Question
There has been significant growth in the use of carbon nanotubes, CNT.
a. Explain these properties of carbon nanotubes.

b(i)CNT can act as Type 2 superconductors. Outline why Type 2 superconductors are generally more useful than Type 1.
b(iiExplain the role of electrons in superconducting materials in terms of the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory.
c(i)Alloying metals changes their properties. Suggest one property of magnesium that could be improved by making a magnesium-CNT alloy.
c(ii)P[ure magnesium needed for making alloys can be obtained by electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride.
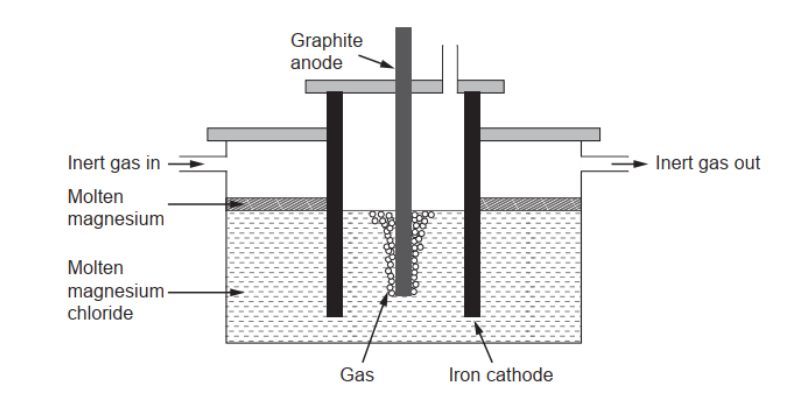
Calculate the theoretical mass of magnesium obtained if a current of $3.00 \mathrm{~A}$ is used for 10.0 hours. Use charge $:(Q)=$ current $(I) \times$ time $(t)$ and section 2 of the data booklet.
c(iii)Suggest a gas which should be continuously passed over the molten magnesium in the electrolytic cell.
d. Zeolites can be used as catalysts in the manufacture of CNT. Explain, with reference to their structure, the high selectivity of zeolites.
e. Experiments have been done to explore the nematic liquid crystal behaviour of CNT. Justify how CNT molecules could be classified as nematic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Excellent strength: defect-free $A N D$ rigid/regular $2 \mathrm{D} / 3 \mathrm{D}$
Excellent conductivity: delocalized electrons
Accept “carbons/atoms are all covalently bonded to each other” for M1.
$\mathrm{b}(\mathrm{i})$ Any two of:
have higher critical temperatures/ $T_{\mathrm{c}}$ «than Type 1 »
OR
can act at higher temperatures
have higher critical magnetic fields $/ B_{\mathrm{c}}$ «than Type $1 »$
less time needed to cool to operating temperature
less energy required to cool down/maintain low temperature
$\mathrm{b}(\mathrm{ii})$ Any three of:
passing electrons «slightly» deform lattice/displace positive ions/cations
electrons couple/form Cooper pairs/condense with other electrons
energy propagates along the lattice in wave-like manner/as phonons
Cooper pair/electron condensate/pair of electrons moves through lattice freely OR
phonons are «perfectly» elastic/cause no energy loss
c(i)Any of:
ductility
strength/resistance to deformation $\boldsymbol{V}$
malleability
hardness
resistance to corrosion/chemical resistance
range of working temperatures
density $\sim$
Do not accept “conductivity”.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { c(ii) } s Q=I \times t=3.00 \times 10.0 \times 3600=» 108000 \mathrm{C} \checkmark \\
& « \frac{Q}{F}=\frac{108000 \mathrm{C}}{96500 \mathrm{Cmol}^{-1}}=» 1.12 \ll \mathrm{mol} \mathrm{e}^{-} » \\
& \text { « } \frac{1.12 \mathrm{~mol}}{2}=0.560 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{Mg} » \\
& \left\langle m=0.560 \mathrm{~mol} \times 24.31 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}=» 13.6 \ll \mathrm{g}\right\rangle \\
&
\end{aligned}
$$
Award [3] for correct final answer.
c(iii)Argon/Ar/helium/He
Accept any identified noble/inert gas.
Accept name OR formula.
Do not accept “nitrogen $/ \mathrm{N}_2$ “.
d. pores/cavities/channels/holes/cage-like structures
«only» reactants with appropriate/specific size/geometry/structure fit inside/go through/are activated/can react
Accept “molecules/ions” for “reactants” in M2.
e. rod-shaped molecules
OR
«randomly distributed but» generally align
OR
no positional order AND have «some» directional order/pattern
Accept “linear” for “rod-shaped”.
Question
Describe the characteristics of the nematic liquid crystal phase and the effect that an electric field has on it.
Shape of molecules:
Distribution:
Effect of electric field:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Shape of molecules:
linear
$O R$
$\operatorname{rod}$ «shaped» $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
Distribution:
no positional order $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ «some» directional order $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept “partly ordered”.
Effect of electric field:
«directional» order increases
OR
molecules align in same direction [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
Question
A soap solution can form a liquid-crystal state.
a. Describe the arrangement of soap molecules in the nematic liquid crystal phase.
b. State how liquid crystals are affected by an electric field.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. molecules point/align in same direction/orientation
OR
molecules have directional order
molecules randomly distributed
OR
molecules not in a layered arrangement
OR
molecules do not have positional order
NOTE: Accept suitable diagram for M1 and M2.
b. molecules align with field
Question
Describe the characteristics of the nematic liquid crystal phase.
Shape of molecules:
Distribution:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Shape of molecules:
linear
OR
rod «shaped» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Distribution:
no positional order $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ «some» directional order $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept “partly ordered”.
Question
While heating solid cholesteryl benzoate, Reinitzer discovered the liquid crystal phase.
a. Outline two observations that he could have made.
b. The structure of biphenyl nitrile is shown.
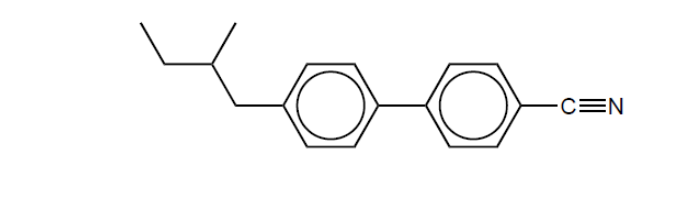
Describe, giving a reason, a feature of the molecular structure, other than its polarity, that allows biphenyl nitrile to show liquid crystal behaviour.
c. Arc discharge, consisting of two inert metal electrodes in a liquid solvent, is one method of producing carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
Predict, giving a reason, the electrode at which the solvent cyclohexane, $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12}$, will decompose to form CNTs.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any two of:
cloudy/foggy/hazy phase «at first melting point»
clear liquid phase «at second melting point/higher temperature»
two «different» melting points
OR
new phase observed over a wide temperature range
Accept “exhibit both liquid and solid properties at the same time” for M3.
b. ALTERNATIVE 1:
«bulky/long» $\mathrm{C}_5 \mathrm{H}_{11} / \mathrm{R} /$ alkyl «group/chain» $A N D$ prevents molecules from packing closer together «to form solid state»
ALTERNATIVE 2:
biphenyl «fragment»/two benzene rings/two aromatic rings $A N D$ «makes molecule» rigid/rod-shaped
Accept “rigid/rod-shaped molecule, so aligns with other molecules” for ALTERNATIVE 2.
c. «average» oxidation state of $\mathrm{C}$ in $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} /$ cyclohexane $=-2$ AND in CNTs $=0$
OR
oxidation state of $\mathrm{C}$ in $\mathrm{CNTs}$ is higher than in $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} /$ cyclohexane
OR
loss of H’s/hydrogens
«oxidation at» anode/positive/+ «electrode»
Accept “oxidation number” for “oxidation state”.
Question
The development of materials with unique properties is critical to advances in industry.
Low density polyethene (LDPE) and high density polyethene (HDPE) are both addition polymers.
a. Outline two properties a substance should have to be used as liquid-crystal in a liquid-crystal display.
b.i. Describe how the structures of LDPE and HDPE affect one mechanical property of the plastics.
b.ii.One of the two infrared (IR) spectra is that of polyethene and the other of polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
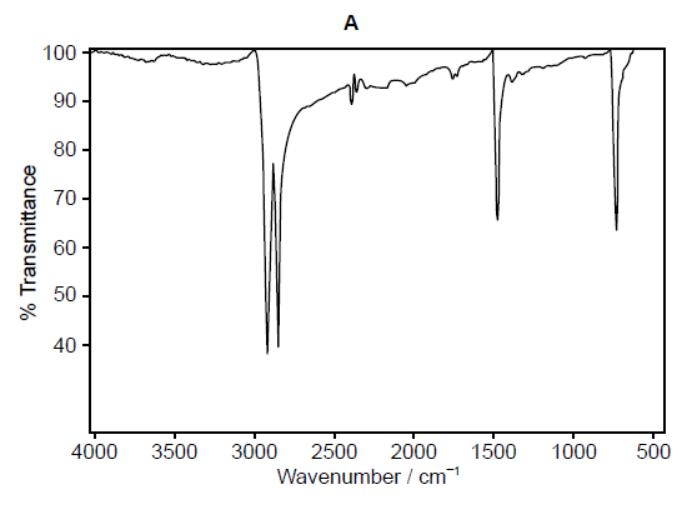
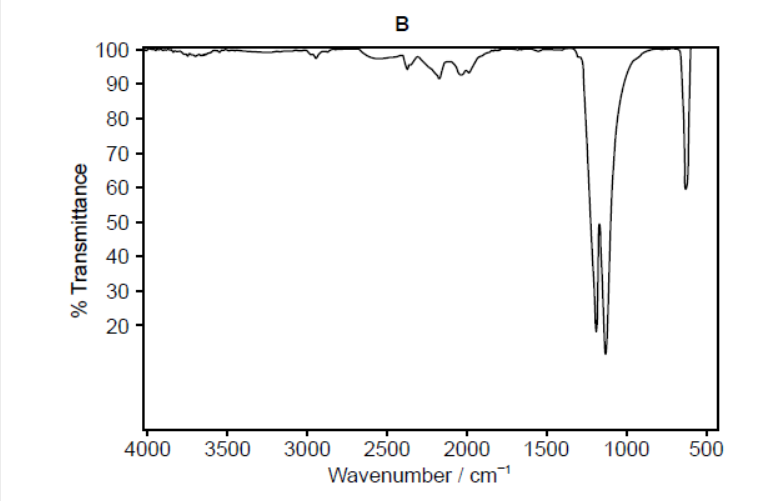
Deduce, with a reason, which spectrum is that of PTFE. Infrared data is given in section 26 of the data booklet.
c. Many plastics used to be incinerated. Deduce an equation for the complete combustion of two repeating units of $\mathrm{PVC},\left(-\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{Cl}-\right)_2$.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any two of:
ability to form a LC phase
chemically stable
«LC phase that is» stable over suitable temperature range
polar
OR
being able to change orientation with applied electric field
rapid switching speed «responds to changes of voltage quickly»
Accept “ability of molecules to transmit light under certain conditions” OR “rodshaped molecules” OR “stable to light/not light sensitive”.
[Max 2 Marks]
b.i. branching in LDPE prevents close packing «of chains»
LDPE is more flexible/less rigid
OR
LDPE has lower «tensile» strength
Do not accept “difference in density”.
Award [1 max] for stating “branching in LDPE AND little/no branching in HDPE”.
b.iiB $A N D$ absence «of absorption of» C-H at $2850-3090$ «cm ${ }^{-1}$ »
OR
B AND presence of «absorption of» C-F at $1000-1400$ «cm ${ }^{-1} »$
c. $\left(-\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{Cl}-\right)_2(\mathrm{~s})+5 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})+2 \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g})$
correct species in reactants and products
balanced
Accept ” $\left(-\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{Cl}\right)_2(\mathrm{~s})+5.5 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})+\mathrm{Cl}_2(\mathrm{~g})$ “.
Award M2 only if M1 correct.
Question
Liquid crystals are widely used in electrically controlled liquid crystal display (LCD) devices such as calculators, computers and watches.
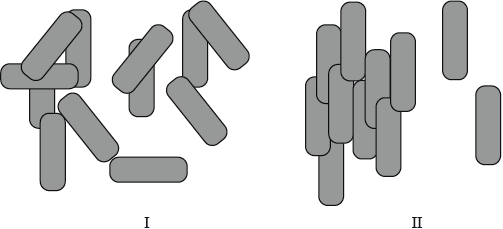
Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals. State and explain which diagram, I or II, represents molecules that are in a liquid crystalline phase.
Distinguish between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals and state one example of each type.
Discuss the properties needed for a substance to be used in liquid crystal displays.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
liquid crystals are fluids that exhibit orientation of the molecules/an orderly arrangement of molecules;
II, since there is one-dimensional order (characteristic of a liquid crystalline phase);
thermotropic liquid crystals are pure substances that show liquid crystal behaviour over a temperature range (between the solid and liquid states);
example (of thermotropic liquid crystals) is biphenyl nitriles;
lyotropic liquid crystals are solutions that show the liquid crystal state at certain concentrations;
example (of lyotropic liquid crystals) is soap in water;
Award marks for examples, only if they are associated with the correct class of liquid crystals.
chemically stable;
a liquid crystal phase stable over a suitable range of temperatures;
polar in order to change orientation when an electric field is applied;
rapid switching speed;
Examiners report
Candidates were able to define liquid crystals but often confused the two diagrams.
Candidates also had difficulty distinguishing between thermotropic and lyotropic crystals and providing suitable examples for each. This emphasised again that candidates had not learnt definitions accurately with correct chemical terminology.
[N/A]
Question
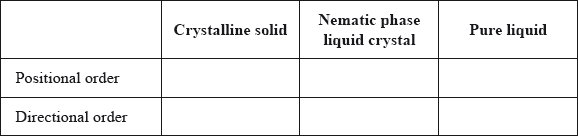
Compare the positional and directional order in a crystalline solid, nematic phase liquid crystal and a pure liquid. Show your answer by stating yes or no in the table below.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
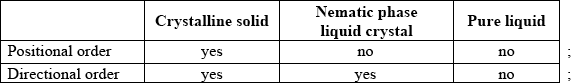
Need all three across table for each mark.
Examiners report
The positional and directional order were generally compared correctly.
Question
Detergents are one example of lyotropic liquid crystals.
State one other example of a lyotropic liquid crystal and describe the difference between lyotropic and thermotropic liquid crystals.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
soap / kevlar / fatty acids / lipid bilayer / cellulose / silk proteins / DNA;
lyotropic liquid crystals
solutions that show the liquid-crystal state at certain concentrations;
thermotropic liquid crystals
(pure substances that) show liquid-crystal behaviour over temperature ranges (between the solid and liquid states);
Examiners report
This was probably the best answered question in this option with many candidates being able to state the difference between the two types of liquid crystals, as well as give an example of a substance that can have a lytropic liquid crystal state.
Question
Liquid-crystal displays are used in digital watches, calculators and laptops.
Describe the liquid-crystal state, in terms of molecular arrangement, and explain what happens as temperature increases.
Discuss three properties a substance should have if it is to be used in liquid-crystal displays.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(rod-shaped) molecules aligned in the same direction;
increasing temperature causes arrangement to lose its directional order/molecules to become more randomly arranged;
until normal liquid state occurs;
chemically stable so that it does not undergo reactions;
liquid-crystal phase stable over a range of temperatures so that frequent malfunctions do not occur;
molecules should be polar so the electronic current can influence direction;
there should be a rapid change in direction / fast switching speed;
Award [2 max] if no reasons are given.
Examiners report
Liquid-crystals were known well by many candidates. Some were ill-prepared to answer these questions.
Liquid-crystals were known well by many candidates. Some were ill-prepared to answer these questions.
Question
It was over a hundred years after the accidental discovery of liquid crystals that liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) came into common use in the 1990s. Liquid crystals are formed over a temperature range between the solid and the liquid state.
Describe the nematic liquid-crystal phase in terms of the arrangement of the molecules.
Explain the effect of increasing the temperature on the nematic liquid crystal.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
no layered arrangement / molecules distributed randomly;
(on average) molecules point in same direction/orientation/directional order;
Accept suitable diagram.
directional order decreases/is lost / starts to behave like a liquid;
extra energy causes greater movement/overcomes intermolecular forces;
Examiners report
Very few of the candidates scored full marks on the description of the nematic liquid-crystal phase.
Probably because of the difficulty of selecting the correct words, and surprisingly only a few scored the mark in terms of the effect of the extra energy, namely causing greater movement or overcoming intermolecular forces.
Question
Petroleum (mineral oil) can be used either as a fuel or a chemical feedstock.
Name two fuels that are obtained from petroleum.
Describe one environmental problem that can result from the combustion of these fuels in the internal combustion engine and identify the specific combustion product responsible.
Plastic litter is an environmental problem that results from the use of petroleum as a chemical feedstock. Identify the property of plastics that is responsible for this.
One product that is made from crude oil is the chemical feedstock that can be used to synthesize commercial liquid-crystal displays. Discuss the properties that a substance must have to make it suitable for use as a liquid-crystal display.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two for [1]
petrol/gasoline
kerosene/paraffin/aviation fuel
diesel
fuel oil/gas oil
petroleum gas/refinery gas
global warming;
carbon dioxide;
OR
air pollution;
carbon monoxide / particulates / oxides of nitrogen/NO/\({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) / \({\text{VO}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{s}}}\);
Accept oxides of sulphur/SO2.
OR
acid rain;
oxides of nitrogen/NO/\({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\);
Accept oxides of sulphur/SO2.
slow decomposition / not biodegradeable;
chemically stable;
liquid crystal phase over a suitable range of temperatures;
rapid switching speed;
Examiners report
In part (a) a significant number of candidates named two fuels obtained from petroleum.
A significant number of candidates described the environmental problem.
The non-biodegradable property of plastics was stated correctly by many candidates.
The properties of a material that made it suitable for use as a liquid crystal display demonstrated poor understanding by many candidates.
Question
Liquid crystals are sometimes used in the construction of “smart windows”.
Smart windows are milky white as their randomly arranged liquid crystals scatter light. When a voltage is applied, the liquid crystals align in the same direction. The light then passes through them without scattering, making the windows transparent.
State the property of the liquid-crystal molecules that allows them to align when a voltage is applied.
List two substances that can behave as liquid crystals.
Distinguish between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals.
Thermotropic liquid crystals:
Lyotropic liquid crystals:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
polarity / presence of dipole (moment);
Any two for [1]
graphite
cellulose
(spider) silk
DNA
biphenyl nitriles
soap
Kevlar
Thermotropic liquid crystals:
pure substances and exhibit liquid-crystal properties in a certain temperature range;
Lyotropic liquid crystals:
solutions and exhibit liquid-crystal properties in a certain concentration range;
Award [1 max] for thermotropic pure substances and lyotropic solutions.
Award [1 max] for thermotropic in a certain temperature range and lyotropic solutions in a certain concentration range.
Examiners report
The majority of candidates recognized polarity as the property of liquid crystals in part (a) and were able to give two substances that could act as liquid crystals in part (b).
The majority of candidates recognized polarity as the property of liquid crystals in part (a) and were able to give two substances that could act as liquid crystals in part (b).
Many candidates knew that thermotropic liquid crystals worked within a temperature range and lyotropic liquid crystals work within a concentration range in part (c), but only few candidates distinguished between the two types fully.
Question
Liquid-crystal displays are used in many electronic appliances. The molecule below has liquid-crystal display properties.
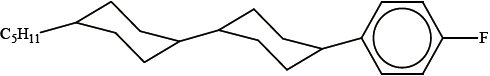
Suggest three reasons why the molecule is suitable for use in liquid-crystal display devices.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
rod shape / rigid;
chemically stable (due to hydrocarbon rings and chain);
polar (due to the presence of F) / OWTTE;
can change orientation / rapid switching in electric field/when voltage is applied;
Examiners report
Examiners reported an average understanding of liquid crystal properties.
Question
Liquid crystals are widely used in devices such as calculators, laptop computers and advanced optical materials.
(i) Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals and state which of the representations below (A, B or C) best describes molecules present in the liquid-crystalline phase.
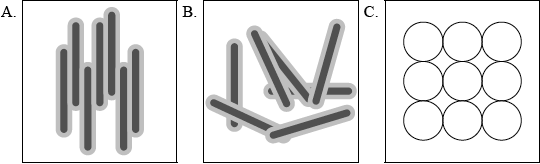
(ii) Deduce, with reasoning, which of the following substance(s) is/are most likely to show liquid-crystalline behaviour.
Substance I:
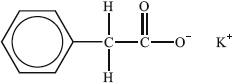
Liquid-crystalline behaviour (yes/no):
Reasoning:
Substance II:
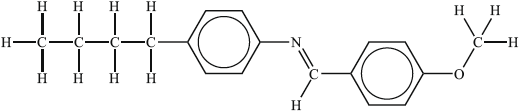
Liquid-crystalline behaviour (yes/no):
Reasoning:
Substance III:
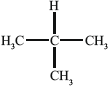
Liquid-crystalline behaviour (yes/no):
Reasoning:
(iii) Suggest why octane does not show liquid-crystalline behaviour.
(i) State one difference between thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals.
(ii) Identify, by stating yes or no, the substance(s) which show(s) thermotropic liquid crystalline behaviour.
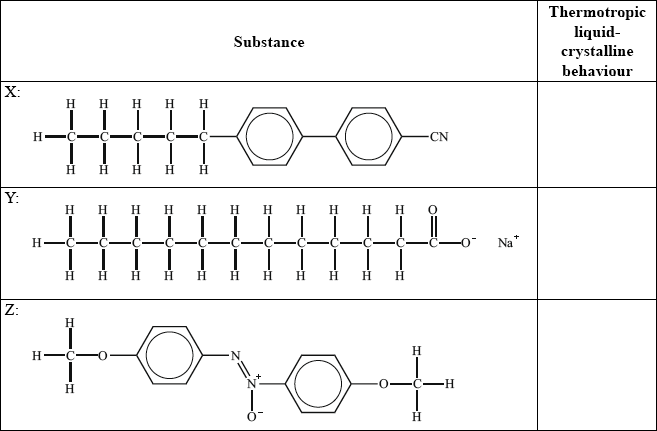
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) (LCs are) fluids that exhibit molecular orientation/orderly molecular arrangement and A;
Accept LCs show properties of liquids and crystals simultaneously and A.
(ii) I: no, since ionic (so high mp) / lacks long axis;
Allow no since it is not a molecule/not rod-shaped.
II: yes, since has long axis present (so limits ability of molecules to pack lowering mp);
Allow yes since rod-shaped.
has polar functional group / is polar (increasing intermolecular interactions) / (planar/flat) benzene ring present (assists stacking);
III: no, since lacks long axis;
Allow no since non-polar.
Allow no since not rod-shaped.
Award [1 max] for stating II only will show LC behaviour OR I: No, II: Yes and III: No.
Award [2 max] if one correct reason is given for each substance but LC behaviour is either incorrect or not given.
Award [3 max] if correct reasons are given for all three substances, but LC behaviour is either incorrect or not given.
(iii) (free) rotation about carbon-carbon single bonds (hence greater flexibility) so octane molecules not rod-shaped / OWTTE;
Do not allow mark for non-polar (molecule) only.
(i) Thermotropic: pure substances and lyotropic: solutions / thermotropic: show LC behaviour over limited temperature range (between solid and liquid states) and lyotropic: shows LC behaviour at certain concentrations;
(ii) X: yes and Y: no and Z: yes;
Award mark if no is stated only for Y or yes is only stated for X and Z.
Examiners report
This proved to be the most challenging question in option C. Candidates were able to identify A as the molecules present in the liquid-crystalline phase but were unable to describe the state for part (a)(i). Majority of the candidates were not able to score more than two marks for part (ii). Most were unable to identify substance I as ionic and substance II was often identified as ‘yes’ but without sound support. For (a)(iii), again students struggled with explicit sound reasoning. Response for (a)(iii) was poor with most stating non-polar as the reason for inability of octane to show liquid-crystalline behavior. Very few candidates were able to identify and explain if molecules will behave as a liquid crystal. Majority of the candidates were unable to score the point. Candidates were able to state the difference between the two liquid crystals in (b)(i) correctly but were not able to apply the information correctly in (b)(ii) to identify which substances shoe thermotropic liquid-crystalline behaviour.
This proved to be the most challenging question in option C. Candidates were able to identify A as the molecules present in the liquid-crystalline phase but were unable to describe the state for part (a)(i). Majority of the candidates were not able to score more than two marks for part (ii). Most were unable to identify substance I as ionic and substance II was often identified as ‘yes’ but without sound support. For (a)(iii), again students struggled with explicit sound reasoning. Response for (a)(iii) was poor with most stating non-polar as the reason for inability of octane to show liquid-crystalline behavior. Very few candidates were able to identify and explain if molecules will behave as a liquid crystal. Majority of the candidates were unable to score the point. Candidates were able to state the difference between the two liquid crystals in (b)(i) correctly but were not able to apply the information correctly in (b)(ii) to identify which substances shoe thermotropic liquid-crystalline behaviour.
Question
Liquid crystals are widely used in displays.
Describe the meaning of the term liquid crystals.
When a liquid-crystal display is warmed with a hairdryer, the display loses its clarity and may no longer be visible. Explain why this happens on a molecular level.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
fluids that have physical properties dependent on molecular orientation/orderly molecular arrangement;
Allow “fluids that exhibit molecular orientation/orderly molecular arrangement”.
Allow “(LCs) show properties of liquids and crystals simultaneously”.
thermal agitation disrupts directional order of liquid crystal / OWTTE;
rotation of plane polarized light disrupted / crystals no longer have ability to affect light in same way / OWTTE;
Examiners report
An understanding of liquid crystals was generally conveyed. Some candidates stated that liquid crystals show properties of liquids and solids simultaneously which did not score as they did not mention the crystalline state explicitly for solids. In (b) only the really top-tier candidates were able to explain the question asked on a molecular level, i.e. the fact that thermal agitation disrupts the directional order of the liquid crystal and as a result the rotation of plane polarized light is disrupted. This question proved to be possibly one of the hardest questions on the paper overall for candidates.
An understanding of liquid crystals was generally conveyed. Some candidates stated that liquid crystals show properties of liquids and solids simultaneously which did not score as they did not mention the crystalline state explicitly for solids. In (b) only the really top-tier candidates were able to explain the question asked on a molecular level, i.e. the fact that thermal agitation disrupts the directional order of the liquid crystal and as a result the rotation of plane polarized light is disrupted. This question proved to be possibly one of the hardest questions on the paper overall for candidates.
Question
Thermotropic liquid crystals are widely used in display devices and sensors.
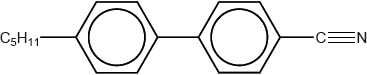
The structure of a material used in electrical display devices is shown below.
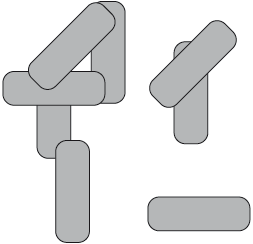
The diagram below shows eight molecules in the liquid state. Suggest, with a diagram, a possible arrangement that these rod-shaped molecules could adopt in the nematic liquid-crystal phase.
Suggest, with reference to the structure, why the molecule is able to change orientation in an electric field.
Suggest how the C5H11 chain contributes to the liquid-crystal properties of the compound.
Explain why a liquid-crystal device may be unreliable at low temperatures.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
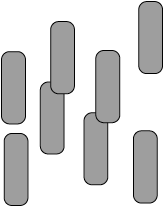
diagram should have molecules with a parallel alignment in any direction (not just upwards);
diagram should have molecules in an irregular arrangement in space;
Ignore relative separation between molecules.
Award [1 max] if number of molecules < 7.
Award [1 max] if stated “molecules align parallel to each other but with an irregular arrangement in space / OWTTE” but with no diagram drawn.
Allow the representation of molecules by lines.
polar/dipole moment due to the presence of C\( \equiv \)N (bond) / difference in electronegativity between C and N;
prevents close packing of molecules / OWTTE;
makes the molecule (longer and) more rod-like;
molecules become more ordered / molecules unable to change orientation (as they approach fixed arrangement of solid state) / molecules move slower / viscosity (of medium) increases (so LCD response time increases);
Examiners report
Well answered by many, although some candidates left the question blank. Candidates were more likely to align molecules in the same direction, but only some of them kept the arrangement of the molecules random and hence received the second mark.
The majority recognized that the alignment is due to the polarity, but only a few candidates attributed that to the CN bond.
Quite well answered about the role of the pentyl group in the liquid-crystal properties of the compound.
The better students were able to explain why a liquid-crystal device is unreliable at low temperature.
Question
Cholesteryl benzoate was one of the first liquid crystals studied.
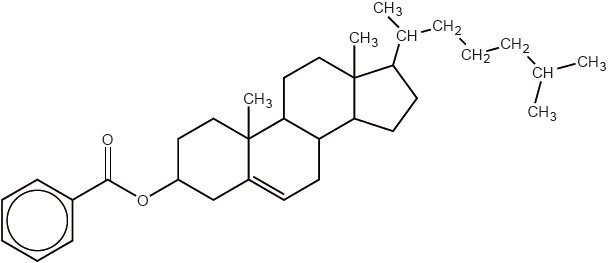
Identify the structural feature of cholesteryl benzoate which makes it suitable for use as a liquid crystal.
Suggest the essential feature a liquid-crystal molecule must have so that the display can be turned “on” and “off”.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
rigid / rod-shaped;
polar (group/molecule);
Examiners report
Many candidates knew the essential feature that a liquid-crystal molecule must have for the display being turned off and on but the description of the principles of a liquid-crystal display device was often poorly presented and not clearly understood.
Many candidates knew the essential feature that a liquid-crystal molecule must have for the display being turned off and on but the description of the principles of a liquid-crystal display device was often poorly presented and not clearly understood.
Question
Biphenyl nitriles, such as the molecule shown below, were the first thermotropic liquid crystal molecules to be synthesized.
Suggest how changing the size or shape of the hydrocarbon chain would affect the molecule’s liquid crystal behaviour.
Explain why the nitrile group enables these molecules to be used in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
alters the temperature range of the liquid-crystal state
OR
alters sensitivity «of the liquid crystal» to electric field«s»
OR
prevents liquid crystal activity
«CN group makes» molecule polar
alignment/orientation of molecules can be controlled by electric field
OR
allows molecules to align in an electric field/when a voltage is applied
Accept “CN is polar”.
Question
Liquid crystals have many applications.
Outline how a lyotropic liquid crystal differs from a thermotropic liquid crystal.
Explain the effect of increasing the temperature of a nematic liquid crystal on its directional order.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Do not award any credit if one type only is described as the question asks how they differ.
decreases AND as energy «added» overcomes interparticle forces
OR
decreases AND as energy «added» causes faster movement «of particles»
Question
Liquid Crystal on Silicon, LCoS, uses liquid crystals to control pixel brightness. The degree of rotation of plane polarized light is controlled by the voltage received from the silicon chip.
Two important properties of a liquid crystal molecule are being a polar molecule and having a long alkyl chain. Explain why these are essential components of a liquid crystal molecule.
Metal impurities during the production of LCoS can be analysed using ICP-MS. Each metal has a detection limit below which the uncertainty of data is too high to be valid. Suggest one factor which might influence a detection limit in ICP-MS/ICP-OES.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Polar molecule:
«orientation of molecule» influenced by electric field/«applied» voltage/«applied» potential «difference»/«applied» current
OR
can be switched on and off
Long alkyl chain:
prevent close packing of molecules
OR
molecules can align
OR
reduces the melting point of the liquid crystal/LC «phase making liquid at room temperature»
Accept “makes molecule rod-shaped” for M2.
[2 marks]
inability to replicate calibrations below certain levels
OR
variation in methodology
OR
variation between machines calibrated with the same samples
OR
variation in plasma torches
OR
different detection limits for MS AND OES
OR
interference from solvents/other chemicals
OR
inability to produce pure standards
OR
chance that low signal AND blank are same
[1 mark]
Question
The development of materials with unique properties is critical to advances in industry.
Low density polyethene (LDPE) and high density polyethene (HDPE) are both addition polymers.
Outline two properties a substance should have to be used as liquid-crystal in a liquid-crystal display.
Describe how the structures of LDPE and HDPE affect one mechanical property of the plastics.
One of the two infrared (IR) spectra is that of polyethene and the other of polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
Deduce, with a reason, which spectrum is that of PTFE. Infrared data is given in section 26 of the data booklet.
Many plastics used to be incinerated. Deduce an equation for the complete combustion of two repeating units of PVC, (–C2H3Cl–)2.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
ability to form a LC phase
chemically stable
«LC phase that is» stable over suitable temperature range
polar
OR
being able to change orientation with applied electric field
rapid switching speed «responds to changes of voltage quickly»
Accept “ability of molecules to transmit light under certain conditions” OR “rodshaped molecules” OR “stable to light/not light sensitive”.
[Max 2 Marks]
branching in LDPE prevents close packing «of chains»
LDPE is more flexible/less rigid
OR
LDPE has lower «tensile» strength
Do not accept “difference in density”.
Award [1 max] for stating “branching in LDPE AND little/no branching in HDPE”.
B AND absence «of absorption of» C–H at 2850–3090 «cm–1»
OR
B AND presence of «absorption of» C–F at 1000–1400 «cm–1»
(–C2H3Cl–)2 (s) + 5O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + 2HCl (g)
correct species in reactants and products
balanced
Accept “(–C2H3Cl–)2 (s) + 5.5O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l) + Cl2 (g)”.
Award M2 only if M1 correct.
Question
Aluminium and high density polyethene (HDPE) are both materials readily found in the kitchen, for example as saucepans and mixing bowls respectively. In these applications it is important that they are impermeable to water.
Both materials are also used in other applications that are more demanding of their physical properties. Carbon nanotubes are often incorporated into their structures to improve certain properties.
Discuss, in terms of its structure, why an aluminium saucepan is impermeable to water.
State the name given to a material composed of two distinct solid phases.
State one physical property of HDPE that will be affected by the incorporation of carbon nanotubes.
Describe how carbon nanotubes are produced by chemical vapour deposition (CVD).
State the property of carbon nanotubes that enables them to form a nematic liquid crystal phase.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«close packed» lattice of metal atoms/ions
no spaces for water molecules to pass though the structure
[2 marks]
composite
[1 mark]
melting point
OR
permeability
OR
density
OR
conductivity
OR
elasticity/stiffness
OR
brittleness/flexibility
OR
«tensile» strength
Accept “colour/transparency”.
[1 mark]
Any three of:
hydrocarbon/carbon-containing gas/compound
mixed with inert gas
heat/high temperature
«transition» metal catalyst
hydrocarbon/carbon compound decomposes to form carbon «nanotubes»
nanotubes form on catalyst surface
Accept “ethanol” or specific hydrocarbons.
Accept “N2”, “H2”, “NH3” or specific inert gases.
Accept temperature or range within 600–800 °C.
Accept specific metals such as Ni, Co or Fe.
[3 marks]
rod shaped molecules
[1 mark]
Question
Both HDPE (high density polyethene) and LDPE (low density polyethene) are produced by the polymerization of ethene.
Both of these are thermoplastic polymers. Outline what this term means.
Compare and contrast the structures of HDPE and LDPE.
State one way in which a physical property of HDPE, other than density, differs from that of LDPE as a result of this structural difference.
The production of HDPE involves the use of homogeneous catalysts. Outline how homogeneous catalysts reduce the activation energy of reactions.
Trace amounts of metal from the catalysts used in the production of HDPE sometimes remain in the product. State a technique that could be used to measure the concentration of the metal.
Suggest two of the major obstacles, other than collection and economic factors, which have to be overcome in plastic recycling.
Suggest why there are so many different ways in which plastics can be classified. HDPE can, for example, be categorized thermoplastic, an addition polymer, having Resin Identification Code (RIC) 2, etc.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
soften/melt when heated
OR
can be melted and moulded
Accept “low melting point” OR “can be moulded when heated”.
[1 mark]
both have «long» hydrocarbon chains
OR
both have chains comprising CH2 units
HDPE has little/no branching AND LDPE has «more» branching
Accept “CH2–CH2 units”.
Accept “HDPE more crystalline”.
[2 marks]
HDPE is more rigid/less flexible
OR
HDPE has a higher melting point
OR
HDPE has greater «tensile» strength
Accept “HDPE has lower ductility”.
[1 mark]
form «temporary» activated complexes/reaction intermediates
Accept “consumed in one reaction/step AND regenerated in a later reaction/step”.
Accept “provides alternative mechanism”.
[1 mark]
inductively coupled plasma/ICP spectroscopy using mass spectroscopy/mass spectrometry/MS/ICP-MS
OR
inductively coupled plasma/ICP spectroscopy using optical emission spectroscopy/OES/ICP-OES
Accept “atomic absorption/aa spectroscopy” or “MS/massspectroscopy/mass spectrometry”.
[1 mark]
Any two of:
many types «of plastics» exist
OR
«plastics» require sorting «by type»
«plastics» need to be separated from non-plastic materials
OR
«often» composites/moulded on/bound to non-plastic/other components
Accept other valid factors such as thermal decomposition of some plastics, production of toxic fumes, etc.
[2 marks]
«different classifications are appropriate for» different properties/applications/purposes
[1 mark]
Question
Chemical vapour deposition (CVD) produces multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) of a more appropriate size for use in liquid crystals than production by arc discharge.
State the source of carbon for MWCNT produced by arc discharge and by CVD.
Discuss three properties a substance should have to be suitable for use in liquid crystal displays.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Arc discharge:
graphite electrode
OR
hydrocarbon solvent
CVD:
gaseous hydrocarbons
Accept “carbon electrode”.
Accept specific examples of suitable hydrocarbon solvents (eg, methyl benzene/toluene OR cyclohexane).
Accept specific examples of suitable gaseous hydrocarbons (eg, methane, ethane, ethyne/acetylene) OR carbon monoxide OR carbon dioxide.
[2 marks]
Any three from:
chemically stable AND does not «chemically» degrade over time
stable over range of temperatures AND to avoid «voltage/random shift» fluctuations ✔
polar AND influenced by an electric field
strong intermolecular forces AND allow molecule to align in specific orientations ✔
rapid switching speed/low viscosity AND change orientation «quickly» when electric field is applied/reversed
Award [1 max] for identifying three correct properties without any discussion or incorrect interpretation of suitability.
Accept “voltage” for “electric field”.
[3 marks]

