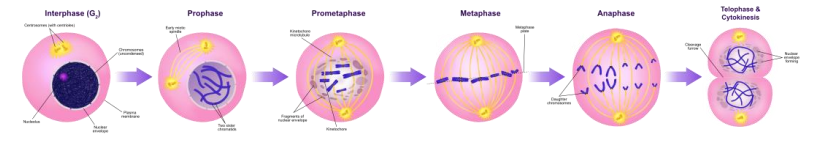
B. Mitosis
➢ Prophase
- Disappearance of the nucleolus and nuclear envelope
- Chromosomes thicken and become visible
■ Now called chromatin - Centrioles in microtubules organizing centers (MTOCs) start to move away from each other towards opposite poles of the cell
■ Centrioles spin out system of microtubules known as spindle fibers
■ Spindle fibers attach to kinetochore located on centromere of each chromatid
➢ Metaphase
- Chromosomes begin to line up along equatorial metaphase plate
■ Moved along by spindle fibers attach to kinetochores on each chromatid
➢ Anaphase
- Sister chromatids of each chromosome separate at the centromere and migrate to opposite
poles - Pulled apart by shortening microtubules
- Non-kinetochore tubules elongate cell
➢ Telophase
- Nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes
- Nucleoli reappear
- Cytokinesis
■ Cytoplasm splits in half
■ Cell splits along cleavage furrow
■ Cell membrane forms along each new cell, split into distinct daughter cells
■ In plant cells, a cell plate forms down the middle instead of a cleavage furrow
➢ Interphase
- Cells re enter initial phase, and are ready to start the cycle over again
- Chromosomes become invisible again
■ Genetic material goes back to being chromatin
➢ Purpose of mitosis
- Produce daughter cells that are identical copies of parent cell
- Maintain proper number of chromosomes from generation to generation
➢ Occurs in almost every cell except for sex cells
➢ Involved in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction