CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQs Solution All Chapters
Free PDF Download of CBSE Physics Multiple Choice Questions for Class 12 with Answers Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields. Physics MCQs for Class 12 Chapter Wise with Answers PDF Download was Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Electric Charges and Fields MCQs Pdf with Answers to know their preparation level.
Nuclei Class 12 Physics MCQs
Question 1. When a β-particle is emitted from a nucleus then its neutron-proton ratio
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains unchanged.
(d) may increase or decrease depending upon the nucleus.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) In P-decay neutron converts to proton with emission of electron and neutrino.
Physics MCQs with Answers for Class 12 Question 2. The relation between half-life T1/2 of a radioactive sample and its mean life x is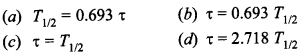
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: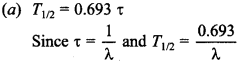
3. The quantity which is not conserved in a nuclear reaction is
(a) momentum.
(b) charge.
(c) mass.
(d) none of these.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) Energy equivalent to mass detect is released.
4. The half-life of a radioactive nucleus is 3 hours. In 9 hours, its activity will be reduced to a factor of
Answer/Explanation
CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQs with Answer: d
Explaination: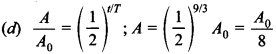
MCQs Of Physics 2nd Year with Answers Chapter 13 Question 5. A radioactive element has half-life period 1600 years. After 6400 years what amount will remain?
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: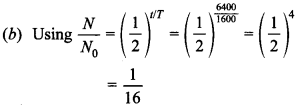
Class 12 Physics MCQs Pdf Question 6. Ratio of the radii of the nuclei with mass numbers 8 and 27 would be
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: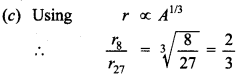
7. A radioactive nucleus emits a beta particle. The parent and daughter nuclei are
(a) isotopes
(b) isotones
(c) isomers
(d) isobars
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) Isobars have the same atomic mass but 1 different atomic number.
Physics MCQs for Class 11 Chapter wise Pdf Question 8. In the disintegration series![]()
the values of Z and A respectively will be
(a) 92, 236
(b) 88, 230
(c) 90, 234
(d) 91, 234
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:![]()
CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQ Pdf Question 9. A nucleus \(_{Z}^{\mathbf{A}} \mathbf{X}\) emits an α-particle. The resultant nucleus emits a β-particle. The respective atomic and mass numbers of the daughter nucleus will be
(a) Z – 3, A – 4
(b) Z – 1, A – 4
(c) Z – 2, A – 4
(d) Z, A – 2
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: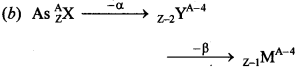
10. In the nuclear reaction![]()
What does X stand for?
(a) Electron
(b) Proton
(c) Neutron
(d) Neutrino
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) By conservation of mass A = 0, and by conservation of charge Z = 0, Hence X is neutrino.
11. The set which represent the isotope, isobar, and isotone respectively is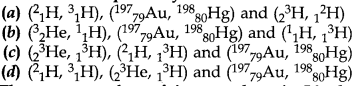
Answer
Answer: d
12. The mass number of iron nucleus is 56 the nuclear density is
(a) 2.29 × 1016 kg m-3
(b) 2.29 × 1017 kg m-3
(c) 2.29 × 1018 kg m-3
(d) 2.29 × 1015 kg m-3
Answer
Answer: b
13. Order of magnitude of density of uranium nucleus is
(a) 1020 kg m-3
(b) 1017 kg m-3
(c) 1014 kg m-3
(d) 1011 kg m-3
Answer
Answer: b
14. The radius of a spherical nucleus as measured by electron scattering is 3.6 fm. What is the mass number of the nucleus most likely to be?
(a) 27
(b) 40
(c) 56
(d) 120
Answer
Answer: a
15. The half life of a radioactive susbtance is 30 days. What is the time taken to disintegrate to 3/4th of its original mass?
(a) 30 days
(b) 15 days
(c) 60 days
(d) 90 days
Answer
Answer: c
16. The number of beta particles emitted by a radioactive substance is twice the number of alpha particles emitted by it. The resulting daughter is an
(a) isomer of parent
(b) isotone of parent
(c) isotope of parent
(d) isobar of parent
Answer
Answer: c
17. During negative β-decay, an antineutrino is also emitted along with the emitted electron. Then,
(a) only linear momentum will be conserved
(b) total linear momentum and total angular momentum but not total energy will be conserved
(c) total linear momentum, and total energy but not total angular momentum will conserved
(d) total linear momentum, total angular momentum and total energy will be conserved
Answer
Answer: d
18. Consider α and β particles and γ-rays each having an energy of 0.5 MeV. In the increasing order of penetrating power, the radiation are respectively
(a) α, β, γ
(b) α, γ, β
(c) β, γ, α
(d) γ β, α
Answer
Answer: a
19. An electron emitted in beta radiation originates from
(a) inner orbits of atom
(b) free electrons existing in the nuclei
(c) decay of a neutron in a nuclei
(d) photon escaping from the nucleus
Answer
Answer: c
20. Complete the series 6He → e– + 6Li +
(a) neutrino
(b) antineutrino
(c) proton
(d) neutron
Answer
Answer: b
21. An element A decays into an element C by a two step process A → B+ 2He4 and B → C + 2e–. Then,
(a) A and C are isotopes
(b) A and C are isobars
(c) B and C are isotopes
(d) A and B are isobars
Answer
Answer: a
22. The equation 41 1H+ → 24He2+ + 2e– + 26 MeV
represents
(a) β-decay
(b) γ-decay
(c) fusion
(d) fission
Answer
Answer: c
23. Light energy emitted by star is due to
(a) breaking of nuclei
(b) joining of nuclei
(c) burning of nuclei
(d) reflection of solar light
Answer
Answer: b
24. In nuclear reaction, there is conservation of
(a) mass only
(b) energy only
(c) momentum only
(d) mass, energy and momentum
Answer
Answer: d
25. In nuclear reactors, the control rods are made of
(a) cadmium
(b) graphite
(c) krypton
(d) plutonium
Answer
Answer: a
26. Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half-life of 1 year. After 1 year, [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) all the containers will have 5000 atoms of the material.
(b) all the containers will contain the same number of atoms of the material but that number will only be approximately 5000.
(c) the containers will in general have different numbers of the atoms of the material but their average will be close to 5000.
(d) none of the containers can have more than 5000 atoms.
Answer
Answer:c
27. Jhe gravitational force between a H-atom and another particle of mass m will be given by Newton’s law: [NCERT Exemplar]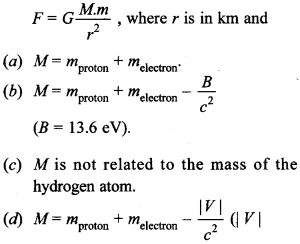
= magnitude of the potential energy of electron in the H-atom).
Answer
Answer: b
28. When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) do not change for any type of radioactivity.
(b) change for α and β radioactivity but not for γ-radioactivity.
(c) change for α-radioactivity but not for others.
(d) change for β-radioactivity but not for others.
Answer
Answer: b
29. Mx and My denote the atomic masses of the parent and the daughter nuclei respectively in a radioactive decay. The Q-value for a β– decay is Q1 and that for a β+ decay is Q2 If me denotes the mass of an electron, then which of the following statements is correct? [NCERT Exemplar]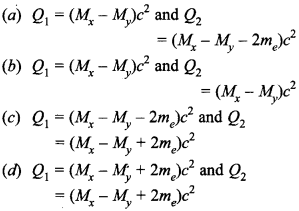
Answer
Answer: a
30. Tritium is an isotope of hydrogen whose nucleus Triton contains 2 neutrons and 1 proton. Free neutrons decay into p + \(\bar{e}+\bar{v}\). If one of the neutrons in Triton decays, it would transform into He3 nucleus. This does not happen. This is because [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Triton energy is less than that of a He3\ nucleus.
(b) the electron created in the beta decay process cannot remain in the nucleus.
(c) both the neutrons in triton have to decay simultaneously resulting in a nucleus with 3 protons, which is not a He3 nucleus.
(d) because free neutrons decay due to external perturbations which is absent in a triton nucleus.
Answer
Answer: a
31. Heavy stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons. This is because of the fact that [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) neutrons are heavier than protons.
(b) electrostatic force between protons are repulsive.
(c) neutrons decay into protons through beta decay.
(d) nuclear forces between neutrons are weaker than that between protons.
Answer
Answer: b
32. Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
(a) Initial rate of decay of A is twice the » initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
(b) Initial rate of decay of A is less than the initial rate of decay of B and λA < λB.
(c) Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
(d) Initial rate of decay of B is same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB = λA.
Answer
Answer: d
33. The variation of decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in figure. Which of the following statements are true?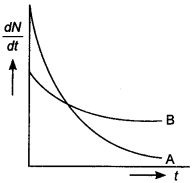
(a) Decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B.
(b) Decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A.
(c) Decay constant of A is equal to that ofB.
(d) Decay constant of B is smaller than that of A but still its decay rate becomes equal to that of A at a later instant.
Answer
Answer: d
34. Radioactivity is the phenomenon associated with
(a) decay of nucleus.
(b) production of radio waves.
(c) transmission of radio waves.
(d) reception of radio waves.
Answer
Answer: a
35. Which of the following are not emitted by radioactive substances?
(a) Electrons
(b) Protons
(c) Gamma rays
(d) Helium nuclei
Answer
Answer: b
36. In an α-decay
(a) the parent and daughter nuclei have some number of protons.
(b) the daughter nucleus has one proton more than parent nucleus.
(c) the daughter nucleus has two protons less than parent nucleus.
(d) the daughter nucleus has two nucleus more than parent nucleus.
Answer
Answer: c
37. When a radioactive nucleus emits a (β-particle, the mass number of the atom:
(a) increases by one.
(b) remains the same.
(c) decreases by one.
(d) decreases by four.
Answer
Answer: b
38. In a β-decay
(a) the parent and daughter nuclei have the same number of protons.
(b) the daughter nucleus has one proton less than parent nucleus.
(c) the daughter nucleus has one proton more than the parent nucleus.
(d) the daughter nucleus has one neutron more than the parent nucleus.
Answer
Answer: c
39. P-rays emitted by a radioactive material are
(a) electromagnetic radiations.
(b) electrons orbiting around the nucleus.
(c) neutral particles.
(d) charged particles emitted by nucleus.
Answer
Answer: d
40. During a mean life of a radioactive element the fraction that disintegrates is
Answer
Answer: c
41. γ-rays are originated from
(a) nucleus.
(b) outermost shell of nucleus.
(c) innermost shell of nucleus.
(d) outermost shell of atom.
Answer
Answer: a
42. Binding energy per nucleon of a stable nucleus is
(a) 8 eV
(b) 8 KeV
(c) 8 MeV
(d) 8 BeV
Answer
Answer: c
43. Sun’s radiant energy is due to
(a) nuclear fission.
(b) nuclear fusion.
(c) photoelectric effect.
(d) spontaneous radioactive decay.
Answer
Answer: b
44. Average binding energy is maximum for
(a) C12
(b) Fe56
(c) U235
(d) Po210
Answer
Answer: b
45. A nucleus undergoes γ-decay due to
(a) excess of protons.
(b) excess of neutrons.
(c) large mass.
(d) its excited state.
Answer
Answer: d
46. The decay constant of a radioactive substance is X. Its half-life and mean life, respectively are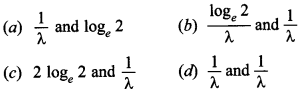
Answer
Answer: b
47. Neutrino is a particle, which is chargeless and has spin.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: ±\(\frac{1}{2}\)
48. Isotones have the same number of _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: neutrons
49. Packing fraction of a nucleus is its _________ its per nucleon.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: mass defect
50. How is the radius of a nucleus related to its mass number? [Panchkula 2019] [AI2011C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The radius if of a nucleus of mass number A is related as if = R0A1/3, where R0 is a constant.
51. Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 27 : 125. What is the ratio of their nuclear radii?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
52. Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 2 : 5. What is the ratio of their nuclear densities?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Nuclear density is independent of mass number. So, the ratio will be 1 : 1.
53. What is the relation between the binding energy per nucleon and stability of a nucleus?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The larger the binding energy per nucleon, the more stable is the nucleus.
54. Write any two characteristic properties of nuclear force. [Chennai-2019] [AI 2012,13]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The following are the two characteristic properties:
(i) Nuclear force is a short range force.
(ii) Nuclear forces show the saturation effect.
55. How is the mean life of a radioactive sample related to its half-life? [Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
56. Define the activity of a given radioactive substance. Write its SI unit.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The rate of disintegration or count rate of sample of radioactive material is called activity. The SI unit of activity is becquerel (Bq).
57. The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence![]()
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is
(i) the mass number
(ii) atomic number of D?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
(i) Mass number of D = 180
(ii) Atomic number of D = 72
58. A nucleus \(_{n} X^{m}\) emits one a-particle and one β-particle. What is the mass number and atomic number of the product nucleus?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
Hence, the mass number of product is m – 4, and the atomic number of product is n – 1.
59. In both β– and β+ decay processes, the mass number of a nucleus remains same, whereas the atomic number Z increases by one in β– decay and decreases by one in β+ decay. Explain, giving reason. [Foreign 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
In β– decay, one neutron inside the nucleus decays into one proton and one electron (β–). The proton remains inside the nucleus and the electron is ejected out.![]()
In β+ decay, the conversion of proton into neutron and position (β+) takes place.![]()
60. Which nucleus has greater mean life, A or B?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: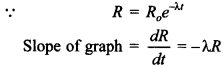
Since, slope of A is more than slope of B.
Therefore, X is high and mean life e = \(\frac{1}{\lambda}\) for A is small.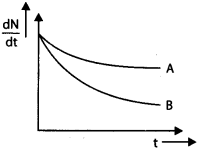
61. Why is a free neutron unstable but a free proton is a stable particle?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
A free neutron is unstable outside the nucleus with an average life of 1000 s. It decays into a proton and emits a β– particle, i.e.![]()
62. A neutron strikes a nucleus of \(_{5}^{\mathbf{10}} \mathbf{B}\) and emits an alpha particle. Write down the nuclear reaction for it.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
63. Write the necessary condition required for fusion reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Nuclear fusion will occur when the kinetic energy of colliding nuclei is enough to overcome the strong electrostatic forces of repulsion between the protons. For this, high temperature is required.
(ii) The density of nuclei should also be very high to increase the number of collisions.
64. Out of \(_{14}^{30} X ;_{3}^{6} Y \text { and }_{40} Z^{130}\), which is more likely to undergo the nuclear fusion?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
A lighter unstable nucleus \(_{3}^{\mathbf{6}} \mathbf{Y}\) can undergo the nuclear fusion.
65. What is the effect of temperature on radioactivity?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No effect. Radioactivity is independent of temperature.
66. What is the difference between an electron and a β-particle?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
An electron resides outside the nucleus, whereas β-particle is an electron like particle of nuclear origin.
67. What is the source of stellar energy?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Nuclear fusion reactions.
68. Four nuclei of an element fuse together to form a heavier nucleus. If the process is accompanied by the release of energy, which of the two—the parent or the daughter nucleus would have a higher binding energy/ nucleons? [CBSE 2018]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Daughter nucleus.
69. You are given two nuelei \(_{3}^{7} X \text { and }_{3}^{4} Y\), which one of the two is likely to be more stable? Give reason.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: \(_{3}^{\mathbf{7}} \mathbf{X}\) is more stable, as it contains more neutrons than protons.
70. The \(_{10}^{\mathbf{23}} \mathbf{Ne}\) decays by β– emission into \(_{11}^{\mathbf{23}} \mathbf{Na}\). Write down the β– decay equation.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
Nuclei Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Beta rays emitted by a radioactive material are
(a) neutral particles.
(b) charged particles emitted by nucleus.
(c) electromagnetic radiations.
(d) electrons orbiting around the nucleus.
Answer
Answer: (b) charged particles emitted by nucleus.
Question 2
How much energy will approximately be released if all the atoms of 1 kg of deuterium could undergo fusion?
(a) 2 × 107 kWh
(b) 9 × 1013J
(c) 6 × 1027 Cal
(d) 8 × 1023 MeV.
Answer
Answer: (b) 9 × 1013J
Question 3.
The packing fraction for \(_{7}^{14}\)N isotope whose mass is 14.003 amu is:
(a) 0.9
(b) 7.8 × 10-3
(c) 1.0002
(d) 2.1 × 10-4
Answer
Answer: (b) 7.8 × 10-3
Question 4.
The binding energy per nucleon is almost constant for many nuclei. It shows that nuclear forces are
(a) Charge independent
(b) saturated in nature
(c) short range in nature
(d) attractive in nature
Answer
Answer: (b) saturated in nature
Question 5.
The binding energies per nucleon for a deutron and an α- particle are x1 and x2 respectively. The energy Q released in reaction
1H² + 1H² → \(_{2}^{4}\)He + Q is
(a) 4 (x1 + x2)
(b) 4 (x1 – x2)
(c) 2 (x1 + x2)
(d) 2 (X1 – x2).
Answer
Answer: (b) 4 (x1 – x2)
Question 6.
The binding energies of the atoms of elements A and B are Ea and Eb respectively. Three atoms of the elements B fuse to give one atom of element A. This fusion process is accompained by release of energy E. Then Ea, Eb and E are related to each other as:
(a) Ea + E = 3 Eb
(b) Ea = 3Eb
(c) Ea – E = 3 Eb
(d) Ea + 3Eb + E = 0
Answer
Answer: (a) Ea + E = 3 Eb
Question 7.
Let mn and mp be the masses of a neutron and a proton respectively. M1 and M2 are the masses of a \(_{10}^{20}\)Ne nucleus and a \(_{20}^{40}\)Ca nucleus respectively. Then
(a) M2 < 2M1
(b) M2 > 2M1
(c) M2 = 2M1
(d) M1 < 10 (mn + mp).
Answer
Answer: (a) and (d).
Question 8.
One requires an energy En to remove a nucleon from a nucleus and an energy Ee to remove an electron from an atom. Then
(a) En = Ee
(b) En > Ee
(c) En < Ee
(d) En > Ee.
Answer
Answer: (b) En > Ee
Question 9.
When the number of nucleons in nuclei increases, the binding energy per nucleon numerically
(a) increases continuously with mass number.
(b) decreases continuously with mass number.
(c) First increases and then decreases with increase of mass number.
(d) Remains constant with mass number.
Answer
Answer: (c) First increases and then decreases with increase of mass number.
Question 10.
For an atomic reactor being critical, the ratio (k) of the average number of neutrons produced and used in chain reaction
(a) depends upon the mass of the fissionable material.
(b) is greater than one.
(c) is less than one.
(d) is equal to one.
Answer
Answer: (a) depends upon the mass of the fissionable material.
Question 11.
Maximum permissible radiation dose a a person may have with no adverse effects is
(a) 250 × 10-1 roentgen’s per week.
(b) 250 × 10-2 roentgen’s per week.
(c) 250 × 10-3 roentgen’s per week.
(d) 250 roentgen’s per week.
Answer
Answer: (c) 250 × 10-3 roentgen’s per week.
Question 12.
For thorium A = 232 and Z = 90. At the end of some radioactive disintegrations we obtain an isotope of lead with \(_{82}^{208}\)pb. Then the number of emitted α and ß particles are
(a) α = 4, ß = 6
(b) α = 5, ß = 5
(c) α = 6, ß = 4
(d) α = 6, ß = 6
Answer
Answer: (c) α = 6, ß = 4
Question 13.
If 10 % of a radioactive material decays in 5 days, then the amount of the original material left after 20 days is nearly.
(a) 60%
(c) 75%
(b) 70%
(d) 66%
Answer
Answer: (d) 66%
Question 14.
If the atomic masses for the parent and daughter element in a radioactive decay are Mp and Md and the mass of the electron me then the Q-value for the radioactive ß decay is given by
(a) Q = Mp C²
(b) Q = (Mp – Md – Mc) C²
(c) Q = (Mp – Md)C²
(d) Q = (Mp – md – 2Me)C².
Answer
Answer: (c) Q = (Mp – Md)C²
Question 15.
For the fission of heavy nucleus, neutron is more effective than the proton or a particle because
(a) Neutron is heavier than α-particle.
(b) Neutron is lighter than α-particle.
(c) Neutron moves with a small velocity.
(d) Neutron is uncharged.
Answer
Answer: (d) Neutron is uncharged.
Question 16.
Which of the following is the best nuclear fuel.
(a) Thorium-236
(b) Plutonium – 239
(c) Neptunium-239
(d) Uranium-236.
Answer
Answer: (b) Plutonium – 239
Question 17.
The energy released in the fission of a single \(_{92}^{235}\)U nucleus is 200 MeV. The fission rate of \(_{92}^{235}\)U fuelled reactor operating a power level of 5 Watt is
(a) 1.56 × 1014 per sec.
(b) 1.56 × 1017 per sec.
(c) 1.56 × 1020 per sec.
(d) 1.56 × 1017 per sec
Answer
Answer: (b) 1.56 × 1017 per sec.
Question 18.
Heavy water is used as a moderator in a nuclear reactor. The function of the moderator is to
(a) absorb neutrons and stop chain reaction
(b) To cool the reactor
(c) To slow down the neutrons to thermal energies.
(d) To control the energy released.
Answer
Answer: (c) To slow down the neutrons to thermal energies.
Question 19.
The volume of a nucleus is smaller than that of an atom by a factor of:
(a) 10
(b) 105
(c) 1015
(d) 1010
Answer
Answer: (c) 1015
Question 20.
Consider the fission reaction :
\(_{96}^{236}\)U → x117 + Y117 + 0n1 + 0n1
i.e., two nuclei of same mass numbers 117 are formed plus two neutrons. The binding energy per nuclear of X and Y is 8.5 MeV whereas U236 is 7.6 MeV. The total energy liberated will be about:
(a) 2 MeV
(b) 20 MeV
(c) 2,000 MeV
(d) 200 MeV
Answer
Answer: (d) 200 MeV
Question 21.
Fusion reations place at high temp, because
(a) Kinetic energy is high enough to overcome repulsion between nuclei.
(b) Nuclei break up at high temperature.
(c) Atoms are ionised at high temperature.
(d) Molecules break up at high temperature.
Answer
Answer: (a) Kinetic energy is high enough to overcome repulsion between nuclei.
Question 22.
Which of the following nuclei is most stable
(a) even-even
(b) odd-odd
(c) odd-even
(d) even-odd
Answer
Answer: (a) even-even
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
Atoms having the same ……………….. but different ……………….. are called isotopes.
Answer
Answer: Atomic number, mass number.
Question 2.
The size of the nucleus varies as ……………….. power of mass number.
Answer
Answer: (\(\frac {1}{3}\))
Question 3
……………….. is the process in which light nuclei fuse together to form a heavy nucleus.
Answer
Answer: Nuclear fusion.
Question 4.
In the fission of 235U nucleus on an average ……………….. neutrons are released.
Answer
Answer: 2.5.
Question 5.
In a nuclear reactor, heavy water is used as a ……………….. which slows down the neutrons.
Answer
Answer: Moderator.
Question 6.
The difference between \(_{92}^{235}\)U and \(_{92}^{238}\)U is that \(_{92}^{238}\)U contains three more ……………….. and fission of \(_{92}^{238}\)U is caused ……………….. by neutrons while fission of \(_{92}^{235}\)U is caused by ……………….. neutrons.
Answer
Answer: neutrons, fast, slow.
Question 7.
The order of magnitude of the density of nuclear matter is ………………..
Answer
Answer: 1017 kg m-3.
Question 8.
The average binding energy per nucleon for the nuclei lying in the middle of periodic table is nearly ………………..
Answer
Answer: 8.5 MeV.
Question 9.
Two deuterium nuclei can combine to form a ……………….. if they possess sufficiently
Answer
Answer: Helium nucleus, high kinetic energy.
Question 10.
The average energy released per fission of \(_{92}^{235}\)U is approximately ……………….. MeV.
Answer
Answer: 200.
Question 11.
Proton was discovered by ……………….. and neutron was discovered by ………………..
Answer
Answer: Rutherford, Chadwick.
Question 12.
The ratio of the radii of the nuclei 13Al27 and 52Te125 is approximately ………………..
Answer
Answer: 3 : 5.
Question 13
……………….. was the fissionable material used in the bomb dropped at Nagasaki in 1945.
Answer
Answer: Plutonium.
Question 14.
An element A decays into element C by a two step process:
A → B + \(_{2}^{4}\)He
B → C + 2e–,
Then A and C are ………………..
Answer
Answer: Isotopes.
Question 15.
The sun obtains its radiant energy from ………………..
Answer
Answer: Fusion process.
Question 16.
The B.E. per nucleon is maximum for ………………..
Answer
Answer: \(_{26}^{56}\)Fe.
Question 17.
Slow neutrons are incident on a sample of uranium containing both \(_{92}^{235}\)U and \(_{92}^{238}\)U isotopes, then only ……………….. atoms will undergo fission. .
Answer
Answer: \(_{92}^{235}\)U
Question 18.
The critical mass of the fissionable material is ………………..
Answer
Answer: The minimum mass needed for chain reaction.
Question 19.
The bulk of energy released in nuclear fission process appears as ………………..
Answer
Answer: Kinetic energy of fission fragments.
Question 20.
In a given reascion:
\(_{Z}^{A}\)X → \(_{Z+1}^{A}\)Y → \(_{Z-1}^{A-4}\)K → \(_{Z-1}^{A-4}\)K
the radioactive radiations are emitted in.the sequence of ………………..
Answer
Answer: ß, α, γ.
Question 21.
A positron has the same mass as ………………..
Answer
Answer: electron.
Question 22.
Neutrino is a particle with ………………..
Answer
Answer: Chargeless property and has spin.
Question 23.
Out of α, ß and γ radiations, ……………….. and ……………….. are affected by a magnetic field.
Answer
Answer: Alpha (α) and, beta (ß) radiations.
