Standard State
- Standard enthalpy (ΔH⁰): the enthalpy change at standard conditions
- ⁰ = recorded in standard state
- Standard State conditions:
- For a gas: pressure is 1 atm
- For a pure substance in a condensed state (liquid or solid) = pure liquid or solid
- For a solution, concentration is 1 molar
- Temp is at exactly 25 C
- Remember:
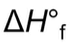 of a pure element is 0
of a pure element is 0 - Standard heats of formation: the amount of heat needed to form 1 mole of a compound from its elements in their standard states (ie. how it exists in nature → oxygen is O2)
- Unit: kJ
- Have to make one mole of product to meet the definition
- SS of an element is the form in which the element exists under 1 atm and 25 C
- Not 0 = not how the element exists in nature
- Ex: Write the equation for the formation of methanol (CH3OH)
- Step 1: write the elements (in standard state)

- Step 1: write the elements (in standard state)
- Note: The elements that exist as diatomic molecules are hydrogen (H2), nitrogen (N2), fluorine (F2), oxygen (O2), iodine (I2), chlorine (Cl2) and bromine (Br2
- Step 2: Balance

- Step 2: Balance
- Formula:
 (on RFS)
(on RFS)- Use chart → add up all of heats of formation of products – all the heats of formation of reactants