Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Master File Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- NCERT Solutions for – Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Mind Map of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Past Many 12th Board Years of Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
Examples and Exercise
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Notes: Amines
This article provides you the revision notes on Class 12 Chemistry: Chapter- Amines, to give you a quick glance of the chapter. These quick notes are prepared strictly according to the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12th Chemistry
This article provides you the revision notes on Class 12 Chemistry: Chapter- Amines, to give you a quick glance of the chapter. These quick notes are prepared strictly according to the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12th Chemistry.
o Amines
• Structure
• Classification
• Nomenclature
• Preparation
• Physical properties
• Basic character
- The key notes of the chapter are as follows:
Amines
Amines are the organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing its one or more hydrogen atoms by alkyl or aryl group.
For example:
CH3NH2 C2H5NH2 C6H5NH2
Methyl Amine Ethyl Amine Aniline
Structure of Amines
Nitrogen atom of amines carries an unshared pair of electrons and is sp3 hybridised with pyramidal shape. Due to the presence of unshared pair of electrons, the angle C–N–E, (where E is C or H) is less than 109.5°.
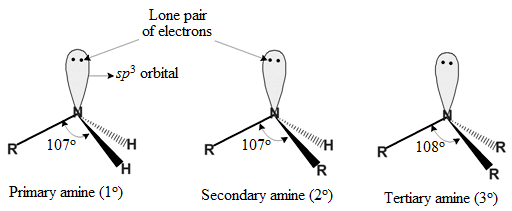
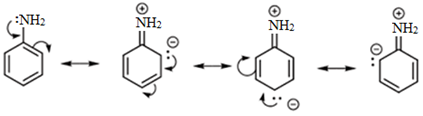
In aromatic amines, the C‒N bond is slightly stronger due to the partial double bond character which arises as a result of delocalisation of lone pair of N with the benzene ring.
Classification of Amines
On the basis of number of hydrogen atoms replaced in NH3 molecule, amines are categorized into three types:
• 1° amine: One hydrogen atom of NH3 is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group.
For example:
CH3NH2
Methyl Amine
• 2° amine: Two hydrogen atoms of NH3 are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups.
For example:
CH3NHCH3
Dimethyl Amine
• 3° amine: All three hydrogen atoms of NH3 are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups.
For example:
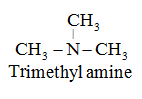
Nomenclature of Amines
Common naming system:
• Aliphatic amines are named by prefixing an alkyl group to a mine, i.e., alkylamine.
For example:
• Secondary and tertiary amines, having two or more similar groups are named by adding prefix ‘di’ or ‘tri’ before the name of alkyl group.
For example:
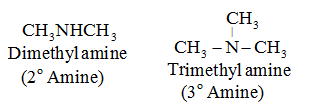
• Aromatic amines are named as derivatives of the parent member, aniline (C6H5NH2).
For example:
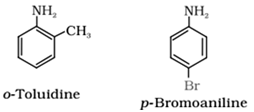
IUPAC naming system:
• Aliphatic or aromatic amines are named by replacing ‘e’ in the end of the parent hydrocarbon by ‘amine’.
For example:
CH3NH2 C6H5NH2
Methanamine Benzenamine
• Amines containing more than one amino groups at different positions in the parent chain, are named by specifying numbers to the carbon atoms bearing –NH2 groups along with attaching a suitable prefix such as di, tri, etc. to the amine. The ending ‘e’ of the hydrocarbon is retained.
For example:
H2N ‒ CH2 ‒ CH2 ‒ NH2
Ethane-1, 2-diamine
Preparation of Amines
1. By reduction of nitro (RNO2) compounds:
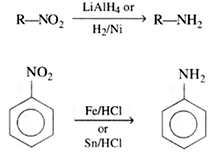
2. By reduction of nitriles (RCN):
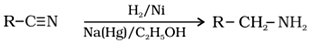
3. By reduction of amides (RCONH2):
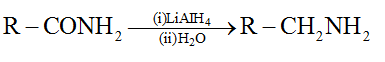
4. By ammonolysis of alkyl halides:
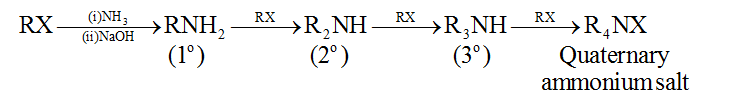
5. Hofmann bromamide reaction:
RCONH2 + Br2 + 4NaOH → RNH2 + 2NaBr + Na2CO3 + 2 H2O
This method gives amine with one carbon less than the parent amide.
6. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis:
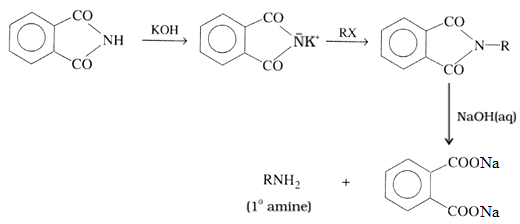
Physical Properties of Amines
• The lower aliphatic amines are gases with fishy smell.
• Primary amines wit three or more carbon atoms are liquid and higher members are all solids.
• Lower amines are soluble in water as they can form hydrogen bonds with water, however the solubility decreases with increase in hydrophobic alkyl group.
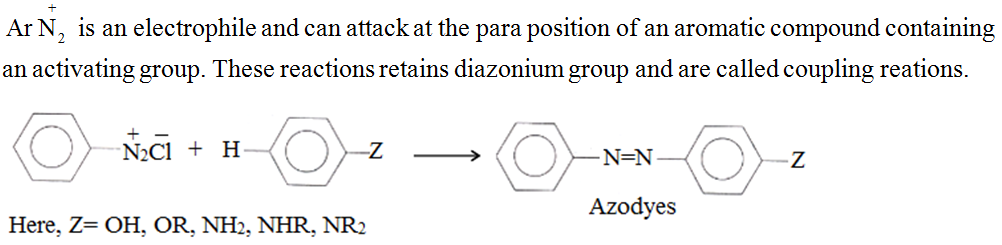
• Amines have a higher boiling point than the hydrocarbon of comparable molecular mass. This is due to their ability to associate via intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
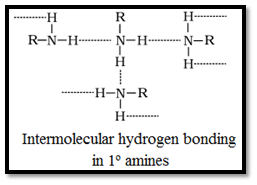
• Boiling points order of various isomeric amines is:
1o > 2o > 3o
Basic strength of amines
Amines act as Lewis bases due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. Basic character of amines can be better expressed in terms of their Kb and pKb values.
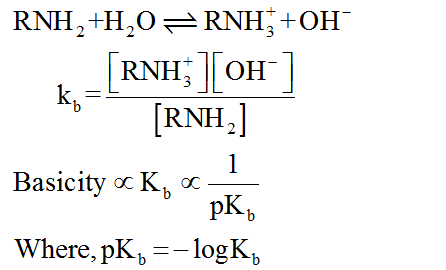
All aliphatic amines are strong bases than NH3 while aromatic amines are weaker bases than NH3 due to the electron withdrawing nature of the aryl group.
o Factors affects the basicity of aliphatic amines are:
• Inductive effect
• Solvation effect
• Steric hinderance
Considering all the above factors the basic strength of methyl substituted amines and ethyl substituted amines in aqueous medium follows the order:
(CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3
(C2H5)2NH > (C2H5)3N > C2H5NH2 > NH3
In Part-II, you will get to know about the various chemical reactions undergone by the amines. Also this part will make you familiar with Diazonium salts. These quick notes are prepared strictly according to the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 12th Chemistry.
The main topics covered in this part are:
• Amines
o Chemical reactions
• Diazonium Salt
o Introduction
o Structure
o Preparation
o Physical properties
o Chemical reactions
• Uses of amines
The key notes of the chapter are as follows:
Chemical Reactions of Amines
1. Reaction with acids:
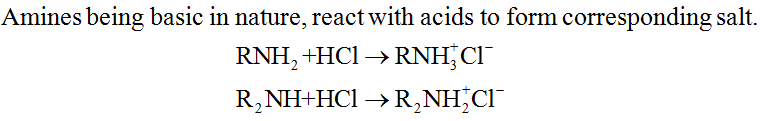
2. Alkylation:
Alkylation of 1o amine generates 2o amine, 3o amine and finally the quaternary salts.
![]()
3. Acylation:
Reaction with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction is known as acylation. The reaction is proceeded by the replacement of hydrogen atom of –NH2 or >N–H group by the acyl group (RCOX).
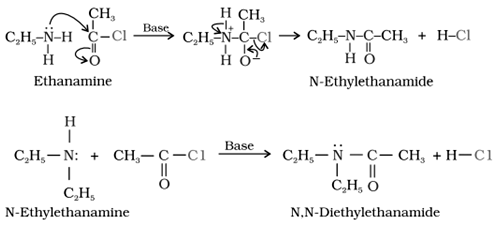
Tertiary (3o) amine cannot be acylated as there is no H bonded to nitrogen.
4. Benzoylation:
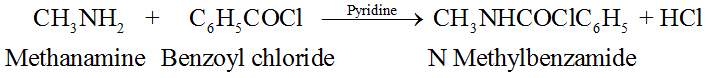
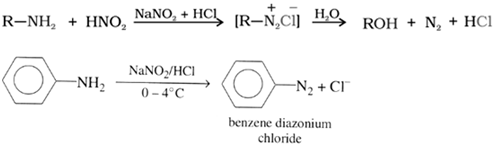
5. Reaction with nitrous acid, HNO2
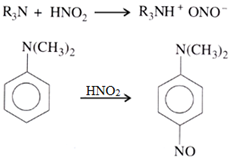
Three classes of amines react differently with nitrous acid
(a) Reaction of 1o amines:
(b) Reaction of 2o amines:
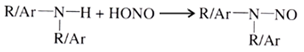
(c) Reaction of 3o amines:
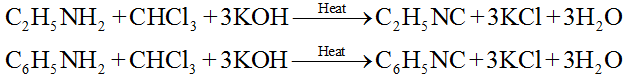
6. Carbylamine reaction:
Primary amine (both aliphatic and aromatic) reacts with CHCl3/KOH to form isocyanides (carbylamines) with unpleasant smell.
7. Reaction with aldehyde and ketones:
1o amines react with aldehydes and ketones to form Schiff’s bases.
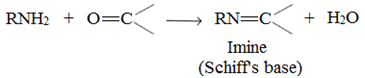
8. Electrophilic substitution reactions
Aniline, due to high electron density at ortho and para-positions, is ortho and para directing towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Some of the electrophilic substitution reactions of aniline are described below:
(a) Bromination:
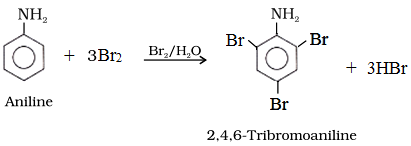
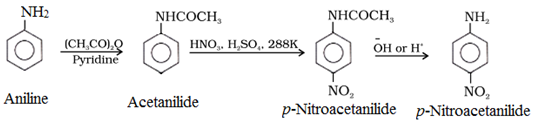
To prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, first acetylation of aniline is carried out with acetic anhydride followed by the desired substitution of the substituted amide which is then hydrolysed to obtain the monosubstituted amine.
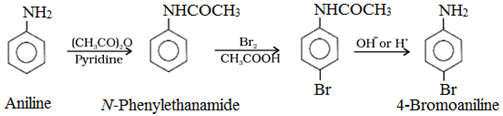
(b) Nitration:
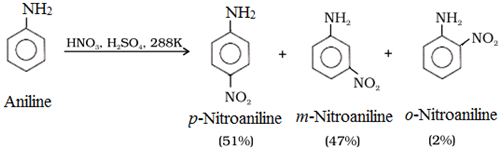
To get p-nitro derivative as major product, acetylation of aniline is carried out with acetic anhydride. Then desired substitution of anilide is carried out followed by hydrolysis of the substituted anilide to the substituted amine.
Diazonium Salts
![]()
Structure of Diazonium Salt
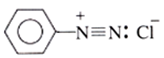
Preparation of Diazonium Salt
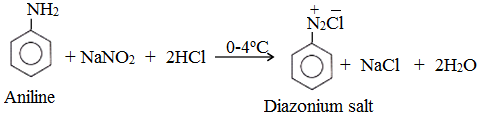
The reaction of preparation of diazonium salt is called Diazotisation.
Physical Properties of Diazonium Salt
• It is a colourless crystalline solid.
• It is readily soluble in water and is stable in cold but reacts with water when warmed.
• It has tendency to explode when dry.
Chemical Reactions of Diazonium Salts
There are two types of reactions given by benzene diazonium chloride.
(1)Substitution reactions involving replacement of diazonium group.
(2) Coupling reactions involving the retention of diazo group acts as an electrophile.
Explanation:
1. Substitution reactions involving replacement of diazonium group:
(a) Replacement by halide or cyanide ion:
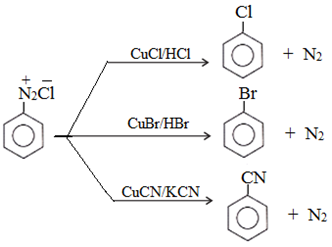
Above reaction taking place in the presence of Cu(I) ion is called Sandmeyer reaction.
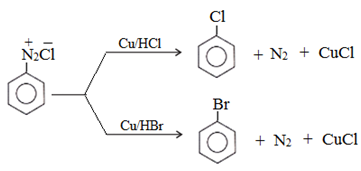
Above reaction taking place in the presence of copper powder is named as Gatterman reaction.
(b) Replacement by iodide ion:
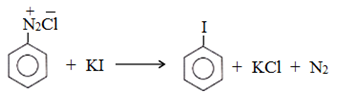
(c) Replacement by fluoride ion:
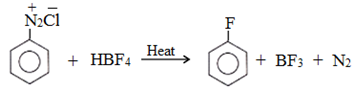
(d) Replacement by H-atom:
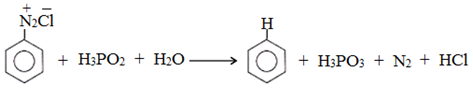
(e) Replacement by hydroxyl group:

(f) Replacement by –NO2 group:
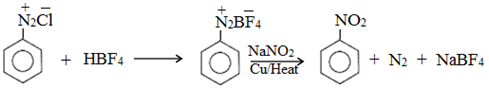
2. Reactions involving retention of diazo group
Coupling recations:
Uses of Amine
• The most important amie is aniline which is used in the synthesis of medicines, dyes, etc
• N , N – Dmethylaniline (DMA) also used in the preparation of Methyl orange and other dyes
• Amines are widely used in developing chemicals for crop protection and water purification
• 1, 6 – Hexamethylenediamine H2N ‒ (CH2)6 ‒ NH2 is used in the production of nylon
• Adrenaline is an amine hormone that prepares the human beings for emergency situation
• Amino acids form the building blocks of proteins in human beings
Amines Class 12 Chemistry MCQs
1.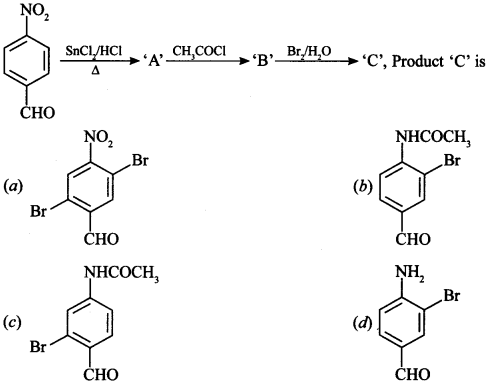
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: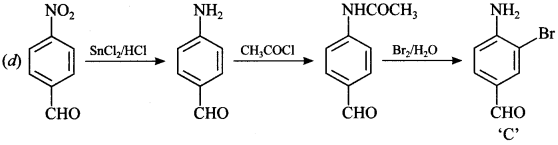
2. The major product of the reaction between /n-dinitro benzene with NH4HS is
(a) p-Dinitro benzene
(b) m-Diamino benzene
(c) m-nitroaniline
(d) p-Diamino benzene
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: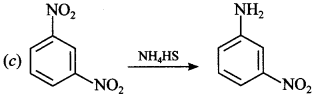
3.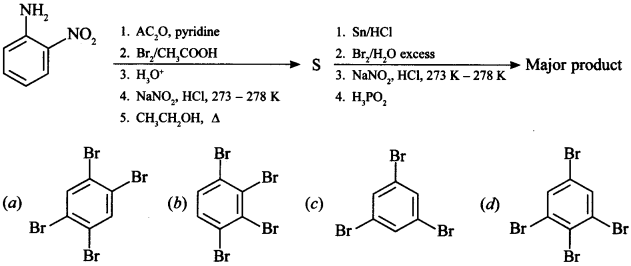
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: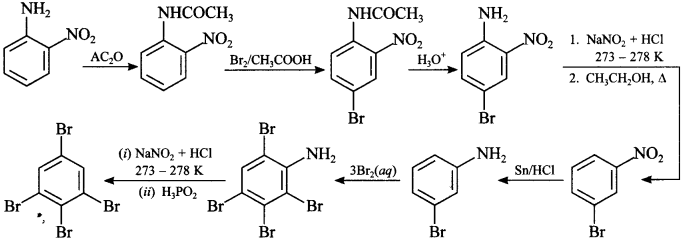
4. An organic compound C7H9N forms clear solution when dissolved in KOH after reacting with C6H5SO2Cl, ‘A’ on diazotisation at 0°C and then reaction with β-naphthol gives orangish red dye. ‘A’ on electrophilic substitution gives single product. ‘A’ is
(a) 4-Methyl aniline
(b) 2-Methyl aniline
(c) 3-Methyl aniline
(d) N-Methyl aniline
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: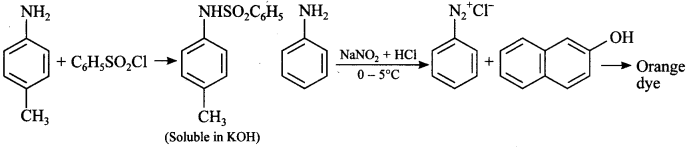
5.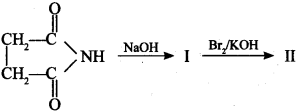
(a) β-Alanine
(b) α-Alanine
(c) Ethylene diamine
(d) Oxamide
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination: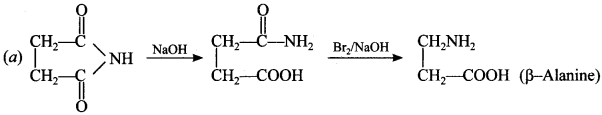
6. The reaction of p-Toluidine with CHCl3 and KOH gives.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) It is carbylamine reaction, leads to formation of isocyanide (carbylamine).
7.![]()
The compound ‘A’ is
(a) propane nitrile
(b) ethane nitrile
(c) nitro methane
(d) methyl isocyanate
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:![]()
8.![]()
The IUPAC name of ‘Y’ is
(a) N-isopropyl methanamine
(b) N-methyl propan-2-amine
(c) N-methyl propanamine
(d) butan-2-amine
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: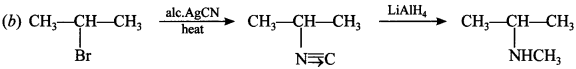
9.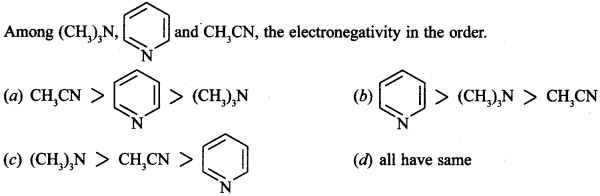
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) sp > sp² > sp³. In CH3C≡N, ‘N’ is sp hybridised, in pyridine sp² hybridised and (CH3)3N, it is sp³ hybridised.
10. The best reagent for converting 2-Phenyl propanamide into 2-phenyl propanamine is
(a) Br2/NaOH
(b) excess of H2
(c) I2/P4
(d) LiAlH4 in ether
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination: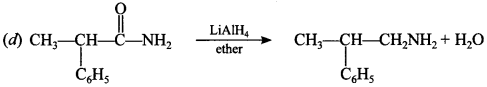
11. Which one of the following can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
(a) Aniline
(b) o-Toluidine
(c) Benzylamine
(d) N-Methyl ethanamine
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: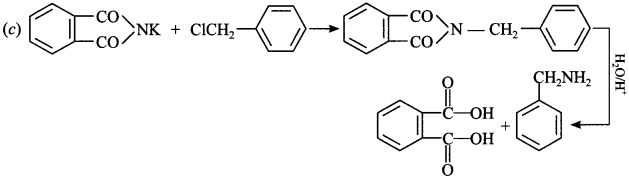
12.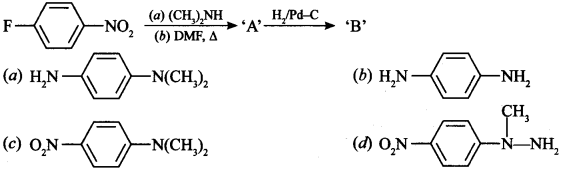
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
13. Diethyl amine, when treated with HN03 gives
(a) Diethyl ammonium nitrite
(b) Ethly alcohol
(c) N-nitroso diethyl amine
(d) Triethyl ammonium nitrite
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:![]()
14. Choose the amide which on reduction with LiAlH4 gives secondary amine.
(a) Ethanamide
(b) N-Methyl ethanamide
(c) N, N-diethyl ethanamide
(d) Benzamid
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: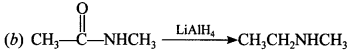
15. 4-Nitrotoluene is treated with bromine to get P. ‘P’ is reduced with Sn/HCl to get compound ‘Q\ ‘Q’ is diazotised and the product is treated with phosphinic acid to get compound ‘R’. ‘R’ is oxidised with alkaline KMn04 to get ‘S’. Compound ‘S’ is
(a) 2-Bromo-4-hydroxy benzoic acid
(b) 2-Bromo benzoic acid
(c) 3-Bromo benzoic acid
(d) 4-Bromo benzoic acid
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: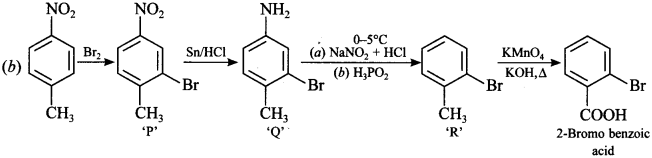
16. In order to prepare a 1° amine from an alkyl halide with simultaneous addition of one CH2 group in the carbon chain, the reagent used as source of nitrogen is ____________ . [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Sodium amide, NaNH2
(b) Sodium azide, NaN3
(c) Potassium cyanide, KCN
(d) Potassium phthalimide, C6H4(CO)2N–K+
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) KCN is used to increase number of carbon atoms.
17. Amongst the given set of reactants, the most appropriate for preparing 2° amine is ____________ . [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) 2° R—Br + NH3
(b) 2° R—Br + NaCN followed by H2/Pt
(c) 1° R—NH2 + RCHO followed by H2/Pt
(d) 1° R—Br (2 mol) + potassium phthalimide followed by H3O+/heat
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
18. The order of basic strength of amines in aqueous solution is
(a) (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > NH3
(b) CH3NH2 > (CH3)2 NH > (CH3)3N > NH3
(c) NH3 > (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2
(d) (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) is correct 2° > 1° > 3° > NH3 because in 3° amines, there is stearic hindrance therefore, lone pair of electron is not readily available.
19. Which of the following is a 3° amine? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) 1-methylcyclohexylamine
(b) Triethyl amine
(c) tert-butylamine
(d) N-methylaniline
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) Triethyl amine (C2H5)3N is tertiary amine.
20. The correct IUPAC name for CH2 = CHCH2 NHCH3 is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Allylmethylamine
(b) 2-amino-4-pentene
(c) 4-aminopent-l-ene
(d) N-methylprop-2-en-l-amine
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) Amino group is preferred over double bond.
21. Which of the following is the weakest Bronsted base? [NCERT Exemplar]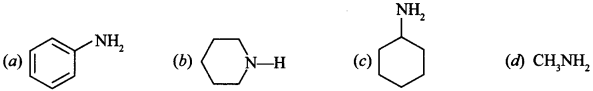
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) Aniline is weakest because C6H5-group is electron withdrawing and there is +ve charge on 3 out of 5 resonating structures.
22. Which of the following reagents would not be a good choice for reducing an aryl nitro compound to an amine? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) H2 (excess)/Pt
(b) LiAlH4 in ether
(c) Fe and HCl
(d) Sn and HCl
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) LiAlH4 is not good reducing agent to reduce nitro group.
23. The correct decreasing order of boiling points among amines and their corresponding acids and alcohols is
(a) R – CH2 NH2 > RCOOH > RCH2OH
(b) RCH2NH2 > RCH2OH > RCOOH
(c) R – CH2OH > R – CH2NH2 > RCOOH
(d) R – COOH > R – CH2OH > R – CH2NH2
Answer
Answer: d
24. Aniline is less basic than ethylamine. This is due to
(a) Conjugation of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring
(b) The insoluble nature of aniline
(c) More Kfc value of aniline
(d) Hydrogen bonding
Answer
Answer: a
25. Primary amine reacts with carbon disulphide and HgCl2 to produce alkyl isothiocyanate. This reaction is
(a) Carbylanine reaction
(b) Hoffmann bromamide reaction
(c) Perkin reaction
(d) Hoffmann mustard oil reaction
Answer
Answer: d
26. Hinsberg’s reagent is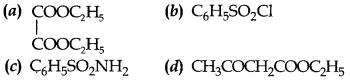
Answer
Answer: b
27. Nitration of aniline is carried out after acylation because
(a) Acylation dectivates the — NH2 group
(b) Oxidation can be prevented
(c) O-and p-products are obtained in good yield
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: d
28. NH2 group in aniline is
(a) Ortho directing
(b) Meta directing
(c) Ortho and para directing
(d) Para directing
Answer
Answer: c
29. Primary and secondary amines cannot be distinguished by
(a) Schiff’s reagent
(b) Carbylamine reaction
(c) Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction
(d) Iodoform test
Answer
Answer: b
30. Which of the following cannot be identified by carbyl amine test?
1. C2H5NH2
2. C6H5NH2
3. C6H5 — NH — C6H5
4. (C2H5)3N
(a) 1, 2
(b) 1, 2, 4
(c) 3, 4
(d) 2, 4
Answer
Answer: c
31.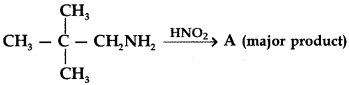
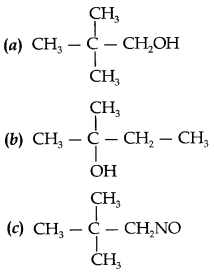
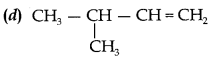
Answer
Answer: b
32.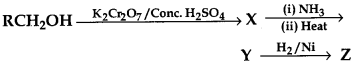
Here, Z is
(a) RCH2 CH2NH2
(b) RCH2NH2
(c) RCH2CONH2
(d) RNH2
Answer
Answer: b
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct. (Q.23 to Q.25)
33. Which of the following cannot be prepared by Sandmeyer’s reaction? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Bromobenzene
(c) Iodobenzene
(d) Fluorobenzene
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(c) and (d). Iodobenzene and fluorobenzene can’t be prepared by Sandmeyer’s reaction.
34. The product of the following reaction is ____________ . [NCERT Exemplar]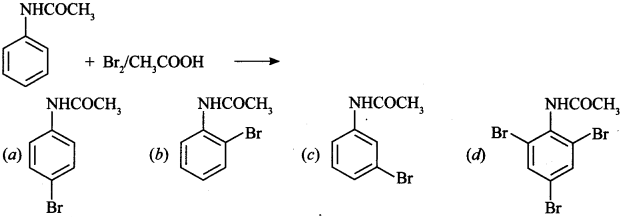
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) and (b) because -NHCOCH3 is o and -directing.
35. Under which of the following reaction conditions, aniline gives p-nitro derivative as the major product? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Acetyl chloride/pyridine followed by reaction with cone. H2SO4+ cone. HNO3.
(b) Acetic anyhdride/pyridine followed by cone. H2SO4 + cone. HNO3.
(c) Dil. HCl followed by reaction with cone. H2SO4 + cone. HNO3.
(d) Reaction with cone. HNO3 + cone. H2SO4.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: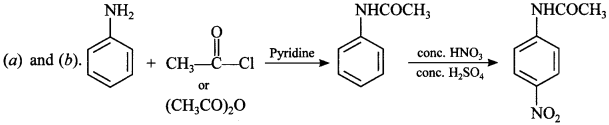
36. Match the compounds given in Column I with the items given in Column II. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) (ii)
(b) (i)
(c) (iv)
(d) (iii)
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (Q.27 and Q.28)
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(c) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong but reason is correct statement. –
(e) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
37. Assertion: Acetanilide is less basic than aniline. [NCERT Exemplar]
Reason: Acetylation of aniline results in decrease of electron density on nitrogen.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
38. Assertion: Only a small amount of HCl is required in the reduction of nitro compounds with iron scrap and HCl in the presence of steam. [NCERT Exemplar]
Reason: FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl during the reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
39. The pKb of N,N-Dimethyl aniline is ____________ than aniline.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: lower
40. -OCH3 ____________ the basic character of amines.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: increases
41. CH3CH2NH2 has ____________ boiling point than (CH3)2NH.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: higher
42. The number of isomers of C7H9N are ____________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: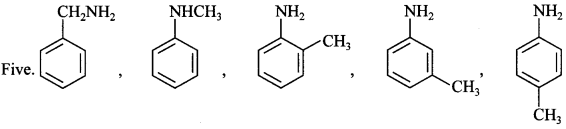
43. Tertiary amines do not react with Hinsberg’s reagent. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
True, because they do not have H attached to Nitrogen.
44. Tertiary amines form salt with HN02 soluble in water [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
True. (CH3)3N + HNO2 → (CH3)3NHNO2
45. Aniline and ethyl amine can be distinguished by Azodye test. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
True. Aniline reacts with NaNO2+ HC;l at 0°C to 5°C and with phenol to give orange azodye, ethyl amine does not.
46. Give the IUPAC name of H2N—CH2—CH2—CH=CH2.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
But-3-en-1 -amine.
47. What is the structure and IUPAC name of the compound, allyl amine?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
48. Give the common and IUPAC name of the compound: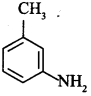
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
3-Methylaniline or 3-Methylbenzenamine is IUPAC name. Common name is w-Toluidine.
49. Write the chemical equations for the following chemical reactions: A primary amine is prepared from a primary alkyl halide.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
RX + NH3 → RNH2 + HX
50. How is aniline obtained from benzoic acid?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: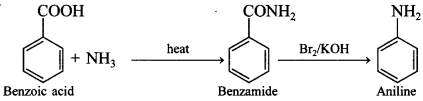
51. How is /n-nitroaniline obtained from nitrobenzene? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: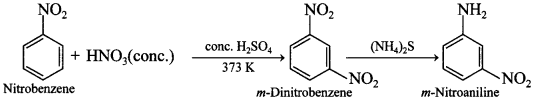
52. Out of CHJNHJ and (CH3)3N, which one has higher boiling point? [Delhi 2014(C)]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
CH3NH2 has higher boiling point.3
53. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of solubility in water:
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2H5NH2 [Delhi 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH2 is the increasing order of solubility in water.
54. Why is an alkylamine more basic than ammonia? [Delhi 2011; Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It is because alkyl groups are electron releasing in alkyl amines, they will increase electron density on ‘N’, therefore, they are more basic than NH3.
55. Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of basic strengths in their aqueous solutions:
NH3, CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N [Delhi 2013,12]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > NH3.
56. Which of the two is more basic and why? [Foreign 2014]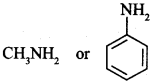
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
CH3NH2 is more basic than aniline because in CH3NH2, —CH3 group is electron releasing, which increases electron density on ‘N’, whereas in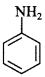 C6H5 group is electron withdrawing which decreases electron density on ‘N’.
C6H5 group is electron withdrawing which decreases electron density on ‘N’.
57. Which of the two is more basic and why? [Similar to CBSE Sample Paper 2018; Foreign 2014]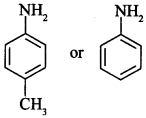
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
p-Toluidine is more basic than aniline because —CH3 group is electron releasing group and increases electron density on ‘N’.
58. Which of the two is more basic and why CH3NH2 or NH3? [Foreign 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
CH3NH2 is more basic than NH3 because methyl group is electron releasing which increases electron density on ‘N’.
59. Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength:
C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5N(CH3)2 [Delhi 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5N(CH3)2 is the increasing order of basic strength because —CH3 group is electron releasing.
60. Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength:
C6H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3, C6H5CH2NH2 [Delhi 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
C6H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5CH2NH2 is the increasing order of basic strength.
61. Arange in decreasing order of basic strength in gas phase:
C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, NH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(C2H5)3N > (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3
62. Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength:
Aniline, p-Nitroaniline, p-Toludine [AI 2015(C)]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
p-Nitroaniline < Aniline < p-Toludine
63. Why do amines react as nucleophiles?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It is due to presence of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen which they can donate and act as nucleophiles.
64. State the reaction taking place when: Bromine water is added to the aqueous solution of aniline. [Delhi 2016]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: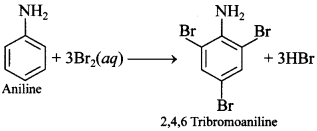
IUPAC name is 2,4,6 Tribromo benzenamine. [Delhi 2016]
65. An organic compound ‘A’ having molecular formula C2H?N on treatment with HN02 gave an oily yellow substance. Identify ‘A’. [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: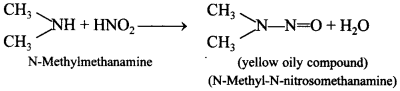
66. Complete the following reaction equation: [Delhi 2015(C)]
C6H5N2CI + H3PO2 + H2O →
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2 + H2O → C6H6 + N2 + HCl + H3PO3
67. Give a chemical test to distinguish between Aniline and Ethanamine. [Uttarakhand 2019]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Add NaNO2 and HCl. Cool it to 0 – 5°C, then add alkaline solution of phenol. Aniline will form orange azodye whereas ethanamine does not.
68. Write one reaction that can be used as a test for primary amines. [Foreign 2011]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
RNH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH > R—N=ifC+ 3KCl + 3H2O is used as a test for primary amine.
Alkyl carbylamine are olfensive smelling compounds.
69. Write a chemical reaction in which the iodide ion replaces the diazonium group in a diazonium salt.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
70. Give the significance of coupling reaction of aryldiazonium salts.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Coupling reaction of aryldiazonium salts with phenol or arylamines involved in the formation of azo dyes.