Table of Content
- CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses
- CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (Tenses in Conditional Sentences)
- CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Present Tense)
- CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Past Tense)
- CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Future Tense)
Related Links
CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses
Read the following sentences carefully:
- I play tennis every day.
- We played a match yesterday.
- They will play with us tomorrow.
In sentence 1, the verb play refers to present time.
In sentence 2, the verb played refers to past time.
In sentence 3, the verb will play refers to future time.
Thus verb may refer to
- Present Time
- Past Time or
- Future Time.
Since three main time divisions are: present, past and future, they may be represented by three main blocks of tenses:
- The Present Tense
- The Past Tense
- The Future Tense
Depending on the interest and attitude of the speaker indicated by them, tenses are divided as
- indefinite or simple,
- continuous or progressive,
- perfect, and
- perfect continuous.
This classification takes into account both form and function.
These four sub-divisions of each tense clearly indicate the stage of action:
e.g.
- The Simple form simply states am action. It does not say anything about the completion of the action—whether it is complete or not.
- The Continuous form indicates that the action is in progress. It is still going on.
- The Perfect form indicates that the action has been completed.
- The Perfect Continuous form shows that the action which began sometime before, is still in progress.
Thus, the tense of a verb shows not only the time of an action or event, but also the state of an action.
In other words, we may say that tense is the form of a verb which shows the time at which an event occurs and the degree of completeness / incompleteness of the event.
Read the following sentences:
- I write a letter (Simple Present)
- I am writing a letter. (Present Continuous)
- I have written a letter. (Present Perfect)
- I have been writing a letter since 7 a.m. (Present Perfect Continuous)
The verbs in the above sentences refer to present time. Therefore, these sentences are in the present tense.
The Past Tense also has the following four forms:
1. I wrote a letter yesterday. (Simple Past)
2. I was writing a letter at that moment. (Past Continuous)
3. I had written before you came. (Past Perfect)
4. I had been writing letters all day yesterday. (Past Perfect Continuous)
Similarly, the Future Tense has the following four forms:
- I shall write to you tomorrow. (Simple Future)
- I shall be writing on reaching home. (Future Continuous)
- I shall have written a letter by evening. (Future Perfect Tense)
- I shall have been writing for an hour before you arrive. (Future Perfect Continuous)
Now study, the following tense chart giving the forms of the verb ‘write’:
TENSE CHART
| Tense | Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous |
| Present | write writes | am writing is writing are writing | has written have written | has been writing have been writing |
| Past | wrote | was writing were writing | had written | had been writing |
| Future | shall write will write | shall be writing will be writing | shall have written will have written | shall have been writing will have been writing |
CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (Tenses in Conditional Sentences)
A conditional sentence has two parts—the main clause and the conditional clause (if—clause). There are three types of conditions:
Type I : Possible — relating to future.
Type II : Probable or Hypothetical —unfulfilled condition of the Present.
Type III : Impossible or Imaginary — unfulfilled condition of the Past.
The tenses of verbs in the two clauses follow this pattern.
The tenses of verbs in the two clauses follow this pattern.
| Type | If-clause (Conditional clause) | Main clause |
| I | First form of the verb (V1 or V1 s/es) | Shall/will/may/can + first form of the verb (V1) |
| II | Second form of the Verb (V2) | Should/would/might/could + first form of the verb (V1) |
| III | Had + third form of the Verb (had + (V3) | Should/would/might/could + have + third form of the verb (V3) |
Examples:
- You will pass if you work hard.
- What shall I do if I miss the last bus?
- If I were you, I would not seek his help.
- She would have come if you had sent a proper invitation.
EXERCISE 1
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in brackets:
- He ……………….. (beat) the thief if he catches the man.
- She might catch the bus if she………………..(run) fast.
- They would have won if they ………………..(play) well.
- If you ……………….. (inform) me I would have reached the station.
- If she ………………..(not work) hard, she will fail.
- Unless they ………………..(request) me, I would not go.
- If you ……………….. (help) me, I would have completed this job.
- If I ……………….. (be) a bird I would fly to you.
- In case you ……………….. (see) Avish, give him this book.
- Unless she ……………….. (mend) her ways, she will suffer.
Answers:
1. will beat 2. ran 3. had played 4. had informed 5. does not work 6. requested 7. had helped 8. were 9. see 10. mends.
Related Links
EXERCISE 2
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks in the following passages with the appropriate tense forms of the verbs given in brackets:
- My younger brother, Tinu, (a) ………………. (fall) off his bicycle yesterday. He (b) ……………….. (hurt) his right ankle and (c) ……………….. (be) in bed since then. The doctor (d) ……………….. just (examine) him and (e) ………………..(advise) him complete rest for a week. He hopes that Tinu (f) ……………….. (recover) soon.
- The match (a) ………………..(begin) before we reached the stadium. There (b)……………….. (be) a great rush at the gate. People (c) ……………….. (argue) with the security guards. Entering the stadium (d)……………….. (prove) a tedious job. I (e)……………….. (be) able to forget this nasty experience in the years to come. I (f) ………………..(decide) never to watch an event in an overcrowded place.
- When I (a)……………….. (look) at the Palace in the morning sunlight, I was amazed. It (b) ……………….. (seem) an architectural wonder. I (c) ……………….. (watch) it from different angles and (d) ……………….. (take) snaps. Perhaps my movements (e) ……………….. (make) the guards suspicious. They at once (f) ……………….. (catch) hold of my camera and spoke rudely to me.
- It is estimated that India (a) ……………….. (make) rapid strides in science in the coming years. For that we (b) ……………….. (need) good science teachers, labs and equipment. Unfortunately, the existing scenario (c) ……………….. (not present) an encouraging sight. The nation (d) ……………….. (lack) administrators with a vision. Scientists (e) ……………….. (be) more interested in foreign assignments than research at home. Students too (f) ……………….. not (lag) behind.
- you ever (a) ………………. (hear) of paperless office? You (b) ……………….. certainly (say), “no”. Well, very soon the old favourite of pen-pushers (c) ……………….. (make) an unceremonious exit. You (d) ……………….. already (see) it happening in the banks. Where (e) ……………….. (be) those bulky ledgers? A smart computer (f) ……………….. (replace) them quietly.
Answers:
- (a) fell (b) hurt (c) has been (d) has examined (e) advised (f) will recover
- (a) had begun (b) was (c) were arguing (d) proved (e) will not be (f) have decided
- (a) looked (b) seemed (c) watched (d) took (e) had made (f) caught
- (a) will (is going to) make (b) need (c) does not present (d) lacks (e) are (f) do not lag
- (a) Have…………heard (b) will………….say (c) will (is going to) make (d) have already seen (e) are (f) has replaced.
EXERCISE 3
(Solved)
Transform the following sentences as directed using suitable form of verbs:’
- They usually go to work by cm. (Use singular subject)
- I was getting ready for college when the phone-bell rang. (Plural subject)
- I visit my parents every Sunday. (Change subject to third person singular)
- Ritu likes only this doll. (Into negative)
- None but the brave deserve the fair. (Into affirmative)
- When can their glory fade? (Into assertive)
- Who would like to be a slave? (Into assertive)
- Navin left no plan untried. (Into affirmative)
- As soon as we had left home it began to rain. (Use No sooner…..Than)
- What a wild attack! (Into assertive)
Answers:
- He usually goes to work by car.
- We were getting ready for college when the phone-bell rang.
- He/she visits his/her parents every Sunday.
- Ritu likes nothing but this doll.
- Only the brave deserve the fair.
- Their glory can never fade.
- None would like to be a slave.
- Navin tried every plan.
- No sooner had we left home than it began to rain.
No sooner did we leave home than it began to rain. - It was a (very) wild attack.
EXERCISE 4
(Solved)
Note. Sometimes passive form of the verb is also used.
- Rewrite using the correct form of the verbs in the brackets:
I (a) ……………… (expect) him here yesterday. He (b)……………… (not come) till today. No-one (c) ……………… (know) what (d) ……………… (happen) to him. I (e) ……………… (worry) about him. I hope he (f) ……………… (be) safe. - Rewrite using the correct form of the verbs in the brackets:
There (a) ……………… (be) a great rush at the counter yesterday. I (b) ……………… (want) to get a ticket for the movie. It (c) ……………… (be) the first day of release. The manager suddenly (d) ……………… (appear) on the scene and (e) ……………… (announce) that the show (f) ……………… (cancel) for reason beyond control. - Read the following paragraph and fill in the blanks with appropriate form of verbs given in the brackets:
Yesterday a blueline bus (a) ……………… (run) over a school boy who (b) ……………… (cross) the road. The boy (c)……………… (injure) seriously and (d)……………… (rush) to the hospital. The passengers (e) ……………… (catch) hold of the driver and (f) ……………… (hand) him over to the police. - Read the following paragraph and fill in the blanks with the correct form of verbs given in the brackets:
The wedding procession was yet (a) ………………(start). It (b) ……………… (wait) for us to reach. We (c) ………………(decide) not (d) ……………… (dance) at all. But when we (e) ……………… (reach) the scene, we (f) ……………… (draw) into it. - Read the following paragraph and fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets:
The wedding procession already (a) ……………… (start) when we (b) ……………… (reach) Mohan’s house. While we (c) ……………… (be) on way to the place we (d) ……………… (decide) not to dance at all. But the scene (e) ……………… (prove) so attractive, that we (f) ……………… (draw) into it. - Rewrite using the correct form of the verbs in the brackets:
The shot wounded the elephant. It (a)……………… (rush) back into the forest. I (b) ……………… (run) after it but (c) ……………… (can) not catch it. I (d) ……………… (lose) it in the dark and (e)……………… (return) empty-handed.
I (f)……………… (disappoint). - Read the following paragraph and fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb:
Once there was a king. He (a) ……………… (know) for his benevolence. Everyday he (b) ……………… (feed) the hungry and (c) ……………… (clothes) the poor before he (d) ……………… (take) his food. He (e) ……………… (do) so for many years. He (f) ……………… (love) by his subjects. - Fill in the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets:
(i) While Rome was (a) ……………… (bum), Nero was (b) ……………… (play) on the fiddle.
(ii) Since India (c) ……………… (become) independent many other countries (d) ……………… (get) their independence too.
(iii) I (e)……………… (have) my lunch when the postman (f) ……………… (knock). - Read the following passage and fill in the blanks with correct forms of the verbs given in brackets:
Joan of Arc (a) ……………… (fight) the enemy, when she (b) ……………… (capture). She (c) ……………… (make) to stand on trial by the enemy. They (d) ……………… (accuse) her of being evil because she said that she (e) ……………… (talk) to the angel. She (f) ……………… (declare) a witch and
sentenced to death. - Read the following matter and fill in the blanks with the correct form of verb: Dear Heena,
I (a) ……………… just (hear) that my mother isn’t very well, and (b) ………………(like) to see her. The trouble is I can’t take my dog Tim with me. (c) ………………you think you (d) ………………(be) able to possibly look after him for a week? If you can have him, I can bring him along any time that (e) ……………… (suit) you. But if it (f) ……………… (be) not convenient, do not hesitate to say so.
Love,
Sarika - Read the following passage and fill in the blanks with correct forms of the verbs given in brackets:
I (a) ……………… (come) in very late last night and unfortunately the dog (b) ……………… (wake) up and (c) ………………(start) to bark. This (d) ……………… (awake) my mother. She (e) ……………… (not hear) my voice because the dog (f) ……………… (bark) very loudly. - Fill in the blanks with suitable form of verbs given in the brackets:
Comrades, you all (a) ……………… (hear) about the strange dream that I (b) ………………have last night. But I (c) ……………… (come) to the dream later. I do not think, comrades that I (d) ……………… (be) with you for many months longer and before I die, I feel it my duty to (e) ……………… (pass) on to you such wisdom as I (f)……………… (acquire).
Answers:
- (a) expected (b) has not come (c) knows (d) has happened (e) am worried (f) is
- (a) was (b) wanted (c) was (d) appeared (e) announced (f) had been cancelled
- (a) ran (b) was crossing (c) was injured (d) was rushed (e) caught (f) handed
- (a) to start (b) had been waiting (c) had decided (d) to dance (e) reached (f) were drawn
- (a) had already started (b) reached (c) were (d) decided (e) proved (f) were drawn
- (a) rushed (b) ran (c) could (d) lost (e) returned (f) was disappointed
- (a) was known (b) fed (c) clothed (d) took (e) did (f) was loved
- (a) burning (b) (i) playing (ii) (c) became (d) have got (iii) (e) was having (f) knocked
- (a) was fighting (b) was captured (c) was made (d) accused (e) talked (f) was declared
- (a) have just heard (b) would like (c) Do (d) would be (e) suits (f) is
- (a) came (b) woke (c) started (d) awoke (e) did not hear (f) was barking
- (a) have heard (b) had (c) will come (d) will be (e) pass (f) have acquired.
INTEGRATED TASKS
I. ERROR CORRECTION
EXERCISE 5
(Solved)
Correct the following sentences using proper tense forms.
- I am liking it very much.
- She is knowing you very well.
- Mohit is seeing the bus coming.
- It rains now, we can’t go out.
- Water vapour is condensing to form clouds.
- Madhu is always writing beautiful poems.
- The poem is going round the earth.
- These students prepare for their exams these days.
- Why do you work so hard today?
- My uncle has arrived from Mumbai last night.
- Ravi is owning two cars. ‘
- Reena reads at this moment.
- She do not finish her home work yet.
- If you will work hard, you will pass.
- I already sent a telegram to Manish, before I received your phone call.
Answers:
- I like it very much.
- She knows you very well.
- Mohit sees the bus coming.
- It is raining now, we can’t go out.
- Water vapour condenses to form clouds.
- Madhu always writes beautiful poems.
- The poem goes round the earth.
- These students are preparing for their exams, these days.
- Why are you working so hard today?
- My uncle arrived from Mumbai last night.
- Ravi owns two cars.
- Reena is reading at this moment.
- She has not finished her homework yet.
- If you work hard, you will pass.
- I had already sent a telegram to Manish, before I received your phone call.
II. EDITING TASK
(i) ERROR CORRECTION
EXERCISE 6
(Solved)
There is an error in the form of verb in each of the following lines. Find the error. Write the incorrect word and the correction in your answer sheet as given below. Remember to underline the word that you have supplied.
Answers:
(ii) OMISSIONS
EXERCISE 7
(Solved)
In the following passage, one word has been omitted in each line. Write the missing word along with the word that comes before and the word that comes after it in your answer sheet. Ensure that the word that forms your answer is underlined as shown below:

Answers: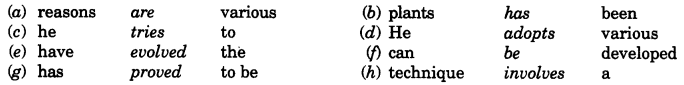
(iii) REORDERING OF SENTENCES
EXERCISE 8
(Solved)
Look at the following sentences given in a disorderly form. Rearrange them to form meaningful sentences.
- Theatre/he/the/goes/seldom/to
- penguin/I/a/seen/never/have
- did/come/he/yesterday/here/not
- gone/mother/just/out/my/has
- don’t/nests/build/cuckoos.
- it/night/heavily/rained/last.
- persons/knows several/he/here
- I/advice/parents’/I/listened/my/had/to/wish
- he/message/I/if/your/give/him/comes/will
- wife/room/he/up/entered/stood/his/the/whenever
Answers:
- He seldom goes to the theatre.
- I have never seen a penguin.
- He did not come here yesterday.
- My mother has just gone out.
- Cuckoos don’t build nests.
- It rained heavily last night.
- He knows several persons here.
- I wish I had listened to my parents’ advice.
- If he comes I will give him your message.
- Whenever his wife entered the room, he stood up OR
He stood up whenever his wife entered the room.
Save
CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Present Tense)
- 1.1 I. THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
- 1.2 2. THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Present Tense)
I. THE SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + the infinitive (without to) + ………….
When the Subject is Third Person singular, ‘s’ or ‘es’ is added to the first form of the verb.
Examples:
- I learn my lesson daily.
- We love our parents.
- You read the Hindu daily.
- A cow lives on grass.
- He/she helps the poor
- They reach the school in time.
SPELLING RULES:
- Add ‘es’ to the first form of the verb if it ends in ‘ch’, ‘sh’, ‘o’ or ‘x’: as —teaches, rushes, goes, passes or fixes.
- If a verb ends in ‘y’ and there is a consonant before ‘y’; change ‘y’ into ‘i ’ and add ‘es’ to the verb; as—
cry —> cries; fly —> flies; try —> tries
Exception. If there is vowel before ‘y’ add only ‘s’ to the first form of the verb; as—
enjoy —> enjoys, obey —> obeys; pray —> prays. - To all verbs, add only ‘s’; as
sits, plays, rims, speaks.
(b) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Do/does + subject + the infinitive (without to) + …………. ?
When the subject is third Person Singular, we use ‘Does’. For other subjects we use ‘do’:
Examples:
- Do you learn your lesson daily?
- Does he help the poor?
- Does she know me?
- Why does the girl cry?
(c) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + do not/does not + the infinitive + …………. .
Use ‘does not’ if the subject is third person singular. With other subjects use ‘do not’:
Examples:
- She does not hate anyone.
- They do not welcome us.
Exceptions. ‘Never’ is followed by bare infinitive or infinitive + s/es as in statements. The negative sense is conveyed by ‘never’ itself; sis—
- I never tease animals.
- She never tells a lie.
(d) Negative Interrogative Sentences
Form. Do not/Does not + subject + the infinitive + …………. ?
Examples:
- Don’t you like this new film?
- Doesn’t she help the poor with money?
(e) Emphatic Use of ‘Do/Does’
Form. Subject + do/does + the infinitive …………. .
Examples:
- She does drink, but not in public.
- I do go to the gym, but only on Sundays.
Important Note. Use only the first form of the verb after do and does.
Adverbs. The Simple Present Tense is used with the words:
always, often, frequently, generally, usually, sometimes, everyday, every week, every month, daily, once a week, twice a week, etc.
The Use of Simple Present Tense
- To express a habitual action; as—
I go to the temple daily.
She always speaks the truth.
My grandmother tells us a story every evening. - To express a universal truth; as—
The earth moves round the sun.
The sun rises in the east.
Water freezes into ice at 0°C. - To express a situation or a fact that is permanent; as—
The Taj stands on the bank of the Yamuna.
My house faces north.
This road leads to Ambala. - To express an action which must happen in the near future; as—
Her marriage comes off next month.
Ravi goes to England next year.
We leave at 7 a.m. tomorrow. - To read or write a subordinate clause (of time or condition) when the main clause refers to future; as
If you come, we shall be happy.
If you work hard, you will pass.
We will not wait here until he comes.
He will come out when the bell rings.
EXERCISE 1
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs given in brackets:
- Birds …………………………….. (fly) in the air.
- She always …………………………….. (keep) her word.
- The Gita…………………………….. (say) : Man is mortal.
- The Muslims …………………………….. (bury) their dead.
- The sun…………………………….. (shine) by day.
- The milkman…………………………….. (not come) here twice a day.
- The Ganga…………………………….. (rise) from the Himalayas.
- …………………………….. you …………………………….. (understand) what I say?
- Wheat…………………………….. (sell) at seven rupees a kilo.
- Beauty…………………………….. (need) no ornaments.
- She usually…………………………….. (write) in black ink.
- Barking dogs seldom…………………………….. (bite).
- This train generally…………………………….. (run) late.
- He often…………………………….. (forget) his purse.
- …………………………….. he …………………………….. (go) to school everyday?
- …………………………….. your friends…………………………….. (play) games?
- If it …………………………….. (rain), we shall cancel the match.
- If she …………………………….. (hear) of my marriage she will be shocked.
Answers:
l. fly, 2.keeps, 3.says, 4. bury, 5.shines, 6.does not come, 7.rises, 8.Do (you) understand, 9. sells, 10. needs, 11. writes, 12. bite, 13. runs, 14. forgets, 15. Does, go, 16. Do, play, 17. rains, 18. hears.
2. THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + is lam/are + Present Participle (Bare infinitive + ing or verb + ing)
Examples:
- I am writing a letter.
- Uday is reading a book.
- Children are playing in the field.
SPELLING RULES:
While adding ‘ing’ to the first form of the verb, remember the following:
- If the verb ends in ‘e’, this final ‘e’ is dropped before adding ‘ing’; as—
come — coming, use — using,
tease — teasing, waste — wasting.
Exception. dye — dyeing; die — dying. - When the verb is of one syllable and has a vowel before the final consonant, double the final consonant before adding ‘ing’; as—
hit—hitting, run—running, shop—shopping. - If the verb is of two or more syllables with stress falling on the last syllable, double the final consonant before adding ‘ing’; as—
begin — beginning, submit — submitting. - If the verb ends in a single ‘l’ preceded by a vowel, double the ‘l’ before adding ‘ing’; as—fulfil—fulfilling.
compel —compelling; quarrel —quarrelling.
(b) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Is/ am/ are + Subject + Present Participle ……………….. ?
Examples:
- Is Madhu watching television?
- Are they coming to the party?
- Why are you making a noise?
Note. The ‘wh’ – question word comes before is/am/are.
(c) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + is / am / are + not + Present Participle.
Examples:
- We are not going out today.
- Hemant is not flying a kite now.
- I am not wasting my time.
(d) Negative Interrogative Sentences
Form. Is I am/are + Subject + not + Present Participle + ?
Examples:
- Is the gardener not watering the plants now?
- Are they not coming to the party this evening?
Important Note:
The following verbs are not normally used in the present continuous tense (The non-conclusive actions can be conveyed by using the Simple Present):
(i) Verbs of Perception : see, hear, smell, notice.
(ii) Verbs of Thinking : think, feel, know, mean, mind, remember, forget, believe, imagine, agree, doubt, understand etc.
(iii) Verbs of Feeling : admire, adore, care, desire, wish, love, hate, like, dislike, forgive, want.
(iv) Verbs of Possession : have, owe, own, belong, possess.
(v) Verbs of Appearance : appear, seem, resemble, etc.
(vi) Miscellaneous Verbs : consist, contain, cost, depend, etc.
Examples:
- I smell something burning.
- He thinks he left his diary in his office.
- It is raining, but she wants to go home.
Adverbs. The Present Continuous Tense is often used with the words these days, at this time, at present, at the moment, etc.
The Use of Present Continuous Tense
- To describe the continuity of an action going on at the moment of speaking; as—
She is singing now.
Look! The postman is coming.
You are speaking too fast, I can’t follow you. - To describe ah action in process, but not necessarily going on at the time of speaking; as—
I am writing a play these days.
What is your sister doing now-a-days?
We are still exporting coal to Japan. - To express an action definitely planned for the near future; as—
He is leaving for Delhi tomorrow.
What are you doing in the evening?
I am taking my mother to the art gallery this afternoon. - To express a temporary situation; as—
Anju is sitting in a chair.
Mother is cooking food now.
We are enjoying the situation. - To express an action that has become a habit but is annoying/unpleasant to others; as—
You are always asking for more?
He is always making excuses.
He is always indulging in baseless gossips.
EXERCISE 2
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with correct form of the verbs (Present Simple or Present Continuous) given in brackets:
- The train ………………….. (leave) for Kolkata shortly.
- What ………………….. you (do) these days?
- What ………………….. she (do) in the afternoons?
- They ………………….. (host) a party tomorrow.
- She always ………………….. (write) with her left hand.
- The players ………………….. (warm) themselves up now.
- The last bus for Agra ………………….. (leave) at 11 p.m.
- I ………………….. (not believe) what you say.
- My mother usually ………………….. (cook) in the morning.
- You ………………….. (hear) the wind?
- He ………………….. (not waste) his time.
- I ………………….. (visit) my parents tomorrow.
- My brother ………………….. (make) a film these days.
- Mohit usually ………………….. (drink) coffee but today he ………………….. (take) tea.
- Hurry up! The taxi ………………….. (wait).
- She ………………….. (resemble) her mother.
- Look! Smoke ………………….. (come) out of that window.
- What ………………….. you (wait) for at this moment?
- Our teacher usually ………………….. (stand) near the lecture stand, but now he ………………….. (sit) near the table.
- He ………………….. still (sleep) in his room.
Answers:
1. is leaving, 2. are (you) doing, 3. does (she) do, 4. are hosting, 5. writes, 6. are warming, 7. leaves, 8. do not believe, 9. cooks, 10. Do (you) hear, 11. does not waste, 12. am visiting, 13. is making, 14. drinks, is taking, 15. is waiting, 16. resembles, 17. is coming, 18. are (you) waiting, 19. stands, is sitting, 20. is (still) sleeping.
3. THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + has/have + Past Participle (III form of the verb)
Examples:
- I have lost my pen.
- He has posted all the invitations.
- She has finished her work.
- They have left for Agra today.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + has not/have not + Third form of the Verb
- I have not taken your book.
- He has not solved all his sums.
- They have not sold their old house yet.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Forms. Has /Have + Subject + Third form of the Verb + ……………… ?
- Have you lost your purse?
- Has he won the first prize?
- Have they scored the winning goal?
Important Note.
- ‘Has’ is always used with singular subjects and ‘have’ with plural subjects,
- The subjects ‘you’ and ‘I’ take ‘have’ with them.
Adverbs. The Present Perfect Tense is used with the words :
Yet, as yet, so far, ever since, already, just, just now, presently, once, twice, etc.
The Use of the Present Perfect Tense
- To express an action that has been recently completed; as—
He has just received an e-mail.
I have solved two questions so far.
Have you finished your meals? - To describe an action which has just occurred, but the time is not given; as—
I have watered the plants.
He has sent a message.
They have contacted all their friends. - To describe a past event, having some connection with the present; as—
She has been to Shimla twice.
I have seen this film.
He has never failed in any public examination. - To express an action having taken place in the Past and continuing in the present; as—
We have lived here for ten years.
He has known her for three years.
I have not heard from you for over a year.
EXERCISE 3
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs given in brackets:
- Devanshi ……………………… (get) a new car now.
- Nidhi ……………………… not (come) back yet.
- I ……………………… already (see) this film.
- The postman ……………………… not (come) so far.
- She ……………………… (be) a teacher since 2000.
- They ……………………… (know) us for several years.
- She ……………………… (join) a college recently.
- The old man ……………………… (live) here all his life.
- He ……………………… not (wear) the new shirt yet.
- Tbm left the school some time ago. He ……………………… not (return) yet.
Answers:
1. has got, 2. has not come, 3. have already seen, 4. has not come, 5. has been, 6.have known, 7. has joined. 8. has lived, 9. has not worn, 10. has not returned.
4. THE PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
Form. Subject + has/have + been + Present I participle (I form of verb +ing)
In negative sentences ‘not’ is placed between has/have and been, while in Interrogative sentences, ‘has’ or ‘have’ is placed before the subject, whereas ‘been’ follows the subject.
Examples:
We have been waiting for you for an hour.
He has been living in this house since 1995.
It has not been raining since morning.
Has she been working in this firm for two months?
The Use of the Present Perfect Continuous Tense
(a) To express an action which began in the past but is still going on; as—
She has been reading a book since morning.
I have been lying in bed for an hour.
Note. ‘Since’ and Tor’ are used with the Perfect Tenses. ‘Since’ is used with a point of time eg. since morning, since Monday, since 15th, since May, since 4 O’clock, since 1985 etc.
‘For’ is used with a period of time eg. for two hours, for three months, for many years etc.
(b) To express an action which began in the past and has been just completed, but whose result is still the present; as—
My clothes are dirty, because I have been washing my car.
I have been clearing my room since morning and I am very much tired now.
(c) To express an action in a sentence which begins with ‘For how long’ or ‘Since when’; as—
Since when have you been waiting for me?
For how long has he been suffering from fever?
EXERCISE 4
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs given in brackets:
- It …………………………………………. (rain) since morning.
- The students …………………………………………. (work) well this year.
- I …………………………………………. (teach) in this school for twenty years.
- How long you …………………………………………. (wait) for me?
- What you …………………………………………. (do) all these years?
- They …………………………………………. (live) in this house since 1990.
- Since when you …………………………………………. (work) in this office?
- I am very much tired, for I …………………………………………. (wash) my car since morning.
- You …………………………………………. (play) tennis all morning?
- Since when she …………………………………………. (stand) there?
- She …………………………………………. (wait) there since 8 a.m.
- He …………………………………………. (study) medicine here since 1999.
- We …………………………………………. (search) the missing pen for half-an-hour.
- The teacher …………………………………………. (mark) the answer books since morning.
- The teachers …………………………………………. (discuss) the problem since lunch.
Answers:
1. has been raining, 2. have been working, 3. have been teaching, 4. have (you) been waiting, 5. have (you) been doing,
6. have been living, 7. have (you) been working, 8. have been washing, 9. Have (you) been playing, 10. has (she) been standing, 11. has been waiting, 12. has been studying, 13. have been searching, 14. has been marking, 15. have been discussing.
CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Past Tense)
1. THE SIMPLE PAST TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. subject + Second form of the verb.
Examples:
- She broke my pen.
- They worked on a big farm.
- I saw her in the market yesterday.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + did not + first form of the verb.
Examples:
- She did not finish her work.
- You did not help me.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Did. + Subject + First form of the verb +……………………….?
- Did you buy this book yesterday?
- Where did they stop on the way?
Adverbs. Words indicating past time such as ‘yesterday’ ‘ago’, ‘last‘ etc.
Important Note. Use First Form of the Verb after did
The Use of the Simple Past Tense
- To express an action completed in the Past with reference to the time of speaking; as,
I met a one-eyed sailor yesterday.
We visited Shimla last year. - To express a habitual or regular action in the Past; as,
When he was young, he always got up at 5 a.m.
She visited the temple every evening to offer prayer. - To express an event which occurred at a particular point in the past; as,
Edison invented the gramophone.
A truck hit a car and killed its driver. - To express an action which occupied a period of time in the Past, but has ended now; as,
He worked for eight hours (= is not working now).
I stayed at Manali with my uncle for ten days (= not staying now) - To express an action going on at the time stated or during the occurrence of another longer action; as,
While Rima sang, Tina danced.
Rohit read the magazine as he took tea.
She was watching the television when I went to her house.
EXERCISE 1
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct Past Tense forms of the verbs given in brackets:
- I told him that he ………………………………… (not care) for me.
- Captain Cook ………………………………… (discover) Australia.
- She ………………………………… (sing) very beautifully at the function.
- A thief ………………………………… (break) into our house last night.
- When he ………………………………… (pass) his BA?
- Prices ………………………………… (rise) by twenty per cent last year.
- Nitish ………………………………… (come) back last evening.
- Gandhiji never ………………………………… (tell) a lie.
- When you ………………………………… (join) this job?
- He ………………………………… (call) on me last night.
- I ………………………………… (work) all day yesterday.
- India ………………………………… (get) freedom in 1947.
- We ………………………………… (buy) a new house last year.
- ………………………………… the sun ………………………………… (rise) at 5.45 a.m. yesterday?
- ………………………………… she………………………………… (visit) this place sometime ago?
- It ………………………………… (not rain) heavily last summer.
- She ………………………………… (eat) her dinner at ten last night.
- He ………………………………… (not do) anything yesterday.
- She has learnt English since she………………………………… (join) this class.
- His health has improved since he ………………………………… (go) to Shimla.
Answers:
1. did not care, 2. discovered, 3. sang, 4. broke, 5. did (he) pass, 6. rose, 7. came, 8. told, 9. did (you) join, 10. called,
11. worked, 12. got, 13. bought, 14. Did………. rise, 15. Did…….. visit, 16. did not rain, 17. ate, 18. did not do, 19. joined,
20. went.
2. THE PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + was/were + Present Participle (V1 + ing).
Examples:
- I was writing letters all night.
- The baby was weeping in the room.
- The children were playing in the ground.
Note. Use ‘was’ with singular subjects. [I, he, she, it and singular Nouns]. Use ‘were’ with plural subjects [We, you, they and Plural Nouns]
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + was not I were not + Present Participle + ……………………………..
Examples:
- She was not singing a song then.
- They were not making a noise at that time.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Was/Were + Subject + Present Participle + …………………………… ?
Examples:
- Was she combing her hair?
- Were they waiting for the train?
- Were you watching television ?
The Use of the Past Continuous Tense
(a) To describe an action that was in progress at a point of time in the Past or over a period of time in the Past; as—
- She was having her breakfast at 8 a.m. yesterday.
- At seven o’clock this morning, Mukul was doing his homework.
- The boys were flying kites.
- The girls were swimming in the lake.
- What were you doing in the morning yesterday?
(b) To describe an action that was in progress when another action took place; as—
- I was taking bath when the postman knocked at the door.
- She was sleeping when the phone rang.
(c) To describe two actions going on at the same time in the past; as—
- When Rome was burning, Nero was playing on the fiddle.
- Father was reading newspaper, while mother was peeling vegetables.
(d) To show gradual development of a happening; as—
- It was getting colder.
- The child was growing like a mimosa plant.
(e) To express disapproval/irritation at a frequently repeated past action; as—
- The servant was continually asking for hike in salary.
- She was always quarrelling with her husband.
- Those students were constantly asking foolish questions.
[The adverbs ‘always’, ‘constantly’, ‘continually’ indicate the frequent repetition of action]
EXERCISE 2
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct Past Tense forms of the verbs given in brackets:
- When you telephoned me, we …………………………….. (play).
- I saw her as I …………………………….. (pass) the street.
- She came into the room while I …………………………….. (write)
- I …………………………….. (rest) on the roof when it started raining.
- She found that the milk …………………………….. (boil) over.
- The dog …………………………….. (limp) because it was wounded.
- We ……………………………..just (leave) when it began to rain.
- He …………………………….. (cross) the road when a car hit him.
- I dropped my watch as I …………………………….. (wind) it.
- She jumped off the train, while it ……………………………..(move).
- His sister was reading, while he …………………………….. (sleep).
- While Anju was singing, Manju ……………………………..(dance).
- Rohit ……………………………..(read) a magazine when the bell rang.
- Who ……………………………..(talk) to you when I joined you?
- What you …………………………….. (do) all day yesterday?
Answers:
1. were playing, 2. was passing, 3. was writing, 4. was resting, 5. was boiling, 6. was limping, 7. were just leaving, 8. was crossing, 9. was winding, 10. was moving, 11. was sleeping, 12. was dancing, 13. was reading, 14. was talking, 15. were (you) doing.
3. THE PAST PERFECT TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + had + Past Participle (V3 or Third form of the Verb).
Examples:
- I had finished my work before sunset.
- They had reached here when you arrived.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + had not + Third form of the verb
Examples:
- They had not solved the sums by then.
- He had not left the office when I reached there.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Had + Subject + Third form of the verb + …………………….. ?
Examples:
- Had you ever been to Kashmir before?
- Had she not made coffee before the guests arrived?
The Use of the Past Perfect Tense
(a) To express an action completed in the past with the words already, before, never, ever, still, etc.’, as—
- I had never visited Cochin before.
- The guests had already left.
(b) To describe an action which was completed before another action took place in the past; as—
- The patient had died before the doctor arrived.
- We went to school after the rain had stopped.
- They had cleaned the rooms when the guests dropped in.
Note. The longer/completed action is reported in the Past Perfect Tense while the shorter action which took place later is reported in Simple Past Tense.
(c) To express an unfulfilled wish/hope/intention etc. (with the verbs hope, wish, want, intend etc).
- She had wished to become a doctor.
- I had hoped to win the first prize.
- He had intended to buy this hotel.
(d) To express an unfulfilled condition in the past; as—
- If she had worked hard, she would have passed.
- If we had hired a taxi, we would have caught the train.
- If you had asked me, I would have helped you.
EXERCISE 3
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of verbs given in brackets:
- The train …………………… (leave) before I reached the station.
- The guard refused us entry till he …………………… (examine) our pass.
- He told me her name after she ……………….. (disappear).
- Before I ………………….. (know) him, he lived in Delhi.
- We …………………… (not brush) our teeth till the servant brought fresh water.
- Scarcely he …………………… (step) out when it began to rain.
- She …………………… (not pay) her fee till yesterday.
- He …………………… (not revise) the course till then.
- She …………………… (finish) her work already.
- After I …………………… (take) rest I started reading.
- The accident …………………… (occur) before you came.
- When he …………………… (sleep) for two hours, I woke him up.
- They left the hotel when they …………………… (take) meals.
- Harit reached the school after the bell …………………… (go).
- Rohit’s father wished he…………………… (pay) more attention to his son’s progress at school.
- I wish I …………………… (accept) the offer.
- I …………………… (never see) such a fine painting.
- Hardly he …………………… (step) out when it began to rain.
- He thanked the audience after he …………………… (finish) his talk.
- The maid …………………… (not wash) the vegetables before mother arrived.
Answers:
1. had left 2. had examined 3. had disappeared 4. had known 5. had not brushed 6. had (he) stepped 7. had not paid 8. had not revised 9. had finished 10. had taken 11. had occurred 12. had slept 13. had taken 14. had gone 15. had paid 16. had accepted 17. had never seen 18. had (he) stepped 19. had finished 20. had not washed.
4. THE PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + had been + Present Participle (V1 + ing)
Examples:
- She had been living in Chandigarh before she moved to Delhi.
- Kapil had been playing cricket since childhood.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + had not been + Present Participle (V1+ ing) ……..
Examples:
- She had not been trying to get a job.
- It had not been raining heavily for a week.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Had + Subject + been + Present Participle (V1 + ing)… ?
Examples:
- Had she been waiting for us since 2.00 p.m.?
- Had he been suffering from fever since Monday?
The Use of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
To describe an action which continued in the past for a given period of time; as—
- We had been reading for two hours when you came.
- The gardener had been watering the plants since morning.
EXERCISE 4
(Solved)
- I ……………… (read) for an hour when the lights went off.
- He ……………… (try) to solve the problems for two hours before he found the answer.
- By 10 p.m. he was tired because he ……………… (work) since dawn.
- They ……………… (wait) for the bus for an hour before it came.
- He ……………… (sleep) for an hour when I went to his house.
- The doctor ……………… (treat) the patient for three weeks before she died.
- The farmers ……………… (plough) their fields for two months before it rained.
- We ……………… (watch) the match for an horn* when it began to rain.
- Ravi ……………… (look) for his pen for two hours when he found it in his pocket.
- The workers …………….. (raise) slogans since morning when the police arrested them.
Answers:
1. had been reading 2. had been trying 3. had been working 4. had been waiting 5. had been sleeping 6. had been treating
7. had been ploughing 8. had been watching 9. had been looking 10. had been raising.
POINTS TO REMEMBER
- Use Simple Present (First Form of the Verb) for
(i) habitual or oft-repeated actions.
(ii) universal truths or natural states.
(iii) permanent states.
(iv) future planned action. - Use Present Continuous (is/am/are + V1 + ing ) for
(i) an action in progress at the present time.
(ii) temporary state
(iii) definite arrangements for future
(iv) speaker’s disapproval of an oft-repeated action. - Use Present Perfect (has/have + V3) for
(i) an action just completed
(ii) an action/experience of past having bearing on present.
(iii) a past action, the time of which is not given.
(iv) a past action, which is still in progress. - Use Simple Past (Second Form of the Verb) for
(i) past habits/routines.
(ii) a series of past actions.
(iii) action occurring in the past, the time of which is given.
(iv) the action has ended and has no connection with the present. - Use Past Continuous (was / were + V1 + ing) for
(i) an action in progress in the past.
(ii) two actions in progress simultaneously.
(iii) an action in progress when another takes place. - Use Past Perfect (had + V3) for
(i) an action completed in the past before another past action.
(ii) an unfulfilled condition/wish/hope or intention.
Students often feel puzzled when a sentence conveys two actions. The following tips will be useful for them:
(a) Two past actions occur at the same time. Use Simple Past for both e.g.
When the police fired, the mob dispersed.
(b) An action in progress in the past when another action took place.
Use Past Continuous for the action in progress in the past.
Use Simple Past for action taking place in between; as—
I was taking my breakfast, when the door bell rang.
(c) Two past actions in progress simultaneously: Use Past Continuous for both the actions; as—
The players were playing while the spectators were watching them.
(d) An action completed in past before another action occurred.
Use Past Perfect for the completed action and Simple Past for the action that took place afterwards; as—
The students went home after they had finished their work.
CBSE Class 11 English Grammar – Tenses (The Future Tense)
1. THE SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
Remember we don’t have any form of the verb to convey future directly. For example, we use the first form of the Verb to convey Simple Present while the second form is used to express the Simple Past. The third form of the verb is the Past Participle form and is used to form perfect tenses, passive voice and other constructions.
Ways of Expressing Future
There are a variety of ways to express the Future. Some of them are listed below:
- the simple present Tense; as—
Our annual function takes place on the 15th of this month.
The marriage of my cousin falls on 22nd March. - the present continuous tense; as—
We are holding a poster competition tomorrow.
I am taking my mother to the doctor this evening. - (is/am/are) + going to + the first form of the verb; as,
We are going to buy a car before Diwali.
It is going to rain in torrents. - be + about to + the first form of the verb; as—
The meeting is about to start.
The chief guest is about to reach. - be + to + first form of the verb; as—
He is to go to Patna for a conference on Monday.
I am to attend an urgent meeting tomorrow. - shall/will + the first form of the verb.
It is the most popular way of expressing future. [For details, see below]
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + shall I will + First Form of the Verb.
‘Shall’ with the First Person and ‘Will’ with the ‘Second and Third Persons’ show simple future.
Example:
- I shall go to Delhi tomorrow.
- He will help you.
- We shall win the match.
- It will rain today.
- They will return by Monday.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + shall I will + not + First Form of the Verb.
Example:
- You will not leave till I return.
- We shall not play the match if it rains.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Shall/Will + Subject + First Form of the Verb …………………….?
Examples:
- Shall I open the window?
- Will you go to Delhi tomorrow.
Note. For other uses of ‘shall’ and ‘will’, please consult the chapter on ‘Modals’.
EXERCISE 1
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs given in brackets.
- He ……………….. (be) sixteen next March.
- I ……………….. (go) to school tomorrow.
- When the bell rings, the students ……………….. (go) to their classrooms.
- If she works hard, she ……………….. (get) good marks.
- I ……………….. (not take) the test tomorrow.
- The teacher ……………….. (give) us a test tomorrow?
- I ……………….. (carry) your luggage to the train?
- I hope you ……………….. (help) me.
- I……………….. (pass) the salt?
- You ……………….. (ring) the bell?
- What we ……………….. (do) now?
- He ……………….. (go) home tomorrow.
- I ……………….. (finish) this work tomorrow.
- When you are in bed I ……………….. (be) at work.
- She ……………….. (attend) the party if she is invited.
- I ……………….. (return) the book before he asks for it.
- Unless you mend your ways, you ……………….(not succeed).
- He……………….. (purchase) a car when he gets promotion.
- Unless you study harder, you ……………….. (not get) good marks.
- When she returns, she ……………….. (tell) you the whole story.
Answers:
1. will be 2. shall go 3. will go 4. will get 5. shall not take 6. will give 7. shall (I) carry 8. will help 9. shall (I) pass 10. will (you) ring 11. shall (we) do 12. will go 13. shall finish 14. shall be 15. will attend 16. shall return 17. will not succeed 18. will purchase 19. will not get 20. will tell.
2. THE FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + will I shall + be + Present Participle (V1 + ing)
Examples:
- We shall be playing football at this time tomorrow.
- He will be sleeping at 6 a.m.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + will /shall + not + be + (V1 + ing).
Examples:
- I shall not be going to school on Sunday.
- You will not be waiting for us after 9 p.m.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. shall twill + Subject + be + Present Participle (V1 + ing)……………………. ?
Examples:
- Shall I be meeting her tomorrow?
- Will they be earning a lot of money next year?
The Use of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
(а) To describe an action that will be in progress at a given point of time in the future; as—
- We shall be taking our test at 9.30 a.m. tomorrow.
- What will you be doing to-night?
(b) To refer to an event that is expected to take place in the normal course. It suggests that something is expected to happen.
- We shall be visiting him tomorrow.
- The chief guest will be arriving soon.
EXERCISE 2
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs given in brackets.
- The farmers………………..(water) their fields in the morning.
- She ……………….. (sing) after lunch.
- When you call on him, he ……………….. (write) a letter.
- She ……………….. (make) tea in the evening?
- When you arrive, I probably……………….. (weed) the plants.
- At 9 a.m. tomorrow he ……………….. (sit) in his office.
- When I reach Shimla, it probably……………….. (snow) there.
- We ……………….. (enjoy) our holidays next month at Ooty.
- She ……………….. (wait) for us at the appointed hour tomorrow.
- The cook ……………….. (cook) food at this time next Sunday.
Answers:
1. will be watering 2. will be singing 3. will be writing 4. will (she) be making 5. shall (probably) be weeding. 6. will be sitting 7. will (probably) be snowing 8. shall be enjoying 9. will be waiting 10. will be cooking.
3. THE FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + will I shall + have + Past Participle (V3)
Examples:
- I shall have finished this book before 5 p.m.
- She will have left the country by the end of the month.
- They will have built the dam before the rainy season sets in.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + will/shall + not have + Past Participle (V3)………………………….
Examples:
- I shall not have read your letter by that time.
- He will not have returned home before she gets there.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. Shall/Will + Subject + have + Past Participle (V3)………………………….?
Examples:
- Will they have crossed the river safely?
- Shall I have completed my work by evening?
The Use of the Future Perfect Tense
To describe an action that will be completed at some point of time in the future; as,
- She will have reached there by evening.
- The train will have left by the time we reach the station.
EXERCISE 3
(Solved)
Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the verbs given in brackets.
- The workers ………………………. (complete) this task by next month.
- I ……………………… (revise) my course by tomorrow.
- The patient ……………………….. (die) before the doctor arrives.
- The shopkeepers ………………………. (close) their shops when we reach there.
- I………………………. (go) to bed by the time father arrives from Chennai.
- Hari ……………………… (finish) this job till lunch tomorrow.
- I ……………………… (take) meals by the time you come back.
- The farmers ………………………. (plough) their fields before the sun sets.
- We……………………… (start) on our journey before the day dawns.
- The bank………………………. (open) when we reach there.
Answers:
1. will have completed 2. shall have revised 3. will have died 4. will have closed 5. will have gone 6. will have finished
7. shall have taken 8. will have ploughed 9. shall have started 10. will have opened.
4. THE FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
(a) Statements
Form. Subject + shall I will + have been + Present Participle (V1 + ing)
Examples:
- I shall have been solving sums since morning.
- She will have been washing clothes for two hours.
(b) Negative Sentences
Form. Subject + shall /will + not + have been + Present Participle (V + ing)
Examples:
- I shall not have been sitting idle for a week.
- They will not have been wasting their time since morning.
(c) Interrogative Sentences
Form. shall /will + Subject + have been + Present Participle +……………………….. ?
Examples:
- Shall we have been waiting since morning?
- Will the fishermen have been catching fish before the sun rises?
The Use of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense
To describe an action that will be in progress even after a given point of time in the future: as,
By the end of March I shall have been working in this branch for two years.
Note. This tense is no longer in use nowadays.
EXERCISE 16
(Solved)
Supply correct form of verbs given in brackets:
- By next month we …………………….. (live) in this city for ten years.
- The team …………………….. (practise) for an hour before the month begins.
- She …………………….. (do) her sums for ten days by tomorrow.
- The guests …………………….. (arrive) since morning by this time tomorrow.
- The child …………………….. (sleep) for three hours before his mother returns from work.
Answers:
1. shall have been living 2. will have been practising 3. will have been doing 4. will have been arriving 5. will have been sleeping.
Related Links