Solid State : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Electrochemistry
- Master File Electrochemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Electrochemistry
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Electrochemistry
- Mind Map of Electrochemistry
- Concept Map of Electrochemistry
- Past Many 12th Board Years of Electrochemistry
Examples and Exercise
Chapters in CBSE Class 12 Physical Chemistry are Solid State, Solutions, Electrochemistry, Chemical Kinetics and Surface Chemistry.
The total weightage of these chapters in CBSE Class 12 Chemistry board exam is of 23 Marks (out of 70). Electrochemistry is an important chapter of CBSE Class 12 Physical Chemistry.
Given below is the Part I of Chapter Notes on Electrochemistry.
Introduction

Electrochemical Cell

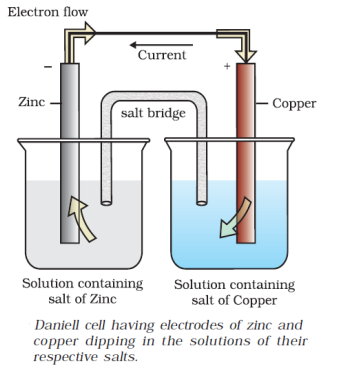
Schematic Diagram of Daniell cell
Electrolytic Cell

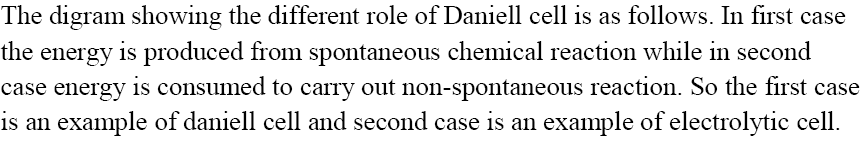
Electrode Potential

Standard Electrode Potential

Anode and Cathode

Cell Potential or EMF of Cell

Inert Electrode

Measurement of Electrode Potential

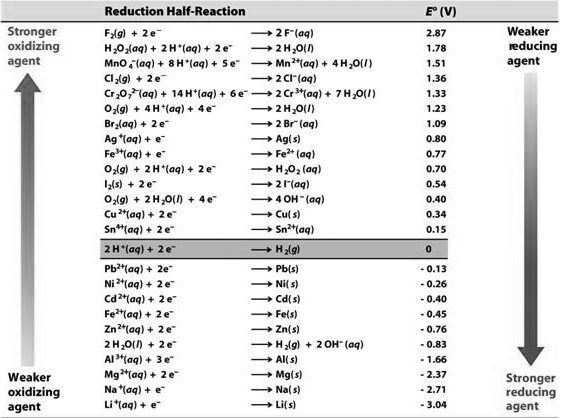
Values of Standard Reduction Potentials for some Important Half-Cells
CBSE Class 12th Physics Notes: Current Electricity
Conclusions from Table

CBSE Class 12th Physics Notes: Ray Optics & Optical Instruments
Nernst Equation
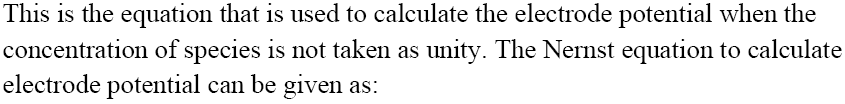

Applications of Nernst Equation

EMF of Cell

How to Solve Difficult Problems in CBSE Board and Engineering Entrance Exams
Equilibrium Constant from Nernst Equation

Intext Questions

In part I of Chapter Notes on the chapter Electrochemistry of CBSE Class 12 we have studied important concepts like Electrochemical Cell, Electrolytic Cell, Electrode Potential, Measurement of Electrode Potential, Nernst Equation etc. Now in this part, we will study some more important concepts and numericals based on them.
Gibbs Free Energy from Nernst Equation

Intext Questions

Types of Materials


Metallic or Electric Conductance

Electrolytic or Ionic Conductance

Resistance

Resistivity or Specific Resistance
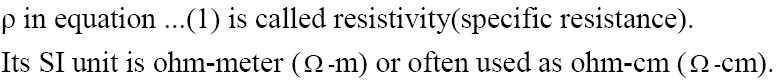
Conductance

Conductivity or Specific Conductance

Measurement of the Conductivity of Ionic Solutions
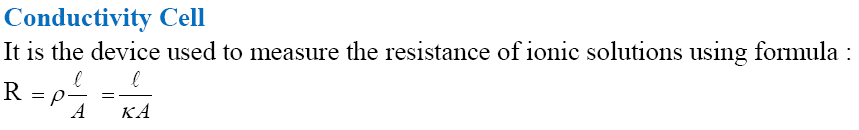




Intext Questions

Variation of Conductivity with Concentration

Limiting Molar Conductivity
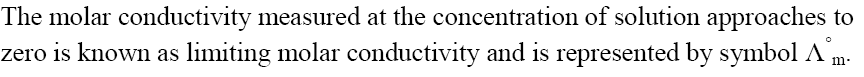
Variation of Molar Conductivity for Strong Electrolyte

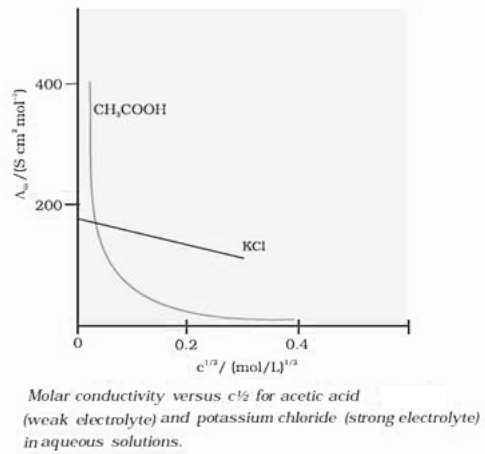
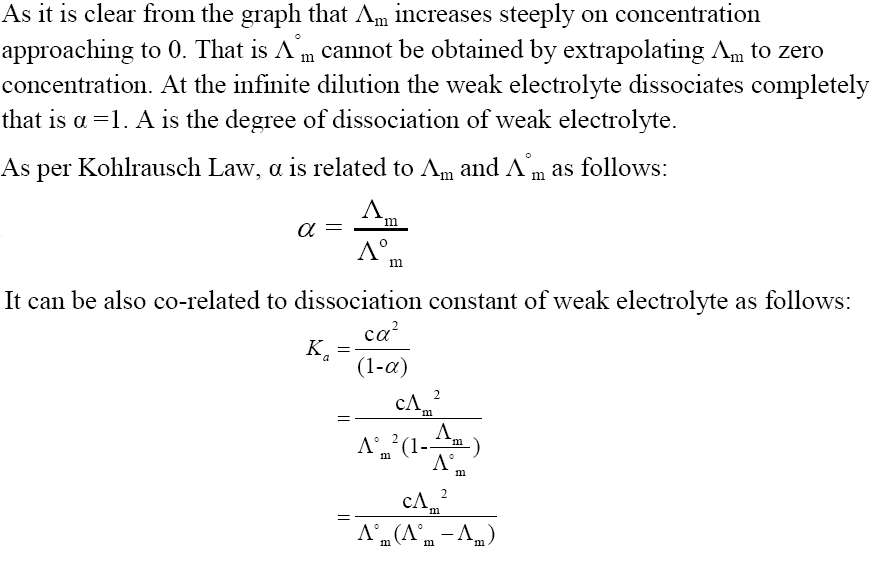
Kohlrausch’s Law

Variation of Molar Conductivity for Weak Electrolyte
Intext Questions
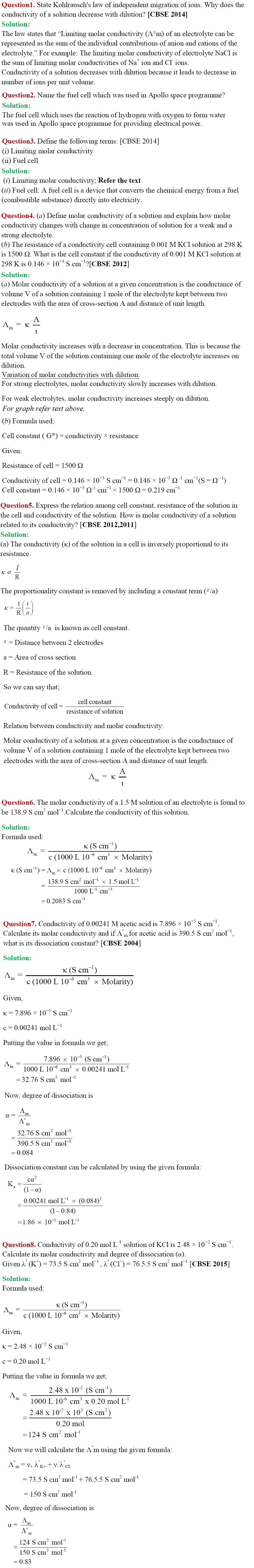
In part – I and part – II of chapter notes on Electrochemistry most of the important topics are already covered. Now in this part, we will study the following topics: Electrolytic Cell, Electrolysis, Faraday’s Law of Electrolysis, Products of Electrolysis, Battery, Fuel Cell and Corrosion. Solved examples are also included in this article for better understanding.
Electrolytic Cell and Electrolysis
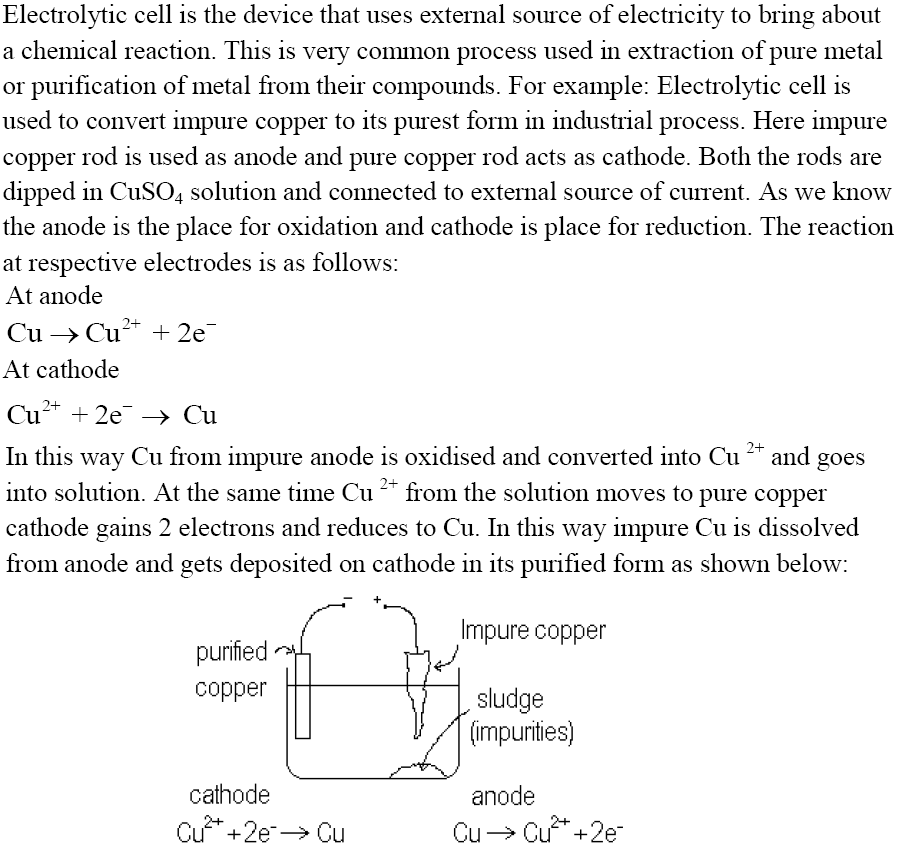
Quantitative aspects of Electrolysis

Intext Questions

Products of Electrolysis



Batteries


Fuel Cell
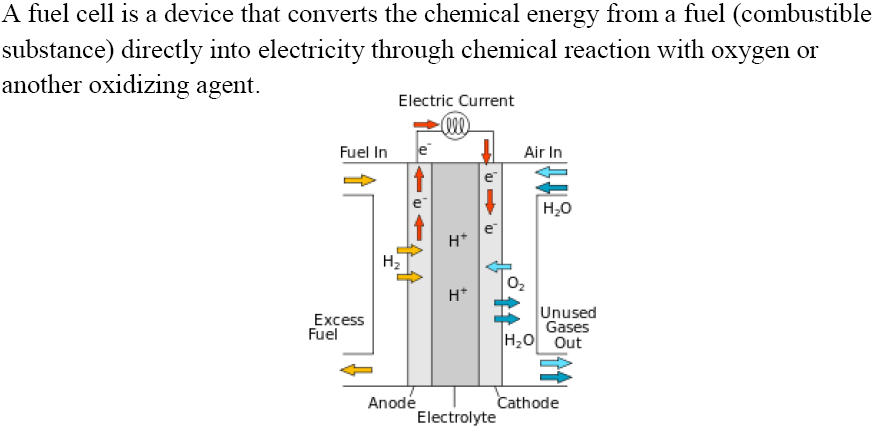
Corrosion

Intext Questions

Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry MCQs
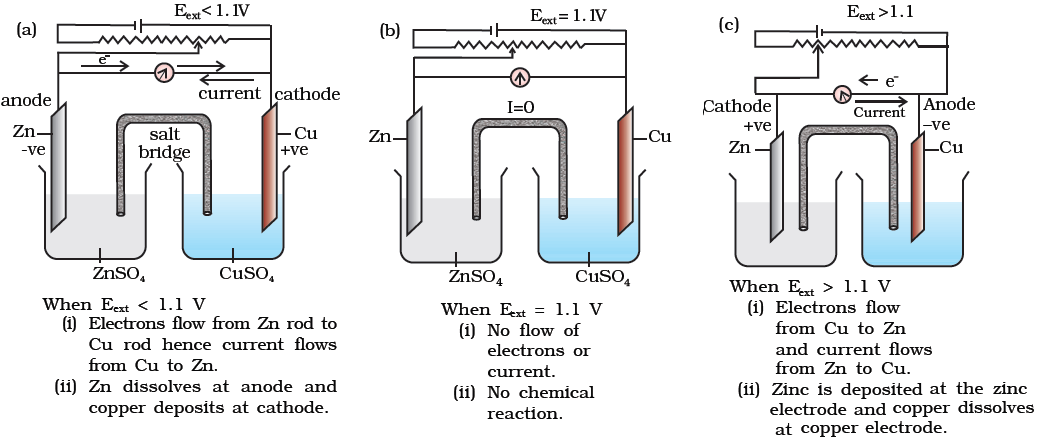
1. A new galvanic cell of Eext more than Eo (1.1 v)of Daniel cell is connected to Daniel cell in a manner that new cell gives electrons to Zn, what will happen
(a) Ecell will increase
(b) Ecell will decrease
(c) No change will take place
(d) Daniel cell will work as electrolytic cell where Zn will be deposite on zinc rod and copper will dissolve from copper rod.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:
(d) is correct.
∵ external emf is greater than emf of Daniel cell.
2. Ag+(aq) + e– → Ag(s) E° = + 0.80 V
Fe2+(aq)+ + 2e– → Fe(s) E° = – 0.44 V
What is emf of
Fe(s) + 2Ag+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
(a) 1.16 V
(b) 1.24 V
(c) 2.04 V
(d) -1.16 V
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: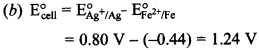
3. A conductivity cell containing electrodes made up of
(a) Gold
(b) Silver
(c) Platinised platinum
(d) Copper
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Electrodes are made up platinised platinum because it is inert.
4. Which of the following expression is correct for ‘Ka’ in terms of Λ° and Λ, where ‘C’ is molarity.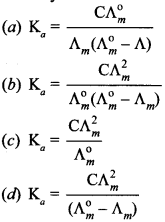
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: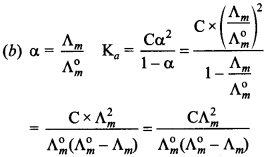
5. What is pH of the half cell Pt|H2fe)|H+ if \(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{H}^{+} \mathrm{H}_{2}}^{\circ}\) =-0.0295 V
(a) 1
(b)2
(c) 0.5
(d) 3
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination: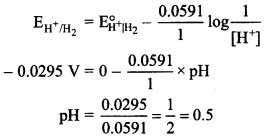
6.![]()
What is the value of ‘K’ for above reaction?
(a) 1 × 108
(b) 1 × 102
(c) 4 × 103
(d) 3 × 104
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination: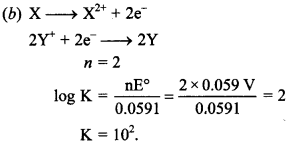
7. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are extensive properties.
(b) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are . intensive properties.
(c) ECell is an intensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction is an extensive property.
(d) ECell is an extensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction is an intensive property.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) \(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{cell}}^{\circ}\) depends upon concentration (amount) of substance therefore, intensive property but AG is extensive property.
8. While charging the lead storage battery _________ . [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) PbSO4 anode is reduced to Pb.
(b) PbSO4 cathode is reduced to Pb.
(c) PbSO4 cathode is oxidised to Pb.
(d) PbSO4 anode is oxidised to PbO2.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) 2PbSO4 + 2H2O → Pb + PbO2 + 2H2SO4
9. On the basis of following E°values, the strongest oxidising agent is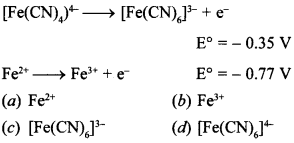
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) It is because \(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{Fe}^{3+} / \mathrm{Fe}^{2+}}\) = 0.77 V, it means Fe3+ can gain electron early to form Fe2+.
10. Λ of M/32 solution of weak acid is 8 S cm2 mol-1 and limiting molar conductivity is 400 S cm2 mol1. Ka for acid is
(a) 1.25 × 10-6
(b) 6.25× 10-4
(c) 1.25 × 10-4
(d) 1.25 × 10-5
Answer/Explanation
Answer: d
Explaination:![]()
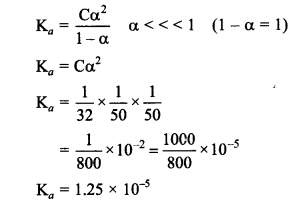
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct. (Q.11 to Q.14)
11. The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu indicates that _________ [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple.
(b) this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2.
(c) Cu can displace H2 from acid.
(id) Cu cannot displace H2 from acid.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: b
Explaination:
(b) and (d) are correct.
Cu is less reactive than H2 so cannot displace H2 from acid. Redox couple is good oxidising
agent as Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu(s) is possible due to +ve emf.
12. \(\mathrm{E}_{\text {cell }}^{\circ}\) for some half cell reactions are given below. On the basis of these mark the correct answer. [NCERT Exemplar]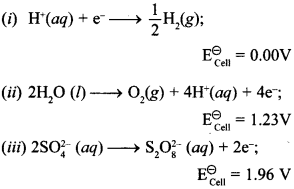
(a) In dilute sulphuric acid solution hydrogen ion will be reduced at cathode.
(b) In concentrated sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidised at anode.
(c) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, water will be oxidised at anode.
(d) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) ion will be oxidised to tetrathionate ion at anode.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) and (c) are correct.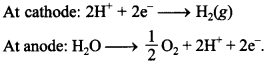
13. \(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{Cell}}^{\ominus}\) = 1.1V for Daniel cell. Which of the following expressions are correct description of state of equilibrium in this cell? [NCERT Exemplar]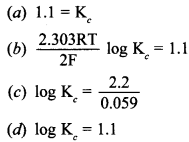
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
14.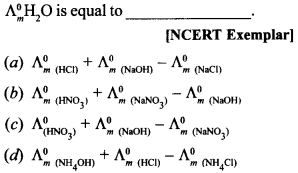
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: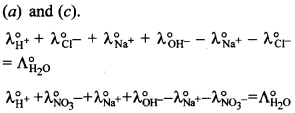
15. The charge required for the reduction of 1 mol of MnO2– to MnO2 is
(a) 1 F
(b) 3 F
(c) 5 F
(d) 6 F
Answer
Answer: b
16. The cell reaction of the galvanic cell.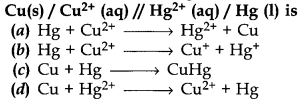
Answer
Answer: d
17. Which of the following reaction is used to make fuel cell?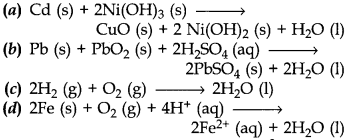
Answer
Answer: c
18. If limiting molar conductivity of Ca2+ and Cl– are 119.0 and 76.3 S cm2 mol-1, then the value of limiting molar conductivity of CaCl2 will be
(a) 195.3 S cm2 mol-1
(b) 271.6 S cm2 mol-1
(c) 43.3 S cm2 mol-1
(d) 314.3 S cm2 mol-1.
Answer
Answer: b
19. NH4NC>3 is used in salt bridge because
(a) it forms a jelly like material with agar-agar.
(b) it is a weak electrolyte.
(c) it is a good conductor of electricity.
(d) the transport number of NH4+ and NO3– ions are almost equal.
Answer
Answer: d
20.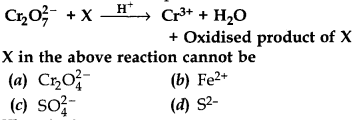
Answer
Answer: b
21. The reaction, 3ClO– (aq) → ClO3 (aq) + 2Cl– (aq) is an example of
(a) Oxidation reaction
(b) Reduction reaction
(c) Disproportionation reaction
(d) Decomposition reaction
Answer
Answer: c
22. The emf of the cell:
Ni / Ni2+ (1.0 M) // Au3+ (1.0 M) / Au (E° = -0.25 V for Ni2+/Ni; E° = 1.5 V for Au3+/Au) is
(a) 1.25 V
(b) -1.25 V
(c) 1.75 V
(d) 2.0 V
Answer
Answer: c
23. The standard emf of a galvanic cell involving cell reaction with n = 2 is formed to be 0.295 V at 25° C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction would be
(a) 1.0 × 1010
(b) 2.0 × 1011
(c) 4.0 × 1012
(d) 1.0 × 102
[Given F = 96500 (mol-1); R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1]
Answer
Answer: a
24. If E°Fe2+/Fe = -0.441 V and E°Fe2+/Fe2+ = 0.771 V, the standard EMF of the reaction,
Fe + 2Fe3+ → 3Fe2+ will be
(a) 1.212 V
(b) 0.111 V
(C) 0.330 V
(d) 1.653 V
Answer
Answer: a
25. Match the terms given in Column I with the units given in Column II. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
26. Match the terms given in Column I with the items given in Column II.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
27. Match the items of Column I and Column II. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(a) Lead storage battery-Pb is anode, Pb02 is cathode
(b) Mercury cell gives steady potential (Constant value)
(c) Fuel cell has maximum efficiency.
(d) Rusting is prevented by galvanisation.
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (Q.18 to Q.20)
(а) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
28. Assertion: ECe|, should have a positive value for the cell to function.
Reason: Ecathode, < Eanode . [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer: c
Explaination:
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
29. Assertion: Am for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
30. Assertion: For measuring resistance of an ionic solution an AC source is used.
Reason: Concentration of ionic solution will change if DC source is used. [NCERT Exemplar]
Answer/Explanation
Answer: a
Explaination:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
31. A° for weak electrolyte is determined by _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Kohlrausch law
32. The quantity of change required to obtain 1 mole of Al from Al2O3 is _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 3F
33. \(\frac{2}{3}\)Al2O3 → \(\frac{4}{3}\)Al + 2O2, number of moles of electrons gained or lost = _________ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: n = 4
34. If \(\mathrm{E}_{\text {cell }}^{\circ}\) is -ve, cell will not work. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
35. If external emf opposing Daniel cell is less than 1.10 V, cell will keep in working. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
36. Salt bridge completes internal circuit and prevents accumulation of charges. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
37. Inert electrolyte in salt bridge reacts with solution of half cells. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
False, (Inert electrolyte does not react with any of the electrolyte present in half cell).
38. Represent the galvanic cell in which the reactions is
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) [Delhi 2013(C)]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Zn | ZnSO4 (1M) || CuSO4 (1M) | Cu(s)
39. Consider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is coupled to an eletrolytic cell. What will be the polarity of electrodes ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the electrolytic cell?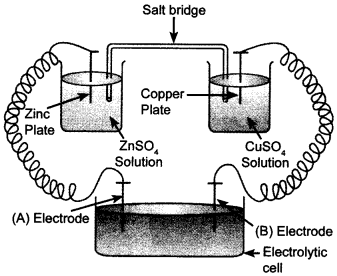
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
‘A’ will have negative polarity, whereas ‘B’ will have positive polarity.
40. Can absolute electrode potential of an electrode be measured?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No, because electrode potential of a single electron cannot be mentioned.
41. The standard reduction potential for Zn2+(aq)/Zn(s) is – 0.76 V. Write the reactions occurring at the electrodes when coupled with NHE or SHE (standard hydrogen electrode).
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e– is reaction at anode
when Zn is coupled with NHE or SHE (Standard Hydrogen Electrode).
2H+ + 2e– → H2 at cathode.
42. E° (reduction potential) of Cu and Zn are + 0.34 V and – 0.76 V respectively. Which of them is stronger reducing agent?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Zn is stronger reducing agent because it has lower standard reduction potential than that of Cu.
43. Predict whether F2 and Na will react with one another. Give reason.![]()
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: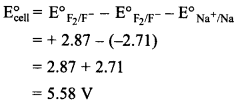
Since E°ell is +ve, ∆G° will be -ve, reaction will take place. Na will react with F2.
44. Write the correct representation of cell:
2Cr(s) + 3Cd2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3Cd(s)
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:![]()
45. Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe3+(aq), E° = +0.77 V
Cl2(g) + 2e– → 2Cl–(aq), E° = +1.36 V
Write the reaction which could be feasible using above half cells.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: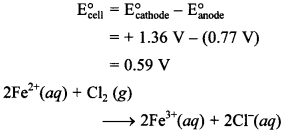
46. If E° for the reaction Fe3+(aq) + e– → Fe2+(aq) is + 0.77 V, what will be E° value for the reaction 2Fe3+(aq) + 2e– → 2Fe2+(aq)?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
E° = 0.77 V, i.e. e.m.f. of cell will remain the same for reaction![]()
47. Write Nemst equation for the following chemical reaction:
2Cr + 3Fe2+ → 2Cr3+ + 3Fe
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
48. Can \(\mathrm{E}_{\text {cell }}^{\circ}\) or ∆rG° for a cell reaction ever be equal to zero?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
No, but Ecell or ArG of reaction can be zero at equilibrium.
49. Define specific conductivity (specific conductance).
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Specific conductance is defined as the conductance of electrolyte when distance between electrodes is 1 cm and area of cross section is 1 cm². It is represented by Greek symbol ‘K’ (kappa) and it is expressed in S cm-1.
50. What is meant by cell constant? What is its use?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It is the ratio of distance between electrodes to the area of cross section. It is used to measure the resistance or conductivity of solution.
51. What do you mean by limiting molar conductivity?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
When the concentration of electrolyte approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity (\(\Lambda_{m}^{\circ}\))
\(\Lambda_{m}^{\circ}\) = (Λm) when C → 0
52. Complete: Λ° Na2SO4 =
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: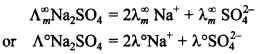
53. HCl does not give acidic solution in benzene. Why?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It does not dissociates ions in benzene (non-polar solvent).
54. How much charge in Faraday is required for the reduction of 1 mol of Ag+ to Ag? [AI 2015 Guwahati]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Ag+ + e– → Ag(5)
1 Faraday of charge is required (charge on 1 mole of electrons).
55. How much charge is required for the reduction of 1 mole of Zn2+ to Zn? [AI 2015 Patna]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn(s)
2 Faradays or 2 × 96500 C of charge is required.
56. How much charge in Faraday is required for reduction of 1 mole of Al3+ to AI? [AI 2015 Chennai & Trivandrum; DoE]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Al3+ + 3e– → Al(s), i.e. 3 Faradays of charge is required.
57. How many Faradays of charge are required to convert:
1 mole of MnO4–“ to Mn2+ ion,
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: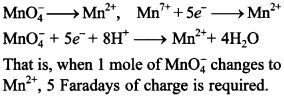
58. What mass of zinc (II) ion will be reduced by 1 mole of electrons?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s)
∵ 2 Faradays, i.e. 2 moles of electrons will deposit 65 g of zinc
∴ 1 Faraday, i.e. 1 mole of electrons will deposit 32.5 g of zinc.
59. How many Faradays are required to liberate 2 moles of hydrogen gas in electrolysis of acidified water?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
4 Faraday. 4H+ + 4e– → 2H2(g)
60. What are the factors which depend on the products of electrolysis?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) The nature of material being used, and
(ii) The type of electrodes being used.
61. What is primary cell? Give an example.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It is a cell in which products cannot be changed back into reactants, i.e. it is not rechargeable, e.g. dry cell and mercury cell. In this cell, electrical energy is produced by the redox reaction occurring in the cell.
62. What are secondary cells? [AI 2014]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Those cells which are rechargeabe, i.e. products can be converted back into reactants.
63. Which electrolyte is used in fuel cell?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Concentrated aqueous KOH solution is used as an electrolyte in fuel cell.
64. Why does alkaline medium inhibit rusting of iron?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
It will remove H+ which are essential for rusting.
65. What is the value of potential of SHE?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The potential of standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is zero.