Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Master File Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- NCERT Solutions for – Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Mind Map of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Concept Map of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Past Many 12th Board Years of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Examples and Exercise
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Notes: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Find important notes on CBSE Class 12 Chemistry: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. These notes will give you a quick glance of the chapter and are important for revision purpose.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes on Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids are provided in this article. With this article, you will get a quick glance of the chapter. These quick notes are based the latest CBSE syllabus for CBSE Class 12th Chemistry and are important for CBSE Class 12 board examinations.
The main topics covered in this article are:
o Nature of Carbonyl Group
o Aldehydes and ketones
• Introduction
• Nomenclature
• Preparation
• Physical properties
Nature of Carbonyl Group
Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids are the compounds containing carbon-oxygen double bond (>C=O) called carbonyl group. The carbon and oxygen of the carbonyl group are sp2 hybridised and the carbonyl double bond is comprised of one σ-bond and one π-bond. The π electron cloud is present above and below the plane and is present between carbonyl carbon and oxygen.
Due to high electronegativity of oxygen compared to carbon, the carbonyl group is polar and the dipole is formed.
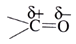
Aldehydes
Aldehydes are the organic compounds in which carbonyl group is attached to one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group.
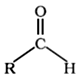
Where R can be an alkyl or aryl group.
Ketones
Ketone are the organic compounds in which carbonyl group is attached to two alkyl group or aryl group or both alkyl and aryl group.
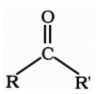
Where R and R’ may be alkyl or aryl groups
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Notes: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Nomenclature of Aldehydes
IUPAC naming system:
• In IUPAC system, the suffix ‘e’ of alkane is replaced by the ‘al’.
For example:
HCHO CH3CHO
Methanal Ethanal
Common naming system:
• The common names of aldehydes are derived from the common names of the corresponding carboxylic acids in which the ending ‘-ic’ is replaced with ‘-aldehyde’of acid with aldehyde.
For example:
HCHO CH3CHO
Formaldehyde Acetaldehyde
Nomenclature of Ketones
IUPAC naming system:
• In IUPAC system, the suffix ‘e’ of alkane is replaced by the ‘one’.
For example:
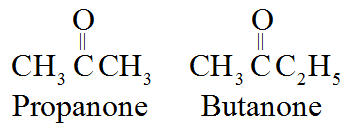
Common naming system:
• The common names of ketones are derived by naming two alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the carbonyl group.
For example:
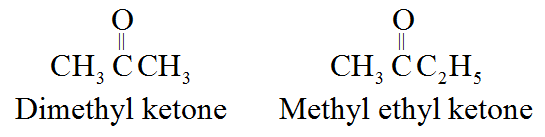
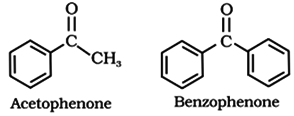
• Alkyl phenyl ketones are usually named by adding the acyl group as prefix to phenone. For example:
Preparation of Aldehyde and Ketones
(a) By oxidation of alcohols:
Oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols in presence or oxidizing agent like K2Cr2O7/H2SO4, KMnO4. CrO3 gives aldehydes and ketones respectively.
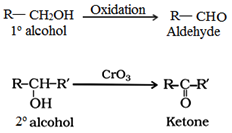
(b) By dehydrogenation of alcohols:
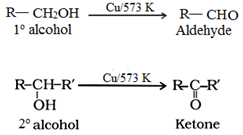
(c) By ozonolysis of alkenes:
Ozonolysis of alkenes followed by reaction with zinc dust and water gives aldehydes, ketones or a mixture of both depending on the substitution pattern of the alkene.
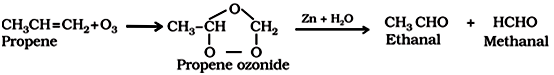
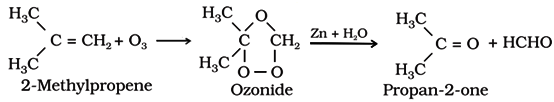
(d) By hydration of alkynes:
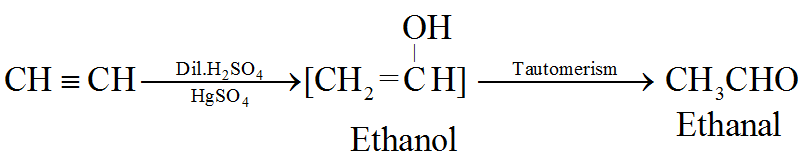
This is a commercial method to prepare ethanal.
All other alkynes gives ketones.
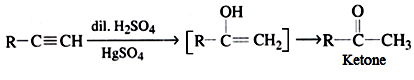
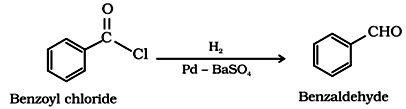
(e) By Rosenmund reduction:
Hydrogenation or acyl chloride over palladium on barium sulphate gives aldehyde.
(f) From nitriles (RCN):
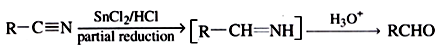
This reaction is called Stephen reaction.
CBSE Class 12 Physics Practice Paper
Preparation of Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(a) By oxidation of methylbenzene:
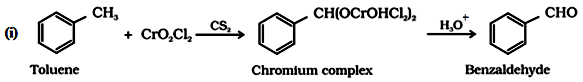
This reaction is called Etard reaction.
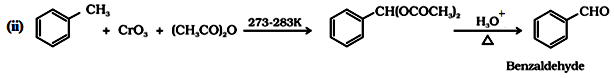
(b) By side chain chlorination of methybenzene followed by hydrolysis:
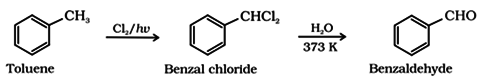
This is a commercial method of manufacture of benzaldehyde.
(iii) By Gatterman – Koch reaction
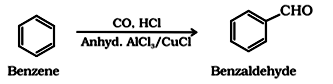
Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
• The intermolecular forces of attraction in aldehydes and ketones are dipole-dipole interactions. These are stronger than van der Waals forces in alkanes but weaker than H- bonding in alcohols. Therefore, the boiling point order is: Alkanes < Aldehyde / Ketones < Alcohols
• Due to the polarity of the carhonyl group, lower aldehydes and ketones are capable of forming hydrogen bond with water and are soluble while solubility decreases down the homologous series as size of R group increases.
• All aldehydes and ketones are fairly soluble in organic solvents like benzene, ether, methanol, chloroform, etc.
In Part-I, we have studied about the nomenclature, methods of preparation and physical properties aldehydes and ketones. In Part-II, we will study the various chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones. These quick notes are prepared strictly according to the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12th Chemistry.
The main topics covered in this part are:
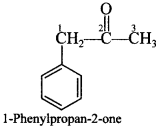
o Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
• Nucleophilic addition reactions
• Reduction
• Oxidation
• Aldol condensation
• Cross-Aldol condensation
• Cannizzaro reaction:
• Perkin’s condensation
• Electrophilic substitution reactions
o Test to Distinguish between Aldehyde and Ketones
o Uses of Aldehyde and Ketones
Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
(a) Nucleophilic addition reactions:
Due to partial positive charge on carbonyl carbon, aldehydes and ketones pose more attraction to the coming nucleophile to add to the carbonyl carbon. Therefore the reactions of aldehydes and ketones are nucleophilic addition reactions.
Aldehydes with one R group is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction than ketones with two alkyl groups at carbonyl carbon. This is due to the +inductive effect of alkyl group.
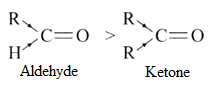
Some important reactions involving the nucleophilic attack are given below:
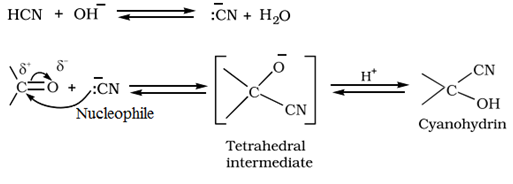
Addition of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) to form cyanohydrins:
Addition of sodium hydrogensulphite (NaHSO3) to form bisulphate addition compound:
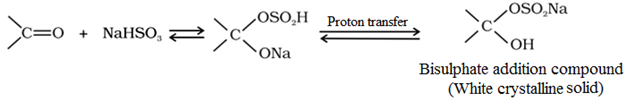
This reaction is used for the separation and purification of aldehydes and ketones. This is because the addition compound formed above is water soluble and can be converted back to the original carbonyl compound by treating it with dilute mineral acid or alkali.
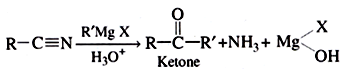
Addition of Grignard reagent (RMgX) to form alcohol:
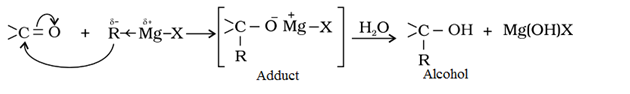
Addition of ammonia and its derivatives:
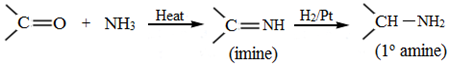
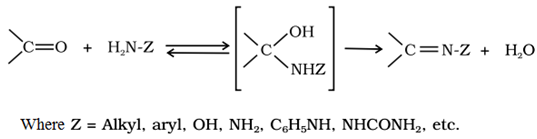
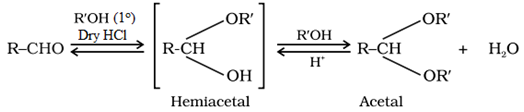
Addition of alcohols:
Aldehydes on addition of monohydric alcohol in presente of dry HC1 forms hemiacetal which further on reacting with one more molecule of alcohol turns to and acetal.
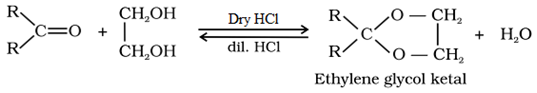
Ketones do not react with monohydric alcohols. Ketones react with ethylene glycol under similar conditions to form cyclic products known as ethylene glycol ketals.
(b) Reduction of aldehydes and ketones:
Reduction to alcohols: Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to primary and secondary alcohols respectively by sodium borohydride (NaBH4) or lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4)
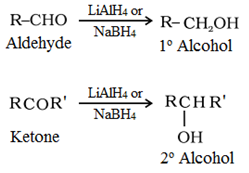
Reduction to alkanes:
Clemmensen reduction:
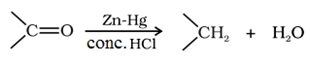
Wolff-Kishner reduction:
![]()
(c) Oxidation of Aldehydes and Ketones:
Due to the presence of hydrogen at carbonyl carbon, aldehydes are easily oxidisable while ketones are difficult to oxidise.
Aldehydes are oxidized to acids in presence of common oxidising agents HNO3, K2Cr2O7, KMnO4.
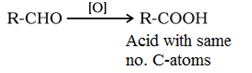
Ketones are oxidized under drastic conditions i.e. with powerful oxidising agents like HNO3, K2Cr2O7/H2SO4, KMnO4/H2SO4 at higher temperature to give a mixture of acids, each containing lesser number of carbon atoms than the parent ketones.
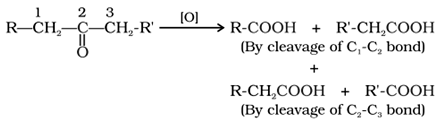
Haloform reaction:
Methyl ketones are oxidized with X2/NaOH to sodium salts of corresponding carboxylic acids having one carbon atom less than that of carbonyl compound.
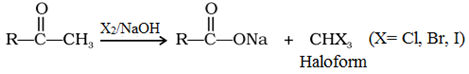
(d) Reactions of aldehydes and ketones due to α -hydrogen:
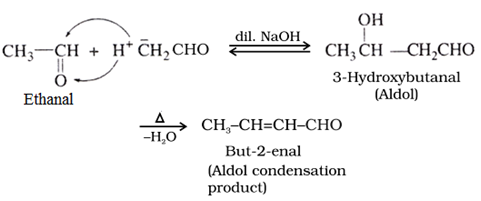
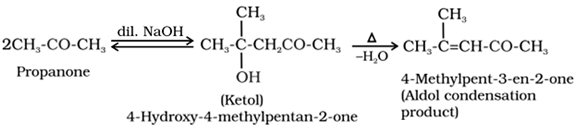
Aldol condensation:
Aldehydes and ketones containing atleast one α -hydrogen undergo self condensation reactions in the presence of dilute alkali to form β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively which on heating in the presence of H+ gives α, β-unsaturated aldehydes or ketones.
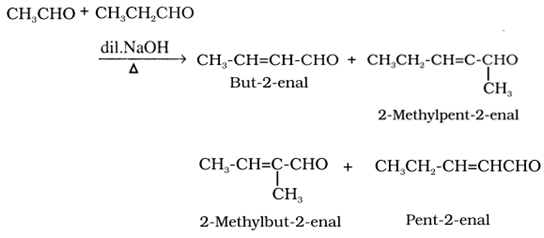
Cross aldol condensation:
When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and / or ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation. If both of them contain α-hydrogen atoms, it gives a mixture of four products
(e) Canizzaro reaction:
Aldehydes which do not have an α -hydrogen atom undergo self-oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali to form alcohol and salt of acid.
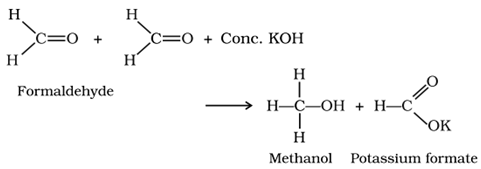
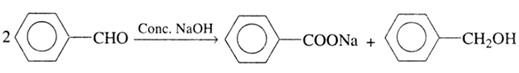
(f) Perkin’s condensation:
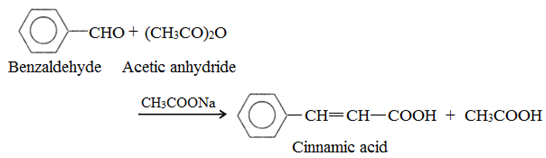
(g) Electrophilic substitution reaction:
Aromatic aldehyde and ketones undergo electrophilic substitution at the meta position. Carbonyl group shows + R effect, therefore acts as a deactivating and meta directing group.
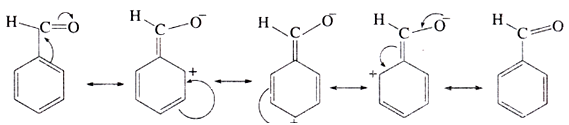
Example of electrophilic susbstitution reaction:
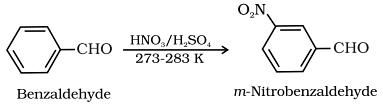
Test to Distinguish between AKdehyde and Ketones
(i) Tollen’s reagent test:
Tollen’s reagent is ammoniacal silver nitrate and is a mild oxidising agent. Aldehydes give silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent.
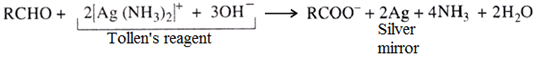
(ii) Fehling’s solution test:
Fehling’s solution is an alkaline solution of CuSO4 (Fehling A) and sodium potassium tartrate, Rochelle salt (Fehling B). Aldehyde gives reddish brown ppt. of brown precipitates of cuprous oxide (Cu2O). Aromatic aldehyde gives poor yield.
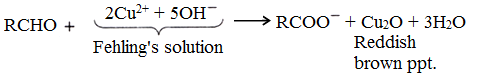
Uses of aldehydes and ketones:
• Aldehyde is mostly used in the formation of resins when it is combined with melamine, urea, phenol etc.
• Formaldehyde in the form of formalin (40%) solution, is used to preserve biological specimens.
• Benzaldehyde is used in perfumery and in dye industries.
• Acetophenone is used as ingredients in flavours and deodorants.
• Ketones are used as solvents and intermediates in the chemical industry.
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry MCQs
Chemistry MCQ Questions for Class 12 Pdf Question 1.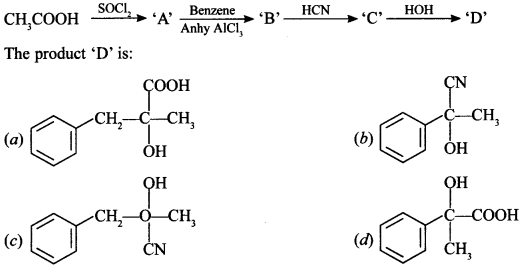
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: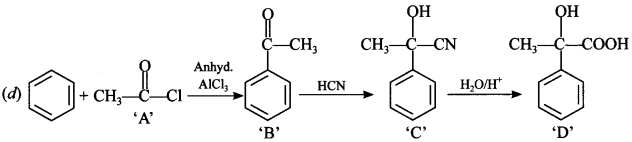
2. Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and cone. HCl is called:
(a) Cope reduction
(b) Dow reduction
(c) Wolff Kishner reduction
(d) Clemensen reduction
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: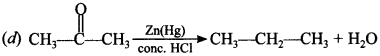
Chemistry MCQs for Class 12 Chapter wise Pdf Question 3. Acetophenone when reacted with base C2H5—ONa, yields a stable product: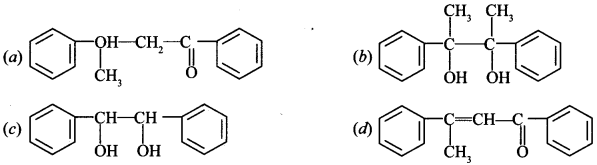
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: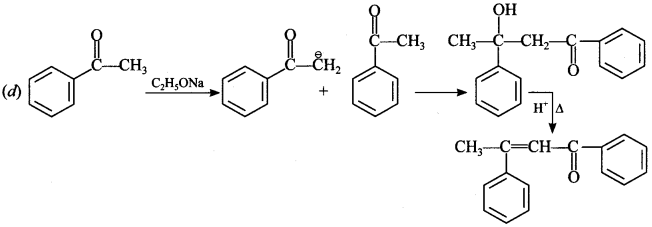
Chemistry MCQs for Class 12 Chapterwise Question 4.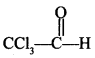
reacts with ch1oobenzene in presence of conc. H2SO4 produces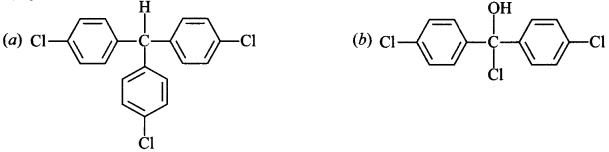

Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: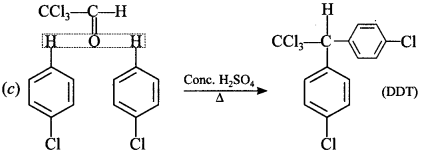
Chemistry MCQs for Class 12 with Answers Pdf Question 5. Propanoic acid with Br2/P4 yields a dibromo product. The structure will be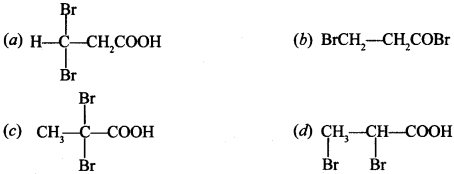
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) ∵ α-hydrogens are replaced by Br atoms.
Chemistry MCQs for Class 12 Question 6.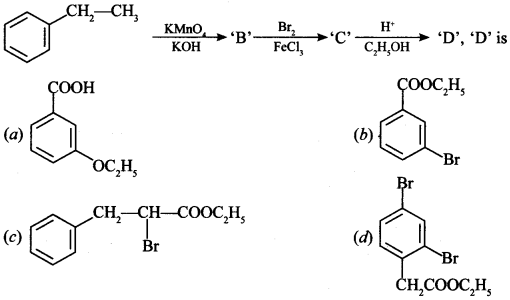
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: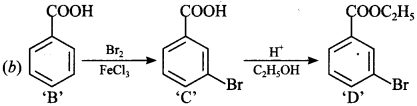
7. CH3CHO and C6H5 CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by
(a) Benedict’s test
(b) Iodoform test
(c) Tollen’s reagent test
(d) Fehling’s solution test
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: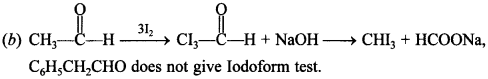
8.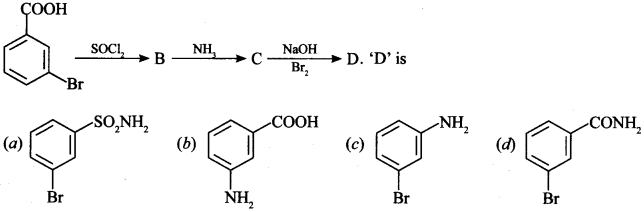
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: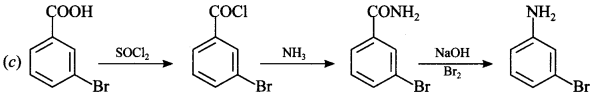
9. Which is most reactive towards Nucleophilic substitution reaction?
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Acetophenone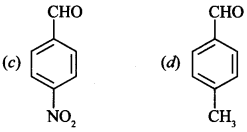
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) ∵ Nitro group is electron withdrawing.
10. Which of the following is not soluble in NaHCO3?
(a) 2, 4, 6-Trinitrophenol
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) o-Nitrophenol
(d) Benzene sulphonic acid
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: (c) o-Nitrophenol is weakly acidic.
11. A single compound of the structure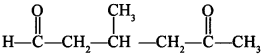
is obtained from ozonolysis of which of the following compound?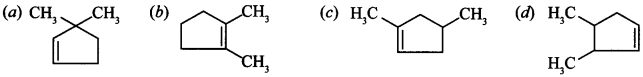
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: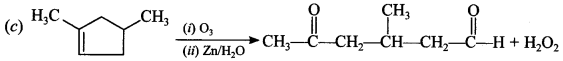
12. Which among the given molecules can exhibit tautomerism?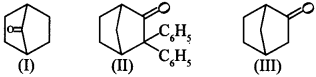
(a) III only
(b) Both I and III
(c) Both I and II
(d) Both II and III
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: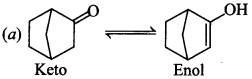
13. The product formed by the reaction of an aldehyde with a primary amine is
(a) Carboxylic acid
(b) Aromatic acid
(c) SchifTs base
(d) Ketone
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: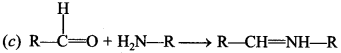
14.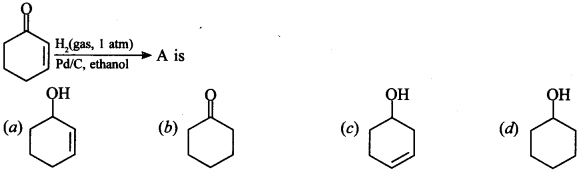
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
15. The correct order of increasing acidic strength is ____________ . [NCERT Exemplarl
(a) Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
(b) Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
(c) Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
(d) Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol < Ethanol
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) It is because C2H5O⊖ is least stable and chloroacetate ion is most stable.
16. Compound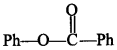
can be prepared by the reaction of __________ . [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Phenol and benzoic acid in the presence of NaOH
(b) Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of pyridine
(c) Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of ZnCl2
(d) Phenol and benzaldehyde in the presence of palladium
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: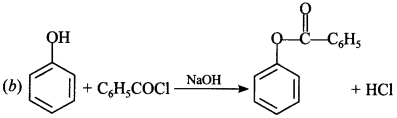
17. Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by ____________ . [NCERT Exemplar]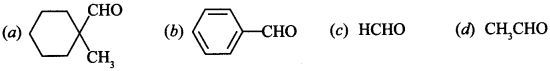
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: (d) Because it has α-hydrogen.
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct. (Q.18 to Q.21)
18. Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation? [NCERT Exemplar]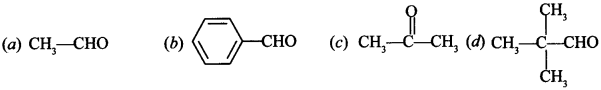
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(b) and (d) because these do not have α-hydrogen.
19. Treatment of compound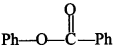
with NaOH solution yields [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Phenol
(b) Sodium phenoxide
(c) Sodium benzoate
(d) Benzophenone
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: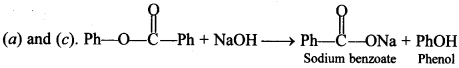
20. Benzophenone can be obtained by ____________ . [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Benzoyl chloride + Benzene + AlCl3
(b) Benzoyl chloride + Diphenyl cadmium
(c) Benzoyl chloride + Phenyl magnesium chloride
(d) Benzene + Carbon monoxide + ZnCl2
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: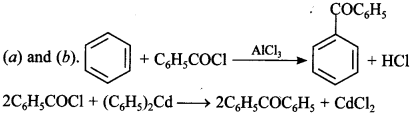
21. Correct order of decreasing reactivity of nucleophillic addition in case of HCHO, CH3CHO and CH3COCH3 is
(a) CH3 COH3 > CH3CHO > HCHO
(b) HCHO > CH3CHO > CH3COCH3
(c) CH3COCH3 > HCHO > CH3CHO
(d) CH3CHO > HCHO > CH3COCH3
Answer
Answer: b
22. The reagent with which both acetaldehyde and acetone react easily is
(a) Fehling’s reagent
(b) Grignard’s reagent
(c) Schiff’s reagent
(d) Tollen’s reagent
Answer
Answer: b
23. ![]()
The above chemical reaction represents
(a) Rosenmund’s reaction.
(b) Cannizaro’s reaction.
(c) Kolbe’s reaction,
(d) Etard’s reaction.
Answer
Answer: b
24. For distinction between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one, which reagent can be employed?
(a) K2Cr2O7/H+
(b) ZnHg/HCl
(c) NaOH/I2
(d) AgNO3/NH4OH
Answer
Answer: c
25. Which of the following will undergo aldol condensation?
(a) CH2 = CHCHO
(b) CH = CCHO
(c) C6H5CHO
(d) CH3CH2CHO
Answer
Answer: d
26. Compound ‘A’ C5H10O forms a phenyl hydrazone and gives a negative Tollen’s reagent test and iodoform test. On reduction with Zn+Hg/HCl, compound A gives n-pentane. The compound ‘A’ is
(a) Primary alcohol
(b) Aldehyde
(c) Secondary alcohol
(d) Ketone
Answer
Answer: b
27. Tert Butyl alcohol can be obtained by treating with CH3MgBr followed by hydrolysis
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) CH3CH2CHO
Answer
Answer: c
28.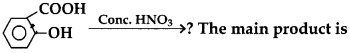
(a) 3-Nitrosalicylic acid
(b) 3, 5-Dinitrosalicylic acid
(c) m-Nitrobenzoic acid
(d) Picric acid
Answer
Answer: d
29. The end product (C) in the following reaction sequence is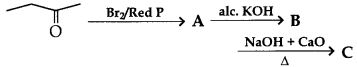
(a) CH3 — CH2 COONa
(b) CH2 = CH2
(c) CH3 — CH3
(d) CH2 = CH-COOH
Answer
Answer: b
30. Benzone acid is weaker than ……… but stronger than ………..
(a) p-toluic acid, o-toluic acid
(b) p-nitrobenzoic acid, p-toluic acid
(c) acetic acid, formic acid
(d) fomic acid, acetic acid
Answer
Answer: d
31. Which of the following is the correct representation for intermediate of nucleophilic addition reaction to the given carbonyl compound (A): [NCERT Exemplar]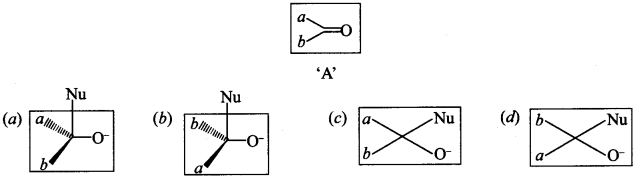
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) and (b) are correct intermediate.
32. Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II. [NCERT Exemplar]
| Column I (Common names) | Column II (IUPAC names) |
| (a) Cinnamaldehyde | (i) Pentanal |
| (b) Acetophenone | (ii) Prop-2-enal |
| (c) Valeraldehyde | (iii) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one – |
| (d) Acrolein | (iv) 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (e) Mesityl oxide | (v) 1-Phenylethanone |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) (iv)
(b) (v)
(c) (i)
(d) (ii)
(e) (iii)
33. Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II. [NCERT Exemplar]
| Column I (Acids) | Column II (IUPAC names) |
| (a) Phthalic acid | (i) Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (b) Oxalic acid | (ii) Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (c) Succinic acid | (iii) Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (d) Adipic acid | (iv) Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (e) Glutaric acid | (v) Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) (ii)
(b) (v)
(c) (iv)
(d) (i)
(e) (iii)
34. Match the reactions given in Column I with the suitable reagents given in Column II. [NCERT Exemplar]
| Column I (Reactions) | Column II (Reagents) |
| (a) Benzophenone → Diphenylmethane | (i) LiAlH4 |
| (b) Benzaldehyde → 1-Phenylethanol | (ii) DIBAL—H |
| (c) Cyclohexanone → Cyclohexanol | (iii) Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCl |
| (d) Phenyl benzoate → Benzaldehyde | (iv) CH3MgBr |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) (iii)
(b) (iv)
(c) (i)
(d) (ii)
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (Q.25 to Q.28)
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(c) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
(e) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
35. Assertion: Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason: It contains sp² hybridised carbon atom. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
36. Assertion: Compounds containing —CHO group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids. Reason: Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(e) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
37. Assertion: The a-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of a-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(d) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement.
38. Assertion: Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizaro reaction.
Reason: Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(c) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
39. Pentan-2-one can be distinguished from pentan-3-one by ____________ test.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Iodoform
40. The pKa of acetic acid is ____________ than that of phenol.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: lower
41. Benzoate ion is more ____________ than acetate ion.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: stable
42. Formic acid does not undergo HVZ reaction because it does not have ____________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: a-hydrogen
43. Phenol does not liberate CO2 with NaHCO3. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True, because it is weakly acidic.
44. All aldehydes turn SchifTs reagent pink. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True
45.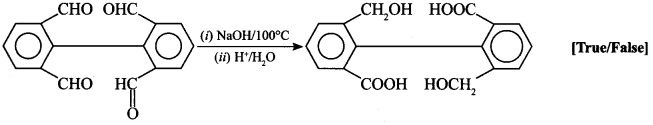
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True
46. 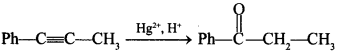 [True/False]
[True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True
47. Write IUPAC name of the following compound: [Delhi 2014(C)]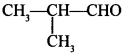
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 2-Methyl propanal.
48. Write the structure of 3-hydroxybutanal. [Foreign 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: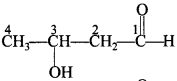
49. Write the structure of 3-methylbutanal. [Delhi 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: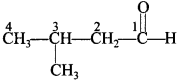
50. Write the IUPAC name of the compound. [Delhi 2014]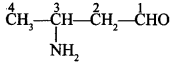
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 3-Amino butanal.
51. Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: [Chennai 2019]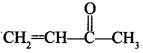
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: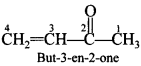
52. Write the structure of the following compound: 3-oxopentanal. [Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: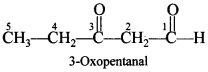
53. Write the structure of p-Methylbenzaldehyde molecule. [AI 2014; Delhi 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: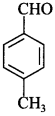
54. Write the IUPAC name of the following compound: [Foreign 2014]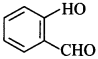
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 2-Hydroxy benzaldehyde.
55. Write the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one. [AI 2014; Delhi 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: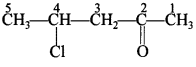
56. Write the structure of 4-methylpent-3-en-2-one. [Foreign 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: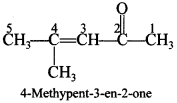
57. Write the IUPAC name of the compound. [Delhi 2014]![]()
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 4-Hydroxy-2-pentanone.
58. Write the IUPAC name of [AI 2011(C)]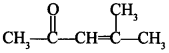
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
59. How will you convert 3-hydroxybutanal from ethanol? Write chemical reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: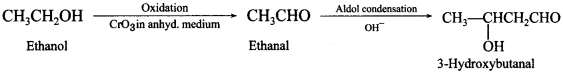
60. Complete the following chemical reaction:![]()
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: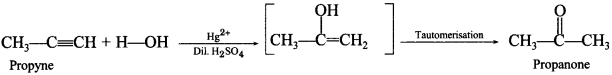
61. Write the chemical equations for the following chemical reactions:
Benzonitrile is converted to acetophenone.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: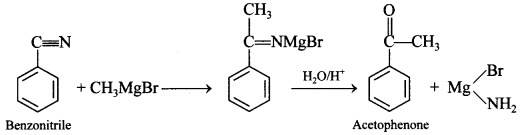
62. Ethanal is soluble in water. Why? [AI 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
63. Which aldehyde does not give Fehling’s solution test?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
64. Write the IUPAC name of compound. [Delhi 2014]![]()
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
65. Write the IUPAC name of the following: [Delhi 2011(C)]![]()
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
66. Write the structure of 2-hydroxy benzoic acid. [AI 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: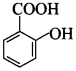
67. Write the structural formula of 2-phenylethanoic acid. [Foreign 2013]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: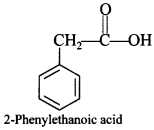
68. Write the IUPAC name of [AI 2011(C)]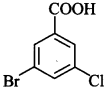
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 3-Bromo-5-chlorobenzoic acid
69. Write IUPAC name of the following compound: [AI 2014(C)]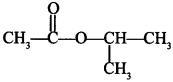
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Isopropyl ethanoate (1-methyl ethyl propanoate).
70. Write the IUPAC name of [Delhi 2011(C)]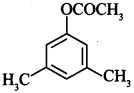
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 3, 5-Dimethylphenylethanoate
71. Higher carboxylic acids are practically insoluble in water. Give reason.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
This is due to the increased hydrophobic interaction of hydrocarbon part.
72. Arrange the following in increasing order of acidic character:
HCOOH, ClCH2COOH, CF3COOH, CCl3COOH
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
HCOOH < ClCH2COOH < CCl3COOH < CF3COOH
73. Compare the strength of following acids:
(i) Formic acid,
(ii) Acetic acid,
(iii) Benzoic acid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
HCOOH > C6H5COOH > CH3COOH
74. Give some industrial uses of methanoic acid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It is used in rubber, textile, leather, dying and electroplating industries.
75. Draw the structural formula of 1-phenylpropan-l-one molecule.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: