Solved CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 6
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
I. The Question Paper comprises of two sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
II. All questions are compulsory.
III. All questions of Section A and all questions of Section B are to be attempted separately.
IV. Question numbers I to 2 in Section A are one mark questions. These are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
V. Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section A are two marks questions. These are to be answered in about 30 words each.
VI. Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section A are three marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
VII. Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section A are five marks questions. These are to be answered in about 70 words each.
VIII. Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section B are questions based on practical skills and are five marks questions.
SECTION A
Question 1:
Mention the purpose of blackening the interior of a solar cooker.
Answer:
The black painted surface is used in the interior of a solar cooker because
black surface absorbs more heat rays of the sun.
Question 2:
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Answer:
Question 3:
The absolute refractive indices of glass and water are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If the speed of light is 2 x 108 m/s, calculate the speed of light in
(i) vacuum,
(ii) water.
Answer:
(i) Given: vg = 2 × 108 m/s (Speed of light in glass) Question 4:
Question 4:
Write a chemical equation to describe how baking soda is produced on a large scale.
Also write chemical name of the products obtained.
Answer:
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is produced on a large scale by reacting a cold and concentrated solution of sodium chloride (called brine) with ammonia and carbon dioxide.![]()
The chemical name of baking soda is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) or sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Question 5:
Name the gland and the hormone secreted by the gland, which are associated with the following problems:
(i) a girl has grown extremely tall.
(ii) a woman has a swollen neck.
Answer:
(i) Pituitary gland → human growth hormone
(ii) Thyroid gland → thyroxine hormone
Question 6:
Illustrate any three chemical properties of acids. With examples.
Answer:
Chemical properties of acid:
(i) Acids react with metals to form H2 gas.
Zn + 2HCl -> ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
(ii) Acids turn blue litmus into red.
(iii) Acids react with bases to form salt and water (neutralization reaction).
HCl + NaOH -> NaCl + H2O
Acid Base Salt Water
Question 7:
Explain how water and minerals are transported in plants?
Answer:
Most plants secure their water and minerals from their roots. Minerals travel dissolved in water. Water and minerals are transported through xylem cells from the soil to the leaves. The xylem cells of roots, stem and leaves are interconnected to form a conducting channel. The root cells take ions from the soil. This creates a difference between the concentration of ions of roots and soil. Therefore, there is a steady movement of water into xylem. An osmotic pressure is formed and water and minerals are transported form one cell to the other due to osmosis. The continuous loss of water takes place due to transpiration.
OR
Explain how the movement of leaves of a sensitive plant is different from
movement of shoots towards light?
Answer:
- The movement of plant shoot towards light is called phototropism.
- It is a directional movement in which there is growth movement of a plant part (shoot) in response to an external stimulus (light).
- The plant stem responds to light and bends towards it due to the action of ’auxin hormone’.
- The movement of the leaves of a sensitive plant is called Nastic movement. It is also called Thigmonasty.
- It is a non-directional movement of plant part (leaves) in response to touch or vibration.
- The folding up of leaves of a sensitive plant (like mimosa) on touching is due to the sudden loss of water from pad like swellings called pulvini present at the base of all leaves.
Question 8:
What are magnetic field lines? List two characteristic properties of these lines.
Answer:
Magnetic field lines are the lines drawn in a magnetic field along which north magnetic pole would move. The direction of a magnetic field at a point is determined with the help of a small magnetic compass. When a compass is moved along the magnetic line, then the line drawn from the south pole of the compass to its north pole indicates the direction of the magnetic field.
Properties of magnetic lines of force:
(i) The magnetic lines originate from the north pole and end at the south pole.
(ii) The magnetic field lines of a magnet form a continuous closed loop.
(iii) The magnetic lines of force do not intersect each other.
Question 9:
Define 1 ohm resistance.
A student has a resistance wire of 1 ohm. If the length of this wire is 50 cm, to
what length he should stretch it uniformly so as to obtain a wire of 4 Ω resistance? Justify your answer.
Answer:
• 1 ohm is the resistance of a conductor such that when a potential difference of 1 volt is applied to its ends, a current of 1 ampere flows through it.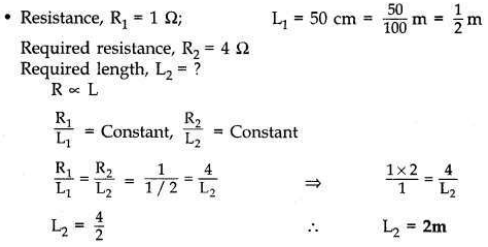
Question 10:
Write any three characteristics of a good fuel.
Answer:
Characteristics of a good fuel:
(i) A good fuel should have a high calorific value. It means it gives more heat per unit mass.
(ii) It should burn without giving out any smoke or harmful gases. So that it does not pollute air on burning.
(iii) The ignition temperature of an ideal fuel should neither be too low nor too high because if the ignition temperature, of the fuel is very low, then the fuel will catch fire too easily and hence it will be very unsafe to use it. If the ignition temperature is too high, then it will be very difficult to light the fuel.
Question 11:
List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed.
Answer:
Test-1—Litmus Test. Take 2 strips of blue litmus paper. Place a drop each of alcohol and carboxylic acid on these strips separately. The blue litmus paper turns red in the case of carboxylic acid and remains unaffected in the case of alcohol.
Test-2—Sodium hydrogen carbonate Test/Sodium carbonate Test. A pinch of sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium carbonate is added to both alcohol and a carboxylic acid separately. If brisk effervescence with the evolution of a colourless gas is observed, it indicates the presence of carboxylic acid whereas no effervescence is seen in case of an alcohol.
OR
Two elements ’P’ and ’Q’ belong to the same period of the modem periodic table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form:
(a) The number of electrons in their atoms
(b) The sizes of their atoms
(c) Their metallic characters
(d) Their tendencies to lose electrons
(e) The formula of their oxides
(f) The formula of their chlorides
Answer:
| Characteristics | PLess than Q | Q More than P |
| (a) No. of electrons in their atoms | 3 | 4 |
| (b) Size of the atom | Bigger | Smaller |
| (c) Metallic character | More metallic | Less metallic |
| (d) Tendency to lose electrons | More | Less |
| (e) Formula of their oxides | P2O | QO |
| (J) Formula of their chlorides | PCI | CCl2 |
Question 12:
List six specific characteristics of sexual reproduction.
Answer:
Characteristics of sexual reproduction are:
- In sexual reproduction, two parents are involved (male and female).
- The new organism produced is genetically different from both parents.
- During gamete formation meiosis occurs. After fertilisation all divisions are mitotic.
- Sexual reproduction helps in evolution.
- Fertilisation of gametes leads to zygote formation. This zygote grows and develops to form a new organism.
- Humans, fish, dogs, hens, cats, cows, horses, deer, rabbit, lions and tigers all reproduce by the method of sexual reproduction. Most of the flowering plants also reproduce by sexual reproduction.
Question 13:
List four points of significance of reproductive health in a society. Name any two areas related to reproductive health which have improved over the past 50 years in our country.
Answer:
The significance of reproductive health of society are:
- Regular medication and check-ups have led to development of reproductive health. Healthy mothers give birth to healthy children.
- Reproductive health should be maintained in order to prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
- Family planning by using various contraceptives enables a couple to decide on the number of children they want to have and when to have them. If a couple has less number of children they can provide good food, clothes and education to each child. So a small family is a happy family.
- Having fewer children also keeps the mother in good health. This will reduce the cases of maternal mortality as well as new born mortality.
Areas which have improved:
(i) Better family planning has led to reduction in family size and better economic stability.
(ii) Decrease in STD cases due to more awareness and wider use of contraceptives.
Question 14:
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Answer:
Convex mirror always forms an erect, virtual and diminished image for all positions of the object placed in front of it.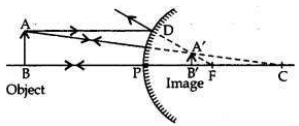
Uses:
1. Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors in vehicles to see the traffic at the rear side (or back side) because —
(i) a convex mirror always produces an erect image of the object;
(ii) the image formed in a convex mirror is highly diminished due to which a convex mirror gives a wide field of view.
2. Big convex mirrors are used as ’shop security mirrors’. By installing a big convex mirror at a strategic point in the shop, the shop owner can keep an eye on the customer to look for thieves and shoplifters among them as convex mirrors always form a virtual, diminished and erect image.
Question 15:
What is meant by scattering of light? Use this phenomenon to explain why the clear sky appears blue or the sun appears reddish at sunrise.
Answer:
Scattering of light is the phenomenon to throw light in various random directions. Light is scattered when it falls on various types of suspended particles in its path. The colour of the scattered light depends on the size of
the scattering particles in the atmosphere.
- The larger particles of dust and water droplets present in the atmosphere scatter the light of longer wavelengths due to which the scattered light appears white.
- The extremely minute particles such as air molecules present in the atmosphere scatter mainly blue light present in the white sunlight.
Colour of the sky appears blue. The molecules of air and other fine particles in the atmosphere have a size smaller than the wavelength of visible light. So these particles scatter more effectively the light rays of shorter wavelength at the blue end than light of longer wavelength at the red end. When the scattered blue light enters our eyes, it gives us the feeling of a blue sky.
Colour of the sun appears red at sunrise and sunset. The sun at sunrise and sunset is very near to the horizon, and near the horizon most of the blue light of shorter wave-lengths is scattered away by the particles in the atmosphere. Therefore, the light that reaches our eyes is of longer wavelengths that gives rise to the reddish appearance of the sun.
Question 16:
(a) A student dropped a few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was passed through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? Write balanced chemical equations for both the changes observed.
(b) State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid
(ii) as a constituent of baking powder.
Answer:
(a) When a piece of marble (CaCO3) is dropped in dil HCl, CO2 gas’ will be evolved
which turns lime water milky.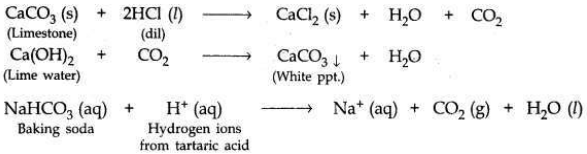
(b)
(i) Being alkaline, sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda) neutralises the excess acid present in the stomach and relieves indigestion.
(ii) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid such as tartaric acid. When baking powder mixes with water (present in dough made for baking cake or bread), then sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with tartaric acid to evolve CO2 gas (on heating).
Question 17:
(a) Explain feed back mechanism for regulation of hormonal secretion with the help of one example.
(b) State two different types of movement in plants. Mention two points of difference between them.
Answer:
(a) The timing and amount of hormones released by various glands are controlled by the ’feedback mechanism’ which is in-built in our body. Example, if the sugar level in the blood rises too much, it is detected by the cells of pancreas which responds by producing and secreting more insulin into the blood; and as the blood sugar falls to a certain level, the secretion of insulin is reduced automatically.
(b) The plant movements made in response to external stimuli fall into two main categories—
(i) tropism and
(if) nasties.
Tropisms. A growth movement of a plant part in response to an external stimuli in which the direction of stimulus determines the direction of response is called tropism. So it is a directional movement.
Nasties. The movement of a plant part in response to an external stimulus in which the direction of response is not determined by the direction of stimulus is called nastic movement.
| Tropism | Nasties |
| (i) The direction of stimulus determines the direction of movement of the plant part. | The direction of movement is not determined by the direction of stimulus. |
| (ii) All the tropisms are growth movements. | Nasties may be growth movements or growth independent movements. |
Question 18:
Name an instrument that measures potential difference between two points in a circuit. Define the unit of potential difference in terms of SI unit of charge and work. Draw the circuit symbols for a
(i) variable resistor,
(ii) a plug key which is closed one.
Two electric circuits I and II are shown below
(i) Which of the two circuits has more resistance?
(ii) Through which circuit more current passes?
(iii) In which circuit, the potential difference across each resistor is equal?
(iv) If R1 > R2 > R3 in which circuit more heat will be produced in Rias compared to other two resistors?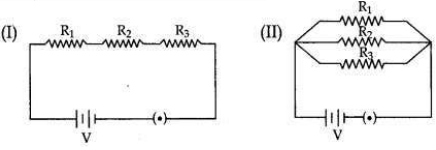
Answer:
• Voltmeter measures potential difference between two points in a circuit.
V = W/Q.
V = Potential difference, W = Work done, Q = Quantity of charge
V = 1J/1C = 1 volt. The SI unit of potential difference is volt.
The potential difference between two points is said to be 1 volt if 1 joule of work is done in moving 1 coulomb of electric charge from one point to the other.
(i) Circuit (l) has more resistance as the combined resistance of any number of resistances connected in series is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
(ii) Circuit (ll).
(iii) In circuit (ll) the potential difference across each resistor is equal.
(iv) If R1 > R2 > R3 in circuit (l) more heat will be produced in R4 as compared to other two resistors.
Question 19:
Both soap and detergent are some type of salts. What is the difference between them? Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap. Why do soaps not form lather in hard water? List two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
Answer:
A soap is the sodium or potassium salt of a long chain carboxylic acid.
Example:
C17 H35 COO– Na+ Sodium stearate
C15 H31 COO– Na+ Sodium palmitate
A detergent is ammonium or sulphonate salt of a long chain carboxylic acid.
Example:
CH3 — (CH2)11 — C6H4 — SO3– Na+
CH3 — (CH2)10 — CH2 — SO4– Na+
Cleansing action of soaps. One part of soap molecule is ionic/hydrophilic and dissolves in water. The other part is non-ionic, i.e., the carbon chain which is hydrophobic and dissolves in oil.
Thus, the soap molecules arrange themselves in the shape of a micelle.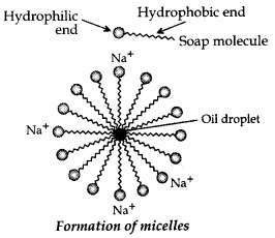
On rinsing with water the soap is washed off, lifting the oily dirt particles with it.
Soaps do not form lather in hard water. Soaps are sodium salts of fatty acids. Fatty acids are a type of carboxylic acids with long chain of carbon atoms. Soaps are not suitable for washing clothes when the water is hard:
• The formation of lather is necessary for removing dirt from clothes during the washing of clothes. Soap does not give lather with hard water as it reacts with the calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water to form insoluble precipitates of calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids.
• The scum (or precipitate) formed by the action of hard water on soap sticks to the clothes being washed and it interferes with the cleaning ability of soap.
This makes the cleaning of clothes difficult.
Problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps:
(i) Detergents are non-biodegradable, i.e., they cannot be decomposed by micro-organisms and hence cause water pollution in lakes and rivers.
(ii) Detergents can also cause skin problems.
Question 20:
How do Mendel’s experiments show that the
(a) traits may be dominant or recessive,
(b) traits are inherited independently?
Answer:
Mendel’s experiments show that the
(a) Traits may be dominant or recessive. When Mendel cross-bred plants of two different traits of character, a tall pea plant (TT) and a dwarf pea plant (tt) to get a progeny (F1 generation), all F1 plants were tall. Only the dominant trait was visible in this generation. But when plants of F1 generation were selfbred then the two traits of character got separated in the plants of F2 generation. All plants obtained in the F2 generation were not tall. One-fourth of the F2 plants were short.
Appearance of tall characters in both the F1 and F2 generations shows that it is a dominant character. Whereas the absence of dwarf character in F1 generation and its reappearance in F2 generation shows dwarfness is the recessive character.
(b) Traits are inherited independently. Mendel cross-bred pea plants showing two different characteristics, rather than just one. When he cross-bred pea plants of round green seeds wrinkled yellow seeds, he got F1 generation with all such seeds which were yellow and round. So, it was concluded that round and yellow character of seeds were dominant traits in the pea plant. On selfing of F1 progeny, different types of F2 progeny were obtained.
F2 progeny along with their ratios obtained in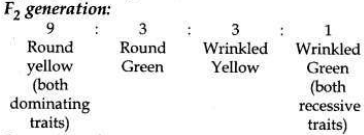
So traits of two different characters were inherited independent of each other and made new combination characteristics independent of their previous combinations.
Question 21:
What is meant by power of a lens? Define its S.l. unit.
You have two lenses A and B of focal lengths +10 cm and -10 cm respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Answer:
Power of a lens and its S.l. unit. The power of a lens is a measure of the degree of con-vergence or divergence of light rays falling on it. The power of a lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length in metres.
The power of a concave lens is negative therefore, lens B is a concave lens. When an object is placed at 8 cm (i.e., between the optical centre and principal focus) only convex lens will form the virtual and magnified image.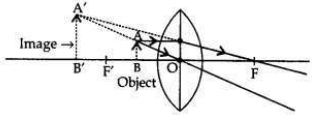
Therefore, lens A will form a virtual and magnified image of the object placed 8 cm from it. When the object is placed between the optical centre and the focus: (i.e., between O and F’) the image formed is behind the object (on the same side), virtual, erect and magnified.
OR
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find nature, position and size of the image.
Answer: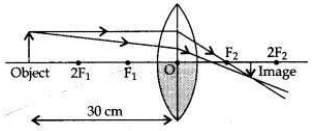
(i) Yes. If a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered one half with a black paper, it can produce an image of the complete object between F2 and 2F2. The rays of light coming from the object get refracted by the upper half of the lens.
The image formed will be real, inverted and diminished.
Positive sign of h2 shows that the image is erect. Therefore, a virtual, erect, magnified (16 cm) image will be formed at a distance of 60 cm on the same side as of the object by the convex lens.
SECTION B
Question 22:
A student took a small piece of solid quick lime in a china dish and poured over it a small amount of water. List two changes he is likely to observe in the china dish immediately after pouring water.
Answer:
When a small amount of water is poured on a piece of quick lime —
• it reacts vigorously with water and a hissing sound is produced and slaked lime is formed.
• the reaction mixture becomes hot as it is an exothermic reaction.
Question 23:
Draw a labelled circuit diagram to study the dependence of current (I) on the
potential difference (V) across a resistor.
Answer: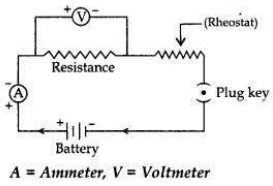
Question 24:
Draw a labelled diagram of a stomatal apparatus with open stomatal pore.
Answer: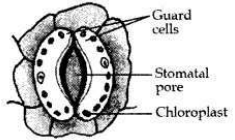
Question 25:
When you add sodium hydrogen carbonate to acetic acid in a test tube, a gas liberates immediately with a brisk effervescence. Name this gas. Describe the method of testing this gas.
Answer:
When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid in a test tube, then a brisk effervescence is observed due to the liberation of CO2 gas which is colourless and odourless.
Question 26:
Students were asked to observe the permanent slides showing different stages of budding in yeast under high power of a microscope.
(a) Which adjustment screw (coarse/fine) were you asked to move to focus the slides?
(b) Draw three diagrams in correct sequence showing budding in yeast.
Answer:
(a) A fine adjustment screw is moved to focus the slides.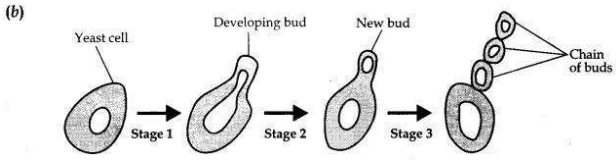
Question 27:
A 4 cm tall object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. The distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 12 cm and its sharp image is
formed at a distance of 24 cm from it on a screen on the other side of the lens. If the object is now moved a little away from the lens, in which way (towards the lens or away from the lens) will he have to move the screen to get a sharp image of the object on it again? How will the magnification of the image be affected?
Answer:
(a) The screen should be moved towards the lens to get a sharp image of the object again.
(b) Magnification of the image decreases on moving the object away from the lens.