Question
The figure shows a diagrammatic view of human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Select the option, which gives correct identification and main function and/or characteristic. [NEET 2013]
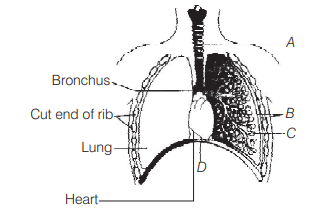
(a) A-trachea-long tube supported by complete cartilaginous rings for conducting inspired air
(b) B-pleural membrane-surround ribs on both sides to provide cushion against rubbing
(c) C-alveoli-thin walled vascular bag-like structures for exchange of gases
(d) D-lower end of lungs-diaphragm pulls it down during inspiration
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
C-Alveoli are thin-walled vascular bag-like structures for exchange of gases.
A–trachea or wind pipe is an air conducting tube through which transport of gases takes place.
B–pleural membrane is double layered which reduces friction on the lung surface.
D–diaphragm is involved in the inspiration and expiration process of breathing.
Question
The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gas takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function. [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
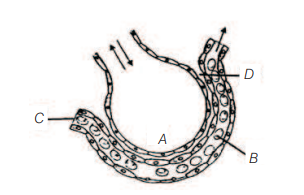
(a) A – Alveolar – main site of cavity exchange of respiratory gases
(b) D – Capillary – exchange of wall gases takes place here
(c) B – Red blood – transport of cell mainly haemoglobin
(d) C – Arterial – passes oxygen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Option (a) is correctly mentioned as alveoli which are the primary sites of exchange of gases. The exchange of gases $\left(\mathrm{O}_2\right.$ and $\left.\mathrm{CO}_2\right)$ between the alveoli and the blood occurs by simple diffusion.
Question
Which one of the following organs in the human body is most affected due to shortage of oxygen? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) Intestine
(b) Skin
(c) Kidney
(d) Brain
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The brain cells are highly specialised. They cannot regenerate and respire without $\mathrm{O}_2$. Therefore, the shortage of $\mathrm{O}_2$ leads to death of brain cells.
Question
In alveoli of the lungs, the air at the site of gas exchange, is separated from the blood by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) alveolar epithelium only
(b) alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium
(c) alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium and tunica adventitia
(d) alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, a thin layer of tunica media and tunica adventitia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The wall of the capillaries consists of only tunica internae which is made up of simple squamous endothelium. The wall of alveoli is also very thin, consisting of squamous epithelium.
