Solved CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 5
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
I. The Question Paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
II. All questions are compulsory.
III. All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
IV. Question numbers I to 2 in Section A are one mark questions. These are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
V. Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30 words each.
VI. Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
VII. Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are five marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70 words each.
VIII. Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are questions based on practical skills and are five marks questions.
SECTION A
Question 1:
Name the two components of peripheral nervous system.
Answer:
Two components of peripheral nervous system:
- Autonomic nervous system.
- Voluntary nervous system.
Question 2:
What is the function of ozone in the upper atmosphere?
Answer:
Ozone layer is very important for the existence of life on earth. The function of the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere is to absorb most of the harmful ultraviolet radiations coming from the sun and prevent them from reaching the earth’s surface.
Question 3:
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
Answer:
The characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors are:
(i) The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect. It cannot be received on a screen.
(ii) The image formed by a plane mirror is of the same size as the object.
(iii) The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
(iv) The image formed in a plane mirror is laterally inverted.
Question 4:
When hydrogen gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide, copper and steam are formed. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction and state (i) the substance oxidized and (ii) the substance reduced in the reaction.
Answer: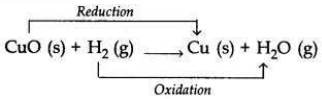
(i) Substance oxidized = H2 (Hydrogen gas)
(ii) Substance reduced = CuO (Copper oxide)
Question 5:
What is meant by “sustainable management”? Why is reuse considered better than recycling?
Answer:
The development and management of resources in such a way which meets the current basic human needs and also preserves the resources for the needs of future generations, is called sustainable management.
The process of ‘reuse’ is considered better than the process of ‘recycling’ because recycling requires the use of a large amount of energy and money whereas no energy is required for reusing materials.
Question 6:
State reason for the following:
(i) Lemon is used for restoring the shine of tarnished copper vessels.
(ii) A metal sulphide is converted into its oxide to extract the metal from the sulphide ore.
(iii) Copper wires are used in electrical connections.
Answer:
(i) When a copper object remains in damp air for a considerable time, then copper reacts slowly with carbon dioxide and water in air to form a green coating of basic copper carbonate on its surface. If corroded copper vessels are treated with lemon which is acidic in nature, the acid solution dissolves green coloured basic copper carbonate and makes them look shiny.
(ii) It is easier to obtain metals from their oxides (by reduction) than from sulphides. So before reduction, the metal sulphide ore is converted into metal oxide.
(iii) Copper metal is the next best conductor of electricity after silver metal. So electric wires are made of copper (as silver being a costly metal can not be used for making electric wires).
Question 7:
State the kind of chemical reactions in the following examples:
(i) Digestion of food in stomach
(ii) Combustion of coal in air
(iii) Heating of limestone
Answer:
(i) Digestion of food in stomach. During digestion, the complex food is broken into simpler form. Therefore, it is a type of decomposition reaction.
(ii) Combustion of coal is air. During combustion the coal bums in air to form CO2, H2O along with the evolution of heat. Thus, it is a type of exothermic decomposition reaction.
(iii) Heating of limestone. When limestone is heated strongly, it breaks into CO2 and lime. Thus, it is a type of thermal decomposition reaction.
Question 8:
The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster than that seen in terrestrial organisms. Give reason. State the pathway of air from nostrils to the lungs in human beings.
Answer:
The animals which live in water (aquatic animals) use the oxygen dissolved in water to carry out respiration. Since the amount of dissolved oxygen in water is low as compared to the amount of oxygen in the air, therefore, the rate of breathing in aquatic animals is much faster than in terrestrial animals. A faster rate of breathing provides more oxygen to aquatic animals.
Pathway of air in human beings:
Nostrils → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Lungs
OR
Mention three characteristic features of hormonal secretions in human beings.
Answer:
(i) A group of endocrine glands which produces various hormones is called an endocrine system. The endocrine system is also called hormonal system.
(ii) The endocrine system also helps in coordinating the activities of our body. The endocrine system in our body consists of a number of glands (or tissues) which make, store, and release chemicals called hormones.
(iii) The working of endocrine glands is controlled by our nervous system. The hormones produced by endocrine glands act as messengers between the nervous system and the organs of our body.
Question 9:
A circuit has la line of 5 A. How many lamps of rating 10W; 220V can simultaneously run on this line safely?
Answer:
Question 10:
Amit lives in Delhi and is much concerned about the increasing electricity bill of his house. He took some steps to save electricity and succeeded in doing so.
(i) Mention any two steps that Amit might have taken to save electricity.
(ii) Amit fulfilled his duty towards the environment by saving electricity. How?
(iii) Which alternative source of energy would you suggest Amit to use?
Answer:
(i)
• He can use energy efficient electrical appliances to save electricity. This can be done by using CFL bulbs and tube lights in place of conventional filament type electric bulbs.
• Use solar water heater instead of electrical geyser.
(ii) By saving electricity, Amit is contributing in his small way towards reducing environmental degradation. Most of the electrical appliances use electrical energy which is generated by burning fossil fuel. The burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution. The production of hydroelectricity causes ecological imbalance. Therefore, by using less electricity he is indirectly causing less pollution.
(iii) He can use solar energy devices like solar cooker, solar water heater and solar cells. With the help of an example, explain the process of hydrogenation.
Question 11:
With the help of an example, explain the process of hydrogenation Mention the essential conditions for the reaction and state the change in physical property with the formation of the product.
Answer:
Process of hydrogenation: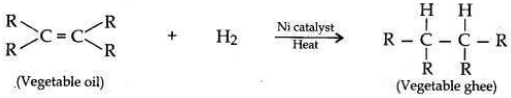
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation.
Essential conditions for the reaction are:
(i) Presence of an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
(ii) Presence of a catalyst such as nickel (Ni) or palladium.
Changes observed:
• Change observed in the physical property is the change of unsaturated compound from the liquid state to saturated compound in solid state.
• The boiling or melting points of a product is increased.
Question 12:
What is the difference between the molecules of soaps and detergents, chemically? Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer:
Difference between molecules of soaps and detergents
Action of soap in removing an oily spot from a piece of cloth. Soaps are molecules in which the two ends have differing properties, one is hydrophilic, that is, it dissolves in water, while the other end is hydrophobic, that is, it dissolves in hydrocarbons. When soap is at the surface of water, the hydrophobic ’tail’ of soap will not be soluble in water and the soap will align along the surface of water with the ionic end in water and the hydrocarbon ’tail’ protruding out of water. Inside water, these molecules have a unique orientation that keeps the hydrocarbon portion out of the water.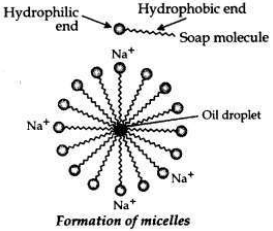
This is achieved by forming clusters of molecules in which the hydrophobic tails are in the interior of the cluster and the ionic ends are on the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle. Soap in the form of a micelle is able to clean, since the oily dirt will be collected in the centre of the micelle. The micelles stay in solution as a colloid and will not come together to precipitate because of ion-ion repulsion. Thus, the dirt suspended in the micelles is also easily rinsed away.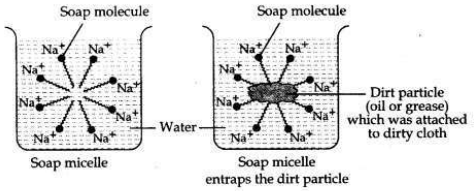
OR
How many groups and periods are there in the modem periodic table? How do the atomic size and metallic character of elements vary as we move:
(i) down a group and (ii) from left to right in a period?
Solution:
There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the modem periodic table.
(i) Atomic size and metallic character of the elements increases down a group.
(ii) • Atomic size and metallic character of elements decreases from left to right in a period.
• Metallic character of the element is decreased.
Question 13:
What is DNA copying? State its importance.
Answer:
A process in which a DNA molecule produces two similar copies of itself in a reproducing cell through chemical reaction is a called DNA copying.
(i) It transmits the characteristics from parents to the next generation (offspring).
(ii) It causes increased variations in the population.
Question 14:
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
Answer:
Ray 1. When an incident ray of light is parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror, its reflected ray must pass through the principal focus of the concave mirror.
Ray 2. A ray passing through the principal focus emerge parallel to the principal axis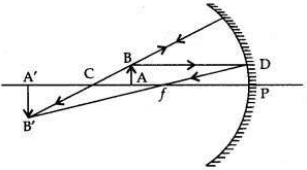
Focal length = 10 cm;
Then centre of curvature, C = 20 cm Object is placed at 15 cm, i.e., between F & C When the object is between F and C (centre of curvature):
The image formed is real, inverted and magnified. It is formed beyond C.
Question 15:
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain why the sun appears reddish at the sunrise and the sunset.
Answer: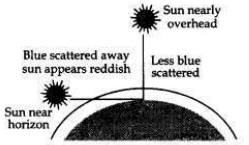
At the time of sunrise and sunset when the sun is near the horizon, the sunlight has to travel the greatest distance through the atmosphere to reach us. During the long journey of sunlight, most of the shorter wavelength blue-colour present in it is scattered out and away from our line of sight so, the light reaching us directly from the rising sun or setting sun consists mainly of longer wavelength red colour due to which the sun appears red.
Due to the same reason, the sky surrounding the rising sun and setting sun also appears red. Thus, at sunrise and sunrise, the sun itself as well as the surrounding sky appear red.
Question 16:
Write balanced chemical equations for the following statements:
(i) NaOH solution is heated with zinc granules.
(ii) Excess of carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water.
(iii) Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with sodium carbonate.
(iv) Egg shells are dropped in hydrochloric acid.
(v) Copper (II) oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer: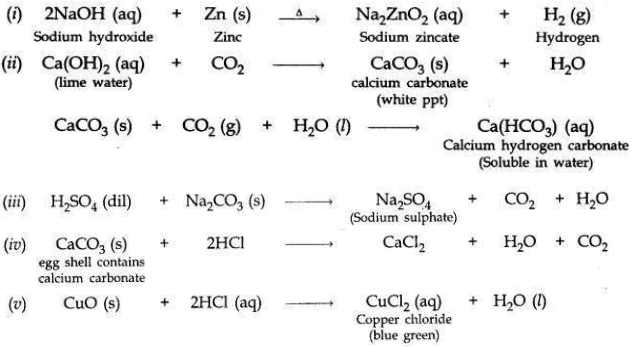
Question 17:
(a) Write three main functions of the nervous system.
(b) In the absence of muscle cells, how do plant cells show movement?
Answer:
(a) Main functions of the nervous system:
• Coordinate the activities of the body.
• Helps all other systems of the body to work together.
• The nervous system receives information from the surroundings, processes it, interprets it and then responds accordingly.
(b) The movement in any part of a plant is usually a growth movement or change in shape of body parts.
- The movements of the plant part are usually caused by an unequal growth in its two regions by the action of plant hormones, under the influence of the stimuli like light, force of gravity, chemical substances, water, touch etc.
- The change in shape occurs by changing the amount of water in the body part. Water causes swelling and shrinking which causes movement.
Question 18:
(a) Draw magnetic field lines of a bar magnet. “Two magnetic field lines never intersect each other.” Why?
(b) An electric oven of 1.5 kW is operated in a domestic circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect in this case? Explain.
Answer: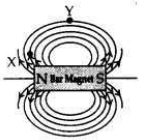
(a) Two magnetic field lines do not intersect one another. The direction of magnetic field lines is always from north pole to south pole. If the two magnetic field lines do intersect, it means at the point of intersection the compass needle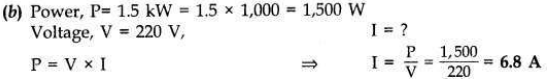
Now the current drawn by the oven is 6.8 A which is very high but the fuse in this circuit is only 5 A capacity. When a very high current of 6.8 A flows through 5 A fuse, the fuse wire will get heated too much, melt and break the circuit, cutting off the power supply.
OR
What is meant by resistance of a conductor? Name and define its SI unit. List the factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends. How is the resistance of a wire affected if —
(i) its length is doubled,
(ii) its radius is doubled?
Answer:
The property of a conductor due to which tends to stop the flow of current through the conductor is called resistance.
SI unit is ohm. When a potential difference of IV across a wire gives rise to IA current through the wire, then the resistance is said to be 1 ohm (1 Q).
The resistance of conductor depends on length, thickness, nature of material and temperature of conductor.
(i) If length is doubled, then R is doubled because the resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to length.
(ii) Resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to the square of its diameter or area of cross-section.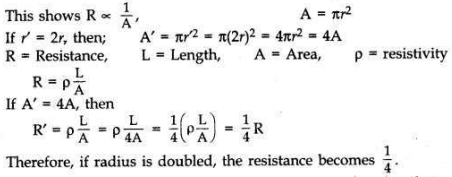
Question 19:
Explain why carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bond. Explain in brief two main reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Why does carbon form strong bonds with most other elements?
Answer:
Since, carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell so, it should either lose or gain 4 electrons to achieve the inert gas configuration and become stable.
(i) It could gain four electrons forming C4- anion. But it would be difficult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons due to inter electronic repulsion.
(ii) It could lose 4 electrons forming C4+ cation. But it would require a large amount of energy to remove four electrons from its outermost shell.
Thus, it forms compounds mainly by covalent bonds.
Two properties of carbon which lead to huge number of carbon compounds are:
(i) Catenation. Catenation is the unique property of carbon atoms to form bonds with other atoms of carbon giving rise to large molecules.
(ii) Tetravalency. Since carbon has a valency of 4, it is capable of bonding with 4 other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other monovalent element.
The reason for the formation of strong bonds by the carbon atoms is their small atomic size. Due to the small size of carbon atoms their nuclei hold the shared pairs of electrons between atoms strongly, leading to the formation of strong covalent bonds. The carbon atoms also form strong covalent bonds with the atoms of other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine and other elements.
Question 20:
How many pairs of chromosomes are present in human beings? Out of these how many are sex chromosomes? How many types of sex chromosomes are found in human beings? “The sex of a newborn child is a matter of chance and none of the parents may be considered responsible for it”. Draw a flow chart showing determination of sex of a newborn to justify this statement.
Answer:
• There are 23 pairs of chromosomes present in human beings.
• There is 1 pair of sex chromosomes present in human beings.
• The chromosomes which determine the sex of a person are called sex chromosomes. There are two types of sex chromosomes, one is called X chromosome and the other is called Y chromosome. Males contain one X chromosome and one Y chromosome (XY), while females contain two X chromosomes (XX).
Flow chart showing determination of sex of a child.
(i) A male has one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome. Thus half the male gametes have X-chromosomes and the other half have Y-chromosomes.
(ii) A female has two X-chromosomes. Thus all female gametes have only X- chromosomes.
(iii) If a sperm carrying Y-chromosome fertilises an ovum carrying X- chromosome, then the child born will be a boy.
(iv) If a sperm carrying X-chromosome fertilises an ovum carrying X- chromosome, then the child born will be a girl.
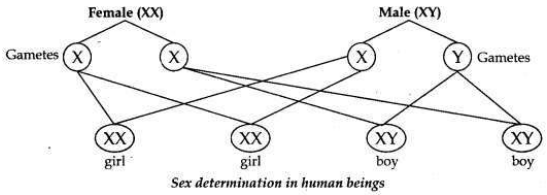
Therefore it is the sperm from the father which determines the sex of the child.
Question 21:
“A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it.” Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
An object of height 4 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position of the image formed. 5 Answer:
Answer:
• A convex lens can form a magnified erect image when the object is placed between the optical centre and principal focus of the convex lens (i.e., between O and F’).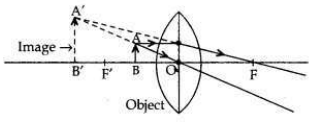
• A convex lens can form a magnified inverted image when the object is placed between focus and the centre of curvature (i.e., between F’ and 2F’).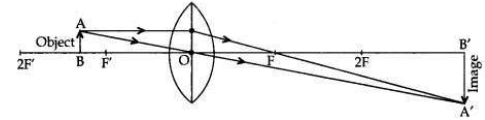
• Object height, n = 4 cm;
Object distance, u = -20 cm Nature of the lens = concave lens; Focal length = f = -10 cm Image distance, v = ?
According to the lens formula,
So, image is formed at 6.66 cm from lens on same side. Image is erect, virtual and diminished in size.
SECTION B
Question 22:
An iron nail is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate for about 30 minutes, state the change in colour observed. Give the reason for the change.
Answer:
Iron is more reactive than Cu. So it displaces Cu from copper sulphate solution. Thus, blue colour of the CuS04 solution fades and colour of the solution turns green due to the formation of ferrous sulphate Solution. This is a displacement reaction.
CuSO4 (aq) + Fe (s) —> FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
(Blue) (Green)
Question 23:
A student while verifying Ohm’s law calculated the value of resistance of the resistor for each set of observation. However, the values of resistance were slightly different from the actual value. Is his experiment wrong? Justify your answer.
Answer:
His experiment is correct since some of the current is utilized to overcome the resistance of the wires of the circuit and instruments like ammeter and
voltmeter. Thus the experimental values of resistance were different from the actual value of resistance.
Question 24:
Draw a labelled diagram of stomatal apparatus with closed stomatal pore.
Answer: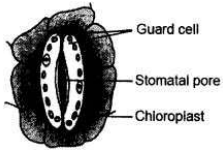
Question 25:
List two observations which you make when you add a pinch of sodium hydrogen carbonate to acetic acid in a test tube. Write the chemical equation for the reaction that occurs.
Answer:
When a pinch of sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid in a test tube, there are two observations:
(i) Brisk effervescence
(ii) Evolution of a colourless and odourless gas which is CO2.
CH3 COOH (aq) + NaHCO3 (s) -> CH3 COONa (aq) + H2O (I) + CO2 (g) ↑
Question 26:
Name the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost.
Draw the initial and the final stages of this type of reproduction. State the event with which this reproduction starts.
Answer:
• Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost.
• This reproduction starts with the elongation of the nucleus.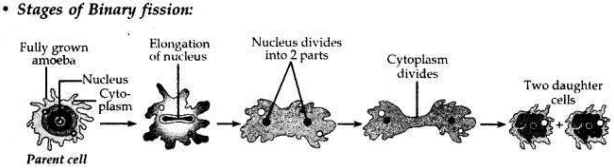
Question 27:
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex
lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image—does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Answer:
fa) He moves the screen away from iens to focus the object, l b) The size of the image increases.
Ic) When the object is placed very close to the lens, then no image will be formed on the screen. As now image formed is erect and virtual.