NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science. Here we have given. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources
1. Answer the following questions.
Question 1(1).
Name any three common minerals used by you every day.
Answer:
- Iron
- Aluminium
- Ore is the raw me tat-found in the earth mixed with other materials or impurities.
Question 1(2).
What is an ore? Where are the ores of metallic minerals generally located? (Hi) Name two regions rich in natural gas resources.
Answer:
An ore is a rock from which minerals are mined. Ores of metallic minerals are found usually in igneous and metamorphic rock formations.
Question 1(3).
Name two regions rich in natural gas resources.
Answer:
- In the world: Russia, Norway, UK, Netherlands (Any two)
- In India: Jaisalmer, Krishna-Godavari Delta, Tripura and some areas offshore in Mumbai High. (Any two)
Question 1(4).
Which sources of energy would you suggest for
(a) rural areas
(b) coastal areas
(c) arid regions
Answer:
(a) Rural areas: Biogas, solar energy
(b) Coastal areas: Tidal energy
(c) Arid regions: Wind and solar energy.
Question 1(5).
Give five ways in which you can save energy at home.
Answer:
- Switching off lights when not in use.
- Keeping gas cylinder off when not in use.
- Repair of equipments regularly.
- Not switching on light during daytime.
- Always replacing the wire fittings when they are aged.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(1) Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of minerals?
(a) They are created by natural processes.
(b) They have a definite chemical composition.
(c) They are inexhaustible.
(d) Their distribution is uneven.
2. Which one of the following is not a producer of mica?
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Karnataka
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Andhra Pradesh
3. Which one of the following is a leading producer of copper in the world?
(a) Bolivia
(b) Ghana
(c) Chile
(d) Zimbabwe
4. Which one of the following practices will NOT conserve LPG in your kitchen.
(a) Soaking the dal for sometime before cooking it.
(b) Cooking food in a pressure cooker.
(c) Keeping the vegetables chopped before lighting the gas for cooking.
(d) Cooking food in an open pan kept on low flame.
3. Give reasons.
Question 3(1).
Environmental aspects must be carefully looked into before building huge dams.
Answer:
Building huge dams cause destabilization of the natural habitats of plants and wild animals living in the area. These environmental aspects should be looked into before building dams.
Question 3(2).
Most industries are concentrated around coal mines.
Answer:
Because coal is used as power. It is also as raw material in some industries.
Question 3(3).
Petroleum is referred to as “black gold”.
Answer:
Petroleum is referred to as “black gold” due to its immense value and use of its
derivatives.
Question 3(4).
Quarrying can become a major environmental concern.
Answer:
Due to dust raised from the quarrying activities and deforestation.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the followings:
(1) Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy
(2) Biogas and natural gas
(3) Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
(4) Metallic and non-metallic minerals
(1) Distinction between Conventional and Non-conventional Sources of Energy
Answer:
| Conventional | Non-conventional Sources of Energy |
| 1. Conventional sources of energy are those sources which have been in use from time- immemorial. | 1. Non-conventional sources of energy have generally been identified in the recent past. |
| 2. They are exhaustible except water. | 2. They are inexhaustible. |
| 3. They cause pollution when used as they emit smoke and ash. | 3. They are generally pollution-free. |
| 4. Their generation and use involves huge expenditure. | 4. Very meager amount of money is required for their use. |
| 5. They are very expensive to be maintained, stored and transmitted as they are carried over long distances through transmission grid and lines. | 5. Less expensive due to local use and easy to be maintained. |
| 6. Examples: Coal, mineral oil, natural gas, atomic power, water | 6. Examples: Geothermal energy, solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy, energy from urban wastes. |
(2) Distinction between Biogas and Natural Gas
Answer:
| Biogas | Natural gas |
| 1. Biogas is obtained from shrubs, farm wastes, animal and human wastes. | 1. Natural gas is found associated generally with petroleum. |
| 2. It is used mainly in rural areas for domestic purposes. | 2. It is used as a means of energy, raw material in fertiliser plants and as a fuel in electricity generation. |
| 3. It produced in rural areas is. | 3. It is produced in Mumbai High, Gujarat and Assam oilfields, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Tripura and Rajasthan. |
| 4. It has no categories. It is only one gas, that is biogas. | 4. Natural gas is called LPG when used indomestic purposes and CNG when used in vehicles. |
(3) Distinction between Ferrous and Non-ferrous Minerals
Answer:
| Ferrous Minerals | Non-ferrous Minerals |
| 1.The minerals having iron contents are called ferrous minerals. | 1.The minerals that do not possess iron contents are called non-ferrous minerals |
| Examples: Iron ore, manganese, chromium, and cobalf. | Examples: Copper ore, tin, zinc, gold, silver, lead, etc. |
| 2. India abounds in ferrous minerals. | 2. India is deficient in non-ferrous minerals. |
(4) Distinction between Metallic and Non-metallic Minerals
Answer:
| Metallic Minerals | Non-metallic Minerals |
| 1. Metallic minerals are those minerals which produce metals after their processing. | 1. Non-metallic minerals are those minerals which do not produce metals. |
| 2. They are often hard and have shine or lustre of their own. | 2. They are neither hard nor do they have lustre of their own. |
| 3. They can be smelted. | 3. They cannot be smelted. |
| 4. Many of them can be drawn into wires and rolled down into sheets. | 4. They can neither be drawn into wires nor can they be rolled down into sheets. |
| 5. When hit they are not broken. Examples: Iron ore, copper, aluminium, tin, silver and gold. | 5. When hit, they get broken. Examples: Sulphur, coal, petroleum, mica,salt. |
Question 5.
Activity
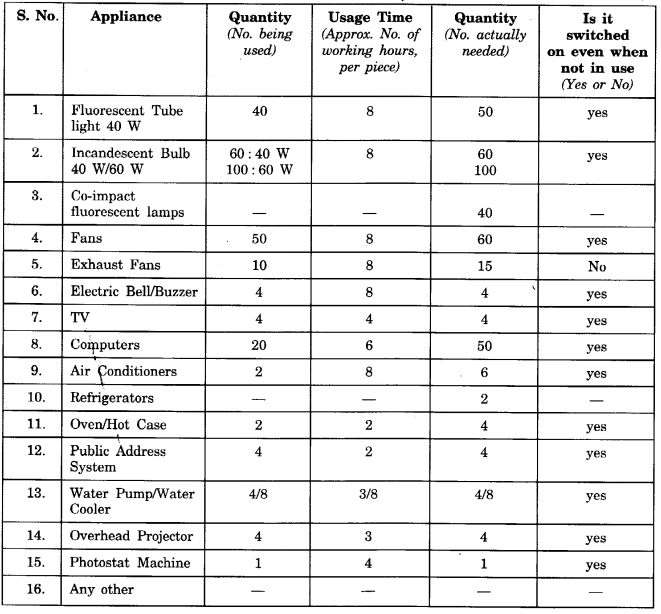
(1) Salma’s class took up an active campaign to do an energy audit of their school by surveying electricity consumption. They prepared survey sheets for the students of the school.
Using the data collected during the survey, students calculated the units consumed for one month and the approximate expenditure and compared it with the electricity bill of the previous month. They also calculated the approximate cost of electricity consumed by fans’ lights and other appliances not switched off. Thus, they highlighted the amount that could be saved and suggested simple energy conservation habits like
- Switching off the appliances when not in use.
- Minimal usage as per requirement.
- Maximising the use of natural breeze and light by keeping the windows open.
- Keeping the lights dust free.
- The appropriate maintenance and usage of appliances as per the given instructions.
Can you add some more tips to this list?
You could conduct a similar survey at home and then extend it to your appartment and make your neighbours also energy wise.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Exercise Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct option.
(i) Which of these is a non-metallic mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Bauxite
(c) Limestone
(d) Manganese ore
(ii) Which continent produces more than half of the world’s tin?
(a) Africa
(b) Asia
(c) Europe
(d) South America
(iii) Which continent is the leading producer of iron ore in the world?
(a) North America
(b) Asia
(c) Europe
(d) Australia
(iv) Which state is a major bauxite producing area?
(a) Goa
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Assam
(d) Tamil Nadu
(v) What is the name given to the electricity produced from coal?
(a) Nuclear power
(b) Thermal power
(c) Fossil fuel
(d) None of these
(vi) Which of these is a conventional source?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Natural gas
(d) All of these
(vii) Which of these is called buried sunshine?
(a) Petroleum
(b) Coal
(c) Solar energy
(d) Tidal energy
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (b), (iii) (c), (iv) (b), (v) (b), (vi) (d), (vii) (b).
Question 2.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- Metallic minerals are classified into …………….. and ………….
- Gold and silver are …………. minerals.
- Minerals can be extracted by ………….,…………., or …………
- Deep bores dug to reach mineral deposits are called …………
- Metallic minerals are generally found in ……….. and…………..rock formations.
- The mineral deposits in North America have located in three zones: …………… the Appalachian region and the mountain ranges of the West.
- …………… is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
- …………. is the most abundantly available fossil fuel.
- Petroleum is drilled from ………
- Bhakra Nangal is an important …………….. station in India.
- …………… and……… are radioactive metals.
Answer:
- ferrous, non-ferrous
- non-ferrous
- mining, drilling, quarrying
- shafts
- igneous, metamorphic
- the Canadian region north of the Great Lakes
- Australia
- Coal
- Oil fields
- hydel power
- Uranium, thorium.
Question 3.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- All ores are rocks but all rocks are not minerals.
- Quarrying is good for the environment.
- Mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are found in sedimentary strata.
- Coal is more predominant in the Canadian Shield Region than the Appalachians.
- Chile and Peru are leading producers of copper.
- Kolar in Karnataka has large deposits of silver.
- Copper is an element used in almost everything.
- Bauxite is the ore of aluminium.
- Nuclear power can be produced from the nuclei of most elements.
Answer:
- Ture
- False
- Ture
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
Question 4.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II.
Answer:
(i) (d), (ii) (a), (iii) (b), (iv) (c), (v) (e).
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between a rock and an ore.
Answer:
A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals. An ore is a rock from which minerals are mined.
Question 2.
Define quarrying.
Answer:
Quarrying is a process of extraction in which minerals lying near the surface are simply dugout.
Question 3.
Name the leading tin producers in Asia.
Answer:
China, Malaysia, and Indonesia are leading tin producers in Asia.
Question 4.
Name two areas in Australia, which have large deposits of gold.
Answer:
Two areas in Western Australia having large deposits of gold are Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie.
Question 5.
Name two minerals in whose production India contributes a significant part.
Answer:
India has vast deposits of high-grade iron ore, and it is also a leading producer of salt.
Question 6.
In which industry is silicon important? From which ore is it obtained?
Answer:
Silicon is important in the computer industry. It is obtained from quartz.
Question 7.
Why are minerals considered non-renewable?
Answer:
Minerals take thousands of years to form. The rate of formation is much smaller than the rate of consumption. So we classify them as non-renewable.
Question 8.
Why is coal called “buried sunshine”?
Answer:
Coal is called “buried sunshine” because it is found buried under the earth, and is as important a source of energy as sunshine.
Question 9.
Why are petroleum and its derivatives called “black gold”?
Answer:
Petroleum and its derivatives are black in colour but as valuable as gold, so we refer to it as “black gold”.
Question 10.
What is natural gas?
Answer:
Natural gas is a fossil fuel obtained with petroleum deposits in oil fields.
Question 11.
Which was the first country to develop hydroelectricity?
Answer:
Norway was the first country to develop hydroelectricity.
Question 12.
Name some important hydel power stations in India.
Answer:
Bhakra Nangal, Gandhi Sagar, Nagaijunasagar, and Damodar Valley Projects are important hydel power stations in India.
Question 13.
Name nuclear power stations in India.
Answer:
Kalpakkam, Tarapur, Ranapratap Sagar, Narora, and Kaiga are the nuclear power stations in India.
Question 14.
Give one advantage of biogas over natural gas.
Answer:
Biogas is a renewable source of energy whereas the amount of natural gas is limited.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name and describe briefly methods of extraction.
Answer:
Mining, drilling, and quarrying are methods of extraction. Mining is a process of extraction of taking out minerals from rocks under the earth’s surface.
- Opencast mining: In this, minerals lying at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer.
- Shaft mining: In this, deep bores (called shafts) are made to reach mineral deposits lying at large depths.
- Drilling: In this, deep wells are bored to take out minerals.
- Quarrying: It is the process of extraction in which minerals lying very close to the surface are extracted just by digging them out.
Question 2.
Where are minerals found?
Answer:
Minerals are found in different types of rocks. Metallic minerals are usually found in igneous and metamorphic rocks that form large plateaus. Examples: iron ore is found in north Sweden, copper, and nickel in Canada. In igneous and metamorphic rocks in South Africa, iron, nickel, chromites, and platinum are found. Non-metallic minerals are found in sedimentary rock formations. Limestone deposits are found in France. Mineral fuels such as coal and petroleum are found in sedimentary strata.
Question 3.
Describe the mineral distribution in North America.
Answer:
The mineral deposits in North America are found in three zones: the Canadian region in the north of the Great Lakes, the Appalachian region, and the Rocky Mountains in the West. Iron ore, nickel, gold, uranium, and copper are mined in the Canadian Shield Region, coal in the Appalachian region. Western Cordilleras have vast deposits of copper, lead, zinc, gold, and silver.
Question 4.
Write common uses of minerals.
Answer:
Minerals are important in many industries. Minerals used in gems are usually very hard. These are then set in varying styles of jewellery. Iron and copper are metals used in almost everything. Copper is present in everything from coins to pipes and electricity wires. Silicon, obtained from the mineral quartz, is the base of the computer industry. Aluminium, obtained from bauxite ore, and its alloys are used in aeroplanes due to their lightweight. Aluminium is also used in kitchen cookware.
Question 5.
How is hydroelectricity, produced?
Answer:
Hydroelectricity is produced from the energy possessed by water falling from great heights. River water is stored in dams. When rainwater or river waterfalls from heights, it flows over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam. The moving blades are connected to a generator which produces electricity from this energy. This electricity is called hydroelectricity. The water discharged after its production is used for irrigation.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name and describe some non- conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
Non-conventional power sources are those power sources that have come into use recently due to the depleting conventional resources and growing awareness. Solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, nuclear power, and tidal energy are examples of non- conventional power sources.
Solar energy is the heat and light energy captured from the sun. Solar cells help to convert this energy to electricity. Solar energy is used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers, etc.
Wind energy is the energy possessed by moving air (wind). Windmills are used to convert wind energy to electricity. Wind farms having clusters of windmills located in coastal regions and mountain passes.
Nuclear power is the energy possessed by the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive elements like uranium-, thorium, etc.
Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the inside of the earth. The temperature inside the earth increases as we go deeper. This heat is used to produce electricity. It is accessed in the form of hot springs. Tidal energy is the energy generated from tides. It is harnessed by building dams at narrow openings of the sea.
Biogas is a gaseous fuel obtained from the decomposition of organic waste like dead plant and animal material or animal dung and kitchen waste. It is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting and is environment-friendly.
Question 2.
Write the advantages and dis¬advantages of non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Non-conventional sources of energy are usually inexhaustible. They do not pollute the environment.
- Nuclear power is emitted in large amounts.
- Most non-conventional sources of energy cost less.
- These forms of energy are safe to use and clean.
Disadvantages:
- Windmills are costly to set up. So using them to harness wind energy is costly, even though the electricity generated from it is cheap.
- Setting up windmills disturbs radio and TV broadcasts.
- Harnessing tidal energy destroys the natural habitats of wildlife.
- Moreover, tidal energy is difficult to harness.
- Obtaining nuclear energy from radioactive material generates radioactive waste. It is expensive too.
- Biogas, although useful and renew¬able, contributes to the greenhouse effect.