CBSE Class 12 Physical Education Important Questions Chapter 7 Physiology and Sports
1 Mark Questions
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
(1 MARK EACH)
Q1. What is flexibility?
Ans. Flexibility is the range of movement of a joint. The range of joints varies significantly from joint to joint & depends on the surrounding tendons, ligaments & muscle tissues.
Q2. What is ageing?
Ans. Ageing is a process of continuous & irreversible decline in the efficiency of various physiological functions.
Q3. What is stroke volume?
Ans. Stroke volume is a volume, which the heart pumps out the blood in a stroke in arota.
Q4. Define oxygen intake?
Ans. It is the amount of oxygen, which can be taken by the lungs from the atmosphere.
Q5. Define physical fitness?
Ans. Physical fitness is considered a measure of the body’s ability to perform effectively & efficiently in work and leisure activities ,to be healthy, resist hyperkinetic dieses & emergency situations.
Q6. What is cardiac output?
Ans. The total volume of blood, pumped by hearth per minute. Cardiac output=heart rate*stroke volume.
Q7. What is oxygen uptake?
Ans. The amount of oxygen, which can be absorbed and consumed by the working muscle from the blood.
Q8. What do you mean by physiology?
Ans. Physiology is the division of biology that deals with the functions and activities of living organisms & their parts as well as physical and chemical process i.e. Nutrition, movement & reproduction, which is the living activities.
Q9. What is Cardio-vascular system?
Ans. It sends oxygen to various muscles, tissues & arteries and at the same time returns The De-oxygenated blood to the lungs to be re-oxygenated and return the fuel to The Active tissues of the different parts of body.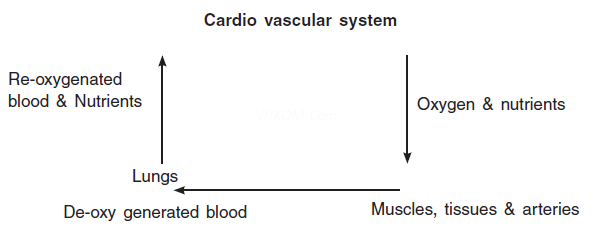
Q10. Define Respiratory system?
Ans. It is a system in which organs to take oxygen inside and throw away carbon dioxide from the body.
Q11. What is Respiration?
Ans. The process of Oxygen supplied to the cells and the transport of carbon dioxide from the cells is called Respiration.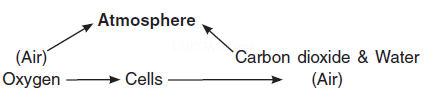
Q12. Define Blood Vessels?
Ans. Blood vessels are, tube like structures in the body, in which, blood flows from heart to cell and vice-versa. Three types of blood cells -arteries, veins & capillaries
Q13. What do you mean by circulatory system?
Ans. The body system, which specialized function of transporting Air, Nutrients, Waste Material, Harmons and Enzymes. It consists Heart, Blood vessels & Glands.
Q14. What is Trachea?
Ans. Trachea is a hollow wind pipe, which permanently kept open and is lined with ciliated epithelium tissues.
Q15. What is the Tidal Volume?
Ans. It is the volume of Air, ventilated with one normal inhalation during ordinary respiration.
Q16. What is Vital Capacity?
Ans. It is the volume of air, that can expelled by the most forcefully expiration after the deepest inspiration.
Q17. What is VO2 Max(Maximum Oxygen uptake).
Ans. It is the maximum amount of Oxygen, utilized by the body in one minute.
Q18. Explain Aerobic capacity?
Ans. It means perform activity with maximum use of oxygen to produce energy for that activity.
Q19. Define Total Lung Volume?
Ans. It is the volume of Air, which, the lungs can accommodate after a deep inspiration.
Q20. Explain Muscle Fibre?
Ans. The Muscle tissues consists of specialized contractile cell. The type of muscle fibre in:
The body— 1. Fast Twitch fibres- White fibres.
2. Slow Twitch fibres (Red Fibres)
Q21. What is Myoglobin?
Ans. The Myoglobin is a type protein present in muscle fibre to store oxygen which produces energy in emergencies.
Q22. Define Anaerobic Capacity?
Ans. It means perform activity without the use of oxygen to produce energy for that activity within the body and it’s resultant products are:-
Lactic Acid
Carbon dioxide
Water
3 Mark Questions
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (80 TO 90 WORDS) –
(3 MARKS EACH)
Q1. Differential between Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism?
Ans.
| Aerobic metabolism | Anaerobic metabolism |
| 1. Aerobic metabolism means the body can convert nutrients into energy with oxygen and it’s waste products are:- Carbon dioxide and water. | 1. Anaerobic metabolism means the body can convert nutrients into energy without oxygen and it’s waste products are:- Lactic acid, water and carbon dioxide. |
| 2. Aerobic metabolism occur in the endurance activities. | 2. Anaerobic metabolism occur in the speed activities. |
Q2. What are capillaries?
Ans. Capillaries are the smallest and thinnest vessels in the circulation system. The wall of capillaries, made up of only one layer of cells. The interchange of gases and substance between the blood and the tissues take place here.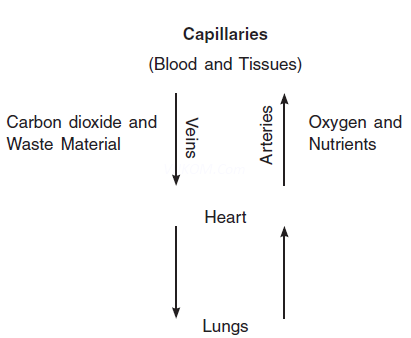
Q3. Write the immediate effects of exercise on Cardio-Vascular system?
Ans. 1. Increase in heart rate:- When and individual starts exercise, his heart rate increases as per the intensity and duration of exercise.
2. Increase in stroke volume:- Stroke volume increases proportionally with exercise intensity. It is measured in ml/beat
3. Increase in cardiac output:- Cardiac output increases proportionally with the intensity of exercise’s t is measured in ltr/ minute.
4. Increase in blood flow:- Cardio-vascular can be distribute more blood to those tissues which have more demand and less blood & those tissues which have less demand for oxygen. The blood is moved away from the main organs such as lever, intestine and kidney in fact it is redirected to the skin to enhance heat loss.
5. Increase in blood pressure:- During the exercise, systolic blood pressure can increase while diastolic blood pressure usually remains unchanged even during the intensive exercise.
Q4. Differentiate between slow twist fibre and fast twist fibre?
| Slow twist fibre (red fibres) | Fast twist fibre (white fibres) |
| The red fibres of muscles are mainly responsible for the endurance activities. | The white fibres of muscles are responsible of strength and speed activities. |
| The red fibres are produced energy by the nutrients in the presence of oxygen only. | The white fibres are produced energy by the nutrients without the presence of oxygen. |
Q5. Write the effects of exercise in muscular system?
Ans. 1. Increase in muscle mass:- Through the regular exercise, the cells of the muscle are enlarged, which change the size and shape of the muscle.
2. Control extra fat:- Regular exercise controls extra fat of the body. Exercise burns the calories, which is taken in the form of fat. This increases the lean mass in the body.
3. Delays fatigue:- Regular exercise delays fatigue. This fatigue is mainly due to formation of carbon dioxide, lactic acid and acid phosphate. The accumulation of carbon dioxide, acid phosphate, lactic acid become less in a person who performs regular exercise.
4. Posture:- Regular exercise helps in improving posture by improving portural deformities.
5. Strength and speed:- Regular exercise improve the strength and speed muscle cells. This Is partially due to the hypertrophy of muscles and partially due to increase in the capacity of giving and receiving stimulus.
Q6. Describe the effects of exercise on respiratory system?
Ans. The effect of exercise on respiratory system is closely linked with the effect of exercise on circulatory and muscular system. This means that the effect produced on respiratory system by training are improved lung capacity and gas exchange.
1. Improved tidal volume and vital capacity of lungs
2. Improved aerobic and anaerobic capacity
3. Avoid second wind
4. Increased will power
5. Unused alveoles become active:-regular exercise activity, the unused alveolus because much amount of oxygen is required in vigorous and prolonged exercise of daily routine. The passive alveoles becomes active.
5 Marks Questions
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTION (150 TO 200 WORDS) –
(5 MARKS EACH)
Q1. Elucidate Physiological changes due to Ageing?
Ans. The Physiological changes, which take place mentioned below.
1. Change in Nervous System:- During the ageing, reaction time and movement time slows done with increase in age. The brain waits, the size of it’s network and it’s blood flow decreases with age.
2. Change in Gastro Intestinal System:- With increase in age, there is a reduction in the production of Hydrochloric Acid, Digestive Enzymes and Saliva. These changes may result In delayed emptying the stomach, impaired swallowing. The breakdown and absorption of food may also be impaired. The liver becomes less efficient in metabolizing drugs and repairing damaged liver cells.
3. Change in Urinal System:- As we age, the mass of the kidney decreases, which leads to reduction in blood filtration by the kidneys. The capacity of the bladders decreases and there is an increase in residual urine. This increases the chance of urinal infections.
4. The change in senses:- With advance in age, the senses such as vision, hearing, taste, smell and touch may become less active. Vision and hearing are the most affected by ageing. The taste buds are reduced with age so they loose interest in food.
5. Change in Respiratory System:- With the age, pulmonary function is impaired with advancing age. The air ways and lung tissues become less elastic and less efficient. There is decreased Oxygen uptake and Oxygen exchange.
6. Change in fitness:- The elasticity of Tendons, ligaments and Joint capsules decrease with Ageing. The range of the movement is restricted and muscle mass decreased as the age Increases. This leads to decrease Flexibility, Endurance, Strength, Speed with shortness of Breath, Blood Flow, Enzymes etc.
Q2. Explain the effect of Exercise on Circulatory System?
Ans. 1. Increase in heart size:- Regular exercise develop the muscles of heart. It increases The size of heart along-with the strengthening of heart. Heart becomes efficient in doing It’s job.
2. Decrease in cholesterol level:- Regular exercise reduces the level of cholesterol in Our blood. The level of cholesterol in our blood is directly linked with blood pressure. Exercise decreases the level of low density protein and increases the level of high density lipo protein. It means that exercise decreases the LDL (bad cholesterol) and Increase HDL (good cholesterol)
3. Faster adaptation to workload:- Due to the regular exercise, the heart can adapt to working load quickly i.e. Quick adjustment ofheart according to body needs.
4. Increase in No. and efficiency of capillaries:- With the regular exercise, efficiency and No of capillaries are increased with the increase of Muscle Mass. The unused and new capillaries become efficient and nurish the various cells effectively.
5. Improve the working capacity of cardio-vascular system:- Regular exercise Improve cardio-vascular system thus the blood travels faster through the blood vessels and increased circulation of blood makes healing faster.
Q3. Discuss the physiological factors determine the flexibility?
Ans. 1. Muscle strength: –The muscle should have minimum level of strength to make the movement, specially against the gravity or external force.
2. Joint structure:- There are different types of joint in human body, some of the joints intrinstically have greater range of motion than others for example-The ball & socket Joint of the shoulder has the greatest range of motion in comparison to the knee joint.
3. Internal environment:- Internal environment of athlete influences the flexibility. For example-warm bath increases body temperature and flexibility whereas 10 minutes outside stay in 10oc temperature reduces the body temperature and flexibility.
4. Injury:- Injuries to connecting tissues and muscles can lead to thickening or fibrocin on the effected area. Fibrous tissues are less elastic and can lead to limb shortening and lead to reduce flexibility.
5. Age and gender:- Flexibility decreases with the advancement of age. However it is trainable. It can be enhanced with the help of training as strength and endurance are enhanced. Gender also determine the flexibility. Females tend to be more flexible than male .
6. Active and sedentary life style:- Regular activities enhance the flexibility, whereas Inactive individual looses flexibility due to the soft tissues and joints shrinking and loosing extensibility.
7. Heredity:- Bony structures of joints and structure length and flexibilities of the joint capsules and surrounding ligaments are genetical and cannot be altered by stretching programs.
Q4. Elaborate the Role of Regular Exercise on Ageing Process?
Ans. Reduces the risk of Age Related Dieses:- Regular exercise reduces the risk of a number of health problems, many aged persons face. Such
Health problems are:-
1. Diabetes, obesity, hypertension and heart disease:- Regular exercise decreases the sugar level, decrease bad cholesterol, increase good cholesterol, decreases blood pressure and blood vessels stiffness.
2. Increase in muscular strength:- Ageing process does not hinder the individual ability to enhance the muscle strength. Regular exercise increases the strength of the muscles. As a matter of fact, exercise increases the size of muscle which ultimately increasesmuscular strength.
3. Reduce the loss of muscle mass:- Muscle mass decreases with advancing age. Ageing has negative effect on metabolism. Regular exercise reduces the loss of lean body mass and drop in the metabolic rate. Regular exercise also reduces the accumulation of fats.
4. Enhances the capacity of lungs and hearts:- Regular exercise enhance the working capacity of lungs and heart, it reduces the loss of electricity of muscle fibers of lungs and heart. It also plays a key role in keeping the lungs strong and increase oxygen update and oxygen exchange.
5. Maintaining the bone density:- The bone density decreases with age. It usually leads to fracture and ostroporosis. Physical exercise helps to maintain bone mass and stimulate bone growth. The ageing persons can increase their bone density with the help of regular exercise.
6. Slow down the brain due to ageing:- The regular exercise reduces the risk of mild cognitive new nerve cells and builds new capillaries to supply the brain with more oxygen.
7. Improve mental Health and mood:- Regular physical activities can help to keep thinking learning and judgement skills sharpen. Aerobic and muscle strengthening activities can also reduce the risk of depression and may help to sleep better.
Q5. Discuss the physiological factors, determine the strength as a component of physical Fitness?
Ans. 1. Muscle size:- Muscle strength directly depends on the cross sectional area of muscle. It is well known that bigger and larger muscle can produce more force. The force produced by the same size of muscles in males and females is approximately the same but males are found to be stronger because they have larger and bigger muscles in comparison to females.
2. Body weight:- There is a positive correlation between the body weight and strength Individuals with the heavier body weight are stronger than the individual with the lighter Weight.
3. Muscle composition:- The muscle composition is genetically determined and cannot be changed by any type of training
4. Nerve impulses:- The nervous system also play a role in muscle strength. The brain and nervous system has power to activate more motor units when they need to generate larger amount of force. Through the strength training, the body learns to recruit more motor units and increase these units.
5. Age and gender:- Age and gender is a factor which effects the muscle strength. Muscle strength decline with the age but it is primarily due to a decrease in muscle cross-sectional area and decline in the amount of contractile tissues within the muscle fibres. Regular strength training limits loss of muscle strength with ageing. Men has greater absolute muscle strength than women.
Q6. Describe the physiological factors which determine the speed as a component of physical fitness?
Ans. Speed is determined to a great extent by the genetic factors. The study of physiological Factors help to select the activity for an individual.
1. Mobility of the nervous system:- The rapid contraction and relaxation of muscles is made possible by the rapid excitation and inhibition of the concerned motor centres. Nervous system can maintain this rapid excitation and inhibition for only for a few seconds. After which the excitation spread to the neighbouring centres causing tension in the entire body. This results in decrease in speed. The mobility of the nervous can be trained only to a very limited extent.
2. Muscle composition:- The muscle, which has more percentage of fast twist fibers, contract with more speed in comparison to the muscle which have lower percentage be slow twist fibres. The muscle position is genetical and cannot be changed by training.
3. Explosive Strength:- For very quick and explosive movements, explosive strength is indispensible. It depends upon metabolic composition, muscle size & muscle coordination. The explosive strength of the muscles can be improved through training.
Q7. Explain the physiological factors determine endurance as a component of physical fitness?
Ans. Endurance is very significant component of physical fitness, which is determined by the following physiological factors.
1. Aerobic capacity:- To perform an activity continuously, energy is required by the muscles which can be supplied by the presence of energy. Therefore the ability of organism to maintain the adequate supply of oxygen to the working muscles for energy liberation is important for endurance performance. The aerobic capacity depends upon:
a. Oxygen intake:- The oxygen intake depends on the vital capacity which further depends on lungs size, no of active alveoli, respiratory muscle and the size of the chest cavity.
b. Oxygen transport:- The oxygen transport depends on the amount of oxygen, which the blood has absorbed from the lungs and the ability of the circulatory system to carry this quickly to the working muscles. The amount of oxygen absorbed into the blood depends on the speed of blood flow through the lungs and on the blood haemoglobin. The concentration of blood haemoglobin can be enhanced by training. The transportation of oxygenated blood depends on the capacity of the heart. This capacity can be improved by training.
c. Oxygen uptake:- This depends on the rate of defusion, which determined the speed of blood flow, temperature & partial pressure of oxygen in the blood and of carbon dioxide in the muscles. The speed and amount of oxygen consumption depends on the no, size & metabolic capacity of mitochondria and fortunatly can be improved to some extent through training.
d. Energy reserves:- The aerobic capacity depends on the muscle glycozen & sugar level in the blood. This can be enhanced by the training
2. Lactic acid tolerance:- The lactic acid tolerance capacity can be improved through the training.
Physical Education Class 12 Important Questions Chapter 8 Physiology and Sports
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Define physiology.
Answer:
Physiology is the study of how the human body functions i.e. how the organs, systems, tissues, cells and molecules work together to maintain our internal environment.
Question 2.
Calculate how much blood is pumped by the heart in one minute.
Answer:
Blood pumped by the heart in one minute is Cardiac output = heart rate × stroke volume
= 72 beats/mm × 70 mL approximately = \(=\frac{5040 \mathrm{mL}}{\min }\)
Question 3.
What is ‘stroke volume’? (All Indio 2016)
Answer:
The amount of blood pumped into the aorta with every heartbeat is known as the stroke volume. In an untrained male, it is 70-90 mL/beat.
Question 4.
What is oxygen uptake? (All India 2017)
Answer:
Oxygen uptake or VO2 is oxygen consumption or uptake per kilogram of body weight. It is a good measure of the respiratory system.
Question 5.
State the amount of blood pumped in one ventricle beat.
Answer:
The amount of blood pumped into the aorta with every heartbeat is known as the stroke volume. In an untrained male, it is 70-90 mL/beat.
Question 6.
What is tidal volume?
Answer:
Tidal volume is the amount of air inspired or expired per breath. This can be increased with the help of endurance training. In untrained individuals, tidal volume is about 500 mL/breath, whereas in trained persons, it is increased to 600-700 mL/breath.
Question 7.
How the muscular system of males and females are different? (All India 2017)
Answer:
The muscular system of males are stronger than females as they have more muscle mass and muscle composition. The bones and ligaments attached to the muscles are stronger in males than in females.
Question 8.
Explain the term hypertrophy of muscles. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Hypertrophy of muscles or muscular, hypertrophy is an increase in muscle mass and cross-sectional area. The increase in dimension is due to an increase in the size (hot length) of individual muscle fibres.
Question 9.
Why do.es involvement in regular exercise delay the onset of fatigue? (All India 2015)
Answer:
Regular exercise delays the oriset of fatigue as exercise develops the fitness levels and increases – endurance thereby delaying fatigue:
Question 10.
Write one physiological change dire to ageing. (Delhi2016)
Answer:
One physiological change which occurs’due to ageing is reduction in muscle size and strength.
Question 11.
Explain the effects of ageing on accumulation of fat.
Answer:
With advancing age, there is. an increasing trend to accumulate fat because the ability to release ‘ stored fatty adds from adipose tissues for energy decreases.
Question 12.
What is physiology and .why is it important in sports?
Answer:
Physiology is the study of how our organs, systems, tissues, cells etc function. This is essential to understand how to attain physical fitness in order to enhance the performance in sports/
3 Marks Questions
Question 13.
Describe the role of regular exercise on ageing process.
Answer:
Regular exercise keeps the human body livelier, fitter and in better condition, thus delaying the ageing processes, as given below
- Exercise reduces the loss of elasticity from the lungs and chest wall.
- Exercise increases muscle strength and hypertrophy by increasing the cross-sectional area of the Slow Twitch Fibres (STF) and Fast Twitch Fibres (FTF). This slows down ageing.
- The body composition changes due to exercise by reducing the fat content of the body, thus slowing down the ageing process.
- Exercise improves flexibility by strengthening the musculoskeletal systems, thereby preventing the stiffening of joints. It improves the elasticity of tendons, ligaments and joint capsules.
Question 14.
Explain the effects of ageing on muscle size and strength.
Answer:
As an individual gets older, there is a decline in muscle size. It is believed that this decline is due, in part, to a reduced amount of protein as well as a decline in the number and size of muscle fibres.
This may be due to degenerative diseases generally associated with advancing age affecting the nerve fibres. Increases in strength are related to muscle fibre hypertrophy, meaning that strength increases parallel to increases in muscle size. As people get old and the muscle size decreases, there is a parallel decrease in muscular strength.
5 Marks Questions
Question 15.
What are the various factors affecting physiological fitness? Explain. (All India 2015)
OR
Describe physiological factors determining components of physical fitness.
Answer:
Physiological factors determining components of physical fitness are
- Muscular Strength This is the maximum force or tension a muscle or a muscle group can exert against a resistance.
Physiologically the muscle will increase in strength only if it has to increase its workload beyond what is ordinarily required of it. - Power This is the ability of the body to release maximum muscle contraction in the shortest possible time.
- Speed This is the rapidity with which one can repeat successive movements of the same pattern.
- Muscular Endurance This is the ability of a muscle or muscle group to perform repeated contractions against a resistance/load or to sustain contraction for an extended period of time with less discomfort and more rapid recovery.
- Agility This is the ability of a person to change direction or body position as quickly as possible and regain body control to proceed with another movement.
- Flexibility This is a quality of the muscles, ligaments and tendons that enables the joints of the body to move easily through a complete range of movements.
Question 16.
Give five physiological differences between males and females. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Physiological differences between males and females are
| Basis | Males | Females |
| Strength | Men are stronger than women because they have greater muscle mass. | Women are not as strong as men because their muscle mass is less. On average, women possess 2/3rd the strength possessed by men. |
Cardiovascular functions | In intense exercises, men have better cardiac output than women. | Women have lower cardiac output than men. |
| Respiratory functions | The respiratory functions are better in men. They have more haemoglobin content and VO2 | The respiratory functions in women lack in certain parameters related to haemoglobin content and VO2 |
| Endurance | The endurance level in men is high by around 10% because of high haemoglobin content and better blood circulation. | The endurance level in women is even higher due to greater number of white fibre in the muscle. |
| Bones and ligaments | Men have longer and stronger bones and ligaments but due to a narrow pelvis and higher centre of gravity, they have poor balance. | Women’s bones and ligaments are not strong, but they have a wider pelvis and lower centre of gravity that provides better balance. |
Question 17.
What is the effect of exercise on the cardiovascular system?
Answer:
The effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system are
- Cardiac Output It is the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. Cardiac output increases with the intensity of the exercises. At rest it is 4 to 6 L/min and during exercises it is 20 to 40 L/min.
- Heart Rate The number of cardiac contractions in one minute is called heart rate. During exercises the heart rate goes?
- Stroke Volume The amount of blood pumped into the aorta with every ’ heartbeat is known as the stroke volume.
The stroke volume increases in response to the intensity of the exercises. - Blood Flow With increasing intensities of exercise, a greater accumulation of lactic acid and the production of other metabolic ‘ end products occurs. This increases blood flow in the cardiac output, while decreases in kidneys and abdomen.
Question 18.
Recall the adaptive effects that take place in our body after engaging in exercise for a longer period.
Answer:
The adaptive effects that take place in body after engaging in exercise for a longer period are
- Increase in Heart Size We cannot do the exercise on our heart directly, but when we perform any exercise regularly, our heart size increases. Exercising develops the muscles of the heart.
- Increase in Heart Rate Generally an adult has a heart rate of 72 beats per minute while resting, but when he exercises, his heart rate increases as per the intensity and duration of the exercise.
- Increase in Stroke Volume Stroke volume is the quantity of blood which the heart pumps out in a single stroke. Due to the heart’s size increasing, the stroke volume increases.
- Decrease in Cholesterol Level Regular exercise reduces the cholesterol level in our blood, which has a direct link with the/blood pressure.
- Increase in Number and Efficiency of Capillaries Regular exercise increases the number of capillaries and their efficiency.
- Reduced Risk of Heart Diseases Regular exercise gradually reduces stress-related hormones from circulating in the ‘ blood. This results in increase of blood flow in the blood vessels, which in turn, lowers the risk of building up of plaque which affects the heart. Hence, regular exercise reduces the risk of heart diseases.
Question 19.
A trainer can improve the respiratory system with the help of exercise. Justify this statement.
Answer:
The respiration system consists of organs responsible for taking in oxygen for respiration and releasing carbon dioxide and water vapour, which are the waste-products-formed during respiration. The passages in the nose, windpipe (trachea), bronchi, lungs and air sacs are the main organs of the respiratory system.
A trainer can improve the respiratory system with the help of exercise by
- Increasing the Lung Volume and Capacity Vital capacity, which is the maximal volume of air forcefully expired after a maximal inspiration, in a normal untrained person may be 3-4 litres; but in atrained athlete this goes upto 5-6 litres.
- Reducing the Breathing Frequency In a normal untrained individual, the resting breathing frequency is about l’2-20 breaths/min, whereas in trained athletes, it comes down to 7-8 breaths/min.
- Maximising the Minute VenJiIation Maximum minute ventilation fit-an untrained individual is about lOO.L/rnin, whereas in trained athletes it increases to.more than 150-160 L/mn.
- Increasing the Tidal Volume Irian untrained individual/tiddl volume is about 500 mL/breath whereas in trained persons, it increases to more than 600-700. mL/breath.
- Increasing the Ventilatory Efficiency Normally, 15 L of air is required, to get 1 L of oxygen but a trained individual gets the same amount of oxygen, i.e. one litre, from less air i.e. 12 L.
- Increasing the Pulmonary Diffusion During maximal level of exercise, more-alveoli become active for diffusion. The size of the alveoli is also increased, which provides more space for diffusion of gases such as oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Question 20.
Participation in physical activity for a longer duration maintains functional fitness among the aged population. Justify. (All India 2016)
Answer:
Regular physical activity keeps the human body livelier, fitter and in better condition for long years before any ageing sets in and keeps it functionally fit, as is discussed below
- Respiratory Changes Endurance training Answer: in the elderly reduces the loss of elasticity from the lungs and chest wall. This is evident in the endurance-trained older athletes, who have very slightly reduced pulmonary ventilatory capacity.
- Muscular Strength Studies report an increase in the strength of males and females following strength training. Physical activity in the form of stimulus to the 22. muscle plays a significant role in the fibre type distribution with advancing age. Moderate levels of physical activity tend to improve muscle strength even in older women.
- Body Composition Changes The body fat content of sedentary subjects (men and women) is significantly higher than their physically active counterparts. This is because the older athletes expend a high number of calories and moreover, their dietary habits are strictly monitored as compared to their sedentary counterparts.
- Flexibility Flexibility is dependent upon the arrangement of attachment of the ligaments to the bones as well as elasticity and length of the tendons that envelop the joints. Low or medium intensity exercise e.g. walking, is reported to significantly improve flexibility. Exercise strengthens the musculoskeletal systems, thereby preventing the joints from stiffening in one position.
Thus a regular and appropriately designed exercise and training programme can maintain functional fitness in most elderly persons.
Value Based Questions
Question 21.
Sports are good for all age groups. Growing children, middle-aged people and older people, everyone can reap the benefits of physical fitness. The physiological benefits of sports can be felt by everyone. This is the reason why people are motivated to play sports as there are lot of physiological benefits?
(i) Write two physiological benefits.
(ii) What are the general disadvantages if old people do not maintain their physical fitness.
Answer:
(i) The physiological benefits are
- It improves the cardiovascular system.
- It improves the circulatory system.
(ii) If old people do not maintain their physical fitness then they can become obese, unhealthy as the internal systems will not work properly. There will be more stress, greater chances of injury and less flexibility.
Question 22.
Mr Ram, a retired person, was regular at district park every morning. He saw that most of the old people complained of joint pains. He discussed with them and from next day he organised exercise classes for aged people. His efforts were appreciated by everyone.
(i) What values are shown by Mr Ram?
(ii) Generally why do the old people complain of joint pains?
(iii) How can exercises help in relieving that pain?
Answer:
(i) The values shown by Mr Ram are good moral character, self-discipline, decisiveness, logical and decision maker.
(ii) Old people complain of joint pains because flexibility and elasticity of the ligaments and length of the tendons enveloping joints decreases with age.
(iii) Exercises strengthen the musculoskeletal systems, thereby preventing the joints from stiffening in one position. This relieves pain.
Question 23.
“Most people say that as you get old, you have to give up things. I think you get old ‘ because you give up things.” Give your opinion what you think about this with the help of physiological changes due to ageing.
Answer:
The saying is correct because, by giving up your usual activities, you speed up the ageing process. In fact, the ageing process can be slowed down by continuing your usual activities.
Regular exercise keeps the human body livelier, fitter and in better condition, thus delaying the ageing processes like loss of elasticity from the lungs and chest wall, reduction in muscle strength and hypertrophy, increase in the fat content of the body, reducing flexibility by weakening of the musculoskeletal systems, thereby causing the stiffening of joints and so on. So we should not reduce our normal activities if we want to slow down our ageing.
1 Mark Questions
Question.1. Calculate how much blood is pumped by the heart in one minute.
Answer. Blood pumped by the heart in one minute is
Cardiac output =‘heart rate x stroke volume’
=72 beats/min x 70 mL approximately
= 5 L approximately.
Question.2. Define physiology and sports.
Answer. Physiology is the study of how the human body functions. Sports physiology is derived from exercise physiology. It applies the concept of exercise physiology to training the athlete and enhancing the athlete’s sports performance.
Question.3. How much blood is found in a normal human being?
Answer. The body of an adult contains about 5 to 7 L of blood which weighs 1/3 rd of the total body weight.
Question.4. What is the systolic pressure exert by the blood?
Answer. The pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the blood vessels is called ‘blood pressure’. It has two limits, i.e. the upper limit called ‘systolic pressure’ and the lower limit called the ‘diastolic pressure’. Systolic pressure is recorded when the blood is ejected into the arteries during ventricular contraction.
Question.5. State the amount of blood pumped in one ventricle beat.
Answer. The amount of blood pumped into the aorta with every heart beat is known as the stroke volume. In an untrained male, it is 70 mL/beat to 90 mL/beat.
Question.6. What is tidal volume?
Answer. Tidal volume is the amount of air inspired or expired per breath. This can be increased with the help of endurance training. In untrained individuals, tidal volume is about 500 mL/breath, whereas in trained persons, it is increased to 600-700 mL/breath.
Question.7. What is the size of the heart and resting heart rate?
Answer. Heart Size is approximately the size of the fist of an athlete. Weight of the normal adult heart is 250-300 gm.
The resting heart rate of a normal adult is approximately 72 beats/min.
3 Marks Questions
Question.8. Explain the effects of ageing on fat, lean body weight and BMR.
Answer. With advancing age, there is an increasing trend to accumulate fat because the ability to release stored fatty acids from adipose tissues for energy decreases. Similarly, lean body weight also decreases due to decrease in muscle size and decline in calcium and phosphorous content of the bones. BMR or Basal Metabolic Rate also reduces with ageing due to the decline in lean body weight.
Question.9. Explain the effects of ageing on muscle size and strength.
Answer. As an individual gets older, there is a decline in muscle size. It is believed that this decline is due, in . part, to a reduced amount of protein as well as a decline in the number and size of muscle fibres, which may be due to degenerative diseases generally associated with advancing age affecting the. nerve fibres. Increases in strength are related to muscle fibre hypertrophy, meaning that strength increases parallel to increases in muscle size. As people get old and the muscle size decreases, there is a parallel decrease in muscular strength.
Question.10. Specify the role of physiology in exercise and sports.
Answer. Exercise physiology is the study of how exercise alters the function and structure of the body. A sports physiologist ^examines the acute responses and chronic adaptations to athletic performance in a variety of environments. While a sports physiologist can test the effect of exercises in a laboratory, which has a controlled environment, it is not always possible to simulate sporting activity in a lab. So physiologists use field based testing as much as possible.
Physiology can improve an athlete’s performance by giving important objective information which can help coaches to adapt training programmes to maximise their desired outcome. This will depend on many factors including the environment, diet, gender, age and health.
Question.11. Describe the role of regular exercise on ageing process.
Answer. Regular exercise keeps the human body livelier, fitter and in better condition, thus delaying the ageing processes, as given below:
- Exercise reduces the loss of elasticity from the lungs and chest wall.
- Exercise increases muscle strength and hypertrophy by increasing the cross-sectional area of the Slow Twitch Fibres (STF) and Fast Twitch Fibres (FTF)., This slows down ageing.
- The body composition changes due to exercise by reducing the fat coment of the body, thus slowing down the ageing process.
- Exercise improves flexibility by strengthening the musculoskeletal systems, thereby preventing the stiffening of joints. This also slows the ageing process.
Question.12. Explain the redistribution of blood flow in our body during rest and during exercise.
Answer. During exercise, the active muscles demand a greater supply of oxygen. The consumption of the skeletal muscle during exhaustive exercise is increased by 10 to 12 times. Such an increased demand is accomplished through an increased cardiac output (which results in a greater blood supply) and redistribution of the blood flow from the inactive areas towards the active muscles. The redistribution of blood flow at rest and during exercise is given below :
5 Marks Questions
Question.13. What is the the effect of exercise on the cardiovascular system?
Answer. The effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system are
- Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped by the heart in 1 min. This increases directly with increasing exercise intensity.
- The heart rate increases from a resting rate of 72 beats / min to 150 beats / min or even more.
- The stroke volume, meaning the amount of blood pumped into the Aorta with every heartbeat, increases from a resting volume of 70 – 90 mL to 100 – 120 mL per beat.
- Exercise increases the plasma volume of blood by 12%, but total blood volume may reduce slightly.
- Blood flow is redistributed with more blood going to the muscles, heart and skin, while blood in the kidneys and abdomen is reduced.
- Blood pressure increases due to exercise because there is more blood flowing in the blood vessels.
- Cardiac hypertrophy occurs, meaning that the heart size increases to take care of the larger requirement of blood during exercise.
Question.14. Describe physiological factors determining component of physical fitness.
Answer. Physiological factors determining components of physical fitness are
- Muscular strength This is the maximum force or tension a muscle or a muscle group can exert against a resistance; Physiologically the muscle will increase in strength only if it has to increase its workload beyond what is ordinarily required of it.
- Power This is the ability’ of the body to release maximum muscle contraction in the shortest possible time.
- Speed This is the rapidity with which one can repeat successive movements of the same pattern.
- Muscular endurance This is the ability of a muscle or muscle group to perform repeated contractions against a resistance / load or to sustain contraction for an extended period of time with less discomfort and more rapid recovery.
- Agility This is the ability of a person to change direction or body position as quickly as possible and regain body control to proceed with another movement.
- Flexibility This is a quality of the muscles, ligaments and tendons that enables the joints of the body to move easily through a complete range of movements.
Question.15. “Most people say that as you get old, you have to give up things. I think you get old because you give up things.” Give your opinion what you think about this with the help of physiological changes due to ageing.
Answer. The saying is correct because, by giving up your usual activities, you speed up the ageing process. In fact, the ageing process can be slowed down by continuing your usual activities. Regular exercise keeps the human body livelier, fitter and in better condition, thus delaying the ageing processes like loss of elasticity from the lungs and chest wall, reduction in muscle strength and hypertrophy, increase in the fat content of the body, reducing flexibility by weakening of the musculoskeletal systems, thereby causing the stiffening of joints and soon. So we should not reduce our normal activities, if we want to slow down our ageing.
Question.16. Recall the adaptive effects that take place in our cardiovascular system after engaging in exercise for a longer period.
Answer. The adaptive effects that take place in our cardiovascular system after engaging in exercise for a longer period are
- Increase in heart size We cannot do the exercise on our heart directly, but when we perform any exercise regularly, our heart size increases. Exercising develops the muscles of the heart.
- Increase in heart rate Generally an adult has a heart rate of 72 beats per minute while resting, but when he exercises, his heart rate increases as per the intensity and duration of the exercise.
- Increase in stroke volume Stroke volume is the quantity of blood which the heart pumps out in a single stroke. Due to the heart’s size increasing, the stroke volume increases.
- Decrease in cholesterol level Regular exercise reduces the cholesterol level in our blood, which has a direct link with the blood pressure.
- Increase in number and efficiency of capillaries Regular exercise increases the number of capillaries and their efficiency.
- Reduced risk of heart diseases Regular exercise gradually reduces stress related hormones from circulating in the blood. This results in increase of blood flow in the blood vessels, which in turn, lowers the risk of building up of plaque which affects the heart. Hence, regular exercise . reduces the risk of heart diseases.
Question.17. A trainer can improve the respiratory system with the help of exercise. Justify this statement.
Answer. The respiration system consists of organs responsible for taking in oxygen for respiration and releasing carbon dioxide and water vapour, which are the waste products formed during respiration. The passages in the nose, windpipe (trachea), bronchi, lungs and air sacs are the main organs of the respiratory system. A trainer can improve the respiratory system with the help of exercise by :
- Increasing the lung volume and capacity Vital capacity, which is the maximal volume of air forcefully expired after a maximal inspiration, in a normal untrained person may be 3-4 litres, but in a trained athlete this goes up to 5-6 litres.
- Reducing the breathing frequency In a normal untrained individual, the resting breathing frequency is about 12-20 breaths/min, whereas in trained athletes, it comes down to 7-8 breaths/min.
- Maximising the minute ventilation Maximum minute ventilation in an untrained individual is about 100 L/min, whereas in trained athletes it increases to more than 150-160 L/min.
- Increasing the tidal volume In an untrained individual, tidal volume is about 500 mL/breath, whereas in trained persons, it increases to more than 600-700 mL/breath.
- Increasing the ventilatory efficiency Normally, 15 L of air is required to get 1 L of oxygen but a trained individual gets the same amount of oxygen, i.e. one litre, from less air i.e. 12 L.
- Increasing the pulmonary diffusion During maximal level of exercise, more alveoli become active for diffusion. The size of the alveoli is also increased, which provides more space for diffusion of gases such as oxygen (o2) and carbon dioxide(co2).