CBSE Class 12 Physical Education Important Questions Chapter 10 Training in Sports
1 Mark Questions
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION (1 MARK EACH)
Q1. What is speed?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to cover a unit distance in minimum time.
Q2. What is strength?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to overcome or act against resistance.
Q3. What is endurance?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to resists the fatigue for long time.
Q4. What is flexibility?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to move his or her joints effectively through a full range.
Q5. What is coordinative ability?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to perform a sequence of movements smoothly and accurately.
Q6. What is speed endurance?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to perform body movements with high speed under the condition of fatigue upto 45 seconds. Ex. -400 metres race.
Q7. What is strength endurance?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to exert force for a long period of time.
Q8. What is acceleration?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to achieve high speed, from a slow moving or stationary position.
Q9. What is explosive strength?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to overcome resistance with high speed.
Q10. What is reaction ability?
Ans. It is that ability of an individual to react effectively and quickly to a signal.
It is of 2 types –
(1) General reaction ability
(2) Complex reaction ability.
Q11. What is movement speed?
Ans. It is the ability of an individual to do movements in minimum time.
3 Mark Questions
SHORT ANSER TYPE QUESTION [80 TO 90 WORDS] –
(3 MARKS EACH)
Q1. What do you understand by maximum strength?
Ans. It is the ability to apply maximum force by a group of muscles against maximum resistance. Maximum strength is usually not used in majority of sports, it is used in those sports where heavy weight, resistance have to be tackled, like – weight lifting, throwing, roman ring and take off in jump. If the resistance is less, less strength is needed to overcome it. The maximum strength is a motor ability and involves face application during a voluntary movement. It serves as the base of good explosive strength and strength endurance.
Q2. What is the difference between active and passive flexibility?
Or
What are the types of flexibility? Discuss.
Ans. Active flexibility is the ability of an individual to do the joint movement for a longer range without any external help. Active flexibility is always greater than passive flexibility Ex.- Doing any stretching exercise without external help.
Passsive – The ability to do a joint movement with a greater range with an external help of a partner. This flexibility is largely determined by joint structure, stretchebility of the muscle and ligament. Passive flexibility helps in the development of active flexibility.
Q3. What are coordinative abilities in sports?
Ans. Coordinative abilities are those abilities which are stabilized and generalized pattern of motor control. These abilities help the sportsman to do a group of movements with better quality and effect. Coordinative abilities primarily depend upon the Central Nervous system. In sports, the coordinative abilities are as under:-
(i) Differentiation ability
(ii) Orientation ability
(iii) Coupling ability
(iv) Reaction ability
(v) Balance ability
(vi) Rhythm ability
(vii) Adaptation ability
Methods for Improvement of coordination abilities :-
(1) Practicing physical exercise
(2) Correct and conscious movement
(3) Additional means to improve motor sense.
(4) Variation in exercises
(5) Degree of difficulty
Q4. Briefly explain the types of Endurance.
Or
“Endurance is one of the most important factor for high performance in games & sports.” Explain.
Ans. Endurance in sports are of different types. These are as follows –
Endurance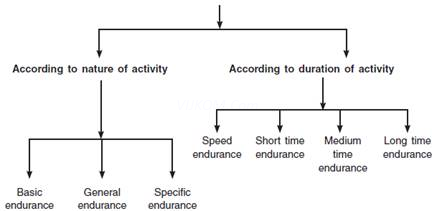
Basic endurance is the ability of an individual to do the movement in which large no. of body muscles involve at slow pace for a long duration such as walking, jogging, swimming at a moderate speed. General endurance is the ability of an individual to do movement under the condition of fatigue.
Specific endurance is the ability of an individual to complete the task without any fatigue. It’s requirement is depends upon the nature of activity (games and sports). Requirement of specific endurance of a boxer is different from that of a wrestler.
Speed endurance is the ability of an individual to perform a movement with high speed under the condition of fatigue upto 45 seconds. In short terms endurance, the activity lasts from 45 seconds to 2 minutes. Ex. 800m race.
The medium time endurance is needed for 1500m race, lasting from 2 min to 11 minutes.
Long term endurance is needed for those sports which require more than 11 minutes time. Ex. 5000m to 10000m race.
5 Marks Questions
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [150 TO 200 WORDS] –
(5 MARKS EACH)
Q1. What are the methods for developing strength?
Or
Write the difference between isometric, istonic and isokinetic exercises.
Ans. The word isometric is comprised of 2 words “iso Same” and “metric length”, means when we do these exercises, there is no change in the length of the muscles. In these exercises work done cannot be observed. These exercises require less time and equipment and can be carried out anywhere. These exercises are useful for maintaining strength in case of injury.
Eg : Archery, weight lifting, gymnastic are the examples of isometric movements.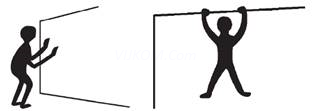
Pushing the wall / Hanging on Pole
Work done = Force × Distance moved
But distance moved is O, therefore work done is zero.
ISOTON IC – EXERCISES :- ‘Iso’ means same and ‘tonic’ means tension. In these types of exercise when we do movements it can be observed directly. The lengthening and shorting of muscles can be seen and called eccentric contraction and concentric contraction accordingly. Ex. When we throw a ball, jump. run, weight training, these type of contraction occurs.
These type of exercise is widely seen in games & sports. We can do these exercise with equipment or without equipment. These exercise increase the flexibility and length of the muscles and are good for conditioning in sports.
ISO-KINETIC EXERCISES:- ‘ISO → same’ and ‘kinetic → motion’. These exercises were introduced by J.J. perrine in 1968. These exercises are done by specially design machine and are combination of isotonic and iso-metric exercises. These exercises develop strength of muscles. These type of movements are usually not applied in games and sports except water sports, skating, climbing, running etc.
Q2. Explain the methods to develop endurance.
Or
Differentiate the continuous method, interval method and farlek method.
Ans. Endurance has a great importance in games and sports. Following are the methods to develop endurance.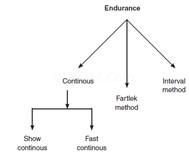
Continous method – In this type of method, the exercise is done for a long duration without taking rest. We do the exercise for a long duration, so the intensity of work is low. The heart rate during the exercise for a sportsman should be between 140-160 beats per-minutes. For fast continous method the heart rate of an athlete should be increased about 175-180/minute.
Fartlek method :- It is another method to develop the endurance ability. This method was developed by a Swedish coach “Gosta Holmer” in 1930, so it is also known as “Swedish Play” or “Speed Play” (Fartlek means speed in swedish). In this method the athlete changes his/her pace, himself/herself according to surrounding (hills, rivers, forest, mud etc.)
This method helps in development of strength and endurance of the sports person. Athelete changes his/her speed according. So it is self – disciplined in nature. The heart-rate fluctuate between 140-180 beats/ minute. Farllek training involves varying our pace throughout our run, alternating between fast and slow pace. Fixed distance in fixed time by variable type of movement/pattern/place of running.
Interval method – This method is very effective for developing endurance for track runners. intervals are given to the athelete in between the repetition for incomplete recovery. The recovery period for athelete varies from person to person. The heart rate should go up to 18 beats/min. And when the heart rate comes down to 120-130 beats/min, again the repetition / work starts. The training load should be given again after checking the heart – rate of the athelete.
Activity – Active Rest – Activity – Active Rest – Activity
[Rest = Recovery]
Q3. What are the methods to develop/improve flexibility? Explain
Or
What is the difference between ballistic method and Post – Isometric Method?
Ans. To maintain feasibility in games and sports, stretching exercises should be done. By following methods, one can improve their feasibility.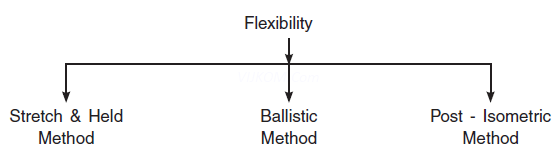
(1) Stretch & hold methods – We stretch our joints to maximum limit and hold it for a few seconds before returning to the initial phase. The holding period must be not more than 3 to 8 secs. This method is also used for improving passive flexibility.
(2) Ballistic method – In this method the stretching exercises are done in a swing, so this is called the ballistic method. A proper warm-up should be done before these exercises. Due to overstretching of the muscle, there may be an injury. The stretching exercise can be done in a rhythm.
(3) Post – isometric method – This method is based on the principle of proprio-ceptive neuro – muscular facilitaion means, if a muscle is contracted maximally for a few seconds, then after the contraction it remains in a static position for a few seconds for 6-7 seconds and gives very low resistance to that stretch. The duration of the stretch should be increased upto 8-10 second and repeated 4-8 times for each muscle group.
Q4. Briefly explain any two methods for improving speed write down the factors determining speed?
Ans.Methods for Improvement of speed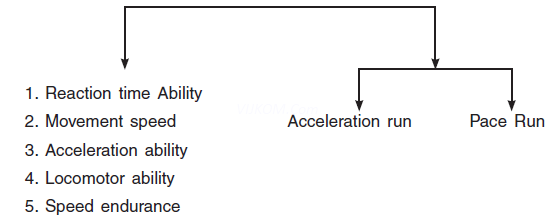
Two methods for developing speed are –
(1) Acceleration Run – Acceleration run are usually used to develop speed indirectly by improving explosive strength, technique, flexibility and movement frequency. It is the ability of a sprinter to achieve high speed from a stationary position. For direct improvement of acceleration speed a sprinter should do 25-30 metres sprints of 6-12 times. The maximum speed should be achieved within 5-6 seconds. Sufficient intervals should be provided
between the repetition.
(2) Pace run – Pace run means sunning the whole distance with a constant speed. Generally 800 m and above races are included in pace races. An athelete can run a distance of 300 m at full
speed but in longer races such as 800 m or above. he must reserve his energy by reducing the speed.
Physical Education Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 10 Training in Sports
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by training?
Answer:
Training means to prepare someone for some assignment. Training is the process of preparation for some task.
Question 2.
Write any two definitions of sports training.
Answer:
According to Mathew, “Sports training is the basic form of preparation of a sportsman.” According to Martin, “It is a planned and controlled process to achieve goals in which the changes of motor performance and behaviour are made through measures of content, methods and organisation.
Question 3.
What is sports training?
Answer:
Sports training is the physical, intellectual, technical, psychological and moral preparation of an athlete or a player by means of physical exercises.
Question 4.
List two impacts of circuit training.
Answer:
- It enhances cardiovascular fitness.
- It enhances muscular endurance.
Question 5.
What is circuit training?
Answer:
Circuit training is a form of body conditioning or resistance training using high-intensity aerobics. It targets strength building and muscular endurance.
Question 6.
What is endurance?
Answer:
Endurance is the ability to do sports movements with the desired quality and speed under conditions of fatigue.
Question 7.
What does the term ‘Fartlek’ mean and who developed this training method? All India 2017
Answer:
Fartlek is a Swedish term which means ‘speed play’ and has been used by distance runner for years. Fartlek is a form of road running or cross country running in which the runner usually changes the pace significantly during the run.
This method was introduced by O Astrand and Gosta Halner. It is good for aerobic and anaerobic fitness. That is why it makes an athlete a better sprinter and a better long-distance runner.
Question 8.
What is speed?
Answer:
It is the ability to cover distance in minimum possible time or the ability to perform movement in the shortest possible time.
Question 9.
What are pace races? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Pace races mean running the whole distance of a race at a constant speed. In pace races, an athlete runs the race with uniform speed, generally 800m and above.
Very young children can maintain their maximum speed for 15 to 20m, whereas a well-trained athlete can maintain maximum speed for 40m. Repetitions can be fixed according to the standard of the athletes.
Question 10.
What is flexibility?
Answer:
Flexibility is the ability to perform a joint action through a range of movement. It is needed to perform everyday activities with relative ease. Flexibility tends to deteriorate with age.
Question 11.
What are the methods for developing flexibility?
Answer:
Methods for developing flexibility are –
- Ballistic method
- Slow-stretching method
- Slow-stretching and Holding method
- Post-Isometric stretching method ‘
3 Marks Questions
Question 12.
Explain the meaning of training.
Answer:
Training means to prepare someone for some assignment. It is the process of preparation for some task. Many countries have recognised the importance of an effective training programme a wide range of activities not only for success in major international competitions but also for the development of healthy participants.
Question 13.
What is strength? What are the different types of strength?
Answer:
Strength is the ability of a muscle to exert force in single muscle contraction or it is the ability to overcome resistance. Strength is an essential component of physical fitness.
Types of strength are
- Maximum Strength
- Explosive Strength
- Strength Endurance
- Static Strength
Question 14.
Explain the advantages of fartlek training, (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Advantages of fartlek training are
- It is good for increasing strength and cardiorespiratory endurance.
- Several athletics can take part in the training programme at a time.
- It does not require any equipment and can be organised easily.
- This training method is not rigid; it is flexible in nature.
- It improves the efficiency of the heart and lungs.
- It provides experience of nature.
Question 15.
Explain interval training method. (All India 2017)
OR
Discuss any two methods of endurance development.
Answer:
- Interval Training Method It is a type of training that involves a series of low to high-intensity exercise workouts interspersed with rest of relief periods. The high-intensity periods are typically at or close to ahaerobic exercise, while the recovery periods involve activity of lower intensity.
- Fartlek Training Method Fartlek is a training method that blends continuous training with interval training. It is a form of speed training that can be.effective in improving an individual’s speed and endurance. Many runners, especially beginners enjoy fartlek training because it involves speed work. It is more flexible and notas demanding as-traditional interval training. Another benefit is that it can be done on all types of terrains-roads, trails or even hills.
Question 16.
What is strength? Discuss any two types of exercises used for strength development.
OR
Explain what is strength and write the -‘ methods of impraving strength. (All India 2016)
Answer:
Strength is the ability of a muscle to exert force in single muscle contraction or it is the ability to overcome resistance. Strength is an essential component of physical fitness.
Types of exercises for strength development% are
- Isometric Exercises Tso’ means ‘constant’ and ‘metric’ means ‘length’. An isometric contraction occurs when there is tension on a muscle blit no movement is made, causing the length of the muscle to remain the same.
- Isotonic Exercise Isotonic exercise is a form of exercise which involves controlled contraction and extension of muscles and- mobilisation of the joints around those muscles.
- Isokinetic Exercises Isokinetic exercises are performed on specially designed machines. These exercises were developed by Perrine in 1968. In these exercises, there is movement along with continuous tension in both flexor and extensor muscles.
Question 17.
Differentiate isometric and isotonic exercises. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
An isometric contraction occurs when there is tension on a muscle without any movement. The length of the muscles remains constant. Isotonic exercises involve controlled contraction and extension of muscles and mobilisation of the joints around those muscles. A comparison between their characteristics is given below
| S.No. | Isometric Exercises | Isotonic Exercises |
| (i) | Less or no equipment required. | Sometimes equipment is required to perform them. |
| (ii) | It develops static strength. | It develops dynamic strength. |
| (iii) | It needs less time. | Muscles which are used in this exercise gain most strength. |
Question 18.
Explain the physiological factors determining speed.
OR
What are various factors of speed?
OR
Explain the types of speed.
OR
Write in brief about any three physiological factors determining speed. Delhi 2016
Answer:
The various factors of speed are
- Reaction Speed It is the ability to respond /to a given stimulus as quickly as possible. In sports, reaction ability is not only significant to react quickly to a signal, but it should also be accurate according to situation.
- Movement Speed It is the ability to do a single movement m the minimum time. Movement speed is of high relevance in sports like jumping, throwing, kicking, boxing etc.
- Acceleration Speed It is the ability to increase speed from minimum to maximum. This form of speed, to a great extent, depends upon explosive strength, frequency of movement and technique. This ability is important in swimming, hockey, football, gymnastics etc.
- Locomotor Ability It can be defined as the ability to maintain maximum speed of locomotion over a period of time as far as possible. This ability is very important in races, speed skating, swimming, hockey, football etc.
- Speed Endurance It is the ability to do sports movements with high speed under conditions of fatigue. Speed endurance is a combination of speed and endurance abilities. This ability depends upon anaerobic capacity, psychic factors and level of skill.
Question 19.
Define speed. Explain the methods of speed development. (Delhi 2016, 15)
OR
How do acceleration runs and pace races develop speed?
Answer:
Speed It is the ability of an individual to cover maximum distance in minimum possible time. Developing Methods
- Acceleration Run Acceleration runs are usually adopted to develop speed specially in attaining maximum speed from a stationary position. Before acceleration runs, proper warm up must be done. After every acceleration run, there should be a proper interval so that the athlete may start the next run without any fatigue. Generally, the athlete should take rest of 4 to 5 minutes in between the runs.
- Pace Races Pace races mean running the whole distance of a race at a constant speed. In pace races, an athlete runs the race with uniform speed, generally 800 m and above. Very young children can maintain their maximum speed for 15 to 20m, whereas a well-trained athlete can maintain maximum speed for 40m. Repetitions can be fixed according to the standard of the athletes.
Question 20.
Briefly explain different types of coordinative abilities. (All India 2016)
Answer:
The different types of coordinative abilities are
- Differentiation Ability It is the ability to achieve a high level of fine-tuning or harmony of individual movement phases and body part movements.
- Orientation Ability It is the ability to determine and change the position and movements of the body in time and space in relation to a definite of action e.g. playing field, boxing ring, apparatus and a moving object e.g. ball, opponent, partner.
- Coupling Ability It is the ability to coordinate body part movements (e.g. movements of hand, feet, trunk etc) with one another and in relation to a definite goal-oriented whole body movement. Coupling ability is especially important in sports in which movements with a high degree of difficulty have to be done e.g. gymnastics, team games.
- Reaction Ability It is the ability to react quickly and effectively to a signal.
- Balance Ability It is the ability to maintain balance during whole body movements and to regain balance quickly after balance disturbing movements.
- Rhythm Ability It is the ability to perceive an externally given rhythm and to reproduce it in motor action.
- Adaptation Ability It. is the ability to adjust or completely change the movement programme during movement on the basis of changes or anticipated changes in the situation.
Question 21.
Suggest different ways to improve reaction ability of a player. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Improved reaction ability is a performance prerequisite to do motor actions under given ‘ conditions in minimum time. There are two methods for improving this.
They are
- Acceleration Runs They test the ability to achieve high speed of locomotion from a stationary position or from a slow-moving position. Acceleration ability is improved indirectly by improving on explosive strength, technique and movement frequency.
- Pace Races Pace races mean running the whole distance of a race at a constant speed, In pace races, an athlete runs the race with uniform speed, generally 800 m and above. Very young children can maintain their maximum speed for 15 to 20m, whereas a well-trained athletes can maintain maximum speed for 40m. Repetitions can be fixed according to the standard of the athletes.
5 Marks Questions
Question 22.
Define strength. Explain the details of strength training methods with the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Answer:
Strength is the ability of our muscles to overcome resistance.
We use the following methods of strength development
(i) Isometric Exercises ‘Iso’ means constant’ and ‘metric’ means ‘length’. An isometric contraction occurs when there is tension on a muscle but no movement is made, causing the length of the muscle to remain the same.
- Develops static strength.
- Needs less time.
- Can be performed anywhere because no equipment is required.
Disadvantages
- Muscles gain most strength at the angle used in exercise.
- AvQid if you have heart problems as they cause a rise in blood pressure due to a drop in blood flow to the muscle during the contraction.
(ii) Isotqnic Exercises Isotonic exercise is a form of exercise which involves controlled contraction and extension of muscles arid mobilisation of the joints around those muscles. . .
Advantages
- Strengthens the muscle throughout the range of motion.
- Can be adapted easily to suit different sports.
Disadvantages
- Muscle soreness after exercise because of the high, stress level.
- Muscles gain dynamic strength when
- they are at their weakest point of action.
(iii) Isokinetic Exercises isokinetic exercises . are performed on’ specially designed machines. These exercises were developed by Perrineiri 1968. In these exercises, there is movement along with continuous tension in both flexor and extensor muscles.
Advantages
- They develop a high level of dynamic as well as explosive strength.
- These are effective for almost every game. Disadvantages
- They require special types of equipment.
- They must be performed under observation of a coach.
Question 23.
Draw ten stations circuit training programme for improving the jumping ability of a player, (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Circuit training is a form of body conditioning or resistance training using high-intensity aerobics. It targets strength building and muscular endurance. An exercise circuit’ is one completion of all prescribed exercise in the programme. When a circuit is complete, one begins the first exercise
again for the new circuit. A specific circuit, however, can consist of several exercises involving the same muscle groups.
An example of circuit training is given below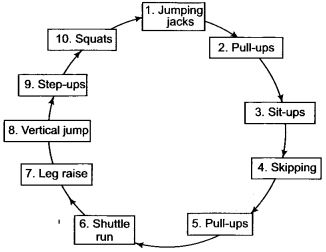
Question 24.
Define flexibility and explain the methods of flexibility development. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Flexibility is the range of movement. It is the ability of joints to move in the maximum range.
Developing methods of flexibility are
- Ballistic Method It is the oldest form of doing stretching exercises. This method involves jerk in movement. A joint or muscle is stretched with just rhythmic actions or movements around a joint. Before performing such exercise, the appropriate warm-up is essential.
- Slow-Stretching Method In this method, the muscle or joint involved is stretched to the maximum possible limit using slow movement. It has an advantage over the ballistic method as it minimises the chances of overstretching of the muscle or joint, preventing injury to the tissue.
- Slow-Stretching and Holding Method It is the extension of slow- stretching method. Here the muscle is stretched to its maximum limit and then the position is held for few seconds before returning to the original position.
- Post-Isometric Stretching This method of flexibility development is based on the principle of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation. In this procedure, the muscle is first contracted maximally for 6-8 seconds using isometric method.
- Then the muscle is gradually stretched to its maximum limit and is held in this position for 8-10 seconds. This process is to be repeated 4 to 8 times for each muscle group.
Question 25.
Draw a circuit training plan for developing strength among school children. (CBSE Model Question Paper 2015)
Answer:
A circuit training plan for developing strength among school children is given below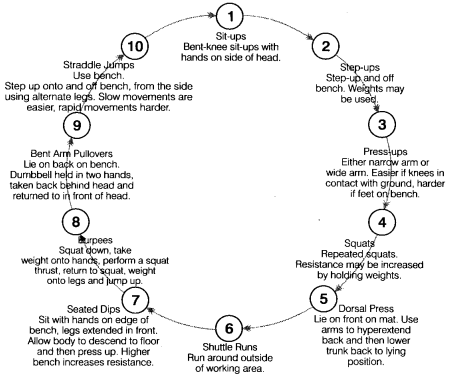
1 Mark Questions
Question.1. What are pace races? [CBSE 2013]
Answer. Pace races are an effective training method for improving speed endurance. A pace race generally means running a race of 800 metres or more at a uniform speed, with another athlete running 10-15 metres ahead of the other athletes who sets the pace of running. This uniform speed running is repeated at intervals fixed according to the standard of the athlete.
Question.2. Define cardiovascular endurance. [CBSE2012]
Answer. It is the ability of the heart, lungs and blood vessels to supply a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients to the cells to meet demands of activities for prolonged performance or large muscle dynamic exercises at moderate to high levels of intensity.
Question.3. What is the interval training method? [CBSE 2011]
Answer. Interval training method is called terrace training. It is a training of the heart through endurance training and based upon the effort and recovery principle.
Question.4. What is sports training?
Answer. Sportstraining is a specialised process of all round physical conditioning aimed at the preparation of sportspersons for improving performance in games and sports.
Question.5. What is speed?
Answer. Speed is the ability of an individual to perform a movement of the same pattern at a faster rate.
Question.6. What is flexibility?
Answer. Flexibility is the range of movement of joints. Flexibility can be defined as the ability to execute movement with greater amplitude or range.
Question.7. What is endurance?
Answer. Endurance is the ability of an individual to sustain any activity for a longer period. It also means the ability to resist fatigue.
Question.8. What is fartlek training?
Answer. Fartlek is a Swedish word which means speed play. In this method, pace and speed are not pre-planned. An individual can change his speed according to the surroundings (hills, forests, rivers, muddy roads, metal roads, grassy ground etc). .
Question.9. What is circuit training?
Answer. Circuit training is a formal type of training in which an athlete goes through a series of selected exercises that are arranged in a circuit. There are usually 5 to 10 stations in a circuit.
Question.10. What do you mean by training?
Answer. Training means to prepare someone for some assignment. Training is the process of preparation for some task.
Question.11. Write any two definitions of sports training.
Answer. According to Mathew “Sports training is the basic form of preparation of a sportsman.”
According to Martin, “It is a planned and controlled process to achieve goals in which the changes of motor performance and behaviour are made through measures of content, methods and organisation.”
Question.12. List any four training methods.
Answer. Some useful training methods are (any four)
- Circuit training
- Interval training
- Continuous training
- Fartlek training
- Weight training
Question.13. What are the methods for developing flexibility?
Answer. Methods for developing flexibility are
- Ballistic method
- Static stretching method
- Dynamic stretching method
- Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation technique
3 Marks Questions
Question.14. Suggest different ways to improve reaction ability of a player. [CBSE 2013 Modified]
Answer. Improved reaction ability is a performance prerequisite to do motor actions under given conditions in minimum time. There are two methods for improving this. They are:
- Acceleration Runs They test the ability to achieve high speed of locomotion from a stationary position or from a slow moving position. Acceleration ability is improved indirectly by improving on explosive strength, technique and movement frequency.
- Short Sprints For direct improvement of acceleration, short sprints of 25 to 80 m are the best means. The maximum speed achieved by a sprinter from a stationary start is for about 6 sec. Various researches have shown that during a sprint run the speed also increases with time.
At the end of 1st sec the approximate speed is 55% of maximum.
At the end of 3rd sec the approximate speed is 91 % of maximum.
At the end of 5th sec the approximate speed is 99% of maximum.
Question.15. Briefly explain the advantages of fartlek training. [CBSE 2012 Modified]
Answer. Advantages of fartlek training are:
- It is good for increasing strength and cardiorespiratory endurance.
- Several athletics can take part in the training programme at a time.
- It does not require any equipment and can be organised easily.
- This training method is not rigid; it is flexible in nature.
- It improves the efficiency of the heart and lungs.
- It provides experience of nature.
Question.16. Explain the meaning of training.
Or
What do you understand by the term sports training?
Answer. The word training means to give practical and theoretical knowledge of a specific field. But in physical education, training is a scientific and systematic way to enhance sports performance. The training methods are based upon scientific principles in a systematic order. In other words, we can say that these are the methods to improve general and specific performance in games and sports.
Question.17. Differentiate isometric and isotonic exercises.
Answer. Isometric is derived from a latin word which means some length. Therefore, in these exercises, the length of muscles remains the same during workout. These exercises have no external movements and work done is zero, hence these are not visible to others.
Isotonic is derived from a latin word which means some tension. In these exercises, the muscular group has tension along with movement. In isotonic exercises, the length of muscles changes (shortens or lengthens) during action along with tension in them.
A comparison between their characteristics is given below: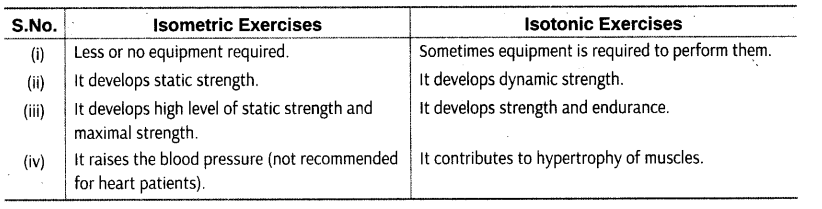
Question.18. Elucidate any two principles of sports training.
Answer. Two principles of sports training are:
- Principle of Progression The principle of progression also makes us realise the need for proper rest and recovery. The overload should not be increased too rapidly. If the overload is increased too rapidly, it may result in injury or muscle damage.
- Principle of Specificity Principle of specificity states that exercising a certain part of component of the body primarily develops that part. It means that to become better at a particular exercise or skill, you must perform that exercise or skill.
Question.19. Discuss two types of flexibility.
Answer. Two types of flexibilities are
- Active Flexibility It is the ability to do movement for a longer distance without external help e.g. exercise without partner. .
- Passive Flexibility It is the ability to do movement for a greater distance with external help e.g. stretching exercise with the help of a partner. It is always more than active flexibility.
Question.20. What are various’ factors of speed?
Or
Explain the types of speed.
Answer. The various factors of speed are:
- Reaction Time Time taken to respond to a given stimulus, e.g. start in races.
- Acceleration Ability Ability of the body to achieve maximum possible speed in’minimum possible time e.g. 50 m run, 60 m run, 80 m run etc.
- Speed of Movement Time taken by a muscle or group of muscles to complete a movement e.g. 100 m race from start to finish.
- Locomotor Ability Ability of the body to maintain maximum speed for maximum duration e.g. maintenance phase in 100 m race.
- Speed Endurance Ability of the body to perform any movement speedily under the condition of fatigue e.g. pace races.
Question.21. Explain the concept of fartlek training.
Answer. Fartlek is a Swedish term which means speed play. In such type of training, an athlete can adopt any pace as .per his wish and ability to complete a specific distance. The main aspect of this training is that he has to cover the distance in fixed time. He can also change his speed or pace according to the various geographical surroundings like hills, rivers, forests, muddy roads and grassy grounds etc. During fartlek training, the rate of heartbeat should range between 140-180 beats/min. It improves the efficiency of the lungs and heart for an activity for duration of not less than 15 min.
Question.22. How would you train for developing speed?
Or
Explain the various methods of speed development.
Answer. Speed is the ability of moving a body part or the whole body with the greatest possible speed or velocity.
To develop speed, we can use the following methods :
- Acceleration runs (sprints)
- Pace races (speed endurance)
For developing speed in sprinting and running over distances of 800 m or more
- An athlete should commence his training with around 75% of his maximum speed.
- He should move gradually towards 100% of his maximum speed.
- The total number of runs per unit (in one day) should be between 6 and 12, depending upon the capacity of the athlete.
- Acceleration runs should be started after proper warming up.
- Training at maximum speed in early morning should be avoided.
- In case of pain or cramp in muscles, training should be discontinued.
Question.23. Define speed. Explain the methods of speed development.
Or
How do acceleration runs and pace races develop speed?
Answer. Speed It is the ability of an individual to cover maximum distance in minimum possible time.
Developing Methods
- Acceleration Runs A good athlete generally accelerates ter the first 30-60 “m, so the acceleration should be performed for 30-60 m only.
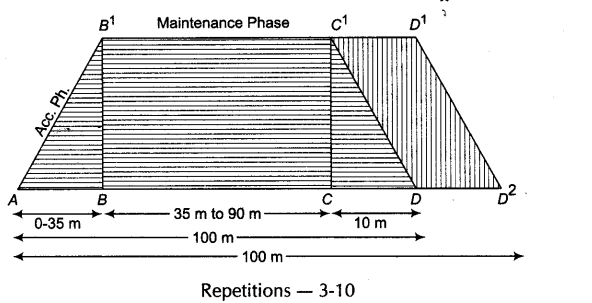
Intensity — High; 90% and above nature - Pace Races When an athlete has accelerated to his maximum speed, he should maintain this speed for maximum duration without any slowing down. The method to be followed in these – races involves the following.
(i) Intensity should be 60-80%
(ii) Repetitions should be 2-6
(iii) Distance should be 60-600 m
In pace races, the speed can be increased by
• increasing the stride length.
• lifting the knee higher.
• developing coordination between arms and legs.
Question.24. Explain the term ‘warming up’. What are its advantages?
Answer. Warming up is a process in which muscles are warmed up by running, jogging and performing some freehand exercises prior to training or competition.
A warming up session is divided into two parts:
- General warming up
- Specific warming up .
Warming up should not be less than 15 min and not more than 40 min.
Advantages:
- It raises the body temperature.
- It creates tension in the muscles and makes the joints comparatively active.
- It improves metabolic reaction.
- It reduces the chances of muscular injuries.
Question.25. What is strength? Discuss any two types of exercises used for strength development.
Answer. Strength It is the ability of muscles to overcome resistance. It is the ability of an individual to work against resistance, e.g. various throws and jump events, swimming etc.
Types of exercises for strength development are:
- Isometric Exercises or Static Contraction The literal meaning of the word isometric is constant length, i.e. iso means constant and metric means length.
In this contraction, muscles work against a resistance but there is no change in the length of muscle. No external movement is visible to a third person, e.g. leg press, pushing a wall, squat position, holding leg at 45°. - Isokinetic Exercises The literal meaning of the term isokinetic is constant speed, i.e. iso means constant and kinetic means motion.
It is defined as maximal contraction with constant speed over the full range of movement, e.g. cycling, arm stroke jn butterfly style swimming etc.
Question.26.Discuss the continuous training method in detail.
Answer.In this method, exercise is done for a long duration without giving any break or pause in between the exercise. It is of three types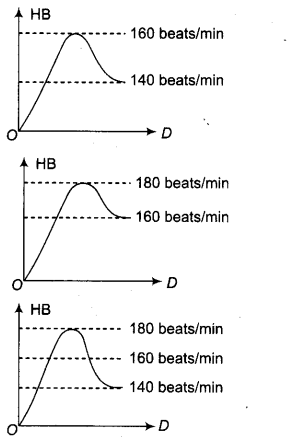
- Slow Pace Continuous Method In this method,
Intensity (rate of doing work) —Low
Distance — Long (10-30 km)
Heart rate — 140-160 beats/m in - Fast Pace Continuous Method
Intensity — High
Distance — Less (2-10 km)
Heart rate— 160-180 beats/min - Variable Pace Method
Intensity— Between low and high
Distance — 8-20 km
Heart rate— 140-180 beats/min (1×3)
Question.27. Discuss any two methods of endurance development.
Answer.
- Interval Training Method In this method, the whole workload is divided into smaller load periods with a rest period in between them. Incomplete recovery is given in intervals.
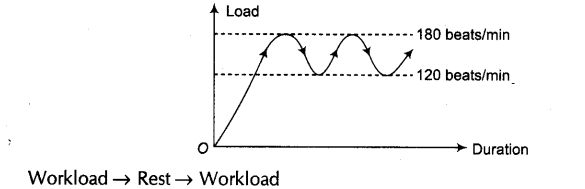
In this method, heart rate increases from normal to 180 beats/min. The bouts of load are repeated when the heart rate comes down to about 120 beats/min.
Interval training method is of two types
(a) Slow or Extensive Interval Method
Intensity — Low (60-80%)
Distance — 400-800 m
Frequency — 15-25 repetitions
(b) Fast or Intensive Interval Method
Intensity — High (80-100%)
Distance — 50-400 m,
Frequency — 8-12 repetitions - Fartlek Training Method
Fartlek training was introduced by Dr Astrand. In this training, the athlete can run at any pace, can select any path, can run for any distance, but the course has to be completed in the specified time. The training involves running through streets, woods, river or seaside, running up and down a hill, forest and muddy track etc.
5 Marks Questions
Question.28. Draw ten stations circuit training programme for improving the jumping ability of a player. [CBSE2013]
Answer. Circuit training is a very popular and effective method of training for the improvement of physical fitness components. In circuit training, several exercises are done one after the other. Completion of one set of each exercise in rotation is called one round. There are normally three or more rounds in circuit training which consists of 7-12 exercises generally.
The exercises in a circuit are arranged in such a manner that different muscle groups are exercised in rotation. A specific circuit, however, can consist of several exercises involving the same muscle groups. An example ofciituit training is given below.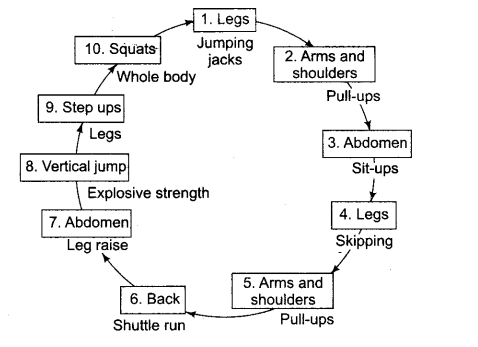
Question.29. Define the term strength. Draw 8 stations circuit training programme for upper body strength. [CBSE 2012]
Answer. Strength It is the ability to resist stress. It is the ability of the muscles to overcome resistance. Strength of the body can be measured in pounds or dynes.
8 Stations Circuit Training Programme: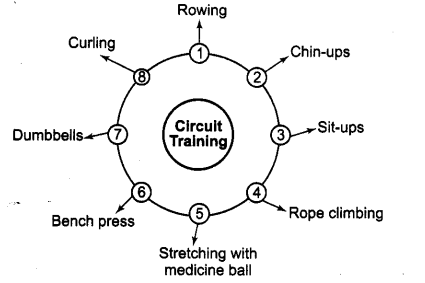
Question.30. Explain the concept of sports training.
Or
Discuss about the three periods of a sports training programme.
Answer. Training is based upon scientific principles in a systematic order. In other words, we can say that sports training consists of methods to improve general and specific performance in games and sports. It gives us knowledge regarding performance and it also guides us how to improve further through different ways.
Sports training consists of training periods which are split into training sessions which are further divided into training schedules. In the training periods, work/load is performed. It is performed in a progressive way through macro, mesoand micro cycles. The training period is a long process which may extend to one year or more.
Training Programme Basically, a training programme can be divided into three periods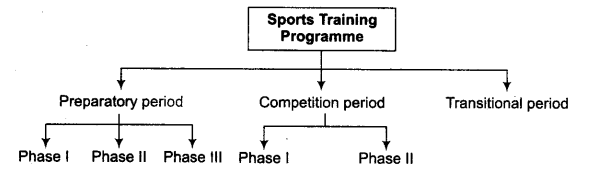
- Preparatory Period In this period, the player achieves the physical fitness and skill efficiency necessary for competition.
It is practiced in three phases:
(a) Phase I In this phase, the player develops general abilities relating to physical fitness like basic skills. It is perfected after about four to six month’s practice.
(b) Phase II In this phase, the player develops specific fitness abilities like speed, flexibility and coordination. It is about two month’s practice.
(c) Phase III In this phase, the player develops tactics and strategies and achieves perfection for competition. - Competition Period In this period, the player actually plays in competition and aims to achieve top performance in competition. It is practiced in two phases
Phase I In this phase, special attention is given towards specific exercises, skills and techniques, practical application of tactics in a game etc.
4 Phase II In this phase, there is actual competition for the players. - Transitional Period This is the relaxation period after each competition.
Question.31. Define strength. Explain the details of strength training methods with the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Answer. Strength is the ability of our muscles to overcome resistance, We use the following methods of strength development
- Isometric Exercises They are those exercises in which the length of the muscles remain the same during workout. No external movement is visible to a third person. During an isometric contraction, the muscle develops tension but does not change its length. In isometric exercises, special instruments may be used, e.g. power rack.
Advantages:
(a) They can be performed anywhere.
(b) In these exercises, less time is required.
(c) In these exercises, less equipment is required.
(d) They develop a high level of static and maximum strength.
Disadvantage: It raises the blood pressure, and therefore it is not recommended for heart patients. - Isotonic Exercises These are exercises in which movements are clearly visible in the concerned body part. Length of the muscles changes and work done is clearly visible. These exercises help muscles to also improve their flexibility along with developing strength in them.
Isotonic contractions are of two types:
(a) Concentric (b) Eccentric
Advantages:
(a) They develop dynamic strength.
(b) They contribute to hypertrophy of muscles.
Disadvantages:
(a) In these exercises, there are chances of strain and stress injuries.
(b) In these exercises, usually some equipment is required. - Isokinetic Exercises In these exercises, there is movement along with continuous tension in both flexor and extensor muscles. Here, both the flexor and extensor muscles develop tension ” along with full range of movement (may be upward or downward) simultaneously. These require special equipment, e.g. cycling upward, swimming, weight training machines etc.
Advantages:
(a) They develop a high level of dynamic as well as explosive strength,
(b) These are effective for almost every game.
Disadvantages:
(a) They require special types of equipment,
(b) They must be performed under observation of a coach.
Question.32. Explain circuit training method in detail.
Or
How does circuit training develop strength, speed and endurance?
Answer. Circuit training programme was designed by GT Adamson and RE Morgan in 1957. It is very effective method for strength, speed and endurance development. Circuit training is a formal type of training in which an athlete goes through a series of selected exercises that are arranged in a circuit with 5 to 10 stations.
Classification of Circuit Training:
- General Circuit Training In this type of training, different muscle groups are given exercises in rotation.
Number of stations – 5-10
Intensity Frequency – 60-80%
Frequency – 3 days per week
Exercise performed – 30 sec, 1 min
Rest between two stations -5 to 15 sec
Rest between two circuits- 2 to 5 min - Specific Circuit Training In this training, specific muscle groups are given exercises at every station. Exercises are also similar to competitive stress e.g. circuit training for football, volleyball, badminton etc.
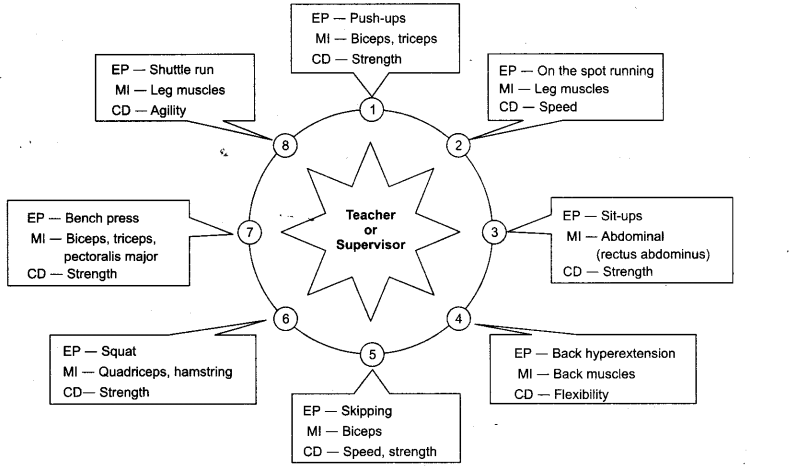
Note: EP represents exercises to be performed, Ml represents muscles involved, CD represents physical fitness component developed.
Advantages of Circuit Training:
- A single teacher can supervise the training programme.
- A large number of athletes (20-30) can be accommodated.
- It can be performed anywhere — indoor, outdoor, on rooftop etc.
- Any specific component of physical fitness can be developed.
- Intensity or load can be increased if required.
- All muscles of body can be exercised.
- It is an interesting method of training.
- It can be performed in bad weather also.
Question.33. Define flexibility and explain the methods of flexibility development.
Answer. Flexibility is the range of movement. It is the ability of joints to move in the maximum range.
Types of Flexibility:
- Active Flexibility It is performed without external help or self-movement of a part to the maximum range.
- Passive Flexibility It is the ability of joints to move in their maximum range with external help.
Developing Methods of Flexibility:
- Ballistic Method In ballistic method, the movement is performed with a swing in a rhythmic way.
- Static Stretching Method In this method, the joint is stretched and held for 10 to 30 sec.
- Dynamic Stretching Method In this method, activities are performed with a motion or movement in a full range.
- Post Isometric Stretch or PNF Technique This method is based on the principle of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation. PNF is a more advanced technique that involves both stretching (static + dynamic) techniques and contraction of the muscle groups being targeted. For gaining flexibility in the shortest possible time, PNF technique is the most appropriate method for developing flexibility