CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Solved Set 7
Section A
1. What are freons? Give its one use.
2. What happen when dialysis is prolonged?
3. Give the IUPAC name of the following organic compound.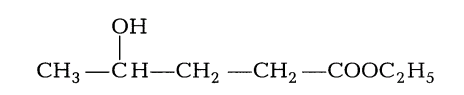
4.Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
5.Complete the reaction and give the name of this reaction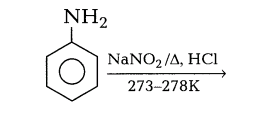
6.First, second, third and fourth ionisation energies of Ni and Pt are given below.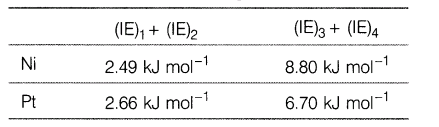
Compare the stability of Ni2+ and Pt2+, and Ni4+ and Pt4+ compounds.
7.Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 50.0 g of ethylene glycol (molecular weight =62) dissolved in 600 g of water. [Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1]
8.What is a secondary cell? Write the reactions taking place when a lead storage battery is in use.
9.An element crystallises into fee unit cell type structure. The edge length of unit cell is 150 pm. If 150 g of this element have 12 x 1023 atoms, then calculate the density of the element.
Or
In a fee arrangement of P and Q atoms, P atoms are at the corners and Q atoms at face centres of the unit cell, what is the formula of the compound?
10.A compound forms hexagonal close packed structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mole of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids?
Section C
11.(i) What is van’t Hoff factor? How is it related to degree of dissociation of an electrolyte?
(ii)A 0.5% aqueous solution of KC1 was found to freeze at -0.24°C. Find the van’t Hoff factor and degree of dissociation of the solute at this concentration. (Kf of water = 1.86 Kkg mol-1)
12.(i) (a) Complete the following reaction.
XeF6 + 2H20 ——– >
(b)KMn04 oxidises H202, why?
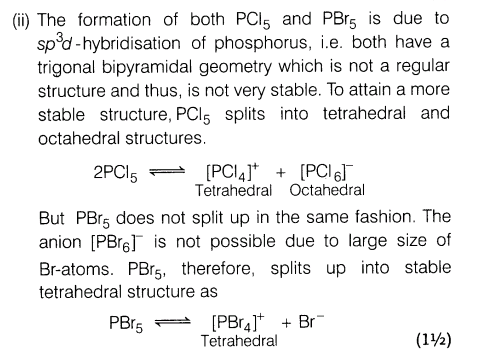
(ii)PC15 exists as [PC14 ]+ [PC16 ]– but PBr5 exists as [PBr4 ]+ Br–. Explain.
13.(i) Which is a better nucleophile, a bromide ion or an iodide ion?
(ii)Give the major organic product in each of the following reactions.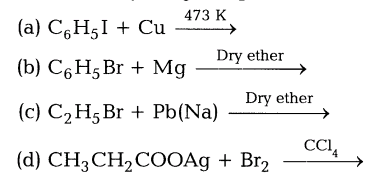
14. (i) Identify and write the names of X, Y and Z in the following reaction.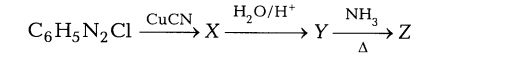
(ii) How would you distinguish between the following?
(a) Ethylamine and diethylamine
(b) Ethylamine and acetamide
15. Give reasons for the following:
(i) The air becomes dry when passed over silica gel.
(ii) Colloidal medicines are more effective in the treatment of diseases.
(iii) Give one example of oil in water and water in oil type of emulsion.
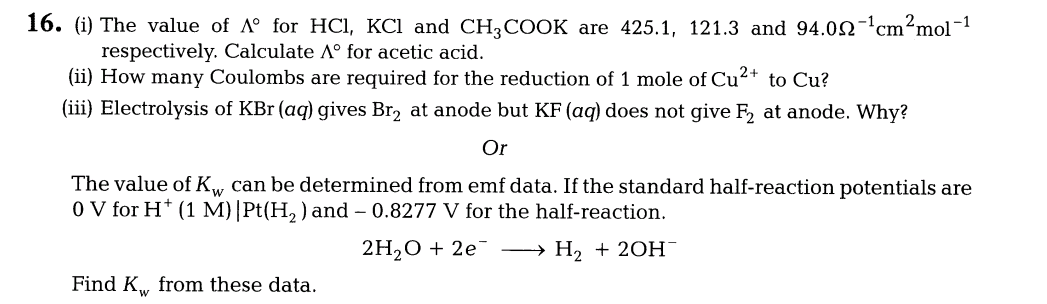
17.(i) Why is the extraction of copper from pyrite difficult than that from its oxide orethrough reduction?
(ii)What is meant by the term pyrometallurgy?
(iii)Although, thermodynamically feasible, in practise, magnesium metal is not used for reduction of alumina in the metallurgy of aluminium. Why?
18.(i) Silver atom has completely filled d-orbital (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
(ii)Ce4+ is used as an oxidising agent in volumetric analysis.
(iii)Which transition metals of the 3d-series exhibits the largest number of oxidation states and why?
19.(i) Write the IUPAC name of [Cr(NH3 )4 (H20)3 ]C13.
(ii)Find the oxidation state of central atom in the following [Co(NH3 )5ONO]Cl2 .
(iii)Predict the geometry and magnetic behaviour of [NiCl4 ]2~.
20.(i) Write structural differences between
(ii)cellulose and amylose
(iii)sucrose and maltose.
(ii) Glucose and fructose form the same osazone, what does it prove?
21.(i) Give the name and structure of one of the initiators used in free radical polymerisation.
(ii)Give the name and structure of monomers of buna-N.
(iii)Name one biodegradable polymer.
22.(i) The increase in molecular mass and large non-polar part (hydrophobic) dominate over the solubilising effect of H-bonding. Hence, cresols are insoluble in H2O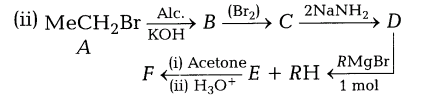
Section D
- Surfactants are the substances which get preferentially adsorbed at the air-water, oil-water and solid-water interfaces, forming an oriented monolayer wherein, the hydrophilic groups point towards the aqueous phase and hydrocarbon chains point towards the air or towards the oil phase. Phosphates were added to commercial detergents but the use of detergents containing phosphates is now discouraged.
Based on the above passage, answer the following questions.
- Why are phosphates added to commercial detergents?
- Why the use of phosphates is being discouraged in detergents/surfactants?
- Name one biodegradable and one non-biodegradable detergent.
- What values do you get from the above passage?
Section E
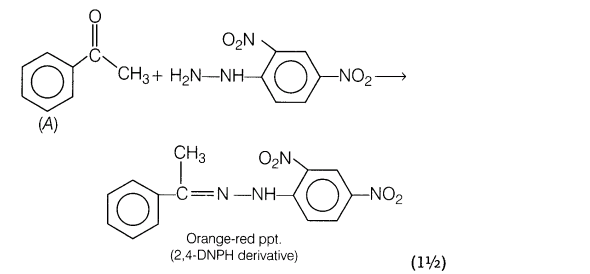
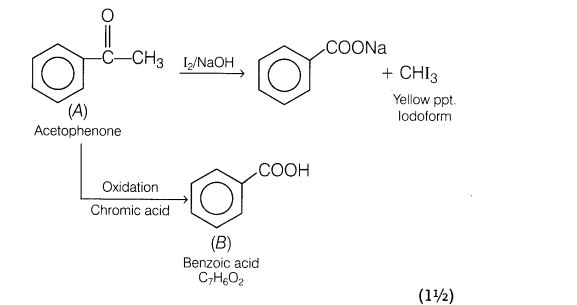
24.An organic compound A with molecular formula, C8H80 forms orange-red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of NaOH. It neither reduces Tollen’s or Fehling’s reagent, nor decolourises bromine water or Baeyer’s reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid B having molecular formula C7H602. Identify the compound A and B and explain the reactions involved.
Or
Complete the following reactions and write the name of the products.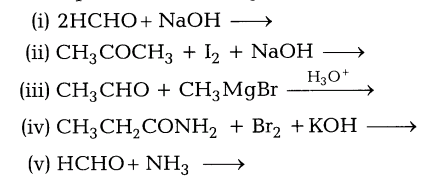
25.Assign reasons for the following:
(i)Helium finds wide application in diving system. Why?
(ii)Oxygen forms n bonds whereas sulphur does not form n
(iii)Nitrogen does not form NC15 but phosphorus forms PC15.
(iv)Acidic strength decreases in order HC1 > H2 S > PH3.
(v)In the noble gases, only xenon forms chemical compounds.
Or
(i)An orange solid A on heating gives a colourless gas The gas B in dry condition is passed over heated Ca to give a solid C. The solid C further reacts with water to produce gas D which forms a blue coloured compound E on reaction with copper sulphate solution. Identify A, B, C, D, E and gives the sequence of reactions involved.
(ii)Draw the structures of PC13 and SO42-.

Answers
Section A
1. What are freons? Give its one use.
Ans.Chlorofluoro compounds of methane and ethane in which all the H-atoms are replaced by halogen atoms are called freons e.g. CCI2F2, CFCI3. It is used as a refrigerant.
2. What happen when dialysis is prolonged?
Ans.Due to excessive dialysis, traces of electrolyte which stabilises the colloids is removed completely, making the colloid unstable. As a result, coagulation takes place.
3. Give the IUPAC name of the following organic compound.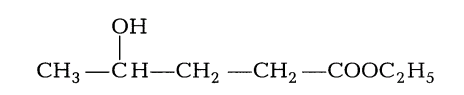
Ans.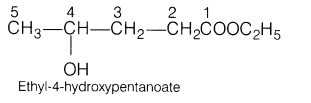
4.Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Ans.Carbohydrates are generally optically active due to the presence of chiral carbon atom and also due to lack of plane of symmetry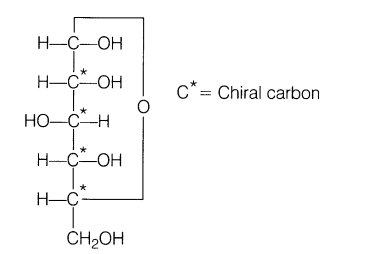
5.Complete the reaction and give the name of this reaction
Ans.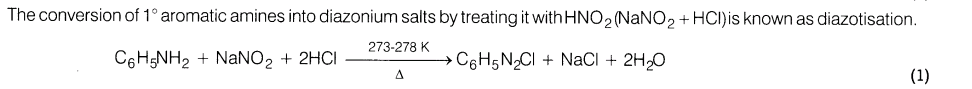
6.First, second, third and fourth ionisation energies of Ni and Pt are given below.
Compare the stability of Ni2+ and Pt2+, and Ni4+ and Pt4+ compounds.
Ans.
7.Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 50.0 g of ethylene glycol (molecular weight =62) dissolved in 600 g of water. [Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1]
Ans.
8.What is a secondary cell? Write the reactions taking place when a lead storage battery is in use.
Ans.The secondary cells are those in which the cell reaction can be reversed by an external electric energy source. They can be recharged and used again and again. Lead storage battery is a secondary cell. Following reactions take place when the cell is used.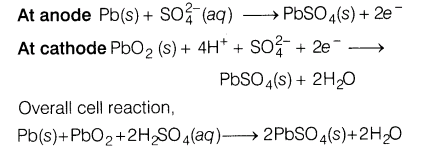
9.An element crystallises into fee unit cell type structure. The edge length of unit cell is 150 pm. If 150 g of this element have 12 x 1023 atoms, then calculate the density of the element.
Or
In a fee arrangement of P and Q atoms, P atoms are at the corners and Q atoms at face centres of the unit cell, what is the formula of the compound?
Ans.
Or
10.A compound forms hexagonal close packed structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mole of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids?
Ans.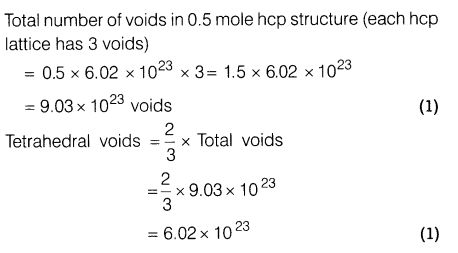
Section C
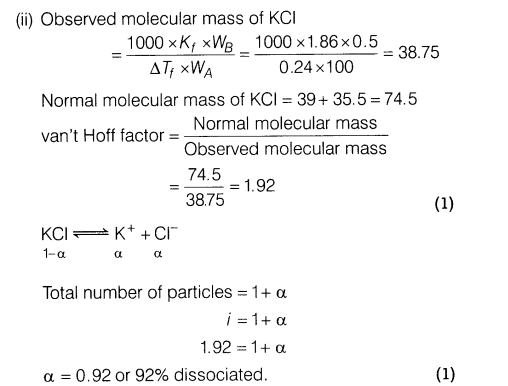
11.(i) What is van’t Hoff factor? How is it related to degree of dissociation of an electrolyte?
(ii)A 0.5% aqueous solution of KC1 was found to freeze at -0.24°C. Find the van’t Hoff factor and degree of dissociation of the solute at this concentration. (Kf of water = 1.86 Kkg mol-1)
Ans.
12.(i) (a) Complete the following reaction.
XeF6 + 2H20 ——– >
(b)KMn04 oxidises H202, why?
(ii)PC15 exists as [PC14 ]+ [PC16 ]– but PBr5 exists as [PBr4 ]+ Br–. Explain.
Ans.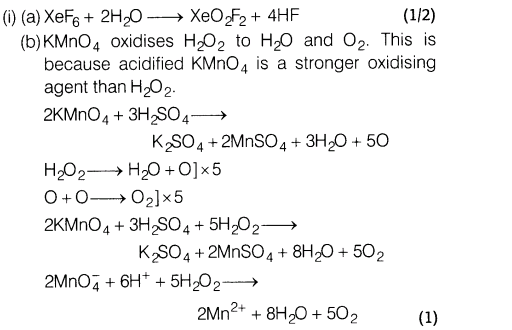
13.(i) Which is a better nucleophile, a bromide ion or an iodide ion?
(ii)Give the major organic product in each of the following reactions.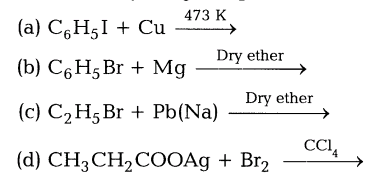
Ans.(i) Nucleophilicity is a kinetic property measured by the rate at which Nu attacks a reference compound under a standard set of experimental condition.Within the group, larger atoms are better nucleophiles because they have more polarisibility. The polarisibility order is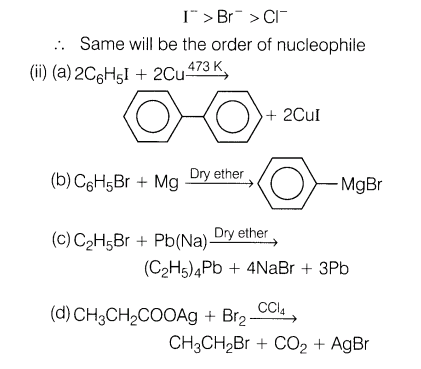
14. (i) Identify and write the names of X, Y and Z in the following reaction.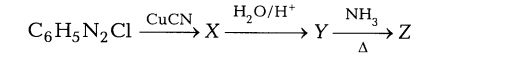
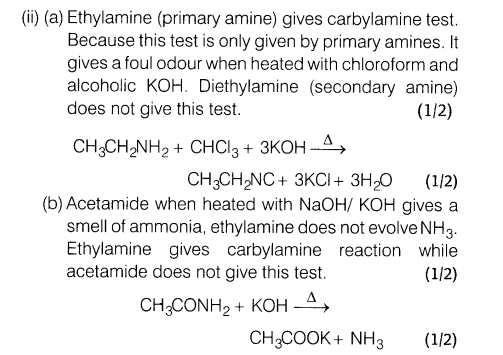
(ii) How would you distinguish between the following?
(a) Ethylamine and diethylamine
(b) Ethylamine and acetamide
Ans.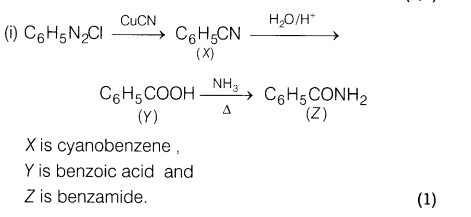
15. Give reasons for the following:
(i) The air becomes dry when passed over silica gel.
(ii) Colloidal medicines are more effective in the treatment of diseases.
(iii) Give one example of oil in water and water in oil type of emulsion.
Ans.(i) The air becomes dry when passed over silica gel because silica gel adsorbs moisture present in the air
(ii)Colloidal medicines are more effective in the treatment of diseases because they have large surface area and are therefore easily assimilated.
(iii) Oil in water type : milk
Water in oil type : butter
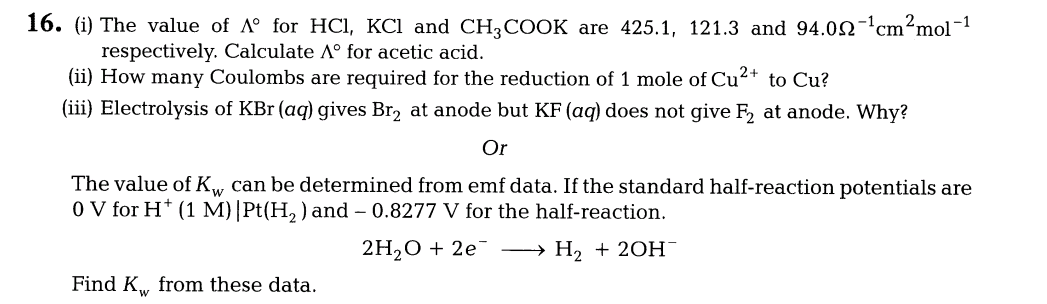
Ans.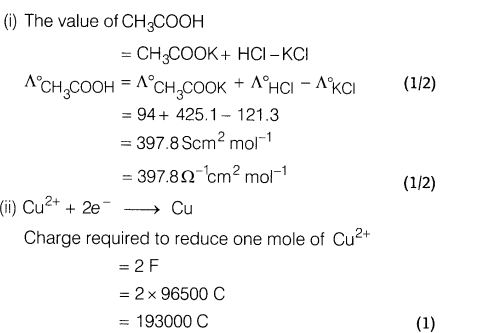


17.(i) Why is the extraction of copper from pyrite difficult than that from its oxide orethrough reduction?
(ii)What is meant by the term pyrometallurgy?
(iii)Although, thermodynamically feasible, in practise, magnesium metal is not used for reduction of alumina in the metallurgy of aluminium. Why?
Ans.

18.(i) Silver atom has completely filled d-orbital (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
(ii)Ce4+ is used as an oxidising agent in volumetric analysis.
(iii)Which transition metals of the 3d-series exhibits the largest number of oxidation states and why?
Ans.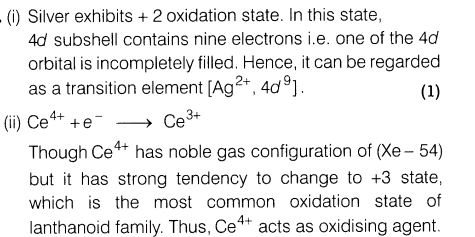

19.(i) Write the IUPAC name of [Cr(NH3 )4 (H20)3 ]C13.
(ii)Find the oxidation state of central atom in the following [Co(NH3 )5ONO]Cl2 .
(iii)Predict the geometry and magnetic behaviour of [NiCl4 ]2-.
Ans.
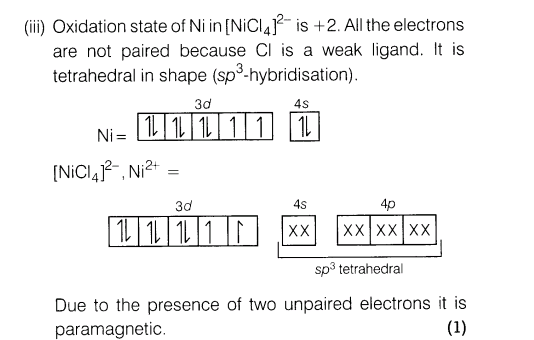
20.(i) Write structural differences between
(ii)cellulose and amylose
(iii)sucrose and maltose.
(ii) Glucose and fructose form the same osazone, what does it prove?
Ans.
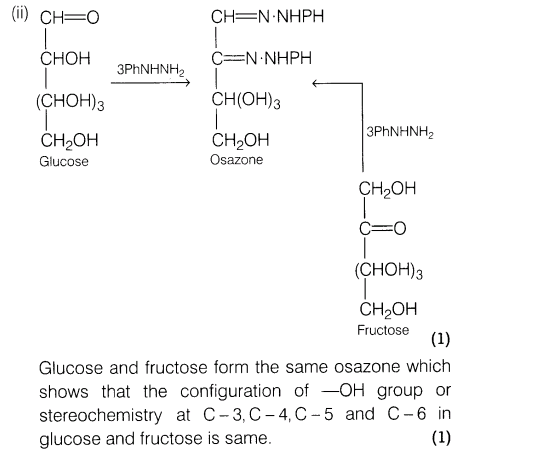
21.(i) Give the name and structure of one of the initiators used in free radical polymerisation.
(ii)Give the name and structure of monomers of buna-N.
(iii)Name one biodegradable polymer.
Ans.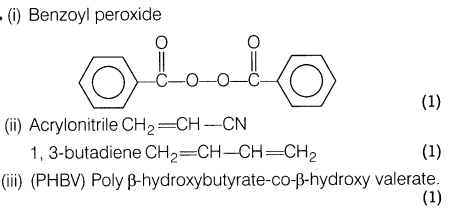
22.(i) The increase in molecular mass and large non-polar part (hydrophobic) dominate over the solubilising effect of H-bonding. Hence, cresols are insoluble in H2O.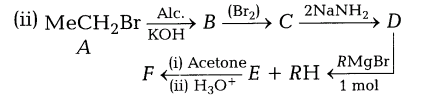
Ans.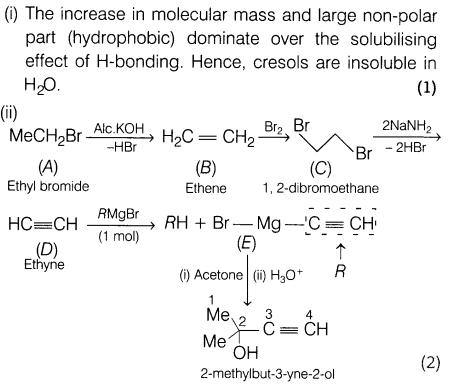
Section D
23.Surfactants are the substances which get preferentially adsorbed at the air-water, oil-water and solid-water interfaces, forming an oriented monolayer wherein, the hydrophilic groups point towards the aqueous phase and hydrocarbon chains point towards the air or towards the oil phase. Phosphates were added to commercial detergents but the use of detergents containing phosphates is now discouraged.
Based on the above passage, answer the following questions.
- Why are phosphates added to commercial detergents?
- Why the use of phosphates is being discouraged in detergents/surfactants?
- Name one biodegradable and one non-biodegradable detergent.
- What values do you get from the above passage?
Ans. (i) Phosphates are added to commercial detergents because
(a)they form complex with the metal ion that contribute to water hardness and kept them dissolved.
(b)they control acidity and influence micelle formation.
(ii)Use of phosphate is being discouraged because
(a)there is an overgrowth of vegetation.
(b)overgrowth and subsequent decay of the dead plants lead to the decreased in dissolved 02 in water.
(iii)Biodegradable detergent LAS (Linear Alkyl Sulphonates) surfactants are biodegradable. Non-biodegradable detergent ABS (Alkyl Benzene Sulphonates) surfactants used in the manufacturing of detergent are non-biodegradable and enter water-bodies through discharge of municipal sewage.
(iv)Concern about environment pollution, awareness about use of biodegradable detergents.
Section E
24.An organic compound A with molecular formula, C8H80 forms orange-red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of NaOH. It neither reduces Tollen’s or Fehling’s reagent, nor decolourises bromine water or Baeyer’s reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid B having molecular formula C7H602. Identify the compound A and B and explain the reactions involved.
Or
Complete the following reactions and write the name of the products.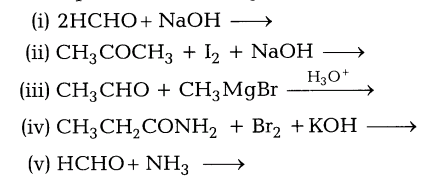
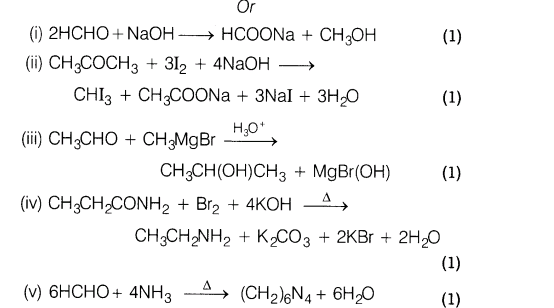
Ans.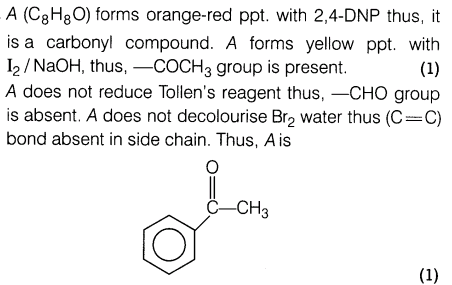
25.Assign reasons for the following:
(i)Helium finds wide application in diving system. Why?
(ii)Oxygen forms n bonds whereas sulphur does not form n
(iii)Nitrogen does not form NC15 but phosphorus forms PC15.
(iv)Acidic strength decreases in order HC1 > H2 S > PH3.
(v)In the noble gases, only xenon forms chemical compounds.
Or
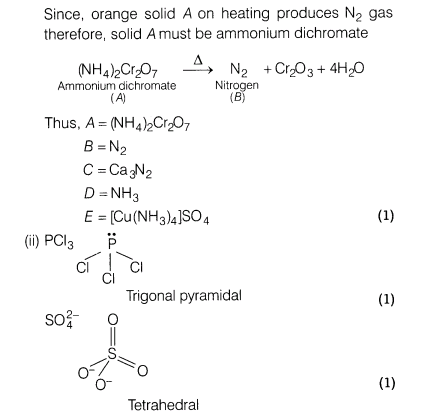
(i)An orange solid A on heating gives a colourless gas The gas B in dry condition is passed over heated Ca to give a solid C. The solid C further reacts with water to produce gas D which forms a blue coloured compound E on reaction with copper sulphate solution. Identify A, B, C, D, E and gives the sequence of reactions involved.
(ii)Draw the structures of PC13 and SO42-.
Ans.



Ans.

