Question
A curve has equation \(y=f\left ( x \right )\) and is such that \(f{}’\left ( x \right )=3x^{\frac{1}{2}}+3x^{-\frac{1}{2}}-10\).
(i)By using the substitution ,or ot6herwise,find the value of x for which the curve y=f(x has stationary points.
(ii) Find and hence ,or otherwise ,determine the nature of each stationary point.
(iii)It is given that the curve y=f(x) passes through the point (4,-7) .Find f(x).
Answer/Explanation
(i)\(3u+\frac{3}{u}-10=0\)
\(3u^{2}-10u+3=0\Rightarrow \left ( 3u-1 \right )\left ( u-3 \right )=0\)
\(\sqrt{x}=\frac{1}{3}\) or 3
\(\sqrt{x}=\frac{1}{9}or 9\)
(ii)\(f{}”\left ( x \right )=\frac{3}{2}x^{-\frac{1}{2}} -\frac{3}{2} x^{-\frac{3}{2}} \)
At \(x=\frac{1}{9}\)
\(f{}”\left ( x \right )=\frac{3}{2}\left ( 3 \right )-\frac{3}{2}\left ( 27 \right )=-36< 0\rightarrow\)Max
At x=9
\(f{}”\left ( x \right )=\frac{3}{2}\times \frac{1}{3}-\frac{3}{2}\times \frac{1}{27}=\frac{4}{9}> 0\rightarrow\)Min
(iii)\(f(x)=2x^{\frac{3}{2}}+6x^{\frac{1}{2}}-10x(+c)\)
-7=16+12-40+c
c=5
Question
The function f is such that \(f{}'(x)=3x^{2}-7 \) and f . Find \(f\left ( x \right )\).
Answer/Explanation
\(f(x)=x^{3}-7x+c\)
5=27-21+c
c=-1\(\rightarrow f(x)=x^{3}-7x-1\)
Question.
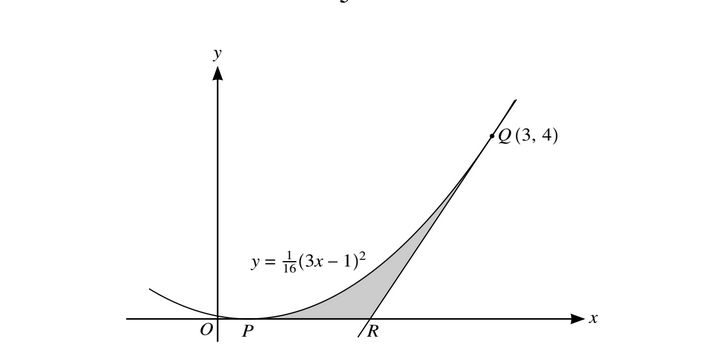
The diagram shows part of the curve \(y =\frac{1}{16}(3x – 1)^2\) which touches the x-axis at the point P. The point Q (3, 4) lies on the curve and the tangent to the curve at Q crosses the x-axis at R.
Showing all necessary working, find by calculation
(i) State the x-coordinate of P.
(ii) the x-coordinate of R.
(iii) the area of the shaded region PQR.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:(i) \(x=\frac{1}{3}\)
(ii) \(\frac{\partial y}{\partial x}=\left [ \frac{2}{16} (3x-1)\right ]\left [ 3\right ]\)
\(when x=3 n \to \frac{\partial y}{\partial x}=3\)
\(Equation or QR is y-4=3(x-3)\)
\(when y=0 \rightarrow x=\frac{5}{3}\)
(iii)Area under curve \(=\left [ \frac{1}{16\times 3}(3x-1)^3 \right ]\times \left [ \frac{1}{3} \right ]\)
\(\left [ \frac{1}{16\times 9}(8^3 -0)\right ]=\frac{32}{9}\)
Area of \(\Delta =\frac{8}{3}\)
Shaded area\( = \frac{32}{9}-\frac{8}{3}=\frac{8}{9}\)
Question.
(a) Find \(\int_{\infty }^{1} \frac{1}{\left ( 3x – 2 \right )^{\frac{3}{2}}}dx\)
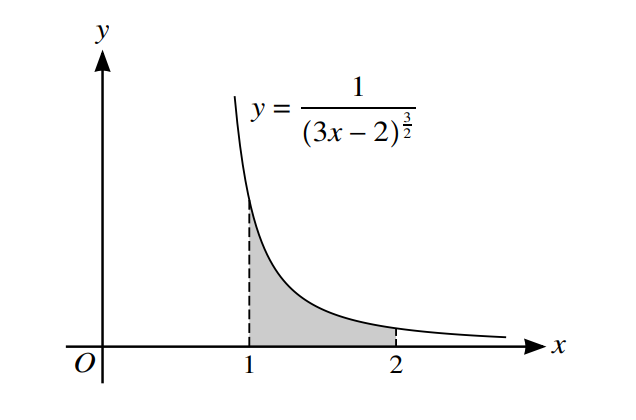
The diagram shows the curve with equation y =\(\frac{1}{\left ( 3x-2 \right )^{\frac{3}{2}}}\) . The shaded region is bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the lines x = 1 and x = 2. The shaded region is rotated through 3600 about the x-axis.
(b) Find the volume of revolution.
The normal to the curve at the point (1, 1) crosses the y-axis at the point A.
(c) Find the y-coordinate of A.
Answer/Explanation
(a) \(\left \{ \frac{\left ( 3x-2 \right )^{-\frac{1}{2}}}{-\frac{1}{2}} \right \}\) ÷{3}
\(-\frac{2}{3}[0-1]\)
(b) \(\left [ \pi \right ]\int y^{2}dx = \left [ \pi \right ]\int \left ( 3x-2 \right )^{-3} dx = \left [ \pi \right ]\frac{\left ( 3x-2 \right )^{-2}}{-2\times 3}\)
\(\left [ \pi \right ]\left [ -\frac{1}{6} \right ]\left [ \frac{1}{16} -1\right ]\)
\(\frac{5\pi }{32}\)
(c) \(\frac{dy}{dx} = – \frac{3}{2}\times 3\left ( 3x-2 \right )^{\frac{5}{2}}\)
\(At x = 1, \frac{dy}{dx} = – \frac{9}{2}\)
[Equation of normal is] y – 1 = \(\frac{2}{9}\) (x-1) OR evaluates c
At A, y = \(\frac{7}{9}\)