IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 3.2 – Modelling a gas
Topic 3 Weightage : 6 %
All Questions for Topic 3.2 – Pressure , Equation of state for an ideal gas , Kinetic model of an ideal gas . Mole, molar mass and the Avogadro constant , Differences between real and ideal gases
This question is in two parts. Part 1 is about ideal gases and specific heat capacity. Part 2 is about simple harmonic motion and waves.
Part 1 Ideal gases and specific heat capacity
a State two assumptions of the kinetic model of an ideal gas.[2]
(i) Define what is meant by the term one mole of argon.
(ii) The temperature of the argon is 300 K. The piston is fixed and the argon is heated at constant volume such that its internal energy increases by 620 J. The temperature of the argon is now 350 K.
Determine the specific heat capacity of argon in J kg–1 K–1 under the condition of constant volume. (The molecular weight of argon is 40)[4]
Explain, in terms of the molecular model of an ideal gas, why the temperature of argon decreases on expansion.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a
point molecules / negligible volume;
no forces between molecules except during contact;
motion/distribution is random;
elastic collisions / no energy lost;
obey Newton’s laws of motion;
collision in zero time;
gravity is ignored;
(i) the molecular weight of argon in grams / 6.02×1023 argon
atoms / same number of particles as in 12 g of C-12;
(allow atoms or molecules for particles)
(ii) mass of gas = 0.040kg ;
specific heat = \(\frac{Q}{{m\Delta T}}\) or 620 = 0.04×c×50;
(i.e. correctly aligns substitution with equation)
\( = \left( {\frac{{620}}{{0.040 \times 50}} = } \right)310{\rm{Jk}}{{\rm{g}}^{{\rm{ – 1}}}}{{\rm{K}}^{{\rm{ – 1}}}}\);
c.
temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules;
(must see “average kinetic” for the mark)
energy/momentum to move piston is provided by energy/momentum of molecules that collide with it;
the (average) kinetic energy of the gas therefore decreases;
Do not allow arguments in terms of loss of speed as a result of collision with a moving piston.
This question is about internal energy and thermal energy (heat).
a Distinguish between internal energy and thermal energy.[3]
Thermal capacity of the piece of iron = 60JK–1
Thermal capacity of the water = 2.0×103JK–1
Initial temperature of the water = 16°C
Final temperature of the water = 45°C
The thermal capacity of the container and insulation is negligible.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a internal energy is the total kinetic and potential energy of the molecules of a body;
thermal energy is a (net) amount of energy transferred between two bodies;
at different temperatures;
(ii) (2.0×103×29)=5.8×104J;
θ=1000°C; (allow 1010°C to 3 sig fig)
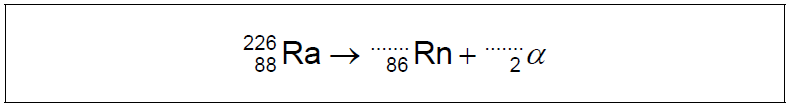
The first scientists to identify alpha particles by a direct method were Rutherford and Royds. They knew that radium-226 (\({}_{86}^{226}{\text{Ra}}\)) decays by alpha emission to form a nuclide known as radon (Rn).
a Write down the missing values in the nuclear equation for this decay.
 [1]
[1]
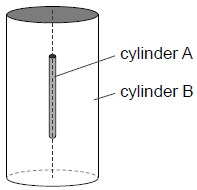
At the start of the experiment all the air was removed from cylinder B. The alpha particles combined with electrons as they moved through the wall of cylinder A to form helium gas in cylinder
B. The wall of cylinder A is made from glass. Outline why this glass wall had to be very thin.[1]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a 222 AND 4
Both needed.
OR
alpha particles have a low penetration power
OR
thin glass increases probability of alpha crossing glass
OR
decreases probability of alpha striking atom/nucleus/molecule
p = 4.5 x 10–9 x 8.31 x «\(\frac{{2.91}}{{1.3 \times {{10}^{ – 5}}}}\)»
OR
p = 2.7 x 1015 x 1.38 x 10–23 x «\(\frac{{2.91}}{{1.3 \times {{10}^{ – 5}}}}\)»
0.83 or 0.84 «Pa»
energy levels are discrete
wavelength/frequency of photon is related to energy change or quotes E = hf or E = \(\frac{{hc}}{\lambda }\)
and is therefore also discrete
OR
means that readers have confidence in the validity of work
OWTTE