Heat Capacity and Calorimetry
- Heat capacity (C): heat absorbed per degree (J/C or J/K)
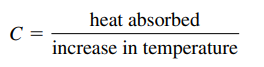
- Extensive property: depend on amount of substance
- Specific heat capacity (cp): heat capacity per gram (J/C g or J/K)
- Amount of heat required to change one gram of a substance temperature by one degree C or K
- Every substance has its own specific heat capacity
- Cp of water is 4.18 J/C g → requires 4.184 J (1 cal) of energy to heat a gram by one degree
- Amount of heat required to change one gram of a substance temperature by one degree C or K
- Molar heat capacity: heat capacity per mol (K/C mol or K/K mol)
- Specific and Molar heat capacity are intensive properties: independent of the amount (of substance)
Heat Transfer Equations
- qA = -qB → heat lost = – heat gained
- qsystem = -qsurroundings; qsolution = -qsurroundings
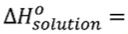
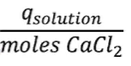
- Questions involving specific heat → the amount of heat (J) gained/lost by a sample (q) can be determined by the formula: q = mcpΔT or ncpΔT
- M = mass
- C = specific heat
- ΔH = -q
- Questions involving two substances: Do two mcats → mcΔT = – (mcΔT)
- Ex:
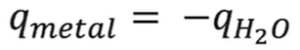
- Ex: