CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Solved Set 4
Section A
1.In what way does cross over chromatids differs from the non-cross over chromatids?
2.Abbreviate the following term given below,
Eco RI
3.MOET is the programme employed for the herd improvement in lesser time.
Which hormone is given to cow to induce follicular maturation?
4.Menstrual cycles in females are absent during pregnancy Justify.
5.Mother secretes a yellowish fluid during the initial days of lactation. What role does it play for infant?
Section B
6.Both mycorrhiza and cyanobacteria possess the similarity of fixing nitrogen yet differ from each other in some aspects. Discuss.
7.Mention the benefits the female wasps derives from the fig trees from mutualistic interaction.
8.A population has been exhibiting genetic equilibrium’. Explain the statement by mentioning any two factors that could upset the genetic equilibrium of the population.
9.The bacteria growing anaerobically on cellulosic material to produce large amount of methane are called methanogens. Prepare a flow diagram to show the action of methanogens.
Or
It has been proved that the success rate of fertilisation is improved during the process of artificial insemination in animal husbandry programmes. How does this happens? Explain.
10.Jhum cultivation has been in practice from earlier days, but is considered more problematic these days. Why?
Section C
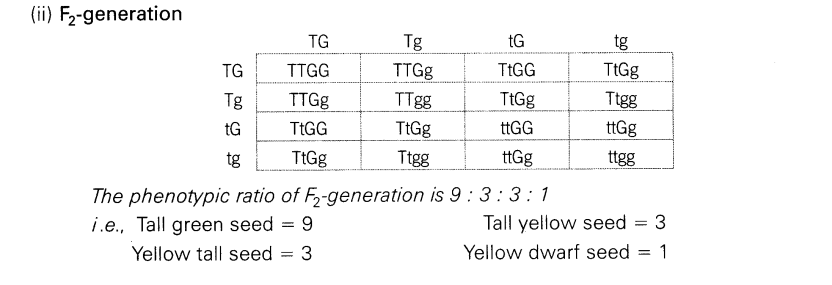
11.Work out a cross between a homozygous tall pea plant with green seeds and a dwarf pea plant with yellow seeds.
(i)State the phenotype and genotype of F1 -generation?
(ii)Predict the phenotypic ratio of F2 -generation using a Punnett square.
12.(i) What are the major techniques that had enabled the birth of modern biotechnology?
(ii)What are the three basic steps in genetic modification an organism?
Or
(i)Identify the different selectable markers ‘A‘, ‘B’ and ‘C’ in diagram of coli vector given below.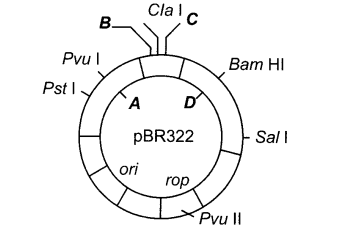
(ii)How is the coding sequence of oc-galactosidase considered a better marker then the ones identified by you in the diagram? Explain.
13.Rohan, a plant breeder was interested in growing new and improved crop varieties in his field. His friend suggested him to cross different plants in order to get hybrid plants. Mention the process to get the improved variety of the following
(i)plants bearing bisexual flowers.
(ii)female parent producing unisexual flowers.
14.Hari was concerned about the stagnant water of his locality. He decided to take step regarding the issue. He advised his locality head that they should setup different plants to treat waste water. Mention the types of treatments to treat the same.
15.Pollen-pistil interaction acts as an essential step in fertilisation of all angiosperms which inturn determines the compatibility and incompatibility of pollen and a pistil. Describe the event that how does the pollen grain grows through the style of the female gametophyte. Explain briefly.
16.Classify the following contraceptives measures into different methods of birth control.
(i) Vasectomy (ii) Tubectomy (iii)Saheli
(iv) Diaphragms (v) Cervical caps (vi) Condoms
17.Transcription is considered to be more complex process in eukaryotic cells. Explain.
18.Populations or organisms of an ecosystem are connected to one another through a sequence of transfer of food and energy from one member to another. State the difference between the types of food chains found in different organisms.
19.Various initiatives at international level were set up by the government for the conservation of biodiversity. Explain.
20.Draw a schematic sketch of pBR322 plasmid and label the following in it.
(i)Any two restriction sites
(ii)Ori and ropgenes
(iii)An antibiotic resistant gene
21.What are fossils? List any two ways in which fossils support biological evolution of an organism.
22.Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
Section D
23.Rohan visited his grandfather’s village and saw on the way that people were cutting the roadside forests on a large scale. He asked his grandfather who told him that some American based organsiation is establishing a factory there. Assuming yourself as Rohan, write some points highlighting the benefits of forest to encourage people out there to stop them from the cutting of forests.
Section E
24.(i) The following is the flowchart highlighting the steps in DNA fingerprinting technique. Identify the steps marked as (A-F).
(ii) What is the differences between DNA and RNA?
Or
How is Human Genome Project (HGP) advantageous for the mankind? Which objectives were associated with it?
25.Drugs like LSD, barbiturates, amphetamines, etc. are used as medicines to help patients with mental illness. However, excessive doses and abusive usage are harmful. Enumerate the major adverse effects of such drugs in humans.
Or
What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency of immune system of the infected person?
26.Answer the following.
(i)What depletes ozone in the stratosphere? How does this affects human life?
(ii)What is El Nino effect? Explain how it accounts for biodiversity loss.
Or
Enumerate the effects of air pollutants on plants and animals and humans.
Answers
Section A
1.In what way does cross over chromatids differs from the non-cross over chromatids?
Ans. Chromatids resulting from interchange of segment are crossover or recombinant chromatids while, those that remain intact are non-cross over chromatids or parental chromatids.
2.Abbreviate the following term given below,
Eco RI
Ans. Eco RI stands for
E – Escherichia
co – coli
R – RY13 (strain)
I – It indicates that it was the first enzyme being isolated from the bacterium E. coli.
3.MOET is the programme employed for the herd improvement in lesser time.
Which hormone is given to cow to induce follicular maturation?
Ans. FSH (Follicular Stimulating Flormone) is given to cow to induce follicular maturation. (1)
4.Menstrual cycles in females are absent during pregnancy Justify.
Ans. High levels of progesterone and oestrogens during pregnancy suppresses the release of gonadotropins required for the development of new follicles. Therefore, new cycles cannot be initiated.
5.Mother secretes a yellowish fluid during the initial days of lactation. What role does it play for infant?
Ans. The yellowish fluid secreted during the initial days of lactation called colostrum which has abundant antibodies (IgA) provide passive immunity to protect the infant.
Section B
6.Both mycorrhiza and cyanobacteria possess the similarity of fixing nitrogen yet differ from each other in some aspects. Discuss.
Ans. Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between fungus and plant roots. It absorbs phosphorus from the soil and passes it onto the plant roots. They also make plants tolerant to environmental stress and pathogen attacks. While, the cyanobacteria are autotrophic microbes found in aquatic and terrestrial environment that helps to fix nitrogen, e.g., Anabaena and Nostoc. Cyanobacteria are also used in paddy fields as an important fertiliser.
7.Mention the benefits the female wasps derives from the fig trees from mutualistic interaction.
Ans. The female wasp uses the fruit not only as an oviposition (egg laying) site but uses the developing seeds within the fruit for nourishing its larvae. The wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence, while searching for suitable egg laying sites. In return the fig provides the wasp some seeds as food for developing the wasp larvae.
8.A population has been exhibiting genetic equilibrium’. Explain the statement by mentioning any two factors that could upset the genetic equilibrium of the population.
Ans. A population has been exhibiting genetic equilibrium’ means that the relative frequency of alleles of sexually reproducing organisms in a given population remains constant from generation to generation. This is known as Hardy-Weinberg’s equilibrium law.
The two factors that can upset the genetic equilibrium of the population are
(i)Gene migration (ii) Recombination
9.The bacteria growing anaerobically on cellulosic material to produce large amount of methane are called methanogens. Prepare a flow diagram to show the action of methanogens.
Or
It has been proved that the success rate of fertilisation is improved during the process of artificial insemination in animal husbandry programmes. How does this happens? Explain.
Ans. Methanogens are naturally occurring bacteria being found in the rumen of cattle and sewage. The action of methogen in cattle is given below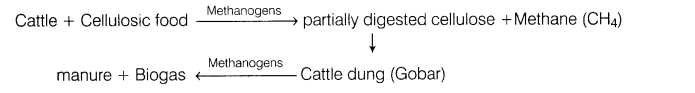
Or
The success rate of fertilisation can be improved in animal husbandry programmes by the multiple ovulation embryo transfer (MOET) technology. In this technique, a cattle is administered with a normal treatment, FSH in order to produce more than one ova/eggs (6-8) per cycle. The embryos after mating or artificial insemination are transferred to different cattles called surrogate mothers at 8-32 celled stage. The technology is also successful in improving the fertilisation rate in sheep, rabbits, mares, buffaloes, etc.
10.Jhum cultivation has been in practice from earlier days, but is considered more problematic these days. Why?
Ans. Jhum cultivation or slash and burn agriculture has been practiced by the tribal groups in the north-eastern states of India like Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Bangladesh, etc. This system involves clearing a piece of land by setting fire and using the area for growing crops of agricultural importance. It is considered to be more problematic these days because enough time gap is not being given for the natural process of recovery of land from the effect of cultivation.
Section C
11.Work out a cross between a homozygous tall pea plant with green seeds and a dwarf pea plant with yellow seeds.
(i)State the phenotype and genotype of F1 -generation?
(ii)Predict the phenotypic ratio of F2 -generation using a Punnett square.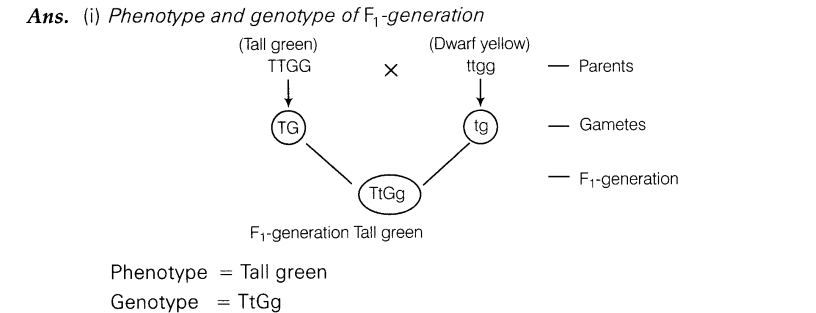
12.(i) What are the major techniques that had enabled the birth of modern biotechnology?
(ii)What are the three basic steps in genetic modification an organism?
Or
(i)Identify the different selectable markers ‘A‘, ‘B’ and ‘C’ in diagram of coli vector given below.
(ii)How is the coding sequence of oc-galactosidase considered a better marker then the ones identified by you in the diagram? Explain.
Ans. (i) Major techniques that had enabled the birth of modern biotechnology are
(a)Genetic Engineering This is a technique to alter the chemistry of genetic material (DNA and RNA) into host organisms to change the phenotypic character of the host organism.
(b)Sterilisation Methods These methods are used to maintain the growth and manipulation of desired microbes or cells. It is required to produce large quantities of products For examples, vaccines, enzymes, antibiotics, etc in sterile conditions.
(ii)Three basic steps in genetic modification of an organism are
(a)Identification of DNA with desirable genes and introduction of the identified DNA into the host.
(b)Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host.
(c)Transfer of the DNA to its progeny.
Or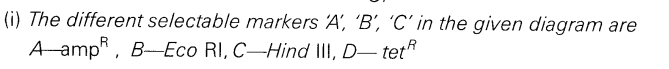
(ii)Alternative selectable markers have been developed that differentiate recombinants from non-recombinants on the basis of their ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. In this step, a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme (3-galactosidase which results into an inactivation of the enzyme. This is referred to as insertional inactivation.
13.Rohan, a plant breeder was interested in growing new and improved crop varieties in his field. His friend suggested him to cross different plants in order to get hybrid plants. Mention the process to get the improved variety of the following
(i)plants bearing bisexual flowers.
(ii)female parent producing unisexual flowers.
Ans. (i) In bisexual flowers, emasculated flowers have to be covered with a bag of suitable size generally made up of butter paper to prevent the contamination of its stigma with unwanted pollen. This process is called bagging. When the stigma is bagged, flower becomes receptive. Mature pollen grains collected from anther of the male parent are dusted on the stigma and the flower are rebagged.
(ii) In unisexual flowers, there is no need for emasculation. The female flower buds are directly bagged before the flowers open. And when the stigma becomes receptive, pollination is carried out using the desired pollen and the flowers again are rebagged.
14.Hari was concerned about the stagnant water of his locality. He decided to take step regarding the issue. He advised his locality head that they should setup different plants to treat waste water. Mention the types of treatments to treat the same.
Ans. Primary Treatment It includes the physical removal of particles from sewage through the filtration and sedimentation stages.
(i)Floating debris is removed by sequential filtration with progressively pore filter.
(ii)Grit (soil and small pebbles) are removed by sedimentation.
(iii)All solids that settle in settling tanks form primary sludge. Supernatantforms the effluents.
Secondary Treatment
(i)During secondary treatment, effluentfrom the primary settling tank is kept in large aeration tanks, it is constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it. Useful aerobic microbes grow into floes.
(ii)Microbes consume major part of organic matter in the effluent while growing and reduce Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of sewage.
(iii)Effluent is passed into a settling tank, where the bacterial floes are allowed to sediment, called as activated sludge. A small part of activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as inoculum.
(iv)Remaining of sludge is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digester.Anaerobic bacteria digest the other bacteria and the fungi in the sludge. Effluent, after treatment is generally released into water-bodies like rivers and streams.
15.Pollen-pistil interaction acts as an essential step in fertilisation of all angiosperms which inturn determines the compatibility and incompatibility of pollen and a pistil. Describe the event that how does the pollen grain grows through the style of the female gametophyte. Explain briefly.
Ans. After reaching the ovary, the pollen tube enters the ovule, either through the micropylar end (pyrogamy), chalazal end (chalazogamy) or lateral end (mesogamy). Pyrogamy is the most common out of this. In this, the tip of the pollen tube enters the micropyle, pushes through the nucellar tissue and finally pierces the egg apparatus from end of the embryo sac.
The synergids direct the growth of the pollen tube by secreting some chemical substances. The tip of the pollen tube enters into one of the synergid. After penetration, the synergid starts degenerating. The tip of the pollen tube enlarges and ruptures releasing most of its contents including the two male gametes and the vegetative nucleus into the synergid.
16.Classify the following contraceptives measures into different methods of birth control.
(i) Vasectomy (ii) Tubectomy (iii)Saheli
(iv) Diaphragms (v) Cervical caps (vi) Condoms
Ans. (i) Surgical method (ii)Surgical method (iii)Oral pills
(iv) Barrier method (v) Barrier method (vi) Barrier Method
17.Transcription is considered to be more complex process in eukaryotic cells. Explain.
Ans. Transcription is considered to be more complex process in eukaryotic cells because of the following reasons
(i)In the nucleus there are three types of RNA polymerases.
- RNA pol I, which transcribes mRNAs (28S, 18S, 5.8S ).
- RNA pol II, which transcribes the precursor of mRNA called mRNA.
- RNA pol III, which transcribes tRNA, SrRNA and SnRNAs.
(ii)Hn RNA (primary transcript of mRNA) contain both coding sequence called exons and non-coding sequences called intros. So, it undergoes splicing, in which non-coding sequences (intros) are removed and the coding sequences (exons) are joined together in a defined order
(iii)In capping, unusual nucleotide, methylguanosine residues are added at the 5′ end of the hnRNA.
(iv)In tailing, 200-300 adenylate residues are added at the 3′-end of the hnRNA.
18.Populations or organisms of an ecosystem are connected to one another through a sequence of transfer of food and energy from one member to another. State the difference between the types of food chains found in different organisms.
Ans. Two types of food chains can be observed in the ecosystem. These are grazing food chain and detritus food chain. Differences between grazing and detritus food chain are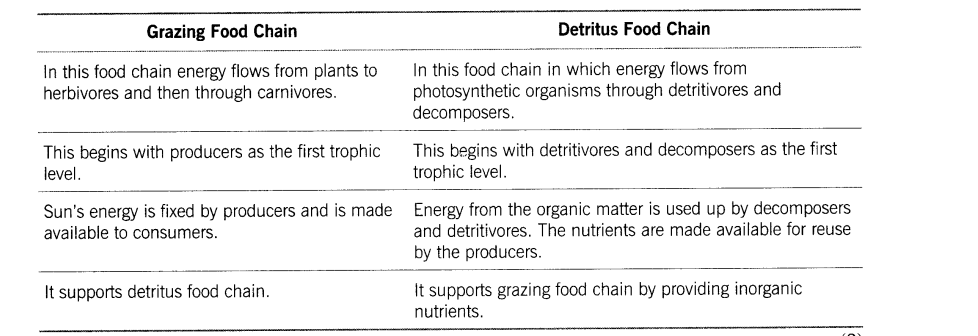
19.Various initiatives at international level were set up by the government for the conservation of biodiversity. Explain.
Ans. At international level, many countries of the world have taken initiatives for biodiversity conservation. For example, the earth summit was held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, which called upon all nations to take appropriate measures for the conservation of biodiversity and sustainable utilisation of its benefit.
The world summit on sustainable development was held in Johannesburg, South Africa in 2002 in which 190 countries pledged to reduce the current rate of biodiversity loss at global, regional and local levels by the year 2010.
20.Draw a schematic sketch of pBR322 plasmid and label the following in it.
(i)Any two restriction sites
(ii)Ori and ropgenes
(iii)An antibiotic resistant gene
Ans.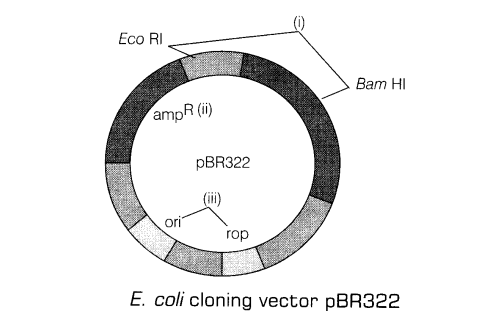
21.What are fossils? List any two ways in which fossils support biological evolution of an organism.
Ans. Fossils are the remains or impressions of pre-historic organisms preserved in sedimentary rocks or other media.
Two ways in which fossils support biological evolution are given under
(i)The habitat and behaviour of extinct organisms can be inferred from well preserved fossils.
(ii)The study of Archaeopteryx reveals that birds have evolved from reptiles depicting fossils
which provide evidence for evolution.
22.Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
Ans. When the symptoms of the disease are not visible and the pathogen concentration is very low, then the detection of that particular disease by conventional diagnostic tests is very difficult. However, detection can be possible by only amplifying their nucleic acids by the technique known as Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
The principle involved here is that a single DNA molecule can be copied endlessly using primers, DNA polymerase enzyme, and free nucleotides under appropriate conditions.
Section D
23.Rohan visited his grandfather’s village and saw on the way that people were cutting the roadside forests on a large scale. He asked his grandfather who told him that some American based organsiation is establishing a factory there. Assuming yourself as Rohan, write some points highlighting the benefits of forest to encourage people out there to stop them from the cutting of forests.
Ans. Forests are important for mankind because it helps to purify the air we breath in, water imitigate floods and droughts, cycle different nutrients, generate fertile soils, provide and protect wildlife, maintain biodiversity, helps to pollinate crops, provide site for storage for carbon. From aesthetic, cultural and spiritual point of view, it is also not correct to cut down trees for our own benefits.
Section E
24.(i) The following is the flowchart highlighting the steps in DNA fingerprinting technique. Identify the steps marked as (A-F).
(ii) What is the differences between DNA and RNA?
Or
How is Human Genome Project (HGP) advantageous for the mankind? Which objectives were associated with it?
Ans. (i) A — Restriction endonuclease B — Ethidium bromide (EtBr)
C — Agarose D — VNTR
E — Apiece F — Autoradiography
(ii) Differences between DNA and RNA are as follows
Advantages of HGP It is a revolutionary way to diagnose, treat and to prevent thousands of disorders that affect human beings. Besides these learning about non-human organisms, DNA sequences can lead to an understanding of their natural capabilities that can be applied toward solving challenges on healthcare, agriculture, energy production, environmental remediation etc.
Objectives of HGP are
(i)To identify all the genes in human DNA.
(ii)To store the informatiqon in databases.
(iii)To improve tools for data analysis.
(iv)To transfer related technologies to other sectors, such as industries.
(v)To address the ethical, legal and social issues that may arise from the project.
25.Drugs like LSD, barbiturates, amphetamines, etc. are used as medicines to help patients with mental illness. However, excessive doses and abusive usage are harmful. Enumerate the major adverse effects of such drugs in humans.
Or
What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency of immune system of the infected person?
Ans. Harmful effects of drugs like LSD, barbiturates, etc are
(i)Anxiety, shakiness, nausea, sweating and loss of mind control.
(ii)Reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence.
(iii)Lack of interest in personal hygiene, fluctuations in weight and appetite.
(iv)Withdrawal, isolation, depression, fatigue, aggressive behaviour.
(v)Social adjustment problems.
(vi)Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and life threatening.
(vii)Excessive doses of drugs may lead to coma and death due to respiratory failure, heart failure or cerebral haemorrhage.
Or
Mechanism by which AIDS virus causes immune deficiency is as follows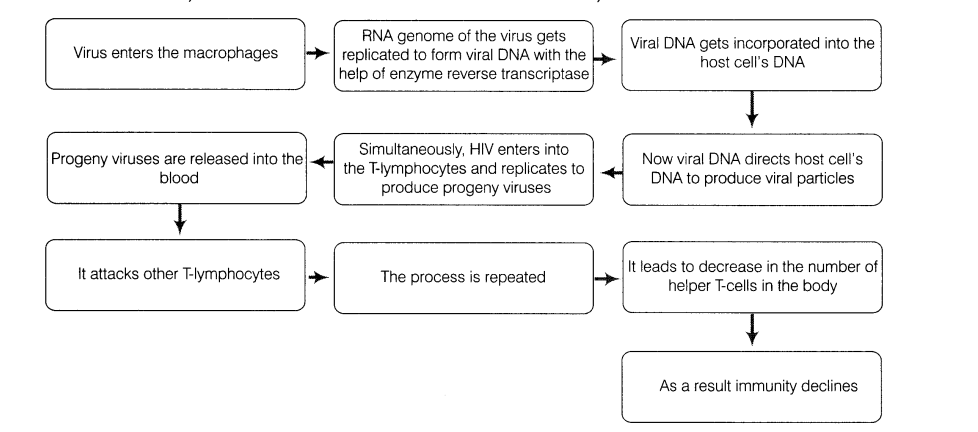
26.Answer the following.
(i)What depletes ozone in the stratosphere? How does this affects human life?
(ii)What is El Nino effect? Explain how it accounts for biodiversity loss.
Or
Enumerate the effects of air pollutants on plants and animals and humans.
Ans. (i) Ozone in the stratosphere is depleted by CFCs, i.e. chlorofluorocarbons, released primarily from refrigerators and other industrial emissions. This affects the human life as it leads to more exposure of UV radiation, which is considered to be harmful for health.
Effects of UV radiation on human health are
- Damage to skin cells.
- UV rays induce breaks in chemical bonds of DNA molecule.
- Skin cancer.
- Inflammation of the cornea, i.e. snow blindness.
(ii) El Nino is an abnormal warming of surface ocean water in the Eastern Pacific Ocean.During El Nino, there is a movement of warm water to east, which causes bleaching and death of coral reefs. It changes the route of migration of birds, fishes and whales thereby, increasing the risk for them. It is also known to be responsible for the sudden changes in rat’nfaiY pattern and drought. Ail this makes E) Nino, a factor for biodiversity loss. Or
Effects of Air Pollutants
Air pollutants are responsible for causing air pollution which can harm environment and person’s health.
On Plants
(i)Causes fruit damage, leaf damage, chlorosis, necrosis, and mottled spots on leaves.
(ii)Weakens plants and increases the infestation by pests.
(iii)Slow the growth yield of crops and cause premature death of plants.
(iv)Acid rain damages the aerial parts and also acidifies the soil. It leads to the production of free radicals and decrease in photosynthesis and productivity.
On Animals and Humans
(i)About 40% of human deaths occur due to air pollution.
(ii)Increased susceptibility to diseases.
(iii)Causes cancer and genetic mutations.
(iv)Causes respiratory ailments, asthma, hay fever and allergic diseases.
(v)Causes cardiovascular diseases and damage to CNS.
(vi)Immediate effects like nausea, headache, irritation to the eyes and nose.