Question
A group of 20 students travelled to a gymnastics tournament together. Their ages, in years, are given in the following table.
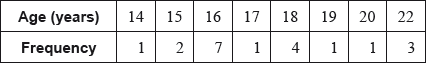
The lower quartile of the ages is 16 and the upper quartile is 18.5.
For the students in this group find the mean age;[2]
For the students in this group write down the median age.[1]
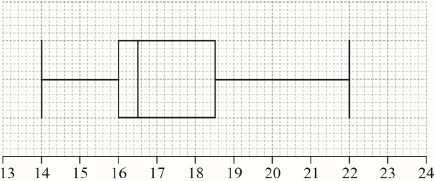
Draw a box-and-whisker diagram, for these students’ ages, on the following grid.
 [3]
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\frac{{14 + 2 \times 15 + 7 \times 16 + 17 + 4 \times 18 + 19 + 20 + 3 \times 22}}{{20}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for correct substitutions into mean formula.
\(( = ){\text{ }}17.5\) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
16.5 (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
 (A1)(A1)(A1)(ft) (C3)
(A1)(A1)(A1)(ft) (C3)
Note: Award (A1) for correct endpoints, (A1) for correct quartiles, (A1)(ft) for their median. Follow through from part (a)(ii), but only if median is between 16 and 18.5. If a horizontal line goes through the box, award at most (A1)(A1)(A0). Award at most (A0)(A1)(A1) if a ruler has not been used.[3 marks]
Question
In a school 160 students sat a mathematics examination. Their scores, given as marks out of 90, are summarized on the cumulative frequency diagram.
Write down the median score.[1]
The lower quartile of these scores is 40.
Find the interquartile range.[2]
The lowest score was 6 marks and the highest score was 90 marks.
Draw a box-and-whisker diagram on the grid below to represent the students’ examination scores.
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
48 (A1) (C1)
\(58 – 40\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for 58 and 40 seen.
\( = 18\) (A1) (C2)
(A1)(A1)(ft)(A1)(ft) (C3)
Note: Award (A1) for the correct maximum and minimum, (A1)(ft) for their correct median and (A1)(ft) for 40 and their upper quartile.
Follow through from parts (a) and (b).
Award a maximum of (A1)(A1)(ft)(A0) if the horizontal line goes through the box or if a ruler has clearly not been used.
Question
Two groups of 40 students were asked how many books they have read in the last two months. The results for the first group are shown in the following table.
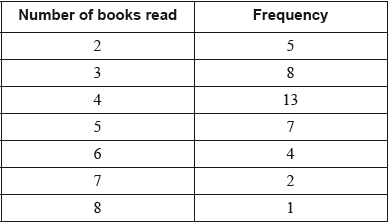
The quartiles for these results are 3 and 5.
Write down the value of the median for these results.[1]
Draw a box-and-whisker diagram for these results on the following grid.
 [3]
[3]
The results for the second group of 40 students are shown in the following box-and-whisker diagram.
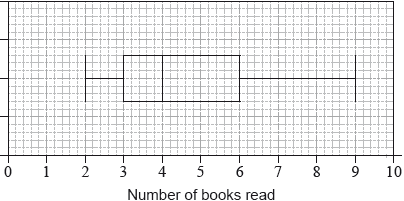
Estimate the number of students in the second group who have read at least 6 books.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(4\) (A1)(C1)
(A1)(ft)(A1)(A1) (C3)
Notes: Award (A1)(ft) for correct median, (A1) for correct quartiles and box, (A1) for endpoints 2 and 8 joined by a straight line that does not cross the box. Follow through from their median from part (a).
\(40 \times 0.25\) (M1)
Notes: Award (M1) for \(40 \times 25\% \;\;\;\)OR\(\;\;\;40 – 40 \times 75\% \).
\(10\) (A1) (C2)
Question
The time, in minutes, that students in a school spend on their homework per day is presented in the following box-and-whisker diagram.
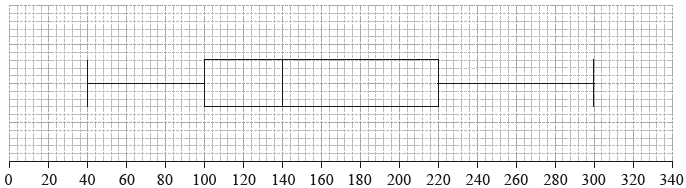
Time, in minutes, students spend on their homework per day
Find
(i) the longest amount of time spent on homework per day;
(ii) the interquartile range.[3]
State the statistical term corresponding to the value of 140 minutes.[1]
Find the percentage of students who spend
(i) between 100 and 140 minutes per day on their homework;
(ii) more than 100 minutes per day on their homework.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) 300 (minutes) OR 5 hours (A1)
Note: If answer given in hours, the unit must be seen.
(ii) 220 – 100 (M1)
Notes: Award (M1) for the two quartiles seen.
= 120 (minutes) OR 2 hours (A1) (C3)
Note: If answer given in hours, the unit must be seen.
median (time spent on homework per day) (A1) (C1)
Note: Do not accept middle or medium etc.
(i) 25 (A1)
(ii) 75 (A1) (C2)
Question
The distribution of rainfall in a town over 80 days is displayed on the following box-and-whisker diagram.
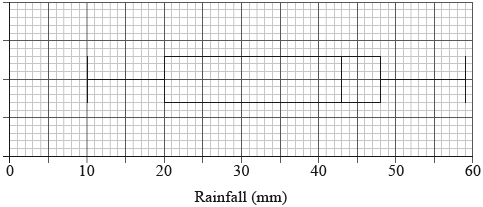
Write down the median rainfall.[1]
Write down the minimum rainfall.[1]
Find the interquartile range.[2]
Write down the number of days the rainfall will be
(i) between 43 mm and 48 mm;
(ii) between 20 mm and 59 mm.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(43 {\text{ (mm)}}\) (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
\(10{\text{ (mm)}}\) (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
\(48 – 20\) (A1)
\( = 28\) (A1) (C2)
Note: Award (A1) for identifying correct quartiles, (A1) for correct subtraction of the quartiles.[2 marks]
(i) 20 (days) (A1)
(ii) 60 (days) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Question
The weights, in kg, of 60 adolescent females were collected and are summarized in the box and whisker diagram shown below.
Write down the median weight of the females.[1]
Calculate the range.[2]
Estimate the probability that the weight of a randomly chosen female is more than 50 kg.[1]
Use the box and whisker diagram to determine if the mean weight of the females is less than the median weight. Give a reason for your answer.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
42 kg (A1) (C1)
Note: The units are required.
58 − 33 (A1)
Note: Award (A1) for correct maximum and minimum seen.
= 25 (A1) (C2)
\(\frac{1}{4}(0.25,25\% )\) (A1) (C1)
Mean weight is more than the median weight. (A1)
The upper half of the distribution is wider (more dispersed) or data is positively (or right) skewed or equivalent reason. (R1)
OR
\(\left( {{\text{The mean is calculated }}\bar x = \frac{{35.5 \times 15 + 40 \times 15 + 54 \times 15}}{{60}}} \right)\)
\(\bar x = 43.875{\text{ }} (kg)\) (R1) (C2)
Note: Do not award (A1)(R0).
Question
The daily rainfall for the town of St. Anna is collected over a 20-day period of time. The collected data are represented in the box and whisker plot below.
Write down
(i) the lowest daily rainfall;
(ii) the highest daily rainfall.[2]
State what the value of 12 mm represents on the given diagram.[1]
Find the interquartile range.[2]
Write down the percentage of the data which is less than the upper quartile.[1]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) 6 (mm) (A1)
(ii) 20 (mm) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Median (A1) (C1)
Note: Award (A1) for Q2 or 50th percentile.[1 mark]
14 – 9 (A1)
Note: Award (A1) for 9 and 14 seen.
5 (mm) (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
75 (%) (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
Question
The weights in kg, of 80 adult males, were collected and are summarized in the box and whisker plot shown below.
Write down the median weight of the males.[1]
Calculate the interquartile range.[2]
Estimate the number of males who weigh between \(61\) kg and \(66\) kg.[1]
Estimate the mean weight of the lightest \(40\) males.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(61\) kg (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
\(66 – 52\) (A1)
\( = 14\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: Award (A1) for identifying quartiles, (A1)(ft) for correct subtraction of their quartiles.[2 marks]
\(20\) (A1) (C1)[1 marks]
\(\frac{{49.5 \times 20 + 56.5 \times 20}}{{40}}\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplication of midpoints by frequencies.
\(= 53\) kg (A1) (C2)[2 marks]
Question
56 students were given a test out of 40 marks. The teacher used the following box and whisker plot to represent the marks of the students.
Write down the median mark.[1]
Write down the 75th percentile mark.[1]
Write down the range of marks.[2]
Estimate the number of students who achieved a mark greater than 32.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
30 (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
32 (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
38 – 10 = 28 (A1)(A1) (C2)
Note: Award (A1) for 10 and 38 seen, (A1) for correct answer only.[2 marks]
0.25 × 56 = 14 (M1)(A1) (C2)Note: Award (M1) for multiplying 0.25 by 56.[2 marks]
Question
The cumulative frequency graph shows the amount of time in minutes, 200 students spend waiting for their train on a particular morning.
Write down the median waiting time.[1]
Find the interquartile range for the waiting time.[2]
Draw a box and whisker plot on the grid below to represent this information.
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Median = 25 mins (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
32 – 16 (A1)
= 16 (A1)(ft) (C2)
Notes: Award (A1) for identifying correct quartiles, (A1)(ft) for correct answer to subtraction of their quartiles.[2 marks]
median shown (A1)(ft)
box with ends at their quartiles (A1)(ft)
end points at 0 and 45 joined to box with straight lines (A1) (C3)
Note: Award (A1)(ft)(A1)(ft)(A0) if lines go right through the box.[3 marks]
Question
A cumulative frequency graph is given below which shows the height of students in a school.
Write down the median height of the students.[1]
Write down the 25th percentile.[1]
Write down the 75th percentile.[1]
The height of the tallest student is 195 cm and the height of the shortest student is 136 cm.
Draw a box and whisker plot on the grid below to represent the heights of the students in the school.
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
170 (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
163 (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
172 (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
(A1)(ft)(A1)(ft)(A1) (C3)
Notes: Award (A1)(ft) for correct median, (A1)(ft) for correct quartiles and box (A1) for correct end points of whiskers.
Award at most (A1)(A1)(A0) if lines go right through the box.[3 marks]
Question
The diagram below shows the cumulative frequency distribution of the heights in metres of \(600\) trees in a wood.
Write down the median height of the trees.[1]
Calculate the interquartile range of the heights of the trees.[2]
Given that the smallest tree in the wood is \(3{\text{ m}}\) high and the tallest tree is \(28{\text{ m}}\) high, draw the box and whisker plot on the grid below that shows the distribution of trees in the wood.
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Median \( = 11{\text{ m}}\) (A1) (C1)
Note: Award A0 for “\(11\)” without units; correct units must be included for the A1 to be awarded.[1 mark]
\({\text{Interquartile range}} = 14 – 10\) (A1)
\( = 4\) (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: (M1) for taking a sensible difference or for both correct quartile values seen.[2 marks]
correct median (A1)(ft)
correct quartiles and box (A1)(ft)
endpoints at \(3\) and \(28\), joined to box by straight lines (A1) (C3)
Notes: Award (A0) if the lines go right through the box. Award final (A1) if the whisker goes to \(20\) with an outlier at \(28\).[3 marks]
Question
A random sample of 200 females measured the length of their hair in cm. The results are displayed in the cumulative frequency curve below.
Write down the median length of hair in the sample.[1]
Find the interquartile range for the length of hair in the sample.[2]
Given that the shortest length was \(6{\text{ cm}}\) and the longest \(47{\text{ cm}}\), draw and label a box and whisker plot for the data on the grid provided below.
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Unit penalty (UP) is applicable where indicated in the left hand column.
(UP) \(26{\text{cm}}\) (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
Unit penalty (UP) is applicable where indicated in the left hand column.
\(33 – 19\) for identifying correct quartiles. (A1)
(UP) \( = 14{\text{ cm}}\) . (A1)(ft) (C2)
Note: (ft) on their quartiles.[2 marks]
correct median (A1)(ft)
correct quartiles and box (A1)(ft)
endpoints at \(6\) and \(47\), joined to box by straight lines. (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
Question
There are \(120\) teachers in a school. Their ages are represented by the cumulative frequency graph below.
Write down the median age.[1]
Find the interquartile range for the ages.[2]
Given that the youngest teacher is \(21\) years old and the oldest is \(72\) years old, represent the information on a box and whisker plot using the scale below.
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({\text{Median }}= 45\) (A1) (C1)
Accept \(45.5\)[1 mark]
\(53 – 37\) for identifying correct quartiles (A1)
\( = 16\) for correct answer to subtraction (A1)(ft) (C2)
(ft) on their quartiles[2 marks]
Median marked correctly. (A1)(ft)
Box with ends at candidate’s quartiles. (A1)(ft)
End points at \(21\) and \(72\) joined to box with straight lines. (A1) (C3)
Note: Award (A0) if lines go right through the box.[3 marks]
Question
State which of the following sets of data are discrete.
(i) Speeds of cars travelling along a road.
(ii) Numbers of members in families.
(iii) Maximum daily temperatures.
(iv) Heights of people in a class measured to the nearest cm.
(v) Daily intake of protein by members of a sporting team.[2]
The boxplot below shows the statistics for a set of data.
For this data set write down the value of
(i) the median
(ii) the upper quartile
(iii) the minimum value present[3]
Write down three different integers whose mean is 10.[1]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(ii) and (iv) are discrete. (A1)(A1)
Award (A1)(A0) for both correct and one incorrect.
Award (A1)(A0) for one correct and two incorrect.
Otherwise, (A0)(A0). (C2)[2 marks]
(i) Median = 10 (A1)
(ii) Q3 = 12 (A1)
(iii) Min value = 1 (±0.2) (A1) (C3)[3 marks]
Any three different integers whose mean is 10 e.g. 9, 10, 11. (A1) (C1)[1 mark]
