 4. USA, Canada, Russia, Australia are major producers of this crop (5) 10. Type of farming to meet family needs (11) 13. Rearing of animals for sale (9) 14. Growing grapes for wines (11) | 1. Coarse grains are also called (7) 3. Cultivation involving slash and bum (8) 5. Growing of crops, fruits and vegetables (11) 6. Tea, coffee, sugarcane and rubber are grown in (11) 7. Requires 210 frost-free days for growth (6) 8. Growing of flowers (12) 9. Also called ‘Golden Fibre’ (4) 11. Also known as paddy (4) 12. Activity concerned with extraction of natural resources (7) |
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Exercise Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct option
(i) Which of these is a tertiary activity?
(a) manufacturing wool
(b) selling grocery
(c) agriculture
(d) none of these
(ii) What is the breeding of fish known as?
(a) agriculture
(b) pisciculture
(c) sericulture
(d) viticulture
(iii) What is the main crop in intensive subsistence agriculture?
(a) rice
(b) maize
(c) wheat
(d) oilseeds
(iv) Which form of farming is also called “slash and bum” agriculture?
(a) subsistence farming
(b) shifting cultivation
(c) plantation
(d) mixed farming
(v) Which of these is not a plantation product?
(a) rubber
(b) coffee
(c) rice
(d) tea
(vi) In what season is wheat grown in India?
(a) summer
(b) winter
(c) monsoon
(d) autumn
(vii) Name the staple diet of tropical and sub-tropical regions.
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c)jute
(d) coffee
Answer:
(i) (b), (ii) (b), (iii) (a), (iv) (b),
(v) (c), (vi) (b), (vii) (b).
Question 2.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- In the world, ………. percent of the population is engaged in agriculture.
- …………. is the commercial rearing of silkworms.
- ………. and …………… are two fundamental types of farming.
- In the thickly populated areas of monsoon regions of Asia, the major class of farming done is ……………..
- …………, ………….., ………….. and …………. are animals usually reared by nomadic herders.
- In ………., the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
- ………….. and ……….. are fibre crops.
- Tea is a major…………… crop in India.
- Wheat thrives best in ……………. soil.
- The three major millets in India are ………….. and ………..
Answer:
- 50
- Sericulture
- Subsistence farming and commercial farming
- intensive subsistence farming
- Yak, sheep, goat, camel
- mixed farming
- Cotton, jute
- plantation
- loamy
- jowar, bajra, ragi
Question 3.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- Favourable topography of soil and climate is vital for agriculture.
- Household labour is involved in subsistence farming.
- A transport network is significant for plantation agriculture.
- Major plantations are found in tundra regions.
- In the USA, the farmer usually resides on the farm.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 4.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II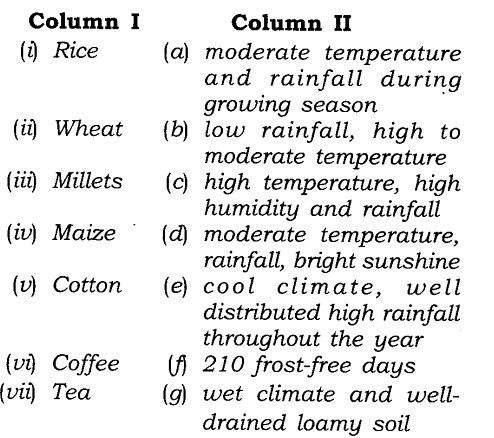
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (a), (iii) (b), (iv) (d), (v) (j), (vi) (g), (vii) (e).
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the basic function of the three basic types of economic activities?
Answer:
The three types of economic activities are involved in the transformation from a plant to a finished product.
Question 2.
What are the tertiary activities?
Answer:
Tertiary activities are those which provide support to primary and secondary activities.
Question 3.
In what sorts of areas are agricultural activities concentrated?
Answer:
Agricultural activities are concentrated in those areas of the world which have suitable conditions of growing crops.
Question 4.
What is arable land?
Answer:
The land on which crops are grown is called arable land.
Question 5.
How is subsistence farming classified?
Answer:
Subsistence farming is classified into intensive and primitive subsistence agriculture.
Question 6.
In what sort of areas is nomadic herding practised?
Answer:
Nomadic herding is practised in semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia, and some parts of India.
Question 7.
Why is mixed farming called so?
Answer:
In mixed farming, the land is used for growing crops as well as rearing livestock.
Question 8.
What is the main feature of plantation agriculture?
Answer:
In plantation agriculture, only a single crop is grown.
Question 9.
What weather conditions are required in the growing and harvesting seasons of wheat?
Answer:
In the growing season, wheat requires moderate temperature and rainfall and in the harvesting season, it needs bright sunshine.
Question 10.
Which two countries lead in the production of jute?
Answer:
India and Bangladesh are the leading producers of jute.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write a short note on the types of economic activities. Give examples.
Answer:
The three types of economic activities are primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary Activities. Activities which involve direct extraction and production of natural resources are called primary activities. Examples: agriculture, fishing, mining. Secondary Activities. Activities which are concerned with the processing of natural resources are called secondary activities. Examples: manufacturing of finished products. Tertiary Activities. Activities which fall neither in the primary category nor the second category are called tertiary activities. They form support to primary and secondary activities. Examples: selling goods, advertising, and banking.
Question 2.
Name the inputs and outputs of agriculture in general. Also mention the various operations involved.
Answer:
The inputs in agriculture are seeds, fertilisers, machinery, labour, etc. The operations involved in agriculture are ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, and harvesting. As outputs of the farming activity, a farmer gets crops, wool, dairy products, and poultry products.
Question 3.
Explain shifting cultivation.
Answer:
Shifting cultivation is a class of primitive subsistence agriculture. In this, a plot of land is cleared by the farmer. This is done by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmer moves to a different place. This type of farming is common in the thickly forested areas of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of south-east Asia, and north-east India. It is also called “slash and burn” agriculture, because of the process of felling and burning the trees is involved.
Question 4.
Enlist the climate conditions required for the proper cultivation of rice. Mention the main regions of its production.
Answer:
Rice is a major food crop‘in tropical and sub-tropical parts of the world. Its cultivation needs high temperatures, high humidity and rainfall. Its growth is best in alluvial clayey soils since they have water retention capacity. China and India are the leading producers in the world. In favourable climatic conditions, even two to three crops are grown in a year.
Question 5.
What do you understand by agricultural development?
Answer:
Agricultural development refers to efforts made to increase production in farms so as to meet the ever¬growing demand of the population. The activities that come under this development are increasing the cropped area, growing more crops, improving irrigation, using fertilizers, sowing HYV (high-yielding variety) of seeds, and promoting mechanization. Mechanization ensures that little labor is done by the farmers; instead, machines are used to provide efficiency.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe subsistence farming and its types in detail.
Answer:
The two main types of farming are:
subsistence farming and commercial farming.
Subsistence farming is practised solely to meet the needs of the farmer’s family. Therefore, the practices involved are usually old- fashioned. Use of modern technology is minimum and most work is done by household labour.
In intensive, subsistence agriculture, simple tools and huge labour are used by a farmer to cultivate a small plot of land. More than one crop is grown annually in favourable conditions. Rice is the major crop. This form of agriculture is seen in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, south-east and east Asia. Shifting cultivation is a class of primitive subsistence agriculture. In this, a plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them.
The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmers move to a different place. This type of farming is common in the thickly forested areas of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of south-east Asia and north-east India. It is also called “slash and burn” agriculture.
Nomadic herding refers to the practice in which herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water. Animals usually reared are the yak, sheep, camel and goats.
Question 2.
Describe commercial farming and its types in detail.
Answer:
Commercial farming is the practice in which crops are grown exclusively for commercial purpose, i.e. for sale in the market. A large area is cultivated and huge capital is involved unlike subsistence farming. Machines are used to a large extent.
Commercial grain farming is a class of commercial farming. Crops like wheat and maize are grown for commercial purpose. The temperate grasslands of North America, Europe and Asia are some common areas where it is seen.
Mixed farming is another type of commercial farming. The land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock. Some areas where it is followed are Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, south-east Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Plantations are a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown. Large amount of labour and capital are required. The produce is processed in the farm itself or nearby factories.