Molecular Structure of Acids and Bases
- For X-H bonds there are two factors for acidity in binary compounds
- Bond Strength (between H and other atom): low = strong acid bcuz H can easily dissociate
- Compare bond dissociation energies
- Bond Polarity (high → weak acid)
- With H: The greater the difference in electronegativity between these two elements, the more polar the bond will be → more polar bond = stronger bond → weaker acid
- For X-H bonds, acid strength increases going down a column because the electronegativity of the elements bonded to hydrogen decreases
- Greater electronegativity of central atom = weaker acid
Oxyacids
- Acid that has oxygen, hydrogen, and at least another element
- The Hydrogen is always bonded to Oxygen
- With oxyacids, acid strength increases with an increase in the number of oxygen atoms
- Why? Oxygens are very electronegative → causes the electron density to be greater and more pulled towards the oxygen side which weakens the bond between H and other atom
- Compare compounds with same number of oxygens but diff elements → more electronegative element = compound will have greater electron density → stronger acid
- For oxyacids, acid strength decreases going down a group because the electronegativity of the central atom decreases
Base
- Base that has more negative charge (-) → more strongly attracts H+ = stronger base
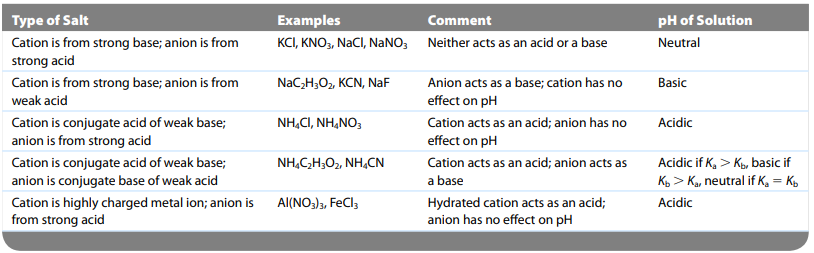
Mixture of Acids
- The process is the same: determine the major species and the stronger (bigger Ka) will dominate
- If both acids are weak → the acid with the larger Ka is slightly stronger → when calculating pH only need to focus on (make ICE table) for dominant acid
- Strong acid + weak acid → focus on strong acid
- Strong acid + strong acid → have to do both
Complex Ions
- Complex ion: a charged species consisting of a metal ion surrounded by ligands → produces an acidic solution
- the higher the charge on the metal ion, the stronger the acidity of the hydrated ion.
- Ligand: a Lewis base
- Common ligands
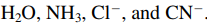
- Coordination number: The number of ligands attached to a metal ion
- Common ligands
Summary