Spectroscopy
- Applying different types of radiation to atoms and molecules can give info
- Energy lvls: UV > Visible > Infrared > Microwave
Ultraviolet/visible radiation: transitions electrons from one energy lvl to another(higher) one
- Gives info about atomic structure/e- energy lvl; e- absorb this type of radiation to move from ground to excited state
- Ultraviolet light is more energetic than visible light → UV can excite lower energy electronic transitions that visible light cannot
- Molecule absorbs UV but not visible → does not have lower energy electronic transitions available
Electron Levels
- Ground state: the lowest energy state for an atom’s electrons
- Excited state: a higher energy state for an atom’s electrons
Infrared radiation: associated with transitions in molecular vibrational lvls
- Gives info about types of bonds/bond order (number of bonds) by the way that they vibrate
Microwave radiation: associated with transitions in molecular rotational lvls
- Gives info about polarity of bonds
Energy of a Photon
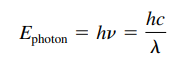 (on RFS)
(on RFS)- E = energy of a photon; H = Planck’s Constant (626 × 10-34 m2 kg / s)