Question
The electron micrograph shows part of a cell including a mitochondrion.
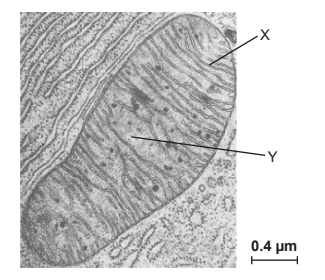
(a) Outline how the structures labelled X and Y are adapted to carry out the function of
the mitochondrion.
X:
Y:
(b) Explain how ATP is generated in mitochondria by chemiosmosis.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
X: large/increased SA area for ATP production/electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation/proton pumping
OR
X: small/narrow intermembrane space for generating proton gradient (rapidly/steeply);
Y: contains enzymes for Krebs cycle/link reaction;
b)
a. protons pumped across inner membrane of mitochondria/into intermembrane space;
b. using energy released by flow of electrons/by electron transport/by electron carriers;
c. proton gradient established/maintained / proton motive force generated;
d. protons pass/diffuse back through inner membrane/membrane of cristae/to matrix;
e. through ATP synthase;
Question
(a) (i) Outline how the amphipathic properties of phospholipids play a role in membrane structure.
(ii) State the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes.
(b) Describe what happens to the membranes of an animal cell during mitosis.
(c) The diagram shows part of two neurons.
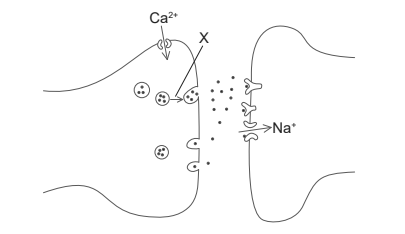
(i) State the name of the structure shown.
(ii) X indicates the movement of a structure in the neuron. Explain what events trigger this movement and what happens next.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a (i)
a. part hydrophobic/not attracted to water/non-polar AND part hydrophilic/attracted to water/polar;
b. bilayer formed (formed naturally by phospholipids in water);
c. hydrophilic heads/parts face outwards and hydrophobic tails/parts face inwards;
a (ii)
a. controls/regulates/reduces fluidity of membrane / prevents crystallization of phospholipids;
b. reduces permeability to some substances;
b
a. nuclear membrane breaks down/disappears (in prophase/at start of mitosis);
b. nuclear membrane reforms around two new nuclei (in telophase/at end of mitosis);
c. plasma membrane pulled inwards at equator / cleavage furrow formed;
d. membrane pinches apart to form two cells / cytoplasm divided / cytokinesis;
c (i) synapse/synaptic
c (ii)
a. depolarization of pre-synaptic membrane / action potential/nerve impulse arrives;
b. uptake of calcium / calcium ions diffuse in / calcium channels open;
c. structures containing neurotransmitter/vesicles move to/fuse with membrane;
