Question
A fixed mass of an ideal gas has a volume V and a pressure p. The gas undergoes a cycle of changes, X to Y to Z to X, as shown in Fig. 2.1.
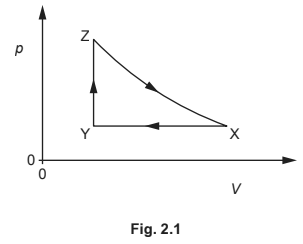
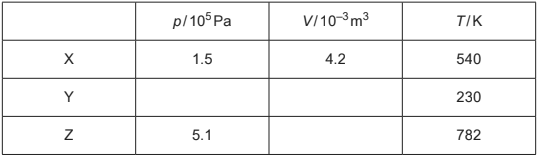
Table 2.1 shows data for p, V and temperature T for the gas at points X, Y and Z.
Table 2.1
(a) State the change in internal energy ΔU for one complete cycle, XYZX.
(b) Calculate the amount n of gas.
(c) Complete Table 2.1.
Use the space below for any working.
(d) (i) The first law of thermodynamics for a system may be represented by the equation
ΔU = q + W.
State, with reference to the system, what is meant by:
(ii) Explain how the first law of thermodynamics applies to the change Z to X.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \(0\)
(b) \(pV\) = \(nRT\)
\((n =) 1.5 \times 10^{5} \times 4.2 \times 10^{–3} / 8.31 \times 540\)
= 0.14 mol
(c) missing pressure \(1.5 ( \times 10^{5})\)
both missing volumes \(1.8 ( \times 10^{–3})\)
(d) (i) \((ΔU:)\) increase in internal energy (of the system)
\((q:)\) thermal energy supplied to the system B1
\((W:)\) work done on system
(ii) volume increases and work is done by the gas
Question
A fixed mass of an ideal gas is at a temperature of 21°C. The pressure of the gas is 2.3 × 105 Pa and its volume is 3.5 × 10–3m3.
(a) (i) Calculate the number N of molecules in the gas.
N = ………………………………………………… [2]
(ii) The mass of one molecule of the gas is 40u.
Determine the root-mean-square (r.m.s.) speed of the gas molecules.
r.m.s. speed = ………………………………………… ms–1 [2]
(b) The temperature of the gas is increased by 84°C.
Calculate the value of the ratio

ratio = ………………………………………………… [2]
[Total: 6]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (i) pV = NkT = or pV = nRT = and N = nNA
\(N=\frac{2.3\times 10^{5}\times 3.5\times 10^{-3}}{1.38\times 10^{-23}\times 294}\)
= 2.0 × 1023
(a) (ii) \(pV=\frac{1}{3}Nmc^{2}\)
\(c^{2}=\frac{3\times 2.3\times 10^{5}\times 3.5\times 10^{-3}}{2.0\times 10^{23}\times 40\times 1.66^{-27}}\)
= 182 000
r.m.s. speed = 430 ms–1
or
\(\frac{1}{2}mc^{2}=\frac{3}{2}kT\)
\(c^{2}=\frac{3\times 1.38\times 10^{-23}\times 294}{40\times 1.66\times 10^{-27}}\)
= 183 000
r.m.s.speed = 430 ms–1
(b) \(c^{2}=\frac{3\times2.0\times10^{23}\times1.38\times 10^{-23}\times(294+84)}{2.0\times 10^{23}\times 40\times 1.66\times 10^{-27}}\)
c = 236000
c= 485
\(ratio=\left ( =\frac{485}{430} \right )=1.1\)
OR
\(v\infty \sqrt{T} \ or\ v^{2}\infty T\)
\(ratio=\sqrt{\frac{273+21+84}{273+21}} \ or\ \sqrt{\frac{378}{294}}\)