CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Solved Set 6
Section A
1.In what way is a sol different from a gel?
2.Predict the product(s) in the following reaction.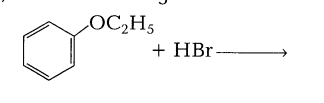
3.Name the reagent(s) reguired to bring about the conversion of but-2-ene to ethanal.
4.Accomplish the following conversion.
Benzyl chloride—— > 2-phenylethanamine
5.(i) Which point defect is shown by AgBr(s) crystal?
(ii)What kind of defects are introduced by doping?
Section B
6.Give reasons for the following:
(i)At higher altitudes, people suffer from a disease called anoxia. In this disease, they become weak and cannot think clearly.
(ii)When mercuric iodide is added to an aqueous solution of KI, the freezing point is raised.
Or
0.90 g of a non-electrolyte was dissolved in 90 g of benzene. This raised the boiling point of benzene by 0.25°C. If the molecular mass of non-electrolyte is 100.0 g mol-1, calculate the molal elevation constant for benzene.
7.The half-life for radioactive decay of14 C is 5730 yr. An archaeological artifact contained wood that had only 80% of the 14 C found in living tree. Estimate the age of the sample.
8.List the uses of neon and argon gases.
9.What are the products in the following?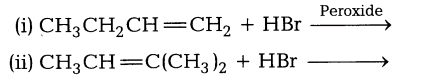
10.Describe the following:
(i)Bacteriostatic and bactericidal
(ii)Anti-fertility agents
Section C
11.(i) What is edema?
(ii) Calculate the molality of 2.5 g ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) in 75 g of benzene.
12.(i) In a compound, nitrogen atom (N) makes cubic close packed lattice and atoms of metal (M) occupy one-third of the tetrahedral voids present. Derive the formula of the compound formed by metal M and non-metal N (nitrogen).
(ii) Calculate the packing efficiency of a metal crystal for body centred cubic (bcc) structure.
13.(i) Differentiate between mineral and ore.
(ii) Explain the basic principles of the following metallurgical operations.
(a)Zone refining
(b)Vapour phase refining
14.(i) CHF3 is less acidic than CHC13, explain.
(ii) What happen when
(a)bromine reacts with CH3 —C = CH?
(b)chloroform kept open with air?
15.Write the chemical reactions for
(i)Meerwein reaction (ii) Schiemann reaction (iii) Gomberg reaction
16.(i) Why are enzymes highly specific in their action?
(ii)Name an amino acid which is not optically active and give reason.
(iii)Show that how three moles of phenyl hydrazine are consumed in reaction with glucose?
17.(i) What do you mean by inner orbital complexes and outer orbital complexes? Explain with
example.
(ii) What is linkage isomerism?
18.How are the following conversions carried out?
(i)Propene to propan-2 -ol
(ii)Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol
(iii)Ethyl magnesium chloride to propan-l-ol
19.Write the main difference between white and red phosphorus.
20.What happens when
(i)phosphorus acid (H3P03)is heated?
(ii)manganese dioxide (Mn02) is heated with cone. HC1?
(iii)sugar (C12H22011) is heated with cone. H2S04?
<
21.(i) Define activation of adsorbent.
(ii)Why is ester hydrolysis slow in the beginning and becomes fast after sometime?
(iii)What modification can you suggest for Hardy Schulze law?
22.If one per cent of the reactant decomposes in 1 minute in a first order reaction, calculate how much reactant would remain undecomposed after 1 h?
Or
A reaction is third order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected, if the concentration of the reaction is
(i) doubled? (ii) reduced to 1/2 ?
Section D
23.A large number of polymers are quite resistant to the environmental degradation processes and are thus responsible for the accumulation of polymeric solid waste materials. These solid wastes remain integraded for a quite long time and cause environmental problems. Due to this, certain new biodegradable synthetic polymers have been designed and developed. These polymers contain functional groups similar to the functional groups present in biopolymer.
Answer the following questions based on the above passage.
(i)Name two biodegradable polymers.
(ii)Name natural biopolymers.
(iii)What are the monomer units of bakelite?
(iv)What values do you get from this passage?
Section E
24.(i) The measured emf at 25°C for the cell reaction,
Zn (s)+ Cu2+(1.0 M)—– > Cu (s)+ Zn2+(0.1 M)is 1.3 V
Calculate E° for the cell reaction.
(ii) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction,
4Br– H O2 T 4H+——— > 2Br2 T 2H20
Given, E°ell = 0.16 V
Or
(i)A 0.05 M NaOH solution offered a resistance of 31.6 Q in a conductivity cell at 298 K. If the cell constant of the conductivity cell is 0.367 cm-1, find out the specific and molar conductance of the sodium hydroxide solution.
(ii)If a current of 0.5 A flows through a metallic wire for 2 h, then how many electrons flow through the wire?
25.(i) Gas A and gas B, both turn K2Cr2Oy / H+ Gas A also turns lead acetate paper black precipitate. When gas A is passed into gas B in an aqueous solution, yellowish white turbidity appears. Identify gas A and B and explain the reactions.
(ii) Explain, why a green solution of potassium manganate turns purple and a brown solid is precipitated when C02 gas is bubbled into the solution?
Or
(i)Give reasons.
(a)Iron is a transition metal while sodium is not.
(b)In permanganate ion, there is a covalency between manganese and oxygen.
(c)Zn, Cd and Hg are quite soft and have low melting points.
(ii)Fe2+ ions can be estimated by MnO^ andCr202- by volumetric titration. Give reactions. Also, relate their equivalent mass to molar mass.
26.An organic compound A (C8H6) on reacting with dilute sulphuric acid containing mercuric sulphate gives a compound B which can also be obtained from the reaction of benzene and acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous A1C13. The compound B when treated with iodine and aqueous NaOH yields C and a yellow compound D. Identify A, B, C and D with justification. Show how B is formed from A?
Or
(i)Show how each of the following compounds can be converted to benzoic acid?
(a)Ethyl benzene
(b)Acetophenone
(c)Phenylethene (styrene)
(ii)Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between following pairs of compounds.
(a)Ethanal and propanal
(b)Phenol and benzoic acid
Answers
Section A
1.In what way is a sol different from a gel?
Ans.Colloidal system in which solid is dispersed in liquid is called sol and that in which liquid is dispersed in solid is called gel.
2.Predict the product(s) in the following reaction.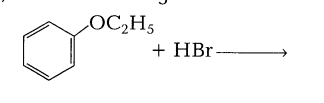
Ans.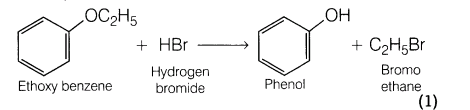
3.Name the reagent(s) reguired to bring about the conversion of but-2-ene to ethanal.
Ans.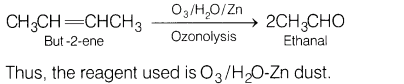
4.Accomplish the following conversion. Benzyl chloride—— > 2-phenylethanamine
Ans.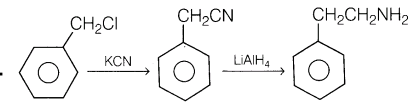
5.(i) Which point defect is shown by AgBr(s) crystal?
(ii)What kind of defects are introduced by doping?
Ans.(i) AgBr(s) crystal shows both, Frenkel as well as Schottky defect
(ii) Doping can be done with an impurity which is electron rich or electron deficient such impurities introduce electronic defects.
Section B
6.Give reasons for the following:
(i)At higher altitudes, people suffer from a disease called anoxia. In this disease, they become weak and cannot think clearly.
(ii)When mercuric iodide is added to an aqueous solution of KI, the freezing point is raised.
Or
0.90 g of a non-electrolyte was dissolved in 90 g of benzene. This raised the boiling point of benzene by 0.25°C. If the molecular mass of non-electrolyte is 100.0 g mol-1, calculate the molal elevation constant for benzene.
Ans. (i) At higher altitudes, partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at ground level, so that concentration becomes less in blood or tissues. Hence, people suffer from anoxia.
(ii) Due to the formation of complex K2[HgI4], number of particles in the solution decreases and hence, the freezing point is raised.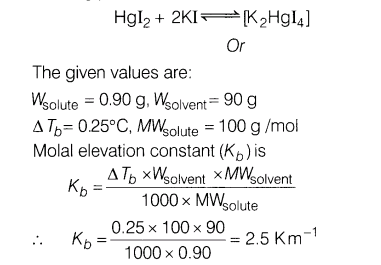
7.The half-life for radioactive decay of14 C is 5730 yr. An archaeological artifact contained wood that had only 80% of the 14 C found in living tree. Estimate the age of the sample.
Ans.
8.List the uses of neon and argon gases.
Ans.Uses of neon
- Neon is used in discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs for advertisement display purposes.
- Neon bulbs are used in botanical gardens and in green houses.
- Neon is used in voltage regulators and indicators. (1)
Uses of argon
- Argon is used for filling electric bulbs.
- It is used to provide an inert atmosphere in high temperature metallurgical operations (or welding of metals or alloys).
- Argon is used in rectifiers and in radio valves.
9.What are the products in the following?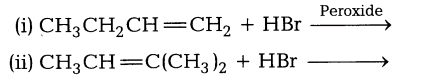
Ans.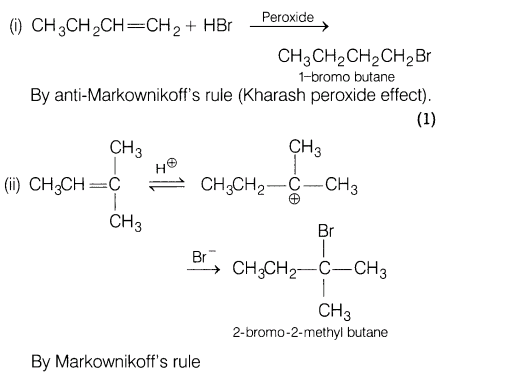
10.Describe the following:
(i)Bacteriostatic and bactericidal
(ii)Anti-fertility agents
Ans.(i) Bactericidal and bacteriostatic are the types of antibiotics. These type of drugs, either kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms by intervening in their metabolic process, e.g.
Bactericidal: Penicillin, ofloxacin. Bacteriostatic: Erythromycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol.
(ii) Anti-fertility agents Birth control pills essentially contains a mixture of synthetic oestrogen and progesterone derivatives. Both of these compounds are hormones. It is known that progesterone suppressed ovulation. These agents are generally hormonal contraceptives. Norethindrone is an example of synthetic progesterone derivative. The oestrogen derivative which is used in combination with progesterone derivative is ethynylestradiol (novestrol).
Section C
11.(i) What is edema?
(ii) Calculate the molality of 2.5 g ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) in 75 g of benzene.
Ans.(i) When a person consumes a lot of salt through food, a condition of puffiness or swelling arises called edema. In this condition, water retention takes place by tissue cell and intercellular spaces, due to osmosis.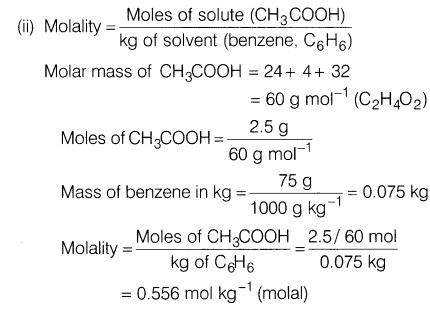
12.(i) In a compound, nitrogen atom (N) makes cubic close packed lattice and atoms of metal (M) occupy one-third of the tetrahedral voids present. Derive the formula of the compound formed by metal M and non-metal N (nitrogen).
(ii) Calculate the packing efficiency of a metal crystal for body centred cubic (bcc) structure.
Ans.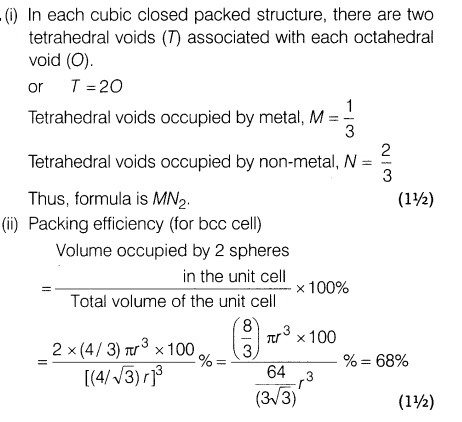
13.(i) Differentiate between mineral and ore.
(ii) Explain the basic principles of the following metallurgical operations.
(a)Zone refining
(b)Vapour phase refining
Ans.(i)The naturally occurring compounds containing metals present in the Earth’s crust are called minerals whereas, ores are those specific minerals from which a metal can be obtained profitably. All ores are minerals but all minerals are not ores.
(ii) (a) Zone refining This process is based upon the principle that impurities are more soluble in the molten state of the metal than in the solid form. Ultra pure metal are obtained by this process. (1)
(b) Vapour phase refining
This process is based upon the principle that metal to be refined should form a volatile compound, while impurities do not. Volatile compounds should be easily decomposable so that pure metal can be recovered easily. Ni is refined by Mond’s process.
14.(i) CHF3 is less acidic than CHC13, explain.
(ii) What happen when
(a)bromine reacts with CH3 —C = CH?
(b)chloroform kept open with air?
Ans.(i) Due to stronger- I-effect of F than Cl, CHF3 should be more acidic than CHCI3. But reverse is true. This is because : CCI3 left after the removal of a proton from CHCI3 is stabilised by resonance due to the presence of d-orbitals on Cl but: CF3 left after the removal of a proton from CHF3 is not stabilise by resonance due to the absence of d-orbitals on F.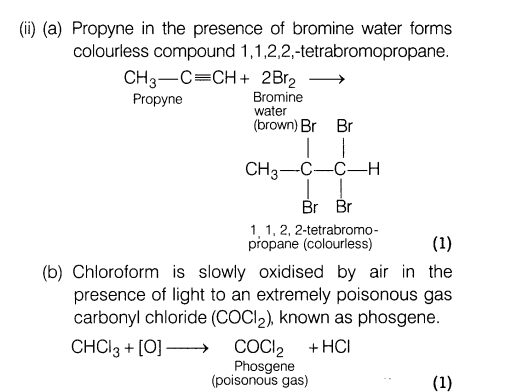
15.Write the chemical reactions for
(i)Meerwein reaction (ii) Schiemann reaction (iii) Gomberg reaction
Ans.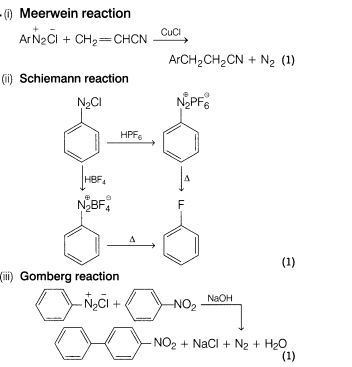
16.(i) Why are enzymes highly specific in their action?
(ii)Name an amino acid which is not optically active and give reason.
(iii)Show that how three moles of phenyl hydrazine are consumed in reaction with glucose?
Ans.(i) Enzymes have active sites on their surface which binds to the specific substrate due to the presence of specific R group. That’s why enzymes are specific in their action.
(ii) Glycine is not optically active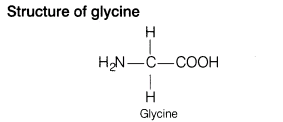
Reason Glycine is optically inactive because there is no stereogenic centre, the 4 groups surrounding the a-carbon atom are not different.
(iii)When the excess of phenyl hydrazine is used, the product formed is an osazone; i.e. glucosazone. Three molecules of phenyl hydrazine are consumed as follows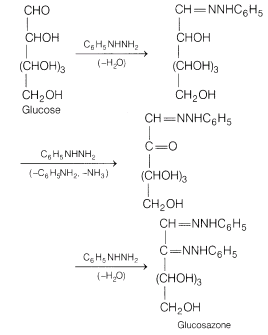
17.(i) What do you mean by inner orbital complexes and outer orbital complexes? Explain with
example.
(ii) What is linkage isomerism?
Ans. (i) (a) Inner orbital complexes When the complex formed involves the inner (n-l)d-orbitals for hybridisation (d2sp3), the complex is called inner orbital complex. In this case, the electrons of the metal are made to pair up, so the complex will be either diamagnetic or will have lesser number of unpaired electrons, this type of complex also called low spin complex.
e.g. [V (H2O)6]3+ , [Co(NH3)6]3+ etc.
(b) Outer orbital complex When the complex formed involves the use of outer nc/-orbitals for hybridisation, (sp3c/2), the complex is called outer orbital complex, having large number of unpaired electrons. This type of complex is also called high spin complex.
e.g. [CoF6]3-,[MnCI6]3-, etc.
(ii) Linkage isomer Isomerism of this type occurs in compounds containing ambidentate ligands. These isomers will have same molecular formula but differ in linkage of ligand atom to central atom, e.g. [Cr (H20)5 (SCN)]2+ and [Cr(H20)5(NCS)]2+
18.How are the following conversions carried out?
(i)Propene to propan-2 -ol
(ii)Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol
(iii)Ethyl magnesium chloride to propan-l-ol
Ans.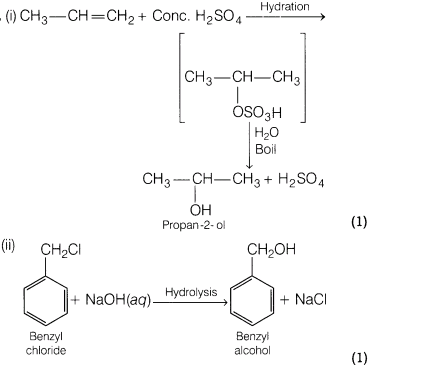
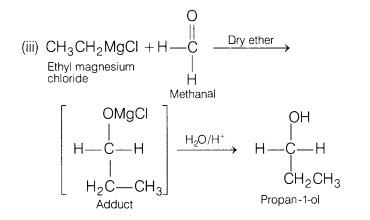
19.Write the main difference between white and red phosphorus.
Ans.The difference between white and red phosphorus are:
20.What happens when
(i)phosphorus acid (H3P03)is heated?
(ii)manganese dioxide (Mn02) is heated with cone. HC1?
(iii)sugar (C12H22011) is heated with cone. H2S04?
Ans.
21.(i) Define activation of adsorbent.
(ii)Why is ester hydrolysis slow in the beginning and becomes fast after sometime?
(iii)What modification can you suggest for Hardy Schulze law?
Ans.(i) Activation of adsorbent means increasing the adsorbing power of an adsorbent. This is achieved by increasing the surface area and also the number of pores and vacant site (active centre) per unit area.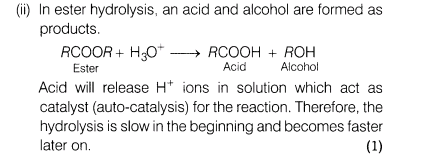
(iii)According to Hardy Schulze law, the ions carrying charge opposite to the charge on sol particles neutralise their charge and thus cause their coagulation or precipitation. But actually, the sol carrying these ions also gets coagulated since, the ions get their charge neutralised.
Thus, Hardy Schulze law may be modified as- ‘When equimolar proportions of two oppositely charged sols are mixed, they mutually neutralise their charge and both get coagulated
22.If one per cent of the reactant decomposes in 1 minute in a first order reaction, calculate how much reactant would remain undecomposed after 1 h?
Or
A reaction is third order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected, if the concentration of the reaction is
(i) doubled? (ii) reduced to 1/2 ?
Ans.


Section D
23.A large number of polymers are quite resistant to the environmental degradation processes and are thus responsible for the accumulation of polymeric solid waste materials. These solid wastes remain integraded for a quite long time and cause environmental problems. Due to this, certain new biodegradable synthetic polymers have been designed and developed. These polymers contain functional groups similar to the functional groups present in biopolymer.
Answer the following questions based on the above passage.
(i)Name two biodegradable polymers.
(ii)Name natural biopolymers.
(iii)What are the monomer units of bakelite?
(iv)What values do you get from this passage?
Ans.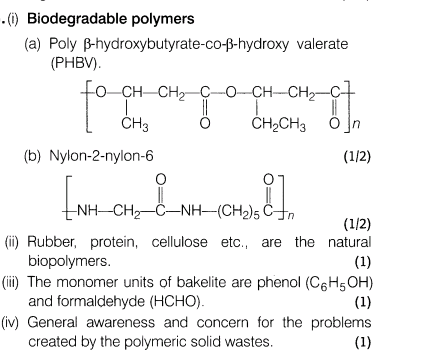
Section E
24.(i) The measured emf at 25°C for the cell reaction,
Zn (s)+ Cu2+(1.0 M)—– > Cu (s)+ Zn2+(0.1 M)is 1.3 V
Calculate E° for the cell reaction.
(ii) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction,
4Br– H O2 T 4H+——— > 2Br2 T 2H20
Given, E°ell = 0.16 V
Or
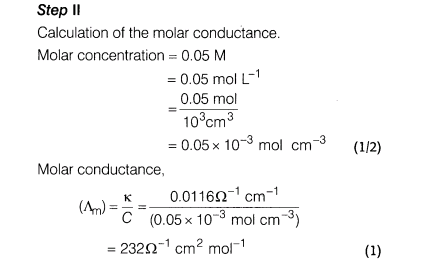
(i)A 0.05 M NaOH solution offered a resistance of 31.6 Q in a conductivity cell at 298 K. If the cell constant of the conductivity cell is 0.367 cm-1, find out the specific and molar conductance of the sodium hydroxide solution.
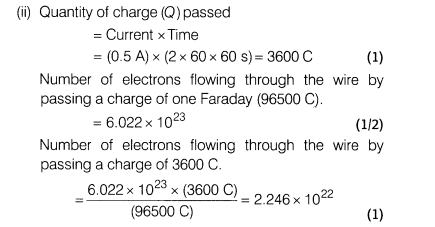
(ii)If a current of 0.5 A flows through a metallic wire for 2 h, then how many electrons flow through the wire?
Ans.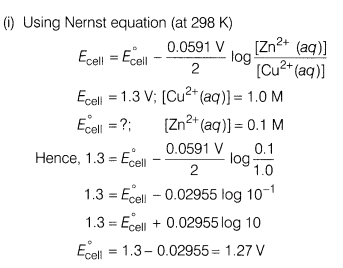
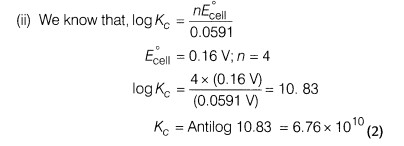

25.(i) Gas A and gas B, both turn K2Cr2Oy / H+ Gas A also turns lead acetate paper black precipitate. When gas A is passed into gas B in an aqueous solution, yellowish white turbidity appears. Identify gas A and B and explain the reactions.
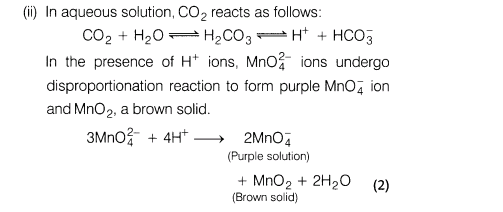
(ii) Explain, why a green solution of potassium manganate turns purple and a brown solid is precipitated when C02 gas is bubbled into the solution?
Or
(i)Give reasons.
(a)Iron is a transition metal while sodium is not.
(b)In permanganate ion, there is a covalency between manganese and oxygen.
(c)Zn, Cd and Hg are quite soft and have low melting points.
(ii)Fe2+ ions can be estimated by MnO4- andCr2072- by volumetric titration. Give reactions. Also, relate their equivalent mass to molar mass.
Ans.


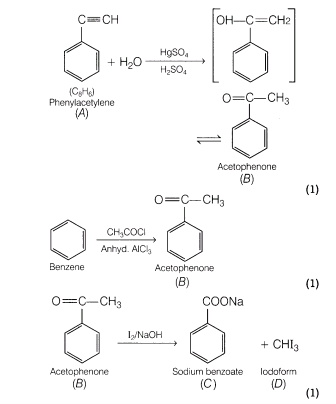
26.An organic compound A (C8H6) on reacting with dilute sulphuric acid containing mercuric sulphate gives a compound B which can also be obtained from the reaction of benzene and acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous A1C13. The compound B when treated with iodine and aqueous NaOH yields C and a yellow compound D. Identify A, B, C and D with justification. Show how B is formed from A?
Or
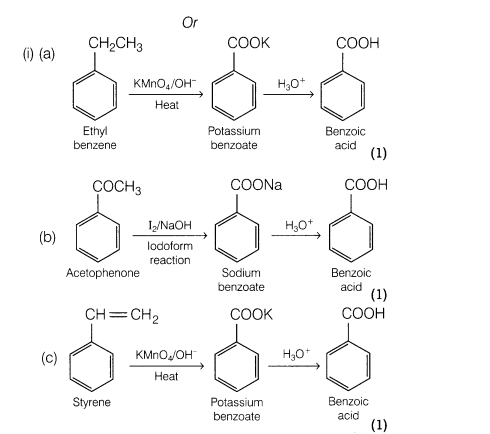
(i)Show how each of the following compounds can be converted to benzoic acid?
(a)Ethyl benzene
(b)Acetophenone
(c)Phenylethene (styrene)
(ii)Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between following pairs of compounds.
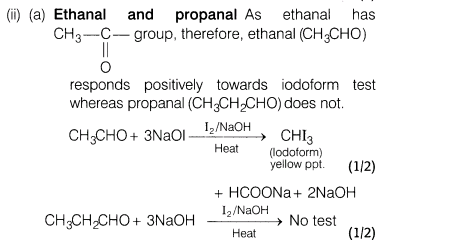
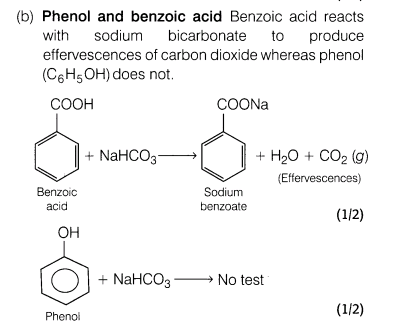
(a)Ethanal and propanal
(b)Phenol and benzoic acid
Ans.Compound 6 is formed by the reaction of benzene and acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous AICI3. So, B is an aromatic ketone.
As compound B, when reacts with iodine and aqueous NaOFI, produces iodoform; B is acetophenone. Compound A should be a derivative of acetylene since, it undergoes hydration under acidic conditions to form 6
which is a ketone i.e. acetophenone. The reactions involved are: