Question
1 Brazilian Real (BRL) = 2.607 South African Rand (ZAR). Giving answers correct to two decimal places,
(i) convert 300 BRL to ZAR,
(ii) find how many Real it costs to purchase 300 Rand.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Financial accuracy penalty (FP) is applicable where indicated in the left hand column.
1 BRL = 2.607 ZAR
(FP) (i) \(300 \times 2.607 = 782.10 {\text{ ZAR}}\) (A1)
Note: 782.1 is (A0)(FP)
(FP) (ii) \(300 \times \frac{1}{{2.607}} = 115.07{\text{ BRL}}\) (A1)(ft)
Note: Follow through only if processes are reversed. (C2)[2 marks]
Question
Jane plans to travel from Amsterdam to Chicago. She changes \(1500\) Euros (\({\text{EUR}}\)) to US Dollars (\({\text{USD}}\)) at an exchange rate of \(1{\text{ EUR}}\) to \(1.33{\text{ USD}}\). Give all answers in this question correct to two decimal places.
Calculate the number of \({\text{USD}}\) Jane receives.[1]
Jane spends \(1350{\text{ USD}}\) and then decides to convert the remainder back to \({\text{EUR}}\) at a rate of \(1{\text{ EUR}}\) to \(1.38{\text{ USD}}\).
Calculate the amount of \({\text{EUR}}\) Jane receives.[3]
If Jane had waited until she returned to Amsterdam she could have changed her \({\text{USD}}\) at a rate of \(1{\text{ EUR}}\) to \(1.36{\text{ USD}}\) but the bank would have charged \(0.8\% \) commission.
Calculate the amount of \({\text{EUR}}\) Jane gained or lost by changing her money in Chicago.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Financial penalty (FP) may apply in this question.
\(1500 \times 1.33\)
(FP) \( = 1995.00\) (accept \(1995\)) (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
Financial penalty (FP) may apply in this question.
\({\text{USD left}} = 1995 – 1350 = 645\) (A1)
\( = \frac{{645}}{{1.38}}{\text{ Euros}}\) (A1)(ft)
(FP) \( = 467.39{\text{ Euros}}\) (A1)(ft) (C3)[3 marks]
Financial penalty (FP) may apply in this question.
\(\frac{{645}}{{1.36}} \times 0.992 = 470.47\) (A1)(ft)
(FP) She lost \(3.08{\text{ Euros}}\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Notes: The word ‘lost’ is not required.
If candidate has divided in (a) and multiplied in (b) and (c) consistently award (A0)(A1)(ft)(A1)(ft) for answers of \( – 222.18\) for \({\text{USD}}\) left and \(306.61{\text{ Euros}}\) in (b) and (A1)(ft)(A1)(ft) for \(299.75\) and \(6.86\) in (c).[2 marks]
Question
The table below shows some exchange rates for the Japanese Yen (\({\text{JPY}}\)).
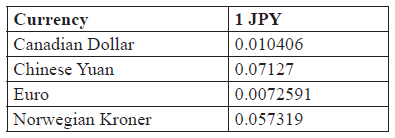
Minbin has \(1250\) Japanese Yen which she wishes to exchange for Chinese Yuan.
Calculate how many Yuan she will receive. Give your answer to the nearest Yuan.[2]
Rupert has \(855\) Canadian Dollars which he wishes to exchange for Japanese Yen.
Calculate how many Yen he will receive. Give your answer to the nearest Yen.[2]
Find how many Norwegian Kroner there are to the Euro. Give your answer correct to 2 decimal places.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Financial accuracy penalty (FP) is applicable where indicated in the left hand column.
Multiplying \(1250\) by \(0.07127\) or \(0.7127\) (M1)
(FP) \(89\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Financial accuracy penalty (FP) is applicable where indicated in the left hand column.
Dividing by \(0.010406\) or \(0.10406\) (M1)
(FP) \(82164\) (A1) (C2)
Note: If candidate has divided in (a) and multiplied in (b) award (M1)(A1)(ft) for \(9\) in (b).[2 marks]
Financial accuracy penalty (FP) is applicable where indicated in the left hand column.
(FP) \(\frac{{0.057319}}{{0.0072591}}\) allow \(0.57319\) and/or \(0.072591\) (M1)
\(7.90\) (A1) (C2)
Note: The (M1) is being allowed for misreading values from the table but do not (ft) to candidate’s answers.[2 marks]
Question
The exchange rate between Indian rupees (INR) and Singapore dollars (S$) is \(100{\text{ INR}} = {\text{S\$ }}3.684\)
Kwai Fan changes \({\text{S\$ }}500\) to Indian rupees.
Calculate the number of Indian rupees she will receive using this exchange rate. Give your answer correct to the nearest rupee.[2]
On her return to Singapore, Kwai Fan has \(2500\) Indian rupees left from her trip. She wishes to exchange these rupees back to Singapore dollars. There is a \(3\% \) commission charge for this transaction and the exchange rate is \(100{\text{ INR}} = {\text{S\$}}3.672\).
Calculate the commission in Indian rupees that she is charged for this exchange.[2]
On her return to Singapore, Kwai Fan has \(2500\) Indian rupees left from her trip. She wishes to exchange these rupees back to Singapore dollars. There is a \(3\% \) commission charge for this transaction and the exchange rate is \(100{\text{ INR}} = {\text{S\$}}3.672\).
Calculate the amount of money she receives in Singapore dollars, correct to two decimal places.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Financial penalty (FP) applies in this question.
\(500 \times \frac{{100}}{{3.684}}\) (M1)
FP \( = 13572\) (A1) (C2)
Note: (M1) for multiplication by \(\frac{{100}}{{3.684}}\)[2 marks]
\(2500 \times 0.03\) (M1)
\( = 75{\text{ }}(75.0{\text{, }}75.00)\) (A1) (C2)
If \(2500 \times 0.03 \times \frac{{3.672}}{{100}}\)
\( = 2.75\)
Award (M1)(A0)[2 marks]
Financial penalty (FP) applies in this question.
\(2425 \times \frac{{3.672}}{{100}}\) (M1)(ft)
FP \( = 89.05\) (A1)(ft)
OR
\(\frac{{3.672}}{{100}} \times 0.97 \times 2500\) (M1)(ft)
FP \( = 89.05\) (A1)(ft)
OR
\(3\% {\text{ of }}91.8 = 2.754\)
\(91.8 – 2.754\) (M1)(ft)
FP \( = 89.05\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: (ft) in (c) if the conversion process is reversed consistently through the question, i.e. multiplication in (a) followed by division in (c).[2 marks]
Question
The following table gives the exchange rate from US dollars to euros and from US dollars to Japanese Yen. Give all answers in this question correct to two decimal places.
Enrico has 475 USD.
How many euros is this worth?[2]
Enrico has 475 USD.
Enrico goes to a bank to exchange his dollars. The bank charges 3 % commission.
How many euros does Enrico receive?[2]
Find the exchange rate from euros to yen.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Note: Financial penalty (FP) applies in this part
(FP) \(475 \times 0.6337 = 301.01\) (M1)(A1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by 0.6337.[2 marks]
Note: Financial penalty (FP) applies in this part\(\frac{3}{{100}} \times 301.01 = 9.03\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by 3/100.
(FP) \(301.01 – 9.03 = 291.98\) (A1)(ft)
OR
\(0.97 \times 301.01\) (M1)
(FP) \(= 291.98\) (A1)(ft) (C4)[2 marks]
Note: Financial penalty (FP) applies in this part
(FP) \(\frac{{{\rm{99}}{\rm{.7469}}}}{{{\rm{0}}{\rm{.6337}}}}{\rm{ = 157}}{\rm{.40}}\) (M1)(A1) (C2)
Notes: Award (M1) for dividing by 0.6337.[2 marks]
Question
The exchange rates between the British pound (GBP) and the United States dollar (USD) and between the USD and the Euro (EUR) are given below.
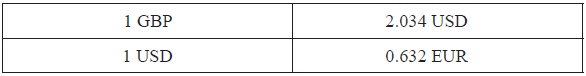
Find the exchange rate between GBP and EUR in the form 1 GBP = k EUR, where k is a constant. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.[2]
Isabella changes 400 USD into Euros and is charged 2 % commission.
Calculate how many Euros she receives. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
k = 2.034 × 0.632 (M1)
= 1.29 (1 GBP = 1.29 EUR) (A1) (C2)
Note: Accept 1.29 only[2 marks]
Financial penalty (FP) applies in part (b).
400 × 0.632 (M1)
= 252.80 EUR (A1)
2 % of 252.80 = 5.06 EUR (A1)
(FP) She receives 247.74 EUR (A1)
OR
(FP) 0.98 × 252.80 = 247.74 EUR (A1)(A1) (C4)
Note: Accept (A1) for 0.98 seen.[4 marks]
Question
Susi travels from Singapore to Thailand and changes 1500 Singapore dollars (SGD) to Thai baht (THB). The exchange rate is 1 SGD buys 21.03464 THB.
Susi leaves Thailand and travels to Indonesia. She has \(20\,000\) THB and uses these to buy Indonesian rupiah (IDR). The exchange rate is 3.28352 THB buys 1000 IDR.
Susi wants to find the approximate exchange rate between Singapore dollars and Indonesian rupiah and uses the exchange rates for Thai baht to do this.
Calculate the number of Thai baht Susi buys. Give your answer correct to the nearest baht.[2]
Calculate the total number of Indonesian rupiah Susi receives, correct to the nearest thousand rupiah.[2]
Calculate Susi’s exchange rate between Singapore dollars and Indonesian rupiah. Give your answer in the form 1 SGD buys x IDR, where x is given correct to the nearest rupiah.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
1500 \( \times \) 21.03464 (M1)
\( = 31\,552\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\({\text{20 000}} \times \frac{{1000}}{{3.28352}}\) (M1)
\( = {\text{6}}\,{\text{091}}\,{\text{000}}\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\(\frac{{21.03464}}{{3.28352}} \times 1000\) (M1)
1 SGD = 6406 IDR (A1) (C2)
Note: Accept 6406.[2 marks]
Question
A manufacturer in England makes \(16 000\) garden statues. \(12\% \) are defective and cannot be sold.
Find the number of statues that are non-defective.[2]
The manufacturer sells each non-defective statue for \(5.25\) British pounds (GBP) to an American company. The exchange rate from GBP to US dollars (USD) is \(1{\text{ GBP}} = 1.6407{\text{ USD}}\).
Calculate the amount in USD paid by the American company for all the non-defective statues. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.[2]
The American company sells one of the statues to an Australian customer for \(12{\text{ USD}}\). The exchange rate from Australian dollars (AUD) to USD is \(1{\text{ AUD}} = 0.8739{\text{ USD}}\) .
Calculate the amount that the Australian customer pays, in AUD, for this statue. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(0.88 \times 16000\) OR \(16000 – 0.12 \times 16000\) (M1)
\(14080\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\(1.6407 \times 5.25 \times 14080\) (M1)
\(121 280.54{\text{ USD}}\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Follow through from their answer to part (a).[2 marks]
\(12 \times \frac{1}{{0.8739}}\) (M1)
\(13.73{\text{ AUD}}\) (A1) (C2)
Note: If division used in part (b) and multiplication used in part (c), award (M0)(A0) for part (b) and (M1)(A1)(ft) for part (c).[2 marks]
Question
In this question give all answers correct to 2 decimal places.
George travelled from the USA to Europe and changed \(1200\) dollars (USD) into Euros (EUR). The exchange rate was \(1{\text{ USD}} = 0.8154{\text{ EUR}}\).
Calculate the number of EUR George received.[2]
On his return, George had \(160\) EUR to change back into USD. There was \(4.5\% \) commission charged on the exchange. The exchange rate was \(1\) USD = \(0.8202\) EUR.
Calculate the value, in EUR, of the commission that George paid.[2]
On his return, George had \(160\) EUR to change back into USD. There was \(4.5\% \) commission charged on the exchange. The exchange rate was \(1\) USD = \(0.8202\) EUR.
Calculate the number of dollars George received.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
The first time the answer is not given to 2 decimal places the final (A1) in that part is not awarded, incorrect rounding, following correct method, can be ignored in subsequent parts.
\(1200 \times 0.8154\) (M1)
\( = 978.48{\text{ EUR}}\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
The first time the answer is not given to 2 decimal places the final (A1) in that part is not awarded, incorrect rounding, following correct method, can be ignored in subsequent parts.
\(160 \times 0.045\) (M1)
\( = 7.20{\text{ EUR}}\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
The first time the answer is not given to 2 decimal places the final (A1) in that part is not awarded, incorrect rounding, following correct method, can be ignored in subsequent parts.
\(152.80 \times \frac{1}{{0.8202}}\) (M1)
Note: Follow through from their answer to part (b).
\( = 186.30{\text{ USD}}\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Follow through from part (b).[2 marks]
Question
Sasha travelled from the USA to Mexico and converted 650 US dollars (USD) to Mexican pesos (MXN). Her bank offered an exchange rate of 1 USD = 12.50 MXN.
Find the number of MXN that Sasha received.[2]
Before her return to the USA, Sasha exchanged 2300 MXN back into USD. The bank charged a commission of 1 %. The exchange rate was still 1 USD = 12.50 MXN.
Write down the commission charged by the bank in MXN.[1]
Before her return to the USA, Sasha exchanged 2300 MXN back into USD. The bank charged a commission of 1 %. The exchange rate was still 1 USD = 12.50 MXN.
Calculate the amount of USD that Sasha received after commission. Give your answer correct to the nearest USD.[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
650×12.50 (M1)
8125 (MXN) (A1) (C2)
Note: Accept 8130.[2 marks]
23 (MXN) (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
\(\frac{{2300 – their{\text{ }}23}}{{12.50}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for setting up the expression.
182.16 (USD) (A1)(ft)
Note: Follow through from their answer to part (b).
182 (USD) (A1)(ft) (C3)
Notes: Award final (A1) for their answer correct to the nearest USD.[3 marks]
Question
In this question give all answers correct to two decimal places.
Chiara is an Italian tourist visiting Sweden. The exchange rate for changing euros (€) into Swedish Krona (SEK) is 1€ = 10.275 SEK. She converts 350 euros into Swedish Krona at a bank which charges 2 % commission.
Calculate the amount of commission charged in SEK.[3]
Write down the amount of money she receives from the bank after commission.[1]
Chiara returns to Italy with 296 SEK. She changes this money back into euros at a bank and receives 32€. The bank does not charge commission.
Calculate the value in SEK of 1€.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
350 × 10.275 × 0.02 (M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for ×10.275, (M1) for ×0.02.
71.93 (SEK) (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
3524.33(SEK) (A1)(ft) (C1)
Note: Accept 3524.32. Follow through from their answer to part (a).[1 mark]
\(\frac{{296}}{{32}}\) (M1)
9.25 (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Question
Give all answers in this question correct to two decimal places.
Isabel is travelling from Geneva to Toronto via Amsterdam.
She changes 1240 Swiss francs (CHF) to Euros (EUR).
The exchange rate is 1 CHF = 0.7681 EUR.
Calculate the amount of Euros Isabel receives.[2]
Isabel then changes 750 EUR into Canadian dollars (CAD) and is charged 3.12 % commission.
The exchange rate is 1 CAD = 0.7470 EUR .
Calculate the amount of Canadian dollars she receives.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
1240 × 0.7681 (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying by 0.7681
= 952.44 (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\(\frac{{750}}{{0.7470}} \times (1 – 0.0312)\) (M1)(M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing by 0.7470, (M1) for subtracting 0.0312 from 1, (M1) for multiplying by the (1 – 0.0312).
OR
\(\frac{{750}}{{0.7470}} (= 1004.016…)\) (M1)
1004.016… × 0.0312 (= 31.325…) (M1)
1004.016… − 31.325… (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing by 0.7470, (M1) for multiplication by 0.0312, (M1) for subtraction of their 31.325 from their 1004.016.
OR
750 × 3.12 % = 23.4 (M1)
750 − 23.4 = 726.60 (M1)
\(\frac{{726.60}}{{0.7470}} \) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by 3.12 %, (M1) for subtraction of their 23.4 from 750, (M1) for division by 0.7470.
= 972.69 (A1) (C4)
Note: If division by 0.7681 is used in part (a) then award (M1) for multiplying by 0.7470 in part (b).[4 marks]
Question
Neung is going home to Vietnam after working in Singapore.
She has 5000 Singapore dollars (SGD) and changes these into American dollars (USD)
to take home.
The exchange rate between Singapore dollars (SGD) and American dollars (USD) is
1 USD = 1.2945 SGD.
There is also a 2.4 % commission on the exchange.
Calculate the amount of commission on the exchange in SGD.[2]
Calculate the number of American dollars (USD) Neung takes home. Give your answer correct to 2 decimal places.[2]
At the airport in Vietnam, Neung changes 150 USD into Vietnamese dong (VND) to pay for her transport home.
The exchange rate between American dollars (USD) and Vietnamese dong (VND) is
1 USD = 19 495 VND.
There is no commission.
Calculate the number of Vietnamese dong that Neung receives. Give your answer correct to the nearest thousand dong.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
5000 × 0.024 (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by 0.024.
=120 (A1) (C2)
\(4880 \times \frac{1}{{1.2945}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by \(\frac{1}{{1.2945}}\).
= 3769.80 (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Correct answer to 2 dp only. Follow through from their part (a).
\(150 \times 19495\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for \( \times 19495\).
\(= 2924000\) (A1) (C2)
Notes: Correct answer to nearest 1000 only. Do not penalize incorrect accuracy in (c) if this has already been penalized in part (b).
Question
Yoshi is spending a year travelling from Japan to Italy and then to the United States of America.
Before Yoshi leaves Japan he changes 100 000 Japanese Yen (JPY) into euro (EUR). The exchange rate is 1 JPY = 0.006 EUR.
Calculate the amount Yoshi receives, in EUR.[2]
Yoshi spends 426.70 EUR in Italy. In an American bank he changes the remaining amount, into US dollars (USD), at an exchange rate of 1 USD = 0.673 EUR.
The bank charges 1.5 % commission.
Calculate the amount, in USD, Yoshi receives after commission. Give your answer correct to the nearest USD.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(0.006 \times 100000\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by 0.006.
\( = 600\) (A1) (C2)
\(\frac{{(600 – 426.70)}}{{0.673}} \times 0.985\) (M1)(M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for subtracting 426.70 from their answer to part (a), (M1) for division by 0.673, (M1) for multiplication by 0.985 (or equivalent).
OR
\(\frac{{173.30 – (600 – 426.70) \times 0.015}}{{0.673}}\) (M1)(M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for subtracting 426.70 from their answer to part (a), (M1) for division by 0.673, (M1) for multiplication by 0.015 (or equivalent) and subtraction from their 173.30.
254 (A1)(ft) (C4)
Notes: Follow through from their part (a). In order to award the final (A1)(ft) the answer must be given correct to the nearest dollar. If division used in part (a) and multiplication in part (b) award at most (M1)(M1)(M1)(A0).
Question
Dumisani has received a scholarship of 5000 US dollars (USD) to study in Singapore.
He has to travel from South Africa and must change USD for his air fare of 6600 South African rand (ZAR).
The exchange rate is 1USD = 8.2421 ZAR.
In this question give all answers correct to two decimal places.
Calculate the number of USD that Dumisani must change to pay for his air fare.[2]
On arrival in Singapore, Dumisani changes 3000 USD to Singapore dollars (SGD) to pay for his school fees. There is a 2.8% commission charged on the exchange.
Calculate the value, in USD, of the commission that Dumisani has to pay.[2]
The exchange rate is \(1{\text{ USD }} = 1.29903{\text{ SGD}}\).
Calculate the number of SGD Dumisani receives.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(6600 \times \frac{1}{{8.2421}}\) (M1)
\( = 800.77\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\(3000 \times 0.028\) (M1)
\( = 84.00\) (accept 84) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\((3000 – 84) \times 1.29903\) (M1)
OR
\(3000 \times 1.29903 \times 0.972\) (M1)
\( = 3787.97\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Notes: Follow through from their answer to part (b).
Note: Do not penalize in part (c) if conversion process has been reversed consistently ie, multiplication by \(8.2421\) in part (a) and division by \(1.29903\) in part (c).[2 marks]
Question
In this question give all answers correct to the nearest whole number.
Fumie is going for a holiday to Great Britain. She changes \({\text{100}}\,{\text{000}}\) Japanese Yen (JPY) into British Pounds (GBP) with no commission charged.
The exchange rate between GBP and JPY is
1 GBP = 129 JPY.
Calculate the value of \({\text{100}}\,{\text{000}}\) JPY in GBP.[2]
At the end of Fumie’s holiday in Great Britain she has 239 GBP. She converts this back to JPY at a bank, which does not charge commission, and receives 30 200 JPY
(i) Find the exchange rate of this second transaction.
(ii) Determine, when changing GBP back to JPY, whether the exchange rate found in part (b)(i) is better value for Fumie than the exchange rate in part (a). Justify your answer.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\frac{{100\,000}}{{129}}\) (M1)
\( = 775{\text{ (GBP)}}\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
(i) \(\frac{{30\,200}}{{239}}\) (M1)
\(1 {\text{ GBP}} = 126 {\text{ JPY}}\) (A1)
Note: Accept \(126\) (\({\text{JPY}}\)).
Award (M1) for \(\frac{{239}}{{30\,300}}\).
Award (A0) for \(1{\text{ JPY}} = 0 {\text{ GBP}}\)
(ii) No, the part (b)(i) rate is not better value than the part (a) rate. (A1)(ft)
\(30\,200 < 30\,831\) (R1)
OR
No, the part (b)(i) rate is not better value than the part (a) rate. (A1)(ft)
\(129 > 126\) (R1) (C4)
Note: Accept “part (a) rate is better” for the (A1)(ft).
Follow through from part (b)(i).
A numerical comparison must be seen to award (R1).[4 marks]
Question
Albena travels to Bulgaria on a business trip. She is paid 3550 Bulgarian levs (BGN) at the end of her trip. She converts all her BGN into euros (EUR), at an exchange bureau that sells 1 EUR for 1.95 BGN and charges 3 % commission.
Calculate the amount that Albena receives in EUR.[4]
At the airport shop, Albena buys chocolates that cost 34.50 BGN. She uses 20 EUR to pay for the chocolates but receives her change in BGN. The shop’s exchange rate is 1 EUR = 1.90 BGN.
Find how many BGN she receives as change.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\frac{{0.97 \times 3550}}{{1.95}}\) (M1)(M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for \(0.97\) seen, (M1) for \(0.97 \times 3550\), (M1) for division by \(1.95\).
OR
\((3550 – 0.03 \times 3550) \times \frac{1}{{1.95}}\) (M1)(M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for \(0.03 \times 3550\) seen, (M1) for subtracting \(0.03 \times 3550\) from \(3550\), (M1) for division by \(1.95\).
\( = 1765.90{\text{ (EUR)}}\) (A1) (C4)
\(20 \times 1.90 – 34.50\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for subtraction of \(34.50\) from their product of \(20 \times 1.90\).
\( = 3.50\,\,\,{\text{(BGN)}}\) (A1) (C2)
Notes: Award at most (M1)(A0) for an answer of \(4\), but only if working seen.
Question
Pietro arrives in Singapore and, at the airport, changes 800 euros (EUR) to Singapore dollars (SGD).
The bank rates quoted at the airport for exchanging EUR with SGD are given in the following table. Also given are the rates for exchanging SGD with British pounds (GBP) and US dollars (USD). There is no commission charged on exchanges.
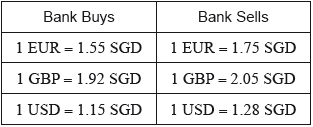
Calculate the number of SGD Pietro receives.[2]
Pietro also has 100 GBP that he wishes to change to USD for a trip to Cambodia.
To perform this transaction, the GBP must first be converted to SGD and then to USD.
Calculate the number of USD Pietro receives.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(800 \times 1.55\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by \(1.55\).
\( = 1240\) (A1) (C2)
\(\frac{{100 \times 1.92}}{{1.28}}\) (A1)(M1)(M1)
Notes: Award (M1) for multiplication by a GBP rate (\(1.92\) or \(2.05\)), (M1) for division by a USD rate (\(1.28\) or \(1.15\)), (A1) for two correct rates used.
\( = 150\) (A1) (C4)
Note: Award a maximum of (A1)(ft)(M1)(M1)(A1)(ft) for \(\frac{{100 \times 2.05}}{{1.15}}\), if in part (a) a rate of \(1.75\) is used.
Award a maximum of (A1)(ft)(M1)(M1)(A1)(ft) if division by an EUR rate is seen in part (a) and multiplication by \(1.28\) and division by \(1.92\) is seen in (b).
Question
In this question give all answers correct to the nearest whole number.
Loic travelled from China to Brazil. At the airport he exchanged 3100 Chinese Yuan, \({\text{CNY}}\), to Brazilian Real, \({\text{BRL}}\), at an exchange rate of \({\text{1}}\,{\text{ CNY = 0}}{\text{.3871 BRL}}\).
No commission was charged.
Calculate the amount of \({\text{BRL}}\) he received.[2]
When he returned to China, Loic changed his remaining \({\text{BRL}}\) at a bank. The exchange rate at the bank was \({\text{1}}\,{\text{ CNY = 0}}{\text{.3756 BRL}}\) and a commission of \(5\% \) was charged. He received \(285\,\,{\text{CNY}}\).
i) Calculate the amount of \({\text{CNY}}\) Loic would have received if no commission was charged.
ii) Calculate the amount of \({\text{BRL}}\) Loic exchanged when he returned to China.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(3100\, \times \,0.3871\) (M1)
\( = 1200\) (A1) (C2)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication by \(0.3871\). Answer must be an integer for the (A1) to be awarded.
i) \(\frac{{285}}{{0.95}}\) (M1)
\( = 300\) (A1)
Note: Award (M1) for division by \(0.95\). Answer must be an integer for the (A1) to be awarded.
ii) \({\text{their }}300 \times 0.3756\) (M1)
\( = 113\) (A1)(ft) (C4)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying their answer to part (b)(i) by \(0.3756\). Follow through from part (b)(i). Answer must be an integer.
Question
Obi travels from Dubai to Pretoria and changes \(2000\) United Arab Emirates Dirham \(({\text{AED}})\) at a bank. He receives \(6160\) South African Rand \(({\text{ZAR}})\).
The exchange rate is \(1\;{\text{AED}} = x\,{\text{ZAR}}\).
Calculate the value of \(x\) .[2]
Obi decides to invest half of the money he receives, \(3080\,\,{\text{ZAR}}\), in an account which pays a nominal interest rate of \(9\,\% \), compounded monthly.
The amount of money in the account will have doubled before the end of the \(n{\text{th}}\) year of the investment.
Calculate the minimum value of \(n\) .[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\frac{{6160}}{{2000}}\) (M1)
\( = 3.08\) (A1) (C2)
Note: Award (M1) for correct division.
\(3080\,{\left( {1 + \frac{9}{{12 \times 100}}} \right)^{n \times 12}} = 6160\) (M1)(A1)
Note: Award (M1) for substitution into compound interest formula equated to \(6160\), (A1) for correct substitution.
OR
\(I = 9\)
\(PV = \pm 3080\)
\(FV = \mp 6160\)
\(P/Y = 1\)
\(C/Y = 12\) (A1)(M1)
Note: Award (A1) for \(C/Y = 12\) seen, (M1) for other correct entries.
\(FV\) and \(PV\) must have opposite sign.
\( = 7.73048…\) (A1)
\( = 8\) (A1)(ft) (C4)
Note: Award the final (A1)(ft) for the correct rounding up, of their unrounded answer, to complete years.
Question
In this question give all answers correct to two decimal places.
Javier takes 5000 US dollars (USD) on a business trip to Venezuela. He exchanges 3000 USD into Venezuelan bolívars (VEF).
The exchange rate is 1 USD \( = \) 6.3021 VEF.
During his time in Venezuela, Javier spends 1250 USD and 12 000 VEF. On his return home, Javier exchanges his remaining VEF into USD.
The exchange rate is 1 USD \( = \) 8.7268 VEF.
Calculate the amount of VEF that Javier receives.[2]
Calculate the total amount, in USD, that Javier has remaining from his 5000 USD after his trip to Venezuela.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
The first answer not given correct to two decimal places is not awarded the final (A1).
Incorrect rounding is not penalized thereafter.
\(3000 \times 6.3021\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying 3000 by 6.3021.
\( = 18906.30\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\(\frac{{18906.30 – 12000}}{{8.7268}}{\text{ + }}(2000 – 1250)\) (M1)(M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for subtracting 12 000 from their answer to part (a) OR for 6906.30 seen, (M1) for dividing their amount by 8.7268 (can be implied if 791.389… seen) and (M1) for \(2000 – 1250\) OR 750 seen.
\( = 1541.39\) (A1)(ft) (C4)
Note: Follow through from part (a).[4 marks]
Question
Daniela is going for a holiday to South America. She flies from the US to Argentina stopping in Peru on the way.
In Peru she exchanges 85 United States dollars (USD) for Peruvian nuevo sol (PEN). The exchange rate is 1 USD = 3.25 PEN and a flat fee of 5 USD commission is charged.
At the end of Daniela’s holiday she has 370 Argentinean peso (ARS). She converts this back to USD at a bank that charges a 4% commission on the exchange. The exchange rate is 1 USD = 9.60 ARS.
Calculate the amount of PEN she receives.[3]
Calculate the amount of USD she receives.[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\((85 – 5) \times 3.25\) (M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for subtracting 5 from 85, (M1) for multiplying by 3.25.
Award (M1) for \(85 \times 3.25\), (M1) for subtracting \(5 \times 3.25\).
\( = 260{\text{ (PEN)}}\) (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
\(\frac{{(370 \times 0.96)}}{{9.6}}\) (M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying by 0.96 (or equivalent), (M1) for dividing by 9.6. If division by 3.25 seen in part (a), condone multiplication by 9.6 in part (b).
\( = 37{\text{ (USD)}}\) (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
Question
Claudia travels from Buenos Aires to Barcelona. She exchanges 8000 Argentine Pesos (ARS) into Euros (EUR).
The exchange rate is 1 ARS = 0.09819 EUR. The bank charges a 2% commission on the exchange.
When Claudia returns to Buenos Aires she has 85 EUR left and exchanges this money back into ARS. The exchange rate is 1 ARS = 0.08753 EUR. The bank charges \(r\)% commission. The commission charged on this exchange is 14.57 ARS.
Find the amount of Euros that Claudia receives. Give your answer correct to two decimal places.[3]
Find the value of \(r\).[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(8000 \times 0.09819 \times 0.98\) (M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying 8000 by 0.09819, (M1) for multiplying by 0.98 (or equivalent).
769.81 (EUR) (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
\(r\% \times \frac{{85}}{{0.08753}} = 14.57\) (M1)(M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing 85 by 0.08753, and (M1) for multiplying their \(\frac{{85}}{{0.08753}}\) by \(r\% \) and equating to 14.57.
OR
\(\frac{{85}}{{0.08753}} = {\text{971.095}} \ldots \) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing 85 by 0.08753.
\(\frac{{14.57}}{{9.71095 \ldots }}\)\(\,\,\,\)OR\(\,\,\,\)\(\frac{{14.57}}{{971.095 \ldots }} \times 100\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing 14.57 by 9.71095… or equivalent.
\(r = 1.50{\text{ }}(1.50036 \ldots )\) (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
Question
In this question, give all answers correct to 2 decimal places.
Jose travelled from Buenos Aires to Sydney. He used Argentine pesos, ARS, to buy 350 Australian dollars, AUD, at a bank. The exchange rate was 1 ARS = 0.1559 AUD.
The bank charged Jose a commission of 2%.
Jose used his credit card to pay his hotel bill in Sydney. The bill was 585 AUD. The value the credit card company charged for this payment was 4228.38 ARS. The exchange rate used by the credit card company was 1 AUD = \(x\) ARS. No commission was charged.
Use this exchange rate to calculate the amount of ARS that is equal to 350 AUD.[2]
Calculate the total amount of ARS Jose paid to get 350 AUD.[2]
Find the value of \(x\).[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Note: In this question, the first time an answer is not to 2 dp the final (A1) is not awarded.
\(\frac{{350}}{{0.1559}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing 350 by 0.1559.
\( = 2245.03{\text{ (ARS)}}\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
\(2245.03 \times 1.02\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying their answer to part (a) by 1.02.
\( = 2289.93{\text{ (ARS)}}\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
OR
\(2245.03 \times 0.02\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying their answer to part (a) by 0.02.
\( = 44.9006\)
\(2245.03 + 44.90\)
\( = 2289.93{\text{ (ARS)}}\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Follow through from part (a).[2 marks]
\(\frac{{4228.38}}{{585}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for dividing 4228.38 by 585.
\( = 7.23\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Question
In this question, give all answers to two decimal places.
Karl invests 1000 US dollars (USD) in an account that pays a nominal annual interest of 3.5%, compounded quarterly. He leaves the money in the account for 5 years.
Calculate the amount of money he has in the account after 5 years.[3]
Write down the amount of interest he earned after 5 years.[1]
Karl decides to donate this interest to a charity in France. The charity receives 170 euros (EUR). The exchange rate is 1 USD = t EUR.
Calculate the value of t.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(1000{\left( {1 + \frac{{3.5}}{{4 \times 100}}} \right)^{4 \times 5}}\) (M1)(A1)
Note: Award (M1) for substitution in compound interest formula, (A1) for correct substitution.
OR
N = 5
I = 3.5
PV = 1000
P/Y = 1
C/Y = 4
Note: Award (A1) for C/Y = 4 seen, (M1) for other correct entries.
OR
N = 5 × 4
I = 3.5
PV = 1000
P/Y = 1
C/Y = 4
Note: Award (A1) for C/Y = 4 seen, (M1) for other correct entries.
= 1190.34 (USD) (A1)
Note: Award (M1) for substitution in compound interest formula, (A1) for correct substitution.[3 marks]
190.34 (USD) (A1)(ft) (C4)
Note: Award (A1)(ft) for subtraction of 1000 from their part (a)(i). Follow through from (a)(i).[1 mark]
\(\frac{{170}}{{190.34}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for division of 170 by their part (a)(ii).
= 0.89 (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Follow through from their part (a)(ii).[2 marks]

