Free Energy and Equilibrium
Free Energy at Nonstandard Conditions
- Enthalpy does not depend on volume or pressure, but entropy does
- Positional probability:
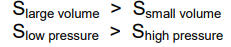
- Positional probability:
- A decreasing ΔG means that the favorability of the forward reaction is increasing (reaction shifts right)
- An increasing ΔG means that the favorability of the forward reaction is decreasing (reaction shifts left)
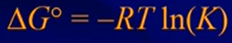
- R = gas constant → in thermodynamic calculations use the units with Joules (8.314)
- ΔG°: free energy change for the reaction at standard conditions
- Remember that K is the equilibrium constant
Equilibrium and Favorability
Value of ΔG° | +ΔG° | ΔG° = 0 | ΔG° = – |
Value of K | K < 1 | K = 1 | K > 1 |
Value of ΔH° & TΔS° | ΔH° > TΔS° | ΔH° = TΔS°
| ΔH° < TΔS° |
- Justify if a reaction is spontaneous: refer to equation and explain if ΔG° will be more negative or more positive
Free Energy and Work
- The maximum amount of useful work obtainable from a process at constant temp and pressure equals the change in free energy (energy “free” to do work)
Calculations with Entropy and Enthalpy
- Find Entropy of heat of vaporization: HV (J) / BP (K)
- Find Entropy for vaporization: + ΔH (J) / BP (K); Find Entropy for condensation: – ΔH (J) / BP (K)