Quantitative versus qualitative
• Most observation in physics are quantitative
• Descriptive observations (or qualitative) are usually imprecise
Qualitative Observations
How do you measure artistic beauty?

Quantitative Observations
What can be measured with the instruments on an aeroplane?


• A physical quantity is one that can be measured and consists of a magnitude and unit.
![]()
Are classified into two types:
• Base quantities
• Derived quantities
Base quantity
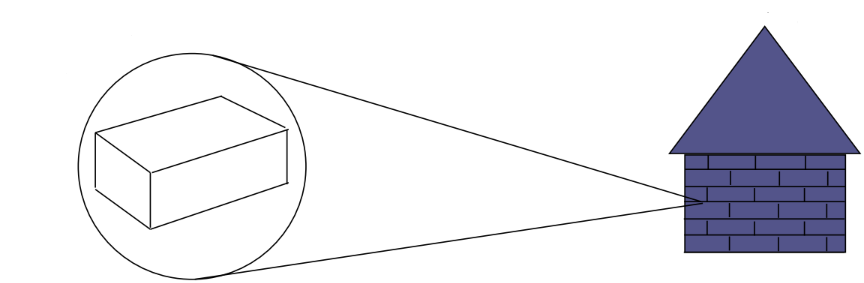
For example : is likethe brick – the basic building block of a house
Derived quantity
For example : is like the house that was build up from a collection of bricks (basic quantity)