Conic Sections : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Conic Sections
Circle
A circle is the set of all points in a plane, which are at a fixed distance from a fixed point in the plane. The fixed point is called the centre of the circle and the distance from centre to any point on the circle is called the radius of the circle.
The equation of a circle with radius r having centre (h, k) is given by (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2.
The general equation of the circle is given by x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 , where, g, f and c are constants.
- The centre of the circle is (-g, -f).
- The radius of the circle is r = g2+f2−c−−−−−−−−−√
The general equation of the circle passing through origin is x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy = 0.
The parametric equation of the circle x2 + y2 = r2 are given by x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, where θ is the parametre and the parametric equation of the circle (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2 are given by x = h + r cos θ, y = k + r sin θ.
Note: The general equation of the circle involves three constants which implies that at least three conditions are required to determine a circle uniquely.
Parabola
A parabola is the set of points P whose distances from a fixed point F in the plane are equal to their distance from a fixed line l in the plane. The fixed point F is called focus and the fixed line l is the directrix of the parabola.
Main Facts About the Parabola
| Forms of parabola | y2= 4ax | y2 = -4ax | x2 = 4ay | x2 = -4ay |
| Axis of parabola | y = 0 | y = 0 | x = 0 | x = 0 |
| Directrix of parabola | x = -a | x = a | y = -a | y = a |
| Vertex | (0, 0) | (0, 0) | (0, 0) | (0, 0) |
| Focus | (a, 0) | (-a, 0) | (0, a) | (0, -a) |
| Length of latus rectum | 4a | 4a | 4a | 4a |
| Focal length | |x + a| | |x – a| | |y + a| | |y – a| |
Ellipse
An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane such that the sum of whose distances from two fixed points is constant.
or
An ellipse is the set of all points in the plane whose distances from a fixed point in the plane bears a constant ratio, less than to their distance from a fixed point in the plane. The fixed point is called focus, the fixed line a directrix and the constant ratio(e) the eccentricity of the ellipse. We have two standard forms of ellipse i.e.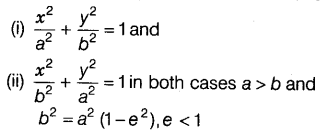
Main Facts about the Ellipse
Hyperbola
A hyperbola is the locus of a point in a plane which moves in such a way that the ratio of its distance from a fixed point in the same plane to its distance from a fixed line is always constant which is always greater than unity. The fixed point is called the focus, the fixed line is called the directrix and the constant ratio, generally denoted bye, is known as the eccentricity of the hyperbola.
We have two standard forms of hyperbola i.e.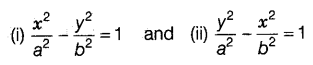
Main Facts About Hyperbola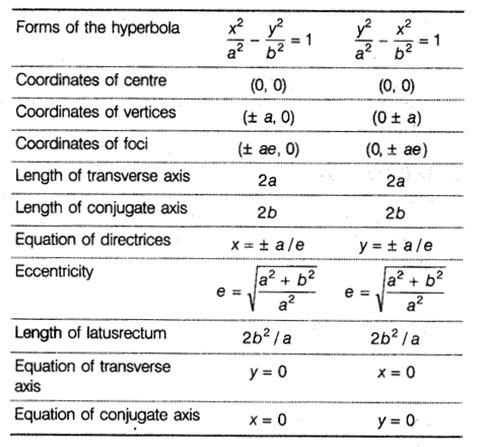
Conic Sections Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
The locus of the point from which the tangent to the circles x² + y² – 4 = 0 and x² + y² – 8x + 15 = 0 are equal is given by the equation
(a) 8x + 19 = 0
(b) 8x – 19 = 0
(c) 4x – 19 = 0
(d) 4x + 19 = 0
Answer
Answer: (b) 8x – 19 = 0
Hint:
Given equation of circles are x² + y² – 4 = 0 and x² + y² – 8x + 15 = 0
Now, the required line is the radical axis of the two circles are
(x² + y² – 4) – (x² + y² – 8x + 15) = 0
⇒ x² + y² – 4 – x² – y² + 8x – 15 = 0
⇒ 8x – 19 = 0
Question 2.
The perpendicular distance from the point (3, -4) to the line 3x – 4y + 10 = 0
(a) 7
(b) 8
(c) 9
(d) 10
Answer
Answer: (a) 7
Hint:
The perpendicular distance = {3 × 3 – 4 × (-4) + 10}/√(3² + 4²)
= {9 + 16 + 10}/√(9 + 16)
= 35/√25
= 35/5
= 7
Question 3.
A man running a race course notes that the sum of the distances from the two flag posts from him is always 10 meter and the distance between the flag posts is 8 meter. The equation of posts traced by the man is
(a) x²/9 + y²/5 = 1
(b) x²/9 + y2 /25 = 1
(c) x²/5 + y²/9 = 1
(d) x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
Answer
Answer: (d) x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
Hint: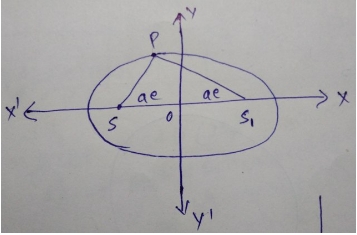
From the question, it is clear that the path traced by the man is an ellipse having its foci at two posts.
Let the equation of the ellipse be
x²/a² + y²/b² = 1
It is given that the sum of the distances of the man from the two flag posts is 10 m
This means that the sum of focal distances of a point on the ellipse is 10 m
⇒ PS + PS1 = 10
⇒ 2a = 10
⇒ a = 5
Again, given that the distance between the flag posts is 8 meters
⇒ 2ae = 8
⇒ ae = 4
Now, b² = a² (1 – e²)
⇒ b² = a² – a² e²
⇒ b² = a² – (ae)²
⇒ b² = 5² – 4²
⇒ b² = 25 – 16
⇒ b² = 9
⇒ b = 3
Hence, the equation of the path is x²/5² + y²/3² = 1
⇒ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
Question 4.
The center of the ellipse (x + y – 2)² /9 + (x – y)² /16 = 1 is
(a) (0, 0)
(b) (0, 1)
(c) (1, 0)
(d) (1, 1)
Answer
Answer: (d) (1, 1)
Hint:
The center of the given ellipse is the point of intersection of the lines
x + y – 2 = 0 and x – y = 0
After solving, we get
x = 1, y = 1
So, the center of the ellipse is (1, 1)
Question 5.
The parametric coordinate of any point of the parabola y² = 4ax is
(a) (-at², -2at)
(b) (-at², 2at)
(c) (a sin²t, -2a sin t)
(d) (a sin t, -2a sin t)
Answer
Answer: (c) (a sin²t, -2a sin t)
Hint:
The point (a sin²t, -2a sin t) satisfies the equation of the parabola y² = 4ax for all
values of t. So, the parametric coordinate of any point of the parabola y² = 4ax is
(a sin²t, -2a sin t)
Question 6.
The equation of parabola with vertex at origin the axis is along x-axis and passing through the point (2, 3) is
(a) y² = 9x
(b) y² = 9x/2
(c) y² = 2x
(b) y² = 2x/9
Answer
Answer: (b) y² = 9x/2
Hint:
A parabola with its axis along the x-axis and vertex(0, 0) and direction x = -a has the equation:
y² = 4ax ………….. 1
Given, point (2,3) lies on the parabola,
⇒ 3² = 4a × 2
⇒ 9 = 4a × 2
⇒ 9/2 = 4a
From equation 1, we get
y² = (9/2)x
⇒ y² = 9x/2
This is the required equation of the parabola.
Question 7.
At what point of the parabola x² = 9y is the abscissa three times that of ordinate
(a) (1, 1)
(b) (3, 1)
(c) (-3, 1)
(d) (-3, -3)
Answer
Answer: (b) (3, 1)
Hint:
Given, parabola is x² = 9y
Let P(h, k) is the point on the parabola such that abscissa is 3 times the ordinate.
So, h = 3k ……… 1
Since P(h, k) lies on the parabola
So, h² = 9k ……… 2
From equation 1 and 2, we get
(3k)² = 9k
⇒ 9k² = 9k
⇒ 9k² – 9k = 0
⇒ 9k(k – 1) = 0
⇒ k = 0, 1
When k = 0, h = 0
So k = 1
Now, from equation 1,
h = 3 × 1 = 3
So, the point is (3, 1)
Question 8.
The number of tangents that can be drawn from (1, 2) to x² + y² = 5 is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) More than 2
Answer
Answer: (b) 1
Hint:
Given point (1, 2) and equation of circle is x² + y² = 5
Now, x² + y² – 5 = 0
Put (1, 2) in this equation, we get
1² + 2² – 5 = 1 + 4 – 5 = 5 – 5 = 0
So, the point (1, 2) lies on the circle.
Hence, only one tangent can be drawn.
Question 9.
In an ellipse, the distance between its foci is 6 and its minor axis is 8 then its eccentricity is
(a) 4/5
(b) 1/√52
(c) 3/5
(d) 1/2
Answer
Answer: (c) 3/5
Hint:
Given, distance between foci = 6
⇒ 2ae = 6
⇒ ae = 3
Again minor axis = 8
⇒ 2b = 8
⇒ b = 4
⇒ b² = 16
⇒ a² (1 – e²) = 16
⇒ a² – a² e² = 16
⇒ a² – (ae)² = 16
⇒ a² – 3² = 16
⇒ a² – 9 = 16
⇒ a² = 9 + 16
⇒ a² = 25
⇒ a = 5
Now, ae = 3
⇒ 5e = 3
⇒ e = 3/5
So, the eccentricity is 3/5
Question 10.
If the length of the tangent from the origin to the circle centered at (2, 3) is 2 then the equation of the circle is
(a) (x + 2)² + (y – 3)² = 3²
(b) (x – 2)² + (y + 3)² = 3²
(c) (x – 2)² + (y – 3)² = 3²
(d) (x + 2)² + (y + 3)² = 3²
Answer
Answer: (c) (x – 2)² + (y – 3)² = 3²
Hint:
Radius of the circle = √{(2 – 0)² + (3 – 0)² – 2²}
= √(4 + 9 – 4)
= √9
= 3
So, the equation of the circle = (x – 2)² + (y – 3)² = 3²
Question 11.
The equation of parabola whose focus is (3, 0) and directrix is 3x + 4y = 1 is
(a) 16x² – 9y² – 24xy – 144x + 8y + 224 = 0
(b) 16x² + 9y² – 24xy – 144x + 8y – 224 = 0
(c) 16x² + 9y² – 24xy – 144x – 8y + 224 = 0
(d) 16x² + 9y² – 24xy – 144x + 8y + 224 = 0
Answer
Answer: (d) 16x² + 9y² – 24xy – 144x + 8y + 224 = 0
Hint:
Given focus S(3, 0)
and equation of directrix is: 3x + 4y = 1
⇒ 3x + 4y – 1 = 0
Let P (x, y) be any point on the required parabola and let PM be the length of the perpendicular from P on the directrix
Then, SP = PM
⇒ SP² = PM²
⇒ (x – 3)² + (y – 0)² = {(3x + 4y – 1) /{√(3² + 4²)}²
⇒ x² + 9 – 6x + y² = (9x² + 16y² + 1 + 24xy – 8y – 6x)/25
⇒ 25(x² + 9 – 6x + y²) = 9x² + 16y² + 1 + 24xy – 8y – 6x
⇒ 25x² + 225 – 150x + 25y² = 9x² + 16y² + 1 + 24xy – 8y – 6x
⇒ 25x² + 225 – 150x + 25y² – 9x² – 16y² – 1 – 24xy + 8y + 6x = 0
⇒ 16x² + 9y² – 24xy – 144x + 8y + 224 = 0
This is the required equation of parabola.
Question 12.
The parametric representation (2 + t², 2t + 1) represents
(a) a parabola
(b) a hyperbola
(c) an ellipse
(d) a circle
Answer
Answer: (a) a parabola
Hint:
Let x = 2 + t²
⇒ x – 2 = t² ……….. 1
and y = 2t + 1
⇒ y – 1 = 2t
⇒ (y – 1)/2 = t
From equation 1, we get
x – 2 = {(y – 1)/2}²
⇒ x – 2 = (y – 1)²/4
⇒ (y – 1)² = 4(x – 2)
This represents the equation of a parabola.
Question 13.
The equation of a hyperbola with foci on the x-axis is
(a) x²/a² + y²/b² = 1
(b) x²/a² – y²/b² = 1
(c) x² + y² = (a² + b²)
(d) x² – y² = (a² + b²)
Answer
Answer: (b) x²/a² – y²/b² = 1
Hint:
The equation of a hyperbola with foci on the x-axis is defined as
x²/a² – y²/b² = 1
Question 14.
The equation of parabola with vertex (-2, 1) and focus (-2, 4) is
(a) 10y = x² + 4x + 16
(b) 12y = x² + 4x + 16
(c) 12y = x² + 4x
(d) 12y = x² + 4x + 8
Answer
Answer: (b) 12y = x² + 4x + 16
Hint:
Given, parabola having vertex is (-2, 1) and focus is (-2, 4)
As the vertex and focus share the same abscissa i.e. -2,
parabola axis of symmetry as x = -2
⇒ x + 2 = 0
Hence, the equation of a parabola is of the type
(y – k) = a(x – h)² where (h, k) is vertex
Now, focus = (h, k + 1/4a)
Since, vertex is (-2, 1) and parabola passes through vertex
So, focus = (-2, 1 + 1/4a)
Now, 1 + 1/4a = 4
⇒ 1/4a = 4 -1
⇒ 1/4a = 3
⇒ 4a = 1/3
⇒ a = /1(3 × 4)
⇒ a = 1/12
Now, equation of parabola is
(y – 1) = (1/12) × (x + 2)²
⇒ 12(y – 1) = (x + 2)²
⇒ 12y – 12 = x² + 4x + 4
⇒ 12y = x² + 4x + 4 + 12
⇒ 12y = x² + 4x + 16
This is the required equation of parabola.
Question 15.
If a parabolic reflector is 20 cm in diameter and 5 cm deep then the focus of parabolic reflector is
(a) (0 0)
(b) (0, 5)
(c) (5, 0)
(d) (5, 5)
Answer
Answer: (c) (5, 0)
Hint: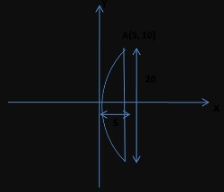
given diameter of the parabola is 20 m.
The equation of parabola is y² = 4ax.
Since this parabola passes through the point A(5,10) then
10² = 4a×5
⇒ 20a = 100
⇒ a = 100/20
⇒ a = 5
So focus of parabola is (a, 0) = (5, 0)
Question 16.
The radius of the circle 4x² + 4y² – 8x + 12y – 25 = 0 is?
(a) √57/4
(b) √77/4
(c) √77/2
(d) √87/4
Answer
Answer: (c) √77/2
Hint:
Given, equation fo the of the circle is 4x² + 4y² – 8x + 12y – 25 = 0
⇒ x² + y² – 8x/4 + 12y/4 – 25/4 = 0
⇒ x² + y² – 2x + 3y – 25/4 = 0
Now, radius = √{(-2)² + (3)² – (-25/4)}
= √{4 + 9 + 25/4}
= √{13 + 25/4}
= √{(13×4 + 25)/4}
= √{(52 + 25)/4}
= √{77/4}
= √77/2
Question 17.
If (a, b) is the mid point of a chord passing through the vertex of the parabola y² = 4x, then
(a) a = 2b
(b) 2a = b
(c) a² = 2b
(d) 2a = b²
Answer
Answer: (d) 2a = b²
Hint:
Let P(x, y) be the coordinate of the other end of the chord OP where O(0, 0)
Now, (x + 0)/2 = a
⇒ x = 2a
and (y + 0)/2 = b
⇒ y = 2b
Now, y² = 4x
⇒ (2b)² = 4 × 2a
⇒ 4b² = 8a
⇒ b² = 2a
Question 18.
A rod of length 12 CM moves with its and always touching the co-ordinate Axes. Then the equation of the locus of a point P on the road which is 3 cm from the end in contact with the x-axis is
(a) x²/81 + y²/9 = 1
(b) x²/9 + y²/81 = 1
(c) x²/169 + y²/9 = 1
(d) x²/9 + y²/169 = 1
Answer
Answer: (a) x²/81 + y²/9 = 1
Hint:
Given a rod of length 12 cm moves with its ends always touching the coordinate axes.
Again given a point P on the rod, which is 3 cm from the end in contact with the x-axis.
It is shown in the figure.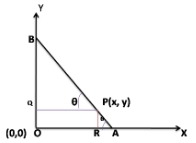
Here AP = 3 cm, AB = 12
Now BP = AB – AP
⇒ BP = 12 – 3
⇒ BP = 9 cm
Again from figure,
∠PAO = ∠BPO = θ (since PQ || OA and are corresponding angles)
Now in ΔBPO,
cosθ = QP/BP
⇒ cosθ = x/9 …………. 1
Again in ΔPAr,
sinθ = PR/PA
⇒ sinθ = y/3 …….. 2
Now square equation 1 and 2 and then add them, we get
cos² θ + sin² θ = x²/81 + y²/9
⇒ x²/81 + y²/9 = 1 (since cos² θ + sin² θ = 1 )
So, the equation of the locus of a point P is x²/81 + y²/9 = 1
Question 19.
The line lx + my + n = 0 will touches the parabola y² = 4ax if
(a) ln = am²
(b) ln = am
(c) ln = a² m²
(d) ln = a² m
Answer
Answer: (a) ln = am²
Hint:
Given, lx + my + n = 0
⇒ my = -lx – n
⇒ y = (-l/m)x + (-n/m)
This will touches the parabola y² = 4ax if
(-n/m) = a/(-l/m)
⇒ (-n/m) = (-am/l)
⇒ n/m = am/l
⇒ ln = am²
Question 20.
The center of the circle 4x² + 4y² – 8x + 12y – 25 = 0 is?
(a) (2,-3)
(b) (-2,3)
(c) (-4,6)
(d) (4,-6)
Answer
Answer: (a) (2,-3)
Hint:
Given, equation fo the of the circle is 4x² + 4y² – 8x + 12y – 25 = 0
⇒ x² + y² – 8x/4 + 12y/4 – 25/4 = 0
⇒ x² + y² – 2x + 3y – 25/4 = 0
Now, center = {-(-2), -3} = (2, -3)