Question:
These hot and cold compresses contain a chemical and an inner bag containing water. By squeezing the outer bag, the inner bag is ruptured and the water mixes with the chemical. The chemical in the hot compress is magnesium sulfate; the cold compress contains ammonium nitrate.
Which reaction is endothermic and which is exothermic?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The hot compress reaction is exothermic and the cold compress reaction is endothermic.
Question:
Describe the energy changes that occur after a sparkler is lit.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: When lit, the energy stored in the fuel of a sparkler is released as light and heat energy.
Question:
How did you know that a reaction had taken place? Give at least two reasons.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The production of a gas is observed when the magnesium metal is placed into the hydrochloric acid; the size of the magnesium metal decreases as the reaction proceeds.
Question:
How did you know that the reaction had finished?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reaction has finished when no more gas is produced.
Question:
Explain why the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The final temperature of the reaction mixture is higher than the initial temperature of the acid; an increase in temperature describes an exothermic reaction.
Question:
Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Question:
Describe the reaction. What energy changes did you observe?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reaction is very vigorous. You cannot see heat energy during this reaction but you can observe molten iron which is a consequence of the amount of heat that is released during this reaction.
Question:
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between iron(III) oxide and aluminium.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: aluminium + iron(III) oxide → iron + aluminium oxide
2Al + Fe2O3 → 2Fe + Al2O3
Question:
What are the advantages of this reaction for railway construction?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Construction of railways occurs on site. In some situations it would be difficult to have equipment on–site used to meld together the steel rails. The thermite reaction is portable and very effective.
Question:
A thermite reaction can occur if rusty steel is covered by aluminium paint and hit by a hammer. Explain why this might happen.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The hammer has a large amount of kinetic energy. Upon striking the rusty steel, its kinetic energy is converted into sound energy and heat energy. If the amount of heat energy is sufficient, the thermite reaction may be initiated.
Question:
What factors influence people’s choice of cooking fuel?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The choice of cooking fuel can be influenced by number of different factors:
- the location for cooking
- the amount of heat needed to be generated
- the level of control over the heat source required
- the availability of the fuel source
- economic considerations
Question:
How did your observations for the two reactions differ?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Mixing calcium chloride with water resulted in an increase in temperature; mixing ammonium nitrate with water resulted in a decrease in temperature.
Question:
Identify whether each was endothermic or exothermic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The reaction of calcium chloride and water is an exothermic reaction; the reaction of ammonium nitrate and water is an endothermic reaction.
Question:
Write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction. Include the state of the reactants and products.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: CaCl2(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
NH4NO3(s) → NH4+(aq) + NO3–(aq)
Question:
Look back at the thermite reaction. Where did the energy come from to start the reaction?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Heat energy from a flame.
Question:
In an endothermic or exothermic reaction, what do you observe when measuring the temperature of the reaction mixture with a thermometer?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: In an endothermic reaction, the temperature of the reaction mixture decreases. In an exothermic reaction, the temperature of the reaction mixture increases.
Question:
Convert the following temperatures to kelvin:
a) 100ºC b) 38ºC c) −48ºC
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) 373 K b) 311 K c) 225 K
Question:
Convert the following temperatures to degrees Celsius:
a) 300 K b) 273 K c) 252 K
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: a) 27°C b) 0°C c) –21°C
Question:
It takes 4,200 J to heat 1 kg of water by 1 K (or by 1ºC). How much energy does it take to raise the temperature of 1 kg of copper by 1 K?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 390 J
Question:
Convert:
a) 2.5 × 105 J into kilojoules
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 2.5 x 102 kJ
b) 298 K into degrees Celsius
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 25°C
c) 0.098 kJ into joules
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 98 J
d) 45°C into kelvin.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 318 K
Question:
The temperature of a 4.0 g block of pure aluminium increases from 25°C to 45°C. If the specific heat capacity of aluminium is 900 J kg−1 K−1, calculate the amount of energy required for this temperature increase.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Q = m c ∆T
= (4 / 1000) × 900 × 20
= 72 J
Question:
To what temperature will 250 g of mercury rise from an initial temperature of 10°C, if 5.425 × 103 joules of heat energy is transferred into the system? The specific heat capacity of mercury is 140 J kg−1 K−1.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Rearrange the equation so that ∆T is the subject
∆T = Q / mc
= 5.425 × 103 / 0.250 × 140
= 155 K
As this is the change in temperature, 155 K is
equivalent to 155°C.
∆T = Tfinal – Tinitial
155°C = Tfinal – 10°C
Tfinal = 165°C
Question:
A 20 g piece of iron absorbs 1251.2 J of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 161°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: c = Q / m ∆T
= 1251.2 / 0.02 × (161 – 25)
= 4.6 × 102 J kg–1 K–1
Question:
Suggest ways in which heat loss to the surroundings can be minimized.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: An insulated lid can be placed on the top of the coffee cup/increase the amount of insulation surrounding the coffee cup/use a calorimeter.
Question:
Is this an exothermic or endothermic reaction?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: This is an exothermic reaction as there is an increase in the temperature of the reaction mixture.
Question:
What is the change in temperature for this reaction?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: ∆T = 30.4°C
Question:
Calculate the energy given out by this reaction, based on the change in temperature of the solution. Assume that the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4,200 J kg−1 K−1.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Q = m c ∆T = 0.0576 x 4200 x 30.4
= 7354 J or 7.35 kJ (3 sf)
Question:
Is your answer likely to be an underestimate or overestimate of the heat given out by this reaction? Explain your reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Your answer is likely to be an underestimate of the heat given out by this reaction due to the fact that heat will be lost to the surroundings because of the lack of insulation of the reaction vessel.
Summative assessment
Where does all the energy go?
Today, China and the United States remain the largest consumers and producers of energy. China has the world’s largest population. It accounts for over 20% of the total world energy consumption. The main energy supply for China comes from coal (65%+) and it is both the largest producer and consumer of coal, a carbon-based non-renewable fossil fuel. It is also one of the largest consumers of renewable energy and is investing record amounts of money in research and development of alternative energy sources. The United States holds the second largest coal and oil reserves in the world.
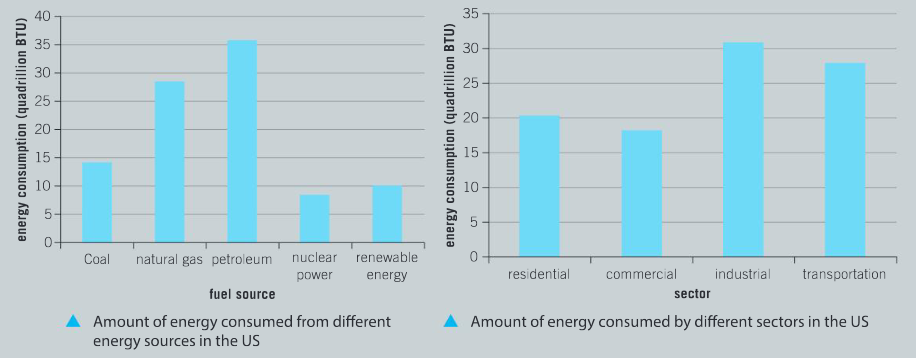
Question:
What is the total number of BTU consumed using coal, natural gas and crude oil energy sources? (The British thermal unit or BTU is a traditional unit of heat energy.)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Coal = 14 BTU; natural gas = 28 BTU; petroleum = 36 BTU. Total = 78 BTU.
Question:
What proportion of energy consumption in the US is from non-renewable fossil fuels?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Approximately 90%
Question:
Compare the energy consumption of China and the United States, using coal as an energy source
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Coal as a proportion of total energy production in China is greater than 65%; while in the US it is less than 15%; possible reason for this include the historic level of infrastructure and the rate of development of alternative energy supplies and natural resources.
Question:
There was agreement among 195 countries in the Paris climate change agreement to limit the increase in global temperature to less than 2°C by 2030. The scientific community has identified that global use of renewable and clean energy needs to increase significantly if the high energy-consuming countries are to meet their targets.
a) What proportion of total consumption does renewable energy represent in the US?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Renewable energy 10 BTU; non–renewable sources of energy include coal, natural gas, petroleum and nuclear power; 10 / 96 × 100% = 10% (approximately).
b) Of the sectors residential, commercial, industry and transportation; which is the largest consumer of energy?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Industrial
Question:
Analyze the greenhouse gas emissions in the graph.
a) Identify and explain the trends in greenhouse gas emissions for renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Traditional non–renewable energy sources, such as lignite (brown coal), black coal and crude oil, remain the main contributors to greenhouse emissions; the amount of use of natural gas, a non–renewable energy source, is increasing and it is the fourth largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions; nuclear power is considered to be the cleanest non–renewable energy source in terms of greenhouse gas emissions; renewable energy sources are the smallest greenhouse gas emitters. Answers for this question may vary. All valid alternatives should be considered.
b) Evaluate and discuss the challenges faced by the US and many of the large industrial nations by comparing the major energy sources identified in the US energy flow diagram and the greenhouse gas emissions graph.
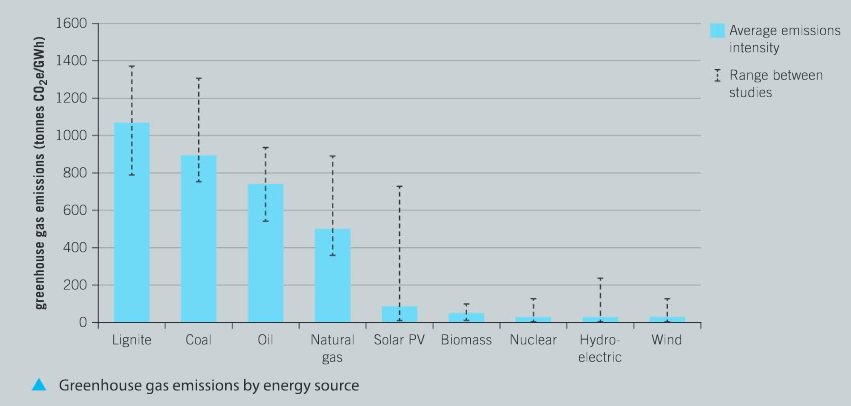
Ans: Challenges faced by the US and large industrial nations include:
- The most commonly used fuel sources such as coal, natural gas and petroleum are also the largest source of greenhouse gases;
- Renewable energy sources are the smallest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, but only represent 10% of energy sources in the US;
- Nuclear power is a clean energy in terms of greenhouse gas emissions, however, a consequence of recent accidents and natural disasters involving nuclear power stations is a negative public perception of the safety of nuclear power;
- Hydroelectric schemes utilize natural resources such as rivers and lakes. However, the initial cost of the infrastructure is significant and historically many of these projects have led to environmental destruction, displaced large populations and impacted on people’s lifestyles and economic well–being;
- Wind farms and solar panel installations create very little greenhouse gas emissions, but require large setup costs and are somewhat unpopular due to visual pollution.
These are some examples of the types of answers that students may construct upon evaluating and discussing the data given in the three graphs. Answers may vary.
Investigating the combustion of alcohols
Different fuels have different energy densities. The combustion of alcohol is an exothermic reaction in which water, carbon dioxide and heat energy are produced. You can compare the energy density of alcohols by using the subsequent heat produced to heat water.
Question:
Formulate a hypothesis for the relationship between the energy density of alcohols and the length of their carbon chain. Explain this using scientific reasoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Suitable hypothesis is suggested; hypothesis is testable; hypothesis is based on scientific reasoning.
Question:
Design an experiment to test your hypothesis using some or all of the materials listed. You should include:
a) the method; include a drawing of your apparatus
b) the dependent, independent and control variables
c) any safety precautions required
d) a table for recording and analyzing results
The following table shows the data collected by a chemist when investigating the combustion of a series of alcohols. They may have used a similar method to the one you designed above.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Design should include clear statement of:
- independent and dependent variables,
- rationale for the method and practical details, including:
- correct names of apparatus and volume
- amounts and/or concentration of chemicals being used
- consideration of safety, ethical and environmental issues
- description of the step–by–step methodology for the investigation, including how the variables are controlled
- description of how qualitative observations will be recorded
- identification of any quantitative data that will be recorded and the design of data tables to present this information
Marks awarded on a scale from 0 marks for a completely inadequate design to 10 marks for an exemplary design.
Question:
Calculate the change in temperature ΔT (1 decimal place) for each of the trails performed, and record in the results table.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 32.9; 31.2; 44.1; 43.5; 45.9; 54.9; 38.0; 39.1.
Question:
Calculate the temperature change per 1 gram of fuel consumed in °C/g, and record in the results table.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 46.3; 45.9; 55.8; 55.1; 67.5; 74.2; 80.9; 81.5.
Question:
Of the four alcohols tested, which set of data is the most valid? State the reasons for your choice.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Methanol; the two data points are the most precise of the four different sets of data.
Question:
a) Which set of data is the least reliable and why?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Propan–1–ol; the two data points are the least precise as they have the largest variation between the two data points.
b) Explain how you could improve the validity of this data.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Perform more trials to minimize the random errors; eliminate any anomalous data.
How is heat energy distributed around the globe?
Advances in science and technology has enabled us to deepen our understanding of the large-scale effects of different types of energy redistribution. Many of Earth’s solid and fluid processes of global significance have the effect of redistributing energy from areas of high concentration towards areas of lower concentration. Examples include:
● the Gulf Stream
● the North Atlantic Drift
● Hadley cells
● hydrothermal venting
● geysers and hot springs
● volcanism.
The scientific community is using some of these systems to track changing global weather patterns. How is energy interconnected within each of these systems?
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
More commonly known as the Atlantic conveyor, the AMOC is a part of the global ocean conveyor belt that is responsible for the transport of heat energy around the globe. Heat is defined as the flow of energy resulting from differences in temperature. In simple terms, warm water in the upper region of the Atlantic Ocean flows north from the Earth’s equator towards the North Pole.
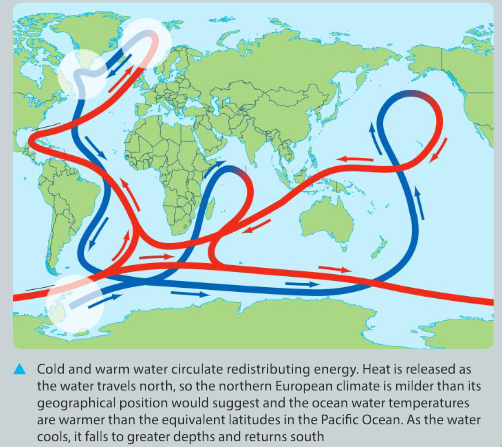
A number of global longitudinal scientific studies into the effects of man-made global warming on the AMOC have found that the amount of warm water being transported has slowed significantly. The exact reasons for this phenomenon are still unclear. What has been concluded is that changes in the AMOC have resulted in higher sea levels in parts of the northern hemisphere and more severe weather patterns in the affected areas.
The following article was published online in 2017 for the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at https://scripps.ucsd.edu/news/ climate-model-suggests-collapse-atlantic-circulation-possible
Read the article and then answer the following questions.
Question:
Numerous organizations and scientists are researching the many aspects of global warming. This article presents the point of view that the AMOC will be stopped by a collapse in circulation.
a) Explain the bias that the scientists have named and why they have reached this conclusion about the collapse of the AMOC.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The scientists have named the bias that the AMOC (Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation) is essentially stable and will not collapse; the doubling of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration is used to simulate circulation collapse.
b) What do they predict will happen in the northern North Atlantic Ocean?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The model predicts that the North Atlantic Ocean will cool and Arctic sea ice will spread.
c) What problem is identified with the IPCC reports (which synthesize climate change research)?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: It is based on possibly false assumptions.
d) As well as modelling, which other scientific method supports the Chinese scientists’ claims?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Data collection of temperature and salinity in the oceans and land–based temperatures; satellite imagery collecting sea surface temperature (SST) and EMS data.
e) List five possible effects created by the collapse in the model.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Cooling of the North Atlantic ocean surface temperatures; cooling of surface air temperatures over northwest Europe; tropical rain belts may move further southward; seasonal weather patterns may change; uncharacteristic storm activity may occur.


