CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQs Solution All Chapters
Free PDF of CBSE Physics Multiple Choice Questions for Class 12 with Answers Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter. Physics MCQs for Class 12 Chapter Wise with Answers PDF was Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Physics Magnetism and Matter MCQs Pdf with Answers to know their preparation level.
Magnetism and Matter MCQ Chapter 5
Below are some of the very important NCERT Magnetism and Matter MCQ Class 12 Physics Chapter 5 with answers. These Magnetism and Matter MCQ have been prepared by expert teachers and subject experts based on the latest syllabus and pattern of CBSE Term 1 examination.
We have given these Magnetism and Matter MCQ Class 12 Physics questions with answers to help students understand the concept.
Magnetism and Matter MCQ 1-45
1 . If a hole is made at the centre of a bar magnet, then its magnetic moment
- does not change
- decreases
- increases
- vanishes
Answer/Explanation
1
2. On cutting a solenoid in half, the field lines remain _______, emerging from one face of the solenoid and entering into the other face.
- alternate
- discontinuous
- continuous
- irregular
Answer/Explanation
3
3. North pole of a magnet is brought near a stationary negatively charged conductor. Will the pole experience any force?
- Yes
- No
- Depends on the magnitude of pole strength
- Can’t say
Answer/Explanation
2
4. The magnetic moment of a bar magnet is thus _________ to the magnetic moment of an equivalent solenoid that produces the same magnetic field.
- same
- different
- unequal
- equal
Answer/Explanation
4
5. The incorrect statement regarding the lines of force of the magnetic field B is
- magnetic lines of force for a closed curve
- due to magnet the magnetic force of the magnetic lines of force never cut each other
- magnetic intensity is a measure of lines of force passing through a unit area held normal to it
- inside a magnet its magnetic lines of force move from north pole of the magnet towards the south pole
Answer/Explanation
4
6. The magnetic dipole moment of a solenoid having N turns is given as
- NIA
- NIA2
- NI2A
- NI2A2
Answer/Explanation
1
7. In the case of bar magnet, lines of magnetic induction
- run continuously through the bar and outside
- emerge in circular path from the middle of the bar
- are produced only at the north pole like rays of light from a bulb
- start from the north pole and end at the south pole
Answer/Explanation
1
8. The magnetic induction B and the force F on a pole m are related by
- F = mB
- F = m / B
- B = mF
- F = B / m
Answer/Explanation
1
9. A north pole of strength 50 Am and south pole of strength 100 Am are separated by a distance of 10 cm in air. Find the force between them.
- 20 x 10-6 N
- 25 x 10-3 N
- 30 x 10-18 N
- 50 x 10-3 N
Answer/Explanation
4
10. The strength of the Earth’s magnetic field is
- zero everywhere
- constant everywhere
- vary from place to place on the earth surface
- having very high value
Answer/Explanation
3
11. Horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field remains is zero at
- magnetic poles
- equator
- an altitude of 60°
- a latitude of 60°
Answer/Explanation
1
12. Which of the following is responsible for the Earth’s magnetic field?
- rotational motion of earth
- translational motion of earth
- convective currents in Earth’s core
- diversify currents in Earth’s core
Answer/Explanation
3
13. The vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field is zero at
- magnetic equator
- magnetic poles
- geographical poles
- north pole
Answer/Explanation
1
14. At neutral point, the horizontal component of the magnetic field due to magnet is
- in the opposite direction of the earth’s horizontal magnetic field
- equal to earth horizontal magnetic field
- in the same direction of the earth horizontal magnetic field
- both 1 and 2
Answer/Explanation
4
15. A dip circle is placed in a plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The opponent angle of dip is
- 0°
- 45°
- 60°
- 90°
Answer/Explanation
4
16. At a certain place, the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is √3 times the vertical component. The angle of dip at that place is
- 30°
- 45°
- 60°
- 90°
Answer/Explanation
1
17. The horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field is 3.6 x 10-5 T where the dip angle is 60°. The magnitude of Earth’s magnetic field is
- 2.1 x 10-4 T
- 7.2 x 10-5 T
- 2.8 x 10-4 T
- 3.6 x 10-5 T
Answer/Explanation
2
18. The Earth’s magnetic field at some place on magnetic equator of earth is 0.5 x 10-4 T. Consider the radius of earth at that place as 6400 km. Then, the magnetic dipole moment of the Earth in Am2 is
- 1.05 x 1023
- 1.15 x 1023
- 1.31 x 1023
- 1.62 x 1023
Answer/Explanation
3
19. At a certain place, horizontal component is √3 times the vertical component. The angle of dip at this place is
- π/8
- π/6
- π/3
- 0
Answer/Explanation
2
20. At a certain place, the angle of dip is 30° and the horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field is 0.5 oersted. The earth’s total magnetic field (in oersted) is
- ½
- √3
- 1/√3
- 1
Answer/Explanation
3
21. A toroid of N turns, mean radius R and cross sectional radius a carries current I. It is placed on a horizontal table taken as x-y plane. Its magnetic moment m
- is non-zero and points in the Z direction by symmetry
- points along the axis of the toroid
- is zero, otherwise there would be a field falling as 1/r3 at large distances outside the toroid
- is pointing radially outwards
Answer/Explanation
3
22. The magnetic field of Earth can be modelled by that of a point dipole placed at the centre of the earth. The dipole axis makes an angle of 11.3° with the axis of earth. At Mumbai, declination is nearly zero. Then
- the declination varies between 11.3° West to 11.3° East
- the least declination is 0°
- the plane defined by dipole axis and the earth axis passes through Greenwich
- declination averaged over Earth must be always negative
Answer/Explanation
1
23. In a permanent magnet at room temperature
- magnetic moment of each molecule is zero
- the individual molecule have non zero magnetic moment which are all perfectly aligned
- domains are partially aligned
- domains are all perfectly aligned
Answer/Explanation
4
24. The magnetic dipole moment of a current loop is independent of
- area of the loop
- current of the loop
- magnetic field in which it is lying
- number of turns
Answer/Explanation
3
25. A circular loop carrying current of radius 100 mm is a magnetic induction of 3.6 x 10-5 T at its centre. Calculate the dipole moment
- 15mAm2
- 45mAm2
- 60mAm2
- 180 mAm2
Answer/Explanation
4
26. The magnetic moment of a circular coil carrying current is
- directly proportional to the square of the length of the wire in the coil
- directly proportional to the length of the wire in the coil
- inversely proportional to the square of the length of the wire in the coil
- inversely proportional to the length of the wire in the coil
Answer/Explanation
1
27. A circular current loop of magnetic moment M is in an arbitrary orientation in an external magnetic field B. The work done to rotate the loop by 30° about an axis perpendicular to its plane is
- MBq
- √3MB / 2
- MB / 2
- 0
Answer/Explanation
4
28. Is a current carrying circular loop of radius R is placed in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Half of the loop with x>0 if now bent so that it now lies in the y-z plane
- the magnitude of magnetic moment now diminishes
- the magnetic moment does not change
- the magnitude of B at (0,0,z), z>>R increases
- the magnitude of B at (0,0,z), z>>R is unchanged
Answer/Explanation
1
29. The lines of force due to horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field are
- straight and parallel
- concentric circles
- parabolic
- elliptical
Answer/Explanation
1
30. In a plane perpendicular to magnetic meridian the dip needle will be
- vertical
- horizontal
- inclined equal to the angle of dip at that place
- pointing in and any direction
Answer/Explanation
1
31. Earth’s magnetic field inside a closed iron box, as compared to outside is
- more
- less
- same
- zero
Answer/Explanation
2
32. In the current (I) is flowing through a circular coil, its radius (R) and number of turns (N) in it are each doubled, the magnetic flux density at its centre becomes
- 2 times
- 4 times
- 8 times
- 6 times
Answer/Explanation
1
33. An alpha particle and proton have same velocity when enter uniform magnetic field. The period of rotation of proton will be
- Four times that of the alpha particle
- One half times that of alpha particle
- Double of that of alpha particle
- Same as that of the alpha particle
Answer/Explanation
3
34. Ferromagnetic substance
- Allows all the electric field lines to pass through it
- Repel the field lines
- Attract the field lines
- None of these
Answer/Explanation
1
35. Out of diamagnetism, paramagnetism, and ferromagnetism the universal property of all substances is
- Diamagnetism (.)
- Paramagnetism
- Ferromagnetism
- Antiferromagnetism
Answer/Explanation
1
36. How many quantities are required to specify the magnetic field of the earth
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer/Explanation
3
37. At the magnetic North pole of the Earth, what is the value of the angle of dip?
- Zero
- Minimum
- Infinity
- Maximum
Answer/Explanation
4
38. Which of the following is another term for magnetisation?
- Magnetic neutrality
- Magnetic polarization
- Magnetic power
- Magnetic moment
Answer/Explanation
2
39. Which is the incorrect statement?
- Magnetic intensity is a vector quantity
- Induced magnetization is a process where you can magnetize a non-magnetic material
- Magnetic intensity and intensity of magnetization are the same
- Total intensity is the measurement from the magnetometer after a model of the earth’s normal magnetic field is removed
Answer/Explanation
3
40. When does a magnetic dipole possess maximum potential energy inside a magnetic field?
- Magnetic moment and magnetic field are antiparallel (.)
- Magnetic moment and magnetic field are parallel
- The magnetic moment is zero
- The magnetic field is zero
Answer/Explanation
1
41. Calculate the surface integral of a magnetic field over a surface.
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Zero
- Equal to its magnetic flux through that surface
Answer/Explanation
4
42. Which of the following is not a consequence of Gauss’s law?
- The magnetic poles always exist as unlike pairs of equal strength
- If several magnetic lines of force enter a closed surface, then an equal number of lines of force must leave that surface
- There are abundant sources or sinks of the magnetic field inside a closed surface
- Isolated magnetic poles do not exist
Answer/Explanation
3
43. Which among the following is the source of the magnetic field?
- Mechanical origin
- Electrical origin
- Chemical origin
- Potential origin
Answer/Explanation
2
44. The line of force in a magnetic field represents the direction at each point that a magnetic needle placed at the point takes up. Do they also represent the direction of the force on a moving charge at each point?
- Not possible
- Represent circular motion
- Represent tangential motion
- Represent translatory motion
Answer/Explanation
1
45. A bar magnet of the magnetic moment 5 Am2 has poles 20 cm apart. Calculate the pole strength.
- 250 Am
- 4 Am
- 100 Am
- 25 Am
Answer/Explanation
4
Assertion-Reasoning Based MCQ
Code
- If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- If both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- If the assertion is true, but the reason is false.
- If the assertion is false, but the reason is true.
1 . Assertion When a magnetic dipole is placed in a non uniform magnetic field, only a torque acts on the dipole.
Reason Force wouldn’t act on dipole if magnetic field were uniform.
Answer/Explanation
1 . (4)
In a non uniform magnetic field, both a torque and a net force acts on the dipole. If magnetic field were uniform, net force on dipole would be zero.
2. Assertion Magnetic moment of helium atom is zero.
Reason All the electron are paired in helium atom orbitals.
Answer/Explanation
2. (1)
Helium atom has paired electrons so their electron spin are opposite to each other and hence its net magnetic moment is zero.
3. Assertion Gauss theorem is not applicable in magnetism.
Reason Mono magnetic poles do not exist.
Answer/Explanation
3. (1)
The magnetic flux through any closed surface is zero.
4. Assertion The true geographic north direction is found by using a compass needle.
Reason The magnetic meridian of the earth is along the axis of rotation of the earth.
Answer/Explanation
4. (4)
The compass needle enables us to locate magnetic north pole. If magnetic declination at that particular place is known, then true geographic north-south direction can be located. Magnetic meridian is the vertical plane passing through magnetic axis. Magnetic axis is inclined at a certain angle θ to geographical axis and earth rotates about geographic axis.
5. Assertion In the northern hemisphere the north pole of the dip needle dips downwards.
Reason The north pole of earth is as a bar magnet lies in the northern hemisphere.
Answer/Explanation
5. (3)
In the northern hemisphere, magnetic needle comes to rest along north-south direction. So, that a greater dip angle is expected in northern hemisphere.
6. Assertion If a compass needle be kept at magnetic north pole of the earth, the compass needle mat stay in any direction.
Reason Dip needle will stay vertical at the north pole of earth.
Answer/Explanation
6. (2)
At magnetic poles of the earth, the only vertical component of the earth’s field acts, horizontal component is zero. A compass needle is free to rotate in horizontal plane and is affected by horizontal component only. Thus there will be no effect on the magnetic field on the compass needle. So the needle may stop in any direction. The angle of dip at the magnetic north pole is 90° and therefore the dip needle will become vertical.
7. Assertion To protect any instrument from external magnetic field, it is put inside an iron box.
Reason Iron is a magnetic substance.
Answer/Explanation
7. (2)
Iron is ferromagnetic in nature. Lines of force due to external magnetic field prefer to pass through iron.
Case- Study Based MCQ
1 . A suspended magnet gets aligned with the earth’s magnetic field at that place. Along the equator, a suspended magnet will align horizontally. The orientation of the magnet depends on the dip angle at that place. Angle of dip is the angle between the net magnetic field of earth and the horizontal. At equator, angle of dip is 0 and at poles it is 90° . This means at equator, the earth’s magnetic field is completely horizontal and at poles. The Earth’s magnetic field is vertical.
If S is the angle of dip at a place and B is the Earth’s magnetic field, then the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field BH = Bcosẟ the vertical component BV = Bsinẟ
B = √(BH2 + BV2)
tan ẟ = BV / BH
(i) A magnet stands vertical at a place when suspended that place will be
(a) At equator
(b) At poles
(c) At 30° latitude
(d) At 60° latitude
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
(ii) The angle of dip of a face where the magnet gets aligned completely horizontal is
(a) 0°
(b) 90°
(c) 30°
(d) 45°
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
(iii) The horizontal and vertical components of the magnetic field at a place are √3/2B and B/2 respectively. When a magnet is left free at that place, the angle made by its magnetic axis with the horizontal is
(a) 45°
(b) 30°
(c) 60°
(d) 15°
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
(iv) Earth’s magnetic field always has a vertical component except at
(a) Poles
(b) Equator
(c) 30° latitude
(d) 75° latitude
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
(v) The magnetic field due to earth has a horizontal component of 26μT at a place where the dip is 60°. Vertical component of the field at that point is
(a) 25 μT
(b) 30 μT
(c) 45 μT
(d) 54 μT
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
2. The study of magnets fascinated scientists around our globe for many centuries and even now, door for research on magnets is still open. The needle in a magnetic compass or freely suspended magnet comes to rest in a position which is approximately along the geographical north-south direction of the earth.
William Gilbert in 1600 proposed that earth itself behaves like a gigantic powerful bar magnet. Goven suggested that the Earth’s magnetic field is due to hot rays coming out from the sun. These rays will heat up the air near equatorial region. Once air becomes hotter, it rises above and will move towards northern and southern hemispheres and get electrified.
This may be responsible to magnetize the ferromagnetic materials near the Earth’s surface. Till date so many theories completely explains the cause for the Earth’s magnetism.
(i) The ultimate individual unit of magnetism in any magnet is called
(a) North pole
(b) South pole
(c) Dipole
(d) Quadrupole
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
(ii) Magnetic meridian is a
(a) point
(b) horizontal plane
(c) vertical plane
(d) line along N-S
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
(iii) At the magnetic poles of the earth, a compass needle will be
(a) vertical
(b) bent slightly
(c) horizontal
(d) inclined at 45° to the horizontal
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
(iv) Due to earth’s magnetic field, the charged cosmic ray particles
(a) require greater kinetic energy to reach the equator than pole
(b) require less kinetic energy to reach the equator than pole
(c) can never reach the pole
(d) can never reach the equator
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
(v) Great circle on the earth’s perpendicular to the magnetic axis is
(a) magnetic meridian
(b) magnetic equator
(c) geographic meridian
(d) magnetic axis
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Physics MCQs
Question 1. A toroid of n turns, mean radius R and cross-sectional radius a carries current I. It is placed on a horizontal table taken as x-y plane. Its magnetic moment m [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) is non-zero and points in the z-direction by symmetry.
(b) points along the axis of the tortoid (m = mΦ).
(c) is zero, otherwise there would be a field falling as \(\frac{1}{r^{3}}\) at large distances outside r3 the toroid.
(d) is pointing radially outwards.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) For any point inside the empty space surrounded by toroid and outside the toroid, the magnetic field B is zero because the net current enclosed in these spaces is zero.
MCQ Physics Class 12 Question 2. The magnetic field of Earth can be modelled by that of a point dipole placed at the centre of the Earth. The dipole axis makes an angle of 11.3° with the axis of Earth. At Mumbai, ‘declination is nearly zero. Then, [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) the declination varies between 11.3° W to 11.3° E.
(b) the least declination is 0°.
(c) the plane defined by dipole axis and Earth axis passes through Greenwich.
(d) declination averaged over Earth must be always negative.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) The axis of the dipole does not coincide with the axis of rotation of the earth and it is tilted at some angle.
3. In a permanent magnet at room temperature [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) magnetic moment of each molecule is zero.
(b) the individual molecules have non-zero magnetic moment which are all perfectly aligned.
(c) domains are partially aligned.
(d) domains are all perfectly aligned.
Answer/Explanation
CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQs with Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) At room temperature, the permanent magnet retains ferromagnetic property for a long period of time.
Physics MCQs For Class 12 with Answers Chapter wise Pdf Question 4. Consider the two idealized systems:
(i) a parallel plate capacitor with large plates and small separation and (ii) a long solenoid of length L » R, radius of cross-section. In (i) E is ideally treated as a constant between plates and zero outside. In (ii) magnetic field is constant inside the solenoid and zero outside. These idealised assumptions, however, contradict fundamental laws as below: [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) case (i) contradicts Gauss’s law for electrostatic fields.
(b) case (ii) contradicts Gauss’s law for magnetic fields.
(c) case (i) agrees with ∫ E.dl = 0 .
(d) case (ii) contradicts ∫ H.dl = Ien
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) The electrostatic field lines do not form a continuous closed path, while the magnetic field lines form the closed paths.
5. A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of 8 Am-1 when placed in an external magnetic field of 0.6 T at a temperature of 4K. When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of 0.2 T at a temperature of 16 K, the magnetisation will be [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) \(\frac{32}{3}\) Am-1
(b) \(\frac{2}{3}\) Am-1
(c) 6 Am-1
(d) 2.4 Am-1
Answer
Answer: b
6. S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
(a) Lines of B are not necessarily continuous across S.
(b) Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S.
(c) Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S.
(d) Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S.
Answer
Answer: d
7. The primary origin(s) of magnetism lies in
(a) Pauli exclusion principle.
(b) polar nature of molecules.
(c) intrinsic spin of electron.
(d) None of these.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) The primary origin of magnetism lies in the fact that the electrons are revolving and spinning about the nucleus of an atom.
8. A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of μr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc .
(a) The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
(b) The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
(c) The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
(d) The magnetisation in the core does not diminishes.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) At normal temperature, a solenoid behaves as a ferromagnetic substance and at the temperature beyond the Curie temperature, it behaves as a paramagnetic substance.
9. Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magne-tostatic shielding is due to
(a) electrostatic field lines cannot end on ’ charges and conductors do not have free charges.
(b) lines of B can also end but conductors cannot end them.
(c) lines of B cannot end. on any material and perfect shielding is not possible.
(d) shells of high permeability materials cannot be used to divert lines of B from the interior region.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) As magnetostatic shielding is done by using an enclosure made of a high permeability magnetic material to prevent a static magnetic field outside the enclosure from reaching objects inside it or to confine a magnetic field within the enclosure
10. Let the magnetic field on earth be modelled by that of a point magnetic dipole at the centre of earth. The angle of dip at a point on the geographical equator
(a) is always zero.
(b) can be zero at specific points.
(c) cannot be positive or negative.
(d) is not bounded.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) As the angle of dip at a point on the geographical equator is bounded in a range from positive to negative value.
11. A magnetic needle is kept in a non-uniform magnetic field. It experiences
(a) a torque but not a force.
(b) neither a force nor a torque.
(c) a force and a torque.
(d) a force but not a torque.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) As magnetic needle experiences both torque and force in a non-uniform magnetic field, because unequal and non-linear forces are exerted on its poles.
MCQ on Magnetism Class 12 Pdf Question 12. A 25 cm long solenoid has radius 2 cm and 500 total number of turns. It carries a current of 15 A. If it is equivalent to a magnet of the same size and magnetisation \(\overline{\mathbf{M}}\), then |\(\overline{\mathbf{M}}\)| is
(a) 3 π Am-1
(b) 30000 π Am-1
(c) 300 Am-1
(d) 30000 Am-1
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: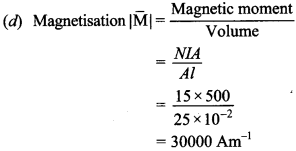
13. Three needles N1 N2 and N3 are made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. A magnet, when brought close to them, will
(а) attract N1 strongly, but repel N2 and N3 weakly.
(b) attract all three of them.
(c) attract N1 and N2 strongly but repel N3.
(d) attract N1 strongly, N2 weakly and repel N3 weakly.
Answer
Answer: d
14. Curie temperature is the temperature above which
(a) a ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic.
(b) a ferromagnetic material becomes diamagnetic.
(c) a paramagnetic material becomes diamagnetic.
(d) a paramagnetic material becomes ferromagnetic.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) A ferromagnetic material becomes paramagnetic above the curie temperature.
15. The material suitable for making electromagnets should have
(a) high retentivity and high coercivity.
(b) low retentivity and low coercivity.
(c) high retentivity and low coercivity.
(d) low retentivity and high coercivity.
Answer
Answer: c
16. Curie law xT = constant, relating magnetic susceptibility (x) and absolute temperature (T) of magnetic substance is obeyed by
(a) all magnetic substances.
(b) paramagnetic substances.
(c) diamagnetic substances.
(d) ferromagnetic substances.
Answer
Answer: b
17. If Mis magnetic moment and B is magnetic field intensity, then the torque is given by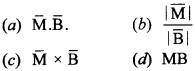
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Torque, \(\bar{\tau}=\overline{\mathbf{M}} \times \overline{\mathbf{B}}\)
18. Angle of dip is 90° at
(a) poles.
(b) equator.
(c) both at equator and poles.
(d) tropic of cancer.
Answer
Answer: a
19. Lines of force, due to earth’s horizontal magnetic field, are
(a) elliptical
(b) curved lines
(c) concentric circles
(d) parallel and straight
Answer
Answer: d
20. If the magnetising field on a ferromagnetic material is increased, its permeability.
(a) is decreased
(b) is increased
(c) is unaffected
(d) may be increased or decreased.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a), Since, \(\mu=\frac{\mathrm{B}}{\mathrm{H}} \Rightarrow \mu \propto \frac{1}{\mathrm{H}}\)
21. A magnetic needle suspended parallel to a magnetic field requires /3 J of work to turn it through 60°. The torque needed to maintain the needle in this position will be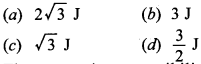
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: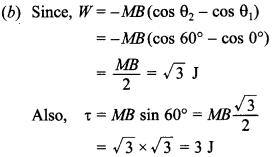
22. The magnetic susceptibility of an ideal diamagnetic substance is
(a) +1
(b) 0
(c) -1
(d) ∞
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) Since, for diamagnetic -1 ≤ xm < 0
23. The best material for the ore of a transformer is
(a) stainless steel
(b) mild steel
(c) hard steel
(d) soft iron
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) Since, soft iron has high permeability and low retentivity.
24. Domain formation is the necessary feature of
(a) diamagnetism.
(h) Paramagnetis.
(c) ferromagnetism.
(d) all of these.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) Ferromagnetism is explained on the basis of domain formation.
Physics Class 12 MCQs Pdf Question 25. The variation of magnetic susceptibility with the temperature of a ferromagnetic material can be plotted as
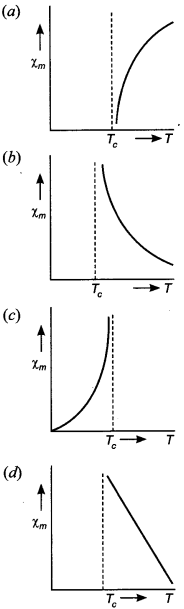
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) Since susceptibility (xm) of ferromagneticmaterial decreases with increase in temperature and above curie temperature Tc, it becomes paramagnetic.
26. In which type of material the magnetic susceptibility does not depend on temperature?
(a) Diamagnetic
(b) Paramagnetic
(c) Ferromagnetic
(d) Ferrite
Answer
Answer: a
27. A diamagnetic material in a magnetic field moves
(a) perpendicular to the field.
(b) from weaker to stronger parts.
(c) from stronger to weaker parts.
(d) in random direction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) A diamagnetic material is repelled by magnetic field so it moves slowly from stronger to weaker part.
28. At a certain place on earth, \(B_{H}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} B_{V}\) angle of dip at this place is
(a) 60°
(b) 30°
(c) 45°
(d) 90°
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: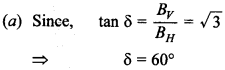
29. The universal property among all substances is
(a) diamagnetism.
(b) paramagnetism.
(c) ferromagnetism.
(d) all of these.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: (a) Diamagnetism is the universal property of all substances.
30. At a point on the right bisector of a magnetic dipole, the magnetic
(a) potential varies as \(\frac{1}{r²}\)
(b) potential is zero at all points on the right bisector.
(c) field varies as r3.
(d) field is perpendicular to the axis of dipole.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) At any point on the right bisector the potential due to the two poles are equal and opposite.
31. A magnet of dipole moment M is aligned in equilibrium position in a magnetic field of intensity B. The work done to rotate it through an angle 0 with the magnetic field is
(a) MB sin θ
(b) MB cos θ
(c) MB (1 – cos θ)
(d) MB(l – sin θ)
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) , At equilibrium position θ = 0,
Work done, W = \(\int_{0}^{\theta}\) MB sin θ d θ
= MB( 1 – sin θ)
32. A magnet can be completely demagnetised by
(a) breaking the magnet into small pieces.
(b) heating it slightly.
(c) dropping it into ice cold water.
(d) a reverse field of appropriate strength.
Answer
Answer: d
33. The primary origin of magnetism lies in
(a) atomic current and intrinsic spin of electrons.
(b) polar and non polar nature of molecules.
(c) pauli exclusion principle.
(d) electronegative nature of materials.
Answer
Answer: a
34. Magnetic moment for solenoid and corresponding bar magnet is
(a) equal for both
(b) more for solenoid
(c) more for bar magnet
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: a
35. Which of the following is correct about magnetic monopole?
(a) Magnetic monopole exist.
(b) Magnetic monopole does not exist.
(c) Magnetic monopole have constant value of monopole momentum.
(d) The monopole momentum increase due to increase at its distance from the field.
Answer
Answer: b
36. Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is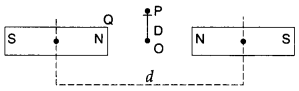
(a) zero
(b) directed along OP
(c) directed along PO
(d) directed perpendicular to the plane of paper
Answer
Answer: a
37. A current carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field in four different orientations as shown in figure. Arrange them in the decreasing order of potential energy.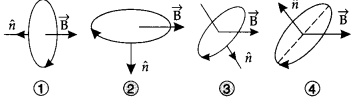
(a) 4, 2, 3,1
(b) 1, 4, 2, 3
(c) 4, 3, 2,1
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4
Answer
Answer: b
38. Which of the following is not showing the essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding?
(a) Electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free charges.
(b) Magnetic field lines can end but conductors cannot end them.
(c) Lines of magentic field cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is not possible.
(d) Shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert lines of magnetic field from the interior region.
Answer
Answer: b
39. The net magnetic flux through any closed surface, kept in a magnetic field is
(a) zero
(b) \(\frac{\mu_{0}}{4 \pi}\)
(c) 4πμ0
(d) \(\frac{4 \mu_{0}}{\pi}\)
Answer
Answer: a
40. Point out the correct direction of magnetic field in the given figures.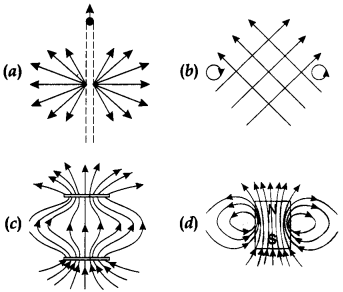
Answer
Answer: d
41. The earth behaves as a magnet with magnetic field pointing approximately from the geographic
(a) North to South
(b) South to North
(c) East to West
(d) West to East
Answer
Answer: b
42. The strength of the earth’s magnetic field is
(a) constant everywhere.
(b) zero everywhere.
(c) having very high value.
(d) vary from place to place on the earths surface.
Answer
Answer: d
43. Which of the following is responsible for the earth’s magnetic field?
(а) Convective currents in earth’s core
(б) Diversive current in earth’s core.
(c) Rotational motion of earth.
(d) Translational motion of earth.
Answer
Answer: a
44. Which of the following independent quantities is not used to specify the earth’s magnetic field?
(a) Magnetic declination (θ).
(b) Magnetic dip (δ).
(c) Horizontal component of earth’s field (BH).
(d) Vertical component of earth’s field (BV).
Answer
Answer: d
45. Let the magnetic field on earth be modelled by that of a point magnetic dipole at the centre of earth. The angle of dip at a point on the geographical equator is
(a) always zero
(b) positive, negative or zero
(c) unbounded
(d) always negative
Answer
Answer: b
46. The angle of dip at a certain place where the horizontal and vertical components of the earth’s magnetic field are equal is
(a) 30°
(b) 75°
(c) 60°
(d) 45°
Answer
Answer: d
47. The vertical component of earth’s magnetic field . at a place is √3 times the horizontal component
the value of angle of dip at this place is
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Answer
Answer: c
48. At a given place on earth’s surface the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 2 × 103-5 T and resultant magnetic field is 4 × 103-5 T. The angle of dip at this place is
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 45°
Answer
Answer: b
49. Which of the following property shows the property of ferromagnetic substances?
(a) The ferromagnetic property depends on tem-perature. ‘
(b) The ferromagnetic property does not depend on temperature.
(c) At high enough temperature ferromagnet becomes a diamagnet.
(d) At low temperature ferromagnet becomes a paramagnet.
Answer
Answer: a
50. Gauss’s law in magnetism indicates that magnetic ________ do not exist.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: monopoles.
51. Magnetic dipole moment associated with an electron due to its orbital motion in first orbit of H-atom is known as ________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Bohr magneton.
52. Magnetic lines of force form closed loop. They converge at ________ pole and diverge at ________ pole.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: south, north
53. Angle between the geographical meridian and magnetic meridian at the given place is known as ________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: magnetic declination (∝)
54. Angle made by the earth’s total magnetic field with the horizontal direction is known as ________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: angle of dipole (δ)
55. S.I. unit of magnetic dipole moment is ________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Am²
56. Magnetic moment developed per unit volume of a material when placed in a magnetising field is known as ________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: intensity of magnetisation.
57. Which orientation of a magnetic dipole in a uniform magnetic field will correspond to its stable equilibrium? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
In stable equilibrium, the dipole moment vector and the magnetic field vector are in same direction.
58. Magnetic field arises due to charges in motion. Can a system have magnetic moments even though its net charge is zero?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Yes. The average of the charge in the system may be zero. Yet, the mean of the magnetic moments due to various current loops may not be zero. In paramagnetic material, the atoms have net dipole moment though their net charge is zero.
59. If magnetic monopoles existed, how would the Gauss’s law of magnetism be modified? [Delhi 2019]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Gauss’s law of magnetism states that the flux of B through any closed surface is always zero \(\oint_{s}\)B .ds = 0. If the monopole existed, then Gauss’s law would have been \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot \overrightarrow{d s}\) = μ0qm where qm is magnetic charge (monopole) enclosed by the surface.
60. Must every magnetic configuration have a north pole and a south pole? What about the field due to a toroid?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Not necessarily. True only if the source of the field has a net non-zero magnetic moment. This is not so for a toroid or even for a straight infinite conductor.
61. Does a bar magnet exert a toque on itself due to its own field? Does on element of a current-carrying wire exert a force on another element of the same wire?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No. There is no force or torque on a element due to the field produced by that element itself. But there is a force (or torque) on an element of the same wire.
62. A magnetised needle in a uniform magnetic field experiences a torque but no net force. An iron nail near a bar magnet, however, experiences a force of attraction in addition to a torque. Why?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No force, if the field is uniform. The iron nail experiences a non-uniform field due to the bar magnet. There is induced magnetic moment in the nail, therefore, it experiences both force and torque. The net force is attractive because the induced south pole (say) in the nail is closer to the north pole of magnet than induced north pole.
63. How does the (i) pole strength, and (ii) magnetic moment of each part of a bar magnet change if it is cut into two equal pieces transverse to its length? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) The pole strength does not change.
(ii) The magnetic moment reduces to half.
64. What happens if a bar magnet is cut into two pieces: (i) transverse to its length, (ii) along its length?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
In either case, one gets two magnets, each with a north and south pole.
65. How does the (i) pole strength and (ii) magnetic moment of each part of a bar magnet change if it is cut into two equal pieces along its length? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) The pole strength becomes half.
(ii) The magnetic magnet becomes half.
66. Magnetic field lines show the direction (at every point) along which a small magnetised needle aligns (at the point). Do the magnetic field lines also represent the lines of force on a moving charged particle at every point?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No. The magntic force is always normal to B (remember magnetic force = q(\(\vec{v} \times \vec{B}\)). Therefore it is misleading to call magnetic field lines as lines of force.
67. Magnetic field lines can be entirely confined ’within the core of a toroid, but not within a straight solenoid. Why?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
According to the Gauss’s law, \(\oint \vec{B} \cdot \overrightarrow{d s}\) =0, which is true for a as has no ends. But, in case of a solenoid, at each end the magnetic flux will not be zero, if the magnetic field lines were entirely confined within the solenoid.
68. What is the angle of dip at a place where the horizontal and vertical components of the earth’s magnetic field are equal? [Foreign 2012]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Angle of dip is 45°.
69. Two identical looking iron bars A and B are given, one of which is definitely known to be magnetised. (We do not know which one.) How would one ascertain which one? [Use nothing else but the bars A and B.]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Let, two bars are A and B. Now, bring one end of A near to B, and move it slowly (from one end to the middle).
If force experienced by bar A reduces as we move towards middle, then bar B is magnetised, and A is not.
If A experiences repulsion, then both the bars are magnetised.
70. A magnetic needle, free to rotate in a vertical plane, orients itself vertically at a certain place on the Earth. What are the values of (i) horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field, and (ii) angle of dip at this placed? [Foreign 2012]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: (i) Zero (ii) 90°
71. At a place, the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is B and angle of dip is 60°. What is the value of horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at equator? [Delhi 2017]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: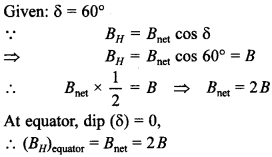
72. Which of the following substances are paramagnetic?
Bi, Al, Cu, Ca, Pb and Ni [Delhi 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Al and Ca.
73. Which of the following substances are diamagnetic?
Bi, Al, Na, Cu, Ca and Ni [Delhi 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Bi and Cu.
74. The susceptibility of a magnetic material is -4.2 × 10-6. Name the type of magnetic material it represents. [Chennai 2019] [Delhi 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Diamagnetic.
75. The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0.9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field. [CBSE 2018]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Paramagnetic
76. What are permanent magnets? Give one example. [Delhi 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Permanent magnets are the materials which retain their ferromagnetic properties for a long time at room temperature, e.g. a bar magnet.
77. The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 1.9 × 10-5. Name the type of magnetic materials it represents.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: Paramagnetic
