CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQs Solution All Chapters
Free PDF of CBSE Physics Multiple Choice Questions for Class 12 with Answers Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism. Physics MCQs for Class 12 Chapter Wise with Answers PDF was Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQs Pdf with Answers to know their preparation level.
Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQ Chapter 2
Magnetism is a phenomenon, which arises from the motion of electric charges and produces magnetic fields.
Below are some of the very important NCERT Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQ Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 with answers. These Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQ have been prepared by expert teachers and subject experts based on the latest syllabus and pattern of CBSE Term 1 examination.
Moving Charges and Magnetism MCQ 1-45
1 . If we double the radius of a coil keeping the current through it unchanged, what happens to the magnetic field on its axis at very very far away points?
- Halved
- Doubled
- Becomes 4 times
- Remains unchanged
Answer/Explanation
3
2. An electron and proton enters a magnetic field with equal velocities. Which one of them experiences more force?
- Proton
- Electron
- Both experience same force
- It cannot be predicted
Answer/Explanation
3
3. Lorentz Force is
- the vector sum of electrostatic and magnetic force acting on a moving charged particle
- the vector sum of gravitational and magnetic force acting on a moving charged particle
- electrostatic force acting on a charged particle
- magnetic force acting on a moving charged particle
Answer/Explanation
1
4. A proton and a deuterium nucleus having certain kinetic energies enter in a uniform magnetic field with the same component of velocity in the direction of the magnetic field. Which of the following is correct?
- Which particle has greater pitch depends on the fact that which particle has greater component of velocity perpendicular to magnetic field
- Deuterium nucleus has greater pitch of helical motion
- Proton has greater pitch of helical motion
- Both particles have same pitch of helical motion
Answer/Explanation
4
5. A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experiences a resultant force
- in the direction perpendicular to both the field and its velocity
- in the direction of the field
- in the direction opposite to that of the field
- none of the above
Answer/Explanation
1
6. Magnetic field can be produced by
- a charge at rest
- a changing electric field
- a moving charge
- both 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
4
7. Two electrons move parallel to each other with equal speed ‘v’. The ratio of magnetic and electric forces between them is
- c/v
- v/c
- c2/v2
- v2/c2
Answer/Explanation
4
8. A charged particle is moving with velocity ‘v’ in a magnetic field of induction B. The force on the particle will be maximum when
- v and B are at angle of 45 degree
- v and B are perpendicular
- v and B are in same direction
- v and B are at opposite directions
Answer/Explanation
2
9. A charge of 1 coulomb is moving in a magnetic field of 0.5 Tesla with velocity of 10 m/s force experienced is
- 0.5 Newton
- 5 Newton
- 10 Newton
- 0 Newton
Answer/Explanation
2
10. A charged particle moving with velocity ‘v’ in a uniform magnetic field B the magnetic force experienced by the particle is
- never 0
- always 0
- 0 if B and v are parallel
- 0 if B and v are perpendicular
Answer/Explanation
3
11. A charged particle of mass M and charge Q travels on a circular path of radius R that is perpendicular to a magnetic field B. At the time taken by the particle to complete one revolution is
- 2πm / qB
- 2πqB / m
- 2πmq / B
- 2πq2B / m
Answer/Explanation
1
12. Magnetic field due to a ring having n turns at a distance ‘x’ on its axis is proportional to (r = radius of ring)
- r / (x2 + r2)
- nr2 / (x2 + r2)3/2
- r2 / (x2 + r2)3/2
- n2r2 / (x2 + r2)3/2
Answer/Explanation
2
13. Ampere circuital law states that
- the line integral of magnetic field along the boundary of open surface is equal to μ0 the total current passing near the surface
- the line integral of magnetic field along the boundary of the open surface is equal to μ0 the total current passing through the surface
- the surface integral of magnetic field over the open surface is equal to μ0 the total current passing through the surface
- the surface integral of magnetic field over the open surface is equal to μ0 the total current passing near the surface
Answer/Explanation
2
14. Magnetic field at any point on the axis of a current element is
- maximum
- minimum
- constant
- zero
Answer/Explanation
4
15. Two thin long parallel wires separated by a distance d carry a current of i A in the same direction. They will
- attract each other with a force of μ0i2 / 2πd
- attract each other with a force of μ0i2 / 2πd2
- repel each other with a force of μ0i2 / 2πd
- repel each other with a force of μ0i2 / 2πd2
Answer/Explanation
1
16. The magnetic induction at any point due to long straight wire carrying a current is
- inversely proportional to the distance from wire
- inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the wire
- does not depend on distance
- proportional to the distance from wire
Answer/Explanation
1
17. A moving coil sensitive galvanometer gives at once much more deflection. To control its speed of deflection.
- the body of galvanometer should be earthed
- high resistance should be connected across the terminals
- a magnet should be placed near the coil
- a small copper wire should be connected across its terminal
Answer/Explanation
3
18. If the current is doubled the deflection is also doubled
- in ohmmeter
- a tangent galvanometer
- a moving coil galvanometer
- both 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
3
19. Which one of the following is experienced by a current carrying loop in uniform magnetic direction?
- Torque only
- Force only
- Neither talk not force
- Both torque and force
Answer/Explanation
1
20. A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 60 ohms shows full scale deflection when a current of 1 A passes through it. It can be converted into an ammeter to read current upto 5A by
- putting in series a resistance of 15 ohm
- putting in parallel resistance of 15 ohm
- putting in series a resistance of 240 ohm
- putting in parallel a resistance of 240 ohm
Answer/Explanation
1
21. An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of current carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true?
- The electron will be accelerated along the axis
- The electron path will be circular about the axis
- The electron will experience a force of 45 degree to the axis and hence execute a helical path
- The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid
Answer/Explanation
4
22. The Galvanometer cannot as such be used as an ammeter to measure the value of current in a given circuit. The following reasons are
(I) the Galvanometer gives full scale deflection for a small current
(II) Galvanometer has a large resistance
(III) Galvanometer can give inaccurate values
- (I) and (III)
- (I) and (II)
- (II) and (III)
- (I), (II) and (III)
Answer/Explanation
2
23. A current of 1 A is passed through a straight wire of length 2 m. The magnetic field at a point in air at a distance of 3m from either end of wire and lying on the axis of wire will be
- Zero
- μ0T / 2π
- μ0T / 4π
- μ0T / 8π
Answer/Explanation
1
24. A current loop of area A, number of turns N is placed in a uniform magnetic induction B. The angle between the plane of slope and B is θ. The torque acting on the loop will be
- NIABtanθ
- NIABsinθ
- NIABcosθ
- NIAB
Answer/Explanation
3
25. The strength of the magnetic field at a point R near a long straight current carrying wire is B. the field at a distance R/2 will be
- 2B
- 4B
- B / 2
- B / 4
Answer/Explanation
1
26. A solenoid of length 0.6m has a radius of 2 cm and is made of 600 turns. If it carries a current of 4 A, then the magnitude of magnetic field inside the solenoid is
- 5.024 x 10-3 T
- 6.024 x 10-3 T
- 7.024 x 10-3 T
- 8.024 x 10-3 T
Answer/Explanation
1
27. Biot-savart law indicates that the moving electron velocity (v) produce a magnetic field B such that
- B ⟂ v
- B || v
- It is along the line joining electron and point of observation
- It obeys inverse cube law
Answer/Explanation
1
28. A milli voltmeter of 25 milli volt range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 A range. The value of required shunt is
- 0.001Ω
- 0.01Ω
- 0.05Ω
- 1Ω
Answer/Explanation
1
29. A galvanometer of resistance 25Ω is shunted by 2.5Ω resistance. The part of the total current that flows through the galvanometer is given as
- IG/I0 = 3/11
- IG/I0 = 1/11
- IG/I0 = 2/11
- IG/I0 = 4/11
Answer/Explanation
2
30. A current carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The torque acting on it does not depend on
- Area of loop
- Number of turns
- Shape of loop
- Angle between normal of coil and magnetic field
Answer/Explanation
3
31. An electron and a proton are moving along the same direction with the same kinetic energy. They enter a uniform magnetic field acting perpendicular to their velocities. The dependence of radius of their path on their masses is
- r ∝ m
- r ∝ √m
- r ∝ 1/m
- 1 / √m
Answer/Explanation
1
32. A charged particle after being accelerated through a potential difference V enters in a uniform magnetic field and moves in a circle of radius r. If V is doubled, the radius of the circle will become
- 2r
- √2r
- 4r
- r / √2r
Answer/Explanation
4
33. A magnetic field doesn’t exerts any force on
- Stream of electrons
- Stream of protons
- Unmagnetised piece of electron
- Stationary charge
Answer/Explanation
4
34. A steady electric current is flowing through a cylinder conductor
- The electric field at the axis of the conductor is zero
- The magnetic field at the axis of the conductor is zero
- The magnetic field in the vicinity of the conductor is zero
- None of these
Answer/Explanation
2
35. What is the shape of a magnet in a moving coil galvanometer to make the radial magnetic field?
- Concave
- Horse shoe magnet
- Convex
- None of the above
Answer/Explanation
1
36. Which of the following materials is used in making the core of a moving coil galvanometer?
- Copper
- Nickel
- Iron
- Both 1 and 2
Answer/Explanation
3
37. The gyromagnetic ratio of an electron in sodium atom is
- Depending upon the atomic number of the atom
- Depending upon the shell number of the atom
- Independent of that orbit it is in
- Having positive value
Answer/Explanation
3
38. A tightly wound 90 turn coil of radius 15 cm has a magnetic field 4 x 10-4T at its centre. The current flowing through it is
- 1.06 A
- 2.44 A
- 3.44 A
- 4.44 A
Answer/Explanation
1
39. A square frame of side carries i produces a field B at its centre. The same current is passed through a circular coil having the same perimeter as the square. The field at the centre of the circular coil is B’. Find the ratio of (B’/B).
- π2 / 3√2
- π2 / 5√2
- π2 / 7√2
- π2 / 8√2
Answer/Explanation
4
40. A charged particle enters into a space and continues to move undeflected then in that space. Which of the following is true for this case?
- A uniform horizontal electric field and a vertical magnetic field may be present
- A vertical electric field alone may be present
- Uniform electric and magnetic fields, both directed vertically downwards, may be present
- A uniform horizontal magnetic field alone may be present
Answer/Explanation
1
41. A right angled triangle has one of the angles as 30°. Two magnetic poles are to be kept at the vertices of the triangle. The ratio of the minimum force of interaction to the maximum force of interaction is
- 1 : 3
- 1 : 2
- 1 : 4
- 1 : √3
Answer/Explanation
1
42. Two parallel wires carrying current I1 and I2 are separated by distance d. Force per unit length of wire is F. Then
- F ∝ d
- F ∝ 1 / d
- F ∝ d2
- F ∝ 1 / d2
Answer/Explanation
2
43. Two free parallel straight wires carrying currents in opposite direction
- Attract each other
- Do not affect each other
- Repel each other
- Get rotated to be perpendicular to the each other
Answer/Explanation
3
44. The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using a
- Moving magnet galvanometer
- Moving coil galvanometer
- Hot wire voltmeter
- Potentiometer
Answer/Explanation
3
45. The restoring couple in the moving coil galvanometer is because of
- magnetic field
- material of the coil
- twist produced in the suspension (.)
- current in the coil
Answer/Explanation
3
Assertion-Reasoning Based MCQ
Code
- If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- If the assertion is true, but the reason is false.
- If the assertion is false, but the reason is true.
1 . Assertion When a test charge moves through the magnetic field, its momentum changes but kinetic energy remains same.
Reason The magnetic force acts as a centripetal force, which is perpendicular to the instantaneous velocity and so does no work.
Answer/Explanation
1 . (1)
Kinetic energy of the charged particle remains same in the circular path while velocity and momentum of the particle changes because of continous change in the direction of motion.
2. Assertion Magnetic field interacts with a moving charge.
Reason A moving charge produces a magnetic field.
Answer/Explanation
2. (1)
A moving charge experience a force in magnetic field. It is because of interaction of two magnetic fields, one which is produced due to the motion of charge and other in which charge is moving.
3. Assertion Free electron always keeps on moving in a conductor even then no magnetic force act on them in magnetic field unless a current is passed through it.
Reason The average velocity of free electron is zero.
Answer/Explanation
3. (1)
In the absence of electric field, the free electron in a conductor are in a state of random motion, like molecules in a gas. Their average velocity is zero, i.e, they do not have any net magnetic force on the free electrons in the magnetic field. On passing the current, the free electrons acquire drift velocity in a definite direction, hence magnetic force acts on them, unless the field has no perpendicular component.
4. Assertion Two beam of electrons traveling in the same direction repel each other.
Reason The electrostatic interaction is less than the magnetic interaction.
Answer/Explanation
4. (3)
Two beams of electron traveling in the same direction repel each other because the electrostatic interaction is more that the magnetic interaction.
5. Assertion If the current in a solenoid is reversed in direction while keeping the same magnitude, the magnetic field energy stored in the solenoid decreases.
Reason Magnetic field energy density is proportional to square of current.
Answer/Explanation
5. (4)
Reversing the direction of the current reverses the direction of magnetic field. However, it has no effect on the magnetic field energy density, which is proportional to the square of the magnitude interaction.
6. Assertion The magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoid is independent of its length and cross-sectional area.
Reason The magnetic field inside the solenoid is uniform.
Answer/Explanation
6. (2)
The earth’s magnetic field is towards north and the velocity of electron is vertically downward. Applying Fleming’s left hand rule, the direction of force is towards west. Therefore, an electron coming from outer space will be deflected toward west.
7. Assertion If two long wire, hanging freely an connected to a battery in series, they come closer to each other.
Reason Force of attraction acts between the two wires carrying current.
Answer/Explanation
7. (4)
When two long parallel wires, are connected to a battery in series. They carry current in opposite directions, hence they repel each other.
8. Assertion In a shunted galvanometer only 10% current passes through the galvanometer. The resistance of the galvanometer is G. Then resistance of the shunt in G/9.
Reason If S is the resistance of the shunt, then voltage across S and G is same.
Answer/Explanation
8. (2)
IgG = (I-Ig)S
S = (Ig / I – Ig) G
Ig = I / 10
S = G / 9
9. Assertion To convert a galvanometer into an ammeter a small resistance is connected in parallel with it.
Reason The small resistance increases the combined resistance of the combination.
Answer/Explanation
9. (3)
An ammeter should have a low resistance which we get when we connect low resistance in parallel with galvanometer.
10. Assertion An ammeter is always connected in series whereas a voltmeter is connected in parallel.
Reason An ammeter is a low resistance galvanometer while a voltmeter is high resistance galvanometer.
Answer/Explanation
10. (1)
An ammeter is a low resistance device and is connected in series so as the whole circuit current flows through it for an accurate measurement. A voltmeter is a device having a high resistance. So, if we connect it in series, it would hinder the current flow in the circuit hence open circuit results.
Case Study Based MCQ
1 . A charged particle enters into a uniform magnetic field and follows a circular path as shown. This happens when the particle enters perpendicular to the magnetic field. It gets deflected by magnetic Lorentz force arrows indicate the direction of motion of the charged particle.
If V the velocity of the particle of charge q and B is the magnetic field, then the force acting on the particle is given by: F = q ( v X B )
In the particle velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field, then the magnetic of the force is F = qvB. This force provides the necessary centripetal force for the particle and the radius of the circular path is given by
r = mv / qB
The direction of deflection also depends on the nature of the charge. If the particle enters the fields at an angle other than 90°, then, the path of the particle will be helical.
(i) Which of the following particles will not get affected if sent into a magnetic field normal to it?
(a) Alpha
(b) Positron
(c) Neutron
(d) Electron
Answer/Explanation
1 . (i) (c) Neutron particles are not affected by magnetic field.
(ii) When a proton and an electron enter a magnetic field normal to it, which of the following statements is correct (Assume that their speeds are equal)?
(a) They will get deflected in opposite directions
(b) Radius of circular path of electron will be less
(c) Radius of circular path of proton will be less
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer/Explanation
(ii) (d) Opposite deflection because of opposite charge. Lighter particles get deflected more.
(iii) A deutron enters a magnetic field parallel to it. Its path inside the field will be
(a) a straight line
(b) circle
(c) helix
(d) parabola
Answer/Explanation
(iii) (a) Straight line
(iv) If a proton, a deuteron and an alpha particle are projected into a magnetic field perpendicular to it with the same speed, which of them will have the path of highest radius?
(a) Proton
(b) Deuteron
(c) Alpha particle
(d) Both (b) and (C)
Answer/Explanation
(iv) (d) r is proportional to m/q
(v) An electron enters a magnetic field making an angle of 45° with it. The path of the electron will be
(a) Straight line
(b) Circle
(c) Helix
(d) Parabola
Answer/Explanation
(v) (c) Helix
2. Biot Savart law was given by Biot and Savart after doing many experiments. This law is related with the magnetic field induced at any point due to a small current carrying element. According to the law, the magnetic field induced at a point near the current carrying element is directly proportional to the current flowing in the conductor, length of the element, sinፀ and inversely proportional to the square of the distance of point from the element.
(i) Biot Savart law was given by
(a) Oersted
(b) Ampere
(c) Biot and Savart
(d) Maxwell
Answer/Explanation
2. (i) (c) Biot and Savart
(ii) Biot Savart law is related with the ______ induced at a point near current carrying element.
(a) Magnetic field
(b) Gravitational field
(c) Electric field
(d) None of these
Answer/Explanation
(ii) (a) Magnetic field
(iii) Induced magnetic field is directly proportional to
(a) i
(b) dl
(c) sinፀ
(d) All of these
Answer/Explanation
(iii) (d) All of these
(iv) The magnetic field induced at a point is inversely proportional to
(a) r2
(b) r3
(c) 1 / r
(d) 1 / r2
Answer/Explanation
(iv) (a) r2
(v) As the distance between the point and current carrying element decreases, dB
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains same
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer/Explanation
(v) (a) Increase, dB is inversely proportional to r2
3. In certain polar regions of splendid display of colours is seen in the sky. The appearance of dancing green pink light is fascinating and equally puzzling.
Consider a charged particle for mass M and charge Q enters a region of magnetic field B with an initial velocity V. Let this velocity have a component Vp parallel to the magnetic field and a component Vn normal to it. There is no force on a charged particle in the direction of field. Hence the particle continue to travel with the velocity Vp parallel to the field.
The normal component Vn of the particle results in a Lorentz Force which is perpendicular to both and the particle does has a tendency to perform a circular motion in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic field. When this is coupled with the velocity parallel to the field, the resulting trajectory will be a helix along the magnetic field line. Even if the field line bends, the helically moving particle is trapped and guided to move around the field line.
Since the Lorentz Force is normal to the velocity of each point, the field does not work on the particle and the magnitude of the velocity remains the same. During a solar flare, a large number of electrons and protons are rejected from the sun. Some of the get trapped in the Earth’s magnetic field and move in a helical path along the field line.
The field lines come closer to each other near the magnetic poles. Hence, the density of charges increases near the poles. These particles collide with atoms and molecules of the atmosphere. Excited oxygen atoms emit green light an excited nitrogen atoms emit pink light. This phenomenon is called Aurora Borealis in physical science.
(i) Which of the following defines the exact meaning of magnetic field?
(a) Magnetic field is a scalar field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents and magnetic materials.
(b) Magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials.
(c) Both scalar and vector fields that describe the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials.
(d) Magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on static electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials.
Answer/Explanation
3. (i) (b) The exact meaning of magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials.
(ii) Which of the following defines the exact meaning of Lorentz Force the Lorentz force?
(a) The Lorentz force is the combination of electric and magnetic field force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields
(b) the Lorentz Force is a combination of electric and magnetic force on a point charge due to gravitational field
(c) the Lorentz Force is a combination of gravitational force and magnetic force on a point charge due to electromagnetic field
(d) the Lorentz Force is the combination of electric and centripetal force on the point charge due to electromagnetic fields
Answer/Explanation
(ii) (a) The Lorentz force is the combination of electron and magnetic force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. A particle of charge q moving with a velocity v in an electric field E and a magnetic field B experiences a force of F = qE + qvB.
(iii) Which of the following defines the exact meaning of circular motion?
(a) Circular motion is apparent outward force on mass with when it is rotated
(b) Circular motion vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges electric currents, and magnetic materials
(c) Circular motion in an object is the rate of change of its position with respect to a frame of reference, and is a function of time
(d) Circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular path
Answer/Explanation
(iii) (d) Circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumstances of a circle or rotation along a circular path. It can be uniform, with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed, or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation. The rotation around a fixed axis of a 3-D body involves circular motion of its parts.
(iv) What does Aurora Borealis mean?
(a) The Aurora Borealis otherwise known as northern lights, is a physics phenomenon that can be magical to observe, striking onlookers to wonder about the cause of the whimsical light that dance overhead.
(b) The Aurora Borealis otherwise known as southern lights, is a physics phenomenon that can be magical to observe, striking onlookers to wander about the cause of the whimsical life that downs overhead
(c) The Aurora Borealis otherwise known as the Eastern lights, is a physics phenomenon that can be magical to observe, striking onlookers to wander about the cause of the whimsical lies that dance overhead
(d) The Aurora Borealis is a apparent outward force on the mass when it is rotated
Answer/Explanation
(iv) (a) The Aurora Borealis otherwise known as northern lights, is a physics phenomenon that can be magical to observe, striking onlookers to wonder about the cause of the whimsical light that dance overhead. This extraordinary display is caused by charged particles being expelled into space from the sun.
(v) Consider a tightly wound 100 turn coil of radius 10cm carrying a current of 1A. What is the magnitude of magnetic field at the centre of the coil?
(a) 2.28 x 10-4 T
(b) 6.28 x 10-4 T
(c) 3.28 x 10-4 T
(d) 5.28 x 10-4 T
Answer/Explanation
(v) (b) B = μ0NI / 2R = (4π x 10-7 x 102 x 1) / (2 x 10-1) = 2π x 10-4 = 6.28 x 10-4 T
Moving Charges and Magnetism Class 12 Physics MCQs
1. Two charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field B = B0\(\hat{k}\). [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) They have equal z-components of momenta.
(b) They must have equal charges.
(c) They necessarily represent a particle- antiparticle pair.
(d) The charge to mass ratio satisfy:
\(\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{1}+\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{2}=0\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) Charged particles traverse identical helical paths in a completely opposite sense in a uniform magnetic field B.
Therefore
\(\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{1}+\left(\frac{e}{m}\right)_{2}=0\)
2. Biot-Savart law indicates that the moving electrons (velocity v) produce a magnetic field B such that [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) B ⊥ v.
(b) B || v.
(c) it obeys inverse cube law.
(d) it is along the line joining the electron and point of observation.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Magnetic field is given by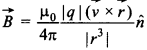
Where n is the direction of \(\vec{B}\) which is in the direction of cross product of \(\vec{v}\) and \(\vec{r}\). Or we can say that \(\vec{B}\) ⊥ to both \(\vec{v}\) and \(\vec{r}\).
3. A current carrying circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Half of the loop with x > 0 is now bent so that it now lies in the y – z plane. [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) The magnitude of magnetic moment now diminishes.
(b) The magnetic moment does not change.
(c) The magnitude of B at (0.0.z), z» R increases.
(d) The magnitude of B at (0, 0, z), z » R is unchanged.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Direction of magnetic moment (M= I A) of circular loop is perpendicular to the loop as per right hand thumb rule.
The magnitudes of magnetic moment of each semicircular loop of radius R lie in the x-y plane and y-z plane is M1 – M2= \(I \frac{\pi R^{2}}{2}\) and the direction of magnetic moments are along z-direction and ^-direction respectively. Their resultant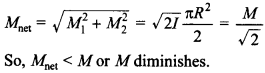
4. An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) The electron will be accelerated along the axis.
(b) The electron path will be circular about the axis.
(c) The electron will experience a force at 45° to the axis and hence execute a helical path.
(d) The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) F = -evB sin 180° = 0 (i.e 0= 0°or 180° in both cases F = 0). The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity or will go undeflected along the axis of the solenoid.
5. In a cyclotron, a charged particle [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) undergoes acceleration all the time.
(b) speeds up between the dees because of the magnetic field.
(c) speeds up in a dee.
(d) slows down within a dee and speeds up between dees.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) It is based on the fact that the electric field accelerates a charged particle and the perpendicular magnetic field keeps it revolving in circular orbits of constant frequency.
6. A circular current loop of magnetic moment Mis in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) MB
(b) √3\(\frac{MB}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{MB}{2}\)
(d) zero
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) The rotation of the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane makes no change in the angle made by axis of the loop with the direction of magnetic field, therefore, the work done to rotate the loop is zero.
7. A rectangular loop carrying a current i is situated near a long straight wire such that the wire is parallel to the one of the sides of the loop and is in the plane of the loop. If a steady current I is established in wire as shown in figure, the loop will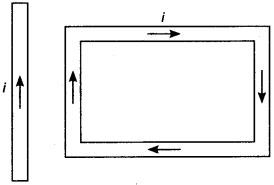
(a) rotate about an axis parallel to the wire.
(b) move away from the wire or towards right.
(c) move towards the wire.
(d) remain stationary.
Answer
Answer: c
8. A circular coil of radius 4 cm and of 20 turns carries a current of 3 amperes. It is placed in a magnetic field of intensity of 0.5 weber/m². The magnetic dipole moment of the coil is
(a) 0.15 ampere-m²
(b) 0.3 ampere-m²
(c) 0.45 ampere-m²
(d) 0.6 ampere-m²
Answer
Answer: b
9. A cubical region of space is filled with some uniform electric and magnetic fields. An electron enters the cube across one of its faces with velocity v and a positron enters via opposite face with velocity -v. At this instant,
(a) the electric forces on both the particles cause identical accelerations.
(b) the magnetic forces on both the particles cause equal accelerations.
(c) Only electron gains or looses energy.
(d) the motion of the centre of mass (CM) is determined by E alone.
Answer
Answer: b
10. Consider a wire carrying a steady current, I placed in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to its length. Consider the charges inside the wire. It is known that magnetic forces do not work. This implies that,
(a) motion of charges inside the conductor is unaffected by B, since they do not absorb energy.
(b) Some charges inside the wire move to the surface as a result of B.
(c) if the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the force.
(d) If the wire moves under the influence of B, no work is done by the electric force on the ions, assumed fixed within the wire.
Answer
Answer: b
11. Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C,
(a) \(\oint_{C}\)B.dl = ± 2µ0I.
(b) the value of \(\oint_{C}\)B.dl is independent of sense of C. c
(c) there may be a point on C where, B and dl are parallel.
(d) B vanishes everywhere on C.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) Ampere’s law gives another method to calculate the magnetic field due to a given current distribution.
Applying the Ampere’s circuital law, we have
\(\oint_{C}\)B.dl = i0(I – I) = 0 (because current is in opposite sense).
Also, there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular and hence \(\oint_{C}\)B.dl = 0
12. The strength of magnetic field at the centre of circular coil is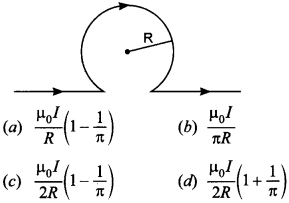
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) B = Field to circular portion
– Field due to straight portion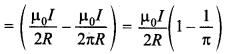
13. If a charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to it
(a) both momentum and energy of particle change.
(b) momentum as well as energy are constant.
(c) energy is constant but momentum changes.
(d) momentum is constant but energy changes.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Since the direction of velocity of a particle varies so momentum changes but direction of magnetic force is always perpendicular to direction of charged particle. So no work is done, i.e. energy remains the same.
14. A current carrying closed loop of an irregular shape lying in more than one plane when placed in uniform magnetic field, the force acting on it
(a) will be more in the plane where its larger position is covered.
(b) is zero.
(c) is infinite.
(d) may or may not be zero.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) A current carrying closed loop of any shape when placed in a uniform magnetic field does not experience any force.
15. The maximum current that can be measured by a galvanometer of resistance 40 Ω is 10 mA. It is converted into voltmeter that can read upto 50 V. The resistance to be connected in the series with the galvanometer is
(a) 2010 Ω
(b) 4050 Ω
(c) 5040 Ω
(d) 4960 Ω
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:![]()
16. A current loop placed in a non-uniform magnetic field experiences
(a) a force of repulsion.
(b) a force of attraction.
(c) a torque but not force.
(d) a force and a torque.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) In non-uniform magnetic field, current loop experiences an unequal opposite force which forms torque.
17. What is the net force on the rectangular coil?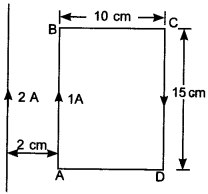
(a) 25 × 10-7 N towards wire.
(b) 25 × 10-7 N away from wire.
(c) 35 × 10-7 N towards wire.
(d) 35 × 10-7 N away from wire.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: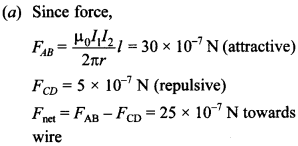
18. If the beams of electrons and protons move parallel to each other in the same direction, then they
(a) attract each other.
(b) repel each other.
(c) no relation.
(d) neither attract nor repel.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) As current carried by electrons and protons are in opposite direction.
19. A conducting circular loop of radius r carries a constant current i. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field B, such that B is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic force acting on the loop is
(a) irB.
(b) 2πriB
(c) zero
(d) πriB
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Net force on a current carrying closed loop is always zero, if it is placed in an uniform magnetic field.
20. The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to Bohr model, is
(a) independent of which orbit it is in.
(b) neutral
(c) positive
(d) increases with the quantum number n.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) The gyro-magnetic ratio is given by
\(\mu_{l}=\frac{-e}{2 m} L, \mathrm{L}\) – Angular momentum of electron
21. An electron is projected along the axis of a circular conductor carrying the same current. Electron will experience
(а) a force along the axis.
(б) a force perpendicular to the axis.
(c) a force at an angle of 4° with axis.
(d) no force experienced.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) Since electron is moving parallel to direction of magnetic field of the conductor
Force (F) = qvB sin 0 = 0
22. Three long, straight parallel wires, carrying current are arranged as shown in the figure. The force experienced by a 25 cm length of wire C is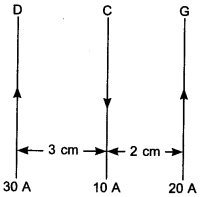
(a) 10-3 N
(b) 2.5 × 10-3 N
(c) zero
(d) 1.5 × 3 N
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Force of repulsion by wire D and G on wire C is equal and opposite.
23. In a circular coil of radius r, the magnetic field at the centre is proportional to
(a) r²
(b) r
(c) \(\frac{1}{r}\)
(d) \(\frac{1}{r²}\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:![]()
24. A positive charge enters in a magnetic field and travels parallel to but opposite the field. If experiences
(a) an upward force.
(b) a downward force.
(c) an accelerated force.
(d) no force.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) Force of repulsion by wire D and G on wire C is equal and opposite.
25. When a magnetic compass needle is carried nearby to a straight wire carrying current, then
(I) the straight wire cause a noticeable deflection in the compass needle.
(II) the alignment of the needle is tangential to an imaginary circle with straight wire as its centre and has a plane perpendicular to the wire
(a) (I) is correct
(b) (II) is correct
(c) both (I) and (II) are correct
(d) neither (I) nor (II) is correct
Answer
Answer: c
26. A strong magnetic field is applied on a stationary electron. Then the electron
(a) moves in the direction of the field.
(b) remained stationary.
(c) moves perpendicular to the direction of the field.
(d) moves opposite to the direction of the field.
Answer
Answer: b
27. In an inertial frame of reference, the magnetic force on a moving charged particle is \(\vec{F}\) Its value in another inertial frame of reference will be
(a) remained same
(b) changed due to change in the amount of charge
(c) changed due to change in velocity of charged particle
(d) changed due to change in field direction
Answer
Answer: c
28. Which one of the following is correct statement about magnetic forces?
(a) Magnetic forces always obey Newton’s third law.
(b) Magnetic forces do not obey Newton’s third law.
(c) For very high current, magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law.
(d) Inside low magnetic field, magnetic forces obey Newton’s third law.
Answer
Answer: b
29. A charged particle is moving on circular path with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B, if the velocity of the charged particle is doubled and strength of magnetic field is halved, then radius becomes
(a) 8 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 2 times
(d) 16 times
Answer
Answer: b
30. Two α-particles have the ratio of their velocities as 3 : 2 on entering the field. If they move in different circular paths, then the ratio of the radii of their paths is
(a) 2 : 3
(b) 3 : 2
(c) 9 : 4
(d) 4 : 9
Answer
Answer: b
31. A charged particle is moving in a cyclotron, what effect on the radius of path of this charged particle will occur when the frequency of the ratio frequency field is doubled?
(a) It will also be doubled.
(b) It will be halved.
(c) It will be increased by four times.
(d) It will remain unchanged.
Answer
Answer: d
32. Which of the following is not correct about cyclotron?
(a) It is a machine to accelerate charged particles or ions to high energies.
(b) Cyclotron uses both electric and magnetic fields in combination to increase the energy of charged particles.
(c) The operation of the cyclotron is based on the fact that the time for one revolution of an ion is independent of its speed or radius of its orbit.
(d) The charged particles and ions in cyclotron can move on any arbitrary path.
Answer
Answer: d
33. If an electron is moving with velocity \(\vec{ν}\) produces a magnetic field \(\vec{B}\), then
(a) the direction of field \(\vec{B}\) will be same as the direction of velocity \(\vec{ν}\) .
(b) the direction of field \(\vec{B}\) will be opposite to the direction of velocity \(\vec{ν}\) .
(c) the direction of field \(\vec{B}\) will be perpendicular to the direction of velocity \(\vec{ν}\) .
(d) the direction of field \(\vec{B}\) does not depend upon the direction of velocity \(\vec{ν}\) .
Answer
Answer: c
34. Current flows through uniform, square frames as shown in the figure. In which case is the magnetic field at the centre of the frame not zero?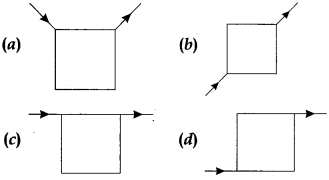
Answer
Answer: c
35. Ampere’s circuital law is given by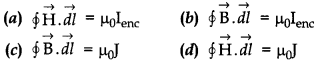
Answer
Answer: b
36. Two identical current carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, then which statement is correct?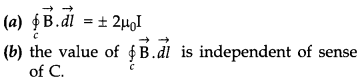
(c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are
parallel.
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: b
37. The correct plot of the magnitude of magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) vs distance r from centre of the wire is, if the radius of wire is R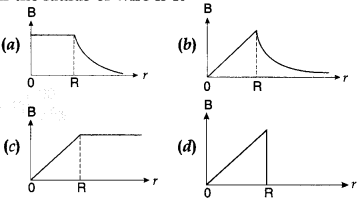
Answer
Answer: b
38. The nature of parallel and anti-parallel currents are
(a) parallel currents repel and antiparallel cur¬rents attract.
(b) parallel currents attract and antiparallel cur-rents repel.
(c) both currents attract. ’
(d) both currents repel.
Answer
Answer: b
39. The magnetic moment of a current I carrying circular coil of radius r and number of turns N varies as
(a) \(\frac{1}{r²}\)
(b) \(\frac{1}{r}\)
(c) r
(d) r²
Answer
Answer: d
40. A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0. 65 J T-1, then the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance 8 cm from the centre of magnet on the axis is
(a) 2.5 × 10-4 T, along NS direction
(b) 2.5 × 10-4 T along SN direction
(c) 4.5 × 10-4 T, along NS direction
(d) 4.5 × 10-4 T, along SN direction
Answer
Answer: b
41. A current carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The torqe acting on it does not depend upon
(a) area of loop
(b) value of current
(c) magnetic field
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: d
42. In a moving coil galvanometer the deflection (Φ) on the scale by a pointer attached to the spring is
Answer
Answer: c
43. A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by
(a) introducing a shunt resistance of large value in series.
(b) introducing a shunt resistance of small value in parallel.
(c) introducing a resistance of small value in series.
(d) introducing a resistance of large value in parallel.
Answer
Answer: b
44. The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by
(a) introducing a resistance of large value in series.
(b) introducing a resistance of small value in parallel.
(c) introducing a resistance of large value in parallel.
(d) introducing a resistance of small value in series.
Answer
Answer: a
45. Deflection produced in a galvanometer when a unit current flows through it is known as _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: current sensitivity.
46. A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into voltmeter by connecting a large resistance R in _________ with it.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: series
47. Maximum torque acts on a current carrying coil when it is suspended in magnetic field such that its plane is _________ to magnetic field.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: parallel
48. An ammeter is _________ resistance galvanometer.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: low
49. The magnetic field due to a straight current carrying conductor of infinite length at a perpendicular distance a is equal to _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: \(B=\frac{\mu_{0} I}{2 \pi a}\)
50. Relation between S.I. unit and C.G.S unit magnetic field is _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 1 T=104 G
51. According to ampere circuital law, the line integral of the magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) around any closed path enclosing current 7, is equal to _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: µ0I
52. Force on a charge q moving in a magnetic field B with velocity v at angle 0 is equal to _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: F = Bqv sin θ
53. Force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field is _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: F = BIl sin θ
54. The magnetic field of a straight solenoid carrying current l and having n turns per unit length is _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: B = µ0nI
55. Why does a moving charge experience a force when placed in a magnetic field? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
A moving charge produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with another magnetic field of a magnet and hence, it experiences force.
56. Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \(\vec{F}\) due to a charge moving with velocity \(\vec{v}\) in a magnetic field \(\vec{B}\). What is the direction of the magnetic force? [Delhi 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Lorentz magnetic force (\(\vec{F}_{m}\)) = q(\(\vec{v}\) × \(\vec{B}\)). The direction of magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane containing velocity and magnetic field vectors.
57. Define one tesla using the expression for the magnetic force acting on a particle of charge q moving with velocity \(\vec{v}\) in a magnetic field \(\vec{B}\). [Foreign 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: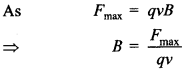
If Fmax = 1N, q = +1C and v = 1 m/s and
θ = 90°, then B = IT
Hence, one tesla is the magnetic field in which a normally entering + 1C charge, moving at 1 ms-1 experiences a maximum force of 1 N.
58. A beam of a-particles projected along +x-axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along the +y-axis. What is the direction of the magnetic field? [AI2010]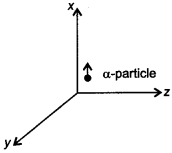
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: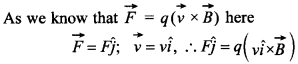
Therefore, the direction of magnetic field is towards the negative direction of z-axis.
59. A long straight wire carries a steady current l along the positive y-axis in a coordinate system. A particle of charge +Q is moving with a velocity \(\vec{v}\) along the x-axis. In which direction will the particle experience a force? [Foreign 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
By the right-hand thumb rule, the direction of magnetic field due to current / acts normally into the plane of paper. So, \(\vec{B}=-B \hat{k}\), i.e. along negative z-axis. The magnetic Lorentz force is given by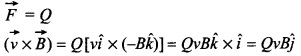
Thus, the force on charge +Q is along +y axis.
60. In a certain region of space, electric field \(\vec{E}\) and magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) are perpendicular to each other. An electron enters in the region perpendicular to the directions of both \(\vec{B}\) and \(\vec{E}\) and moves undeflected. Find the velocity of the electron. [Foreign 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
∵ qvB = qE ⇒ v = \(\frac{E}{B}\)
61. An electron and a proton moving with the same speed enter the same magnetic field region at right angles to the direction of the field. For which of the two particles will the radius of circular path be smaller? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
As r = \(\frac{mv}{qB}\) for same v and B r ∝ \(\frac{m}{q}\).
Since \(\frac{m}{q}\) is smaller for an electron, the radius of the circular path followed by the electron will be smaller.
62. A proton and an electron travelling along parallel paths enter a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their paths. Which of them will move in a circular path with higher frequency? [CBSE 2018]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Electron
Reason: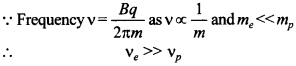
Thus electron will move in circular path with higher frequency.
63. Write the expression for the magnetic moment of a circular coil of area A carrying a current I, in a vector form. [Foreign 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
M\(\vec{M}=\overrightarrow{I A}\), as vector \(\vec{A}\) is perpendicular to the surface, the magnetic moment M will also be perpendicular to the plane of circular coil.
64. Magnetic field lines can be entirely confined within the core of a toroid, but not within a straight solenoid. Why?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
At the edges of a solenoid, the field lines get diverged due to other fields or non-availability of dipole loops, while in a toroid, the dipoles (in loops) orient continuosly.
65. Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current. [A1 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
One ampere is that amount of current which when flows through two thin infinitely long straight conductors kept parallel to each other at 1 m distance produces a force per unit length of magnitude 2 × 107 N/m.
66. Which has greater resistance
(a) milliammeter or ammeter
(b) milliammeter or voltmeter?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) Milliammeter
(b) Voltmeter
67. A voltmeter, an ammeter and a resistance are connected in series with a battery. The voltmeter gives same deflection but the deflection of ammeter is almost zero. Explain why?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
When a voltmeter is connected in series, the current in the circuit decreases because the resistance of voltmeter is high. Therefore, it will show some deflection. But in an ammeter, the majority of this current will pass through the shunt and a very small fraction will pass through the galvanometer.
68. State the law used to determine the direction of magnetic field at the centre of current carrying circular coil.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The right-hand thumb rule gives the direction of magnetic field which is stated as under:
Curl the palm of your right hand around a circular wire with the fingers, pointing in the direction of the current and the right hand thumb gives the direction of magnetic field.
69. A narrow beam of protons and deuterons, each having the same momentum, enters a region of uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular to their direction of momentum. What would be the ratio of the radii of the circular paths described by them? [Similar Delhi 2019, Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: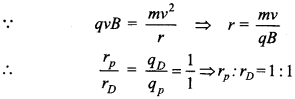
70. Write two properties of a material used as a suspension wire in a moving coil galvanometer.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Low value of k (torsional constant), (ii) High conductivity.
71. A charged particle enters into a uniform magnetic field and experiences an upward force as indicated in the figure. What is the charge sign on the particle?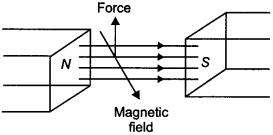
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: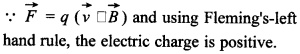
72. How does the magnetic moment of an electron in a circular orbit of radius r and moving with a speed v change, when the frequency of revolution is doubled?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
As M ∝ v, the magnetic moment also gets doubled, when the frequency of revolution is doubled.
73. A current carrying loop is free to turn in a uniform magnetic field B. Under what conditions, will the torque acting on it be
(i) minimum and
(ii) maximum?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
T = MB sin θ
(i) Torque is minimum when the area vector of the loop and the magnetic field vector are in the same direction, i.e. A\\B.
(ii) Torque is maximum when ALB.
74. Write two factors by which voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer can be increased.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
As we know that \(V_{s}=\left(\frac{N A B}{k}\right) \frac{1}{R}\)
Thus, (i) Resistance should be less.
(ii) Torsional constant should be less.
75. An ammeter and a milliammeter are converted from the same galvanometer. Out of the two, which current measuring instrument has higher resistance? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The higher is the range, the lower will be the value of shunt, so a milliammeter will be having higher resistance.
76. What is the advantage of using radial magnetic field in a moving coil galvanometer? [HOTS] [Delhi 2019]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Maximum torque is experienced.
(ii) Current is directly proportional to the deflection.
(iii) The plane of the coil is parallel to the direction of magnetic field.
77. Why is it necessary for voltmeter to have a high resistance?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Since voltmeter is to be connected across two ends of a conductor in parallel, if it has high resistance, then only a very small part of current will pass through, and it will not affect the actual potential difference to be measured.
78. What is figure of merit of a galvanometer? [DoE]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Figure of merit is defined as the amount of current which produces unit deflection in the galvanometer.
79. Define gyromagnetic ratio.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It is the ratio of the magnetic dipole moment to the angular momentum of the electron revolving round the nucleus.
80. Can we decrease the range of an ammeter?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:![]()
Explaination: will become negative, which is not possible.
