IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye, resulting in blurred vision.
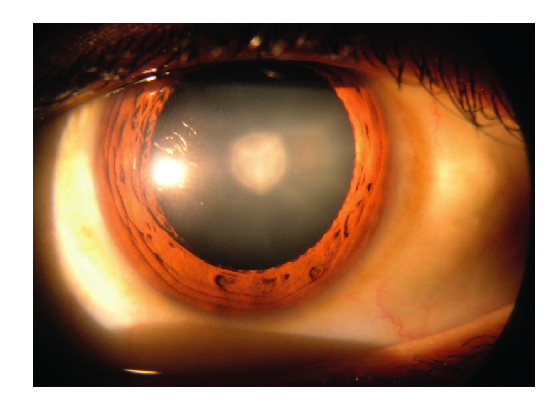
[Source: Cataract in Human Eye, Rakesh Ahuja, MD (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cataract#/media/File:Cataract_in_human_eye.png)]
Explain the use of a local anesthetic during surgery to remove the cataract.
Describe red-green colour blindness.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. reduction/elimination of pain
OR
to block sensory perception
b. blocks synaptic transmission between «sensory neurons and CNS»
OWTTE
c. allows patient to remain aware
d. prevent reflex causing blinking/eye movement
OWTTE
[Max 2 Marks]
a. sex/X-linked «genetic trait»
b. results from absent/defective cone cells
c. cannot distinguish between red and green
[Max 2 Marks]
Question
The diagram shows the mechanism of action of the psychoactive drug cocaine.
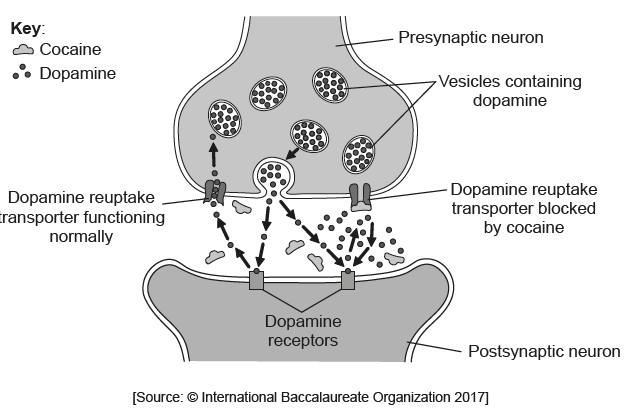
Suggest how cocaine might influence the brain.
Dopamine acts as a slow-acting neurotransmitter. Outline one function of slow-acting neurotransmitters.
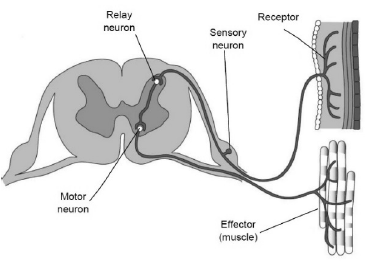
Outline the structure of a reflex arc.
State the type of receptor that detects odours.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «cocaine» is an excitatory drug OWTTE
OR
excitatory influence on the brain
b. increase the concentration/level of dopamine in the synapse OWTTE
c. prolonged effect/continuous stimulus of dopamine on the brain/postsynaptic neuron
d. addiction/dependence on high levels of dopamine for the same effect/addiction
a. they contribute to memory/learning
b. they modulate fast synaptic transmission «in the brain»
c. by causing the release of secondary messengers in the postsynaptic neuron
a. receptor cell
b. sensory neuron passes stimulus
c. to interneuron/relay neuron
d. which transmit response to motor neuron
e. effector
Award marking points for a clearly annotated diagram.
eg:
olfactory «receptor»
OR
chemoreceptor
Question
Explain, using examples, the neurological effects of inhibitory psychoactive drugs.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. examples are benzodiazepines / THC / cannabis / alcohol
b. block / decrease synaptic transmission
c. causing less transfer of information to the brain / decreasing brain activity
d. benzodiazepines increase effect of GABA
e. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter
f. Increase permeability of neural membrane to chloride ions/hyperpolarizes the neuron
g. alcohol enhances effect of GABA
h. «alcohol» also decreases activity of glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter
i. THC/cannabis can block cannabinoid receptors
j. «THC» inhibits release of neurotransmitters that excite postsynaptic neurons/membranes
k. use of psychoactive drugs can lead to dependence/addiction / alter dopamine levels
Question
General anesthetics act on the neurotransmitters in neuron synapses. Explain the effect of anesthetics on patients and how they affect synaptic transmission.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. patient loses awareness/does not feel pain/analgesia
b. interfere/block neural/synaptic transmission between «areas of» sensory perception and the CNS
OR
block «sensory» neural pathways to the brain that detect pain
c. increase presynaptic inhibition
OR
block receptors on the presynaptic membrane
d. increase release of inhibitory neurotransmitters
OR
prevent release of excitatory neurotransmitters
e. inhibit binding of neurotransmitters «to receptors» on postsynaptic membrane
f. decrease «likelyhood of» depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron
OR
hyperpolarize the postsynaptic neuron
g. prevent propagation of action potential on the postsynaptic neuron
h. vital physiological functions/breathing/maintenance of blood pressure continue to function
i. the effects are reversible
j. anesthetics mimic effect/stimulate release of endorphins «which are natural painkillers»/OWTTE
Question
The graphs compare the changes in membrane potential that result from a combination of stimuli. Graph A shows two excitatory post-synaptic potentials (E1 and E2) acting on a neuron. Graph B shows one excitatory (E1) and one inhibitory (I1) post-synaptic potential, both acting on a neuron.
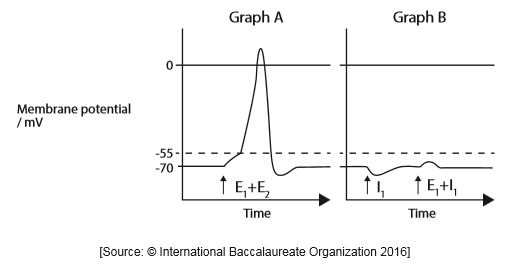
With respect to the graphs, explain what is meant by summation.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
More than one presynaptic neuron can form a synapse with the same postsynaptic neuron
Summation involves combining the effects of «excitatory and inhibitory» neurotransmitters/potentials
OR
action potentials form depending on the balance of signals of excitatory and inhibitory signals
E1 and E2/two excitatory potentials/effects are added
«E1 and E2/two excitatory potentials» depolarizes membrane
«Membrane potential» goes above threshold
OR
Generate action potential
Effect of inhibitory neurotransmitter/potential/ I1 cancels effect of excitatory neurotransmitter/E1
OR
Effect of inhibitory neurotransmitter/potential/ I1 prevents threshold being reached when E1 applied
Question
Regions of the brain that perceive pain also contain receptors for pain-killers, such as morphine (from poppy plants) or endorphins (produced in the brain). Teams of young men competed in pain-endurance tests by repeatedly squeezing hand-springs until reaching unbearable pain.
During pre-competition training, some teams received injections of morphine. During competition, no morphine was administered. However, some teams thought they were receiving morphine injections. Instead, they were injected with a placebo (a saline solution) or the placebo plus naloxone (an endorphin blocking drug) as shown in the following data.
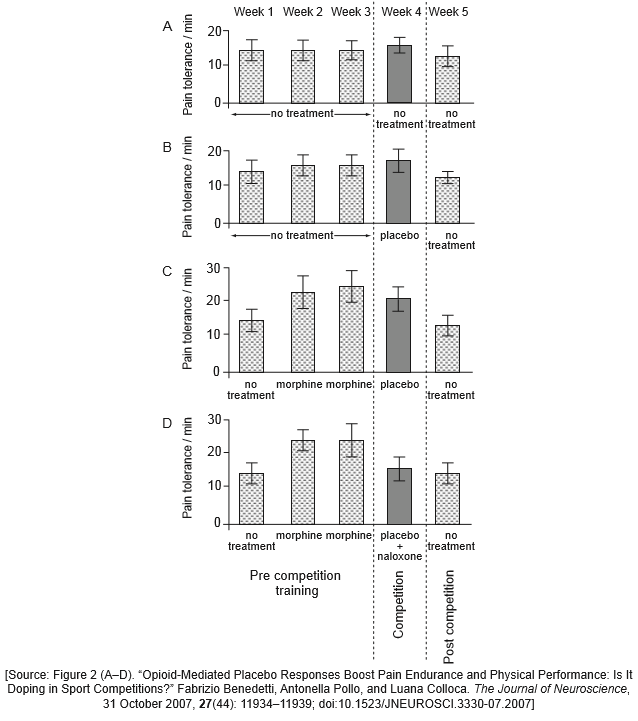
State the effect of morphine during pre-competition training for team C.
Identify which team showed the greatest tolerance to pain on competition day.
Analyse the effect of the placebo as seen in the data.
Suggest a reason for the reduced pain tolerance in team D during competition.
Analyse the data collected in the week following competition.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
increases tolerance to pain (when given in weeks 2 and 3)
team C
a. placebo has no effect in team B where morphine was not administered previously;
b. team B thought they were getting morphine but their performance was the same as team A;
c. placebo has a greater effect if morphine has been administered previously as in team C;
d. naloxone negates the (expected) effect of placebo (even if morphine administered previously) in team D;
e. error bars overlap so results may not be statistically significant/no difference;
naloxone (an endorphin blocking drug) blocks the receptors for endorphins / stops endorphins from acting as pain killers
a. pain tolerance goes down in all groups / all have same level of pain tolerance;
b. morphine-like effect/morphine effect is temporary;
c. endorphins/naturally produced pain-killers levels/number of receptors for pain-killers decreases;
d. decrease in pain tolerance is evidence for motivation/determination during competition and training / lack of motivation when no competition;
Question
State one excitatory and one inhibitory psychoactive drug.
Excitatory: ……………………………………………………
Inhibitory: ……………………………………………………
Describe, using one specific example of an animal, how the process of learning can improve its chances of survival and reproduction.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. excitatory: nicotine / cocaine / amphetamines / other drugs;
b. inhibitory: benzodiazepines / alcohol / THC / other drugs;
a. named animal;
b. description of learned action allowing a more flexible response that improves health/survival/reproduction;
eg:
a. chimpanzees;
b. poking sticks in the wood increases chances to get more food/termites/insects;
a. blue jays;
b. avoidance of certain bad taste / poisonous insects prevents them from being sick/poisoned;
a. hedgehogs;
b. running across roads instead of rolling up when vehicles approach more likely prevents them from being killed;
Accept any other verifiable examples.
Question
The diagram shows the procedure used by Pavlov during his experiment on dogs.
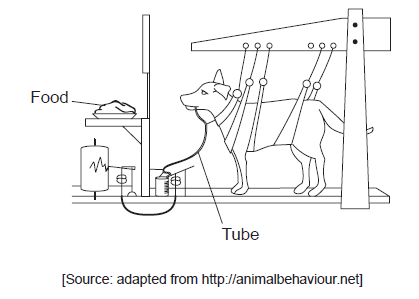
State the type of stimulus provided by the sight and smell of the food.
State the function of the tube.
State two effects presynaptic neurons could have on postsynaptic transmission.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
unconditioned (stimulus)
to collect the saliva (for measurement of volume)
excitation and inhibition
Question
A study was conducted into the influence of genetic factors on occasional cocaine use, abuse and dependency. Pairs of female twins were interviewed to determine if either or both of them had used cocaine at all and also whether they had become abusers of cocaine or dependent upon it. Abuse was diagnosed if cocaine was having harmful consequences on the life of the person and dependence by signs that the person would suffer withdrawal symptoms without it. For each of these three stages of cocaine use, concordance rates were calculated for both identical and non-identical twins. The concordance rate is how many pairs of twins are both at a particular stage, expressed as a percentage of the total number of pairs in which either or both are at that stage. The bar chart shows the results.
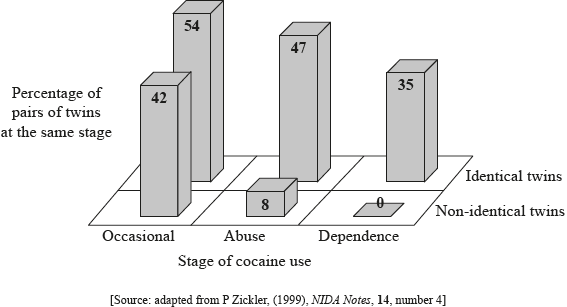
Identify which stage of cocaine use shows the least percentage difference between identical twins and non-identical twins.
Compare the results for identical twins and non-identical twins.
Analyse the data to find whether it supports the hypothesis that genetic factors cause some people to have a much higher chance of cocaine dependence than others.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
occasional
both (identical and non-identical twins) show lower percentages going from occasional to abuse to dependence;
at every stage, the percentage is higher for identical twins;
non-identical twins percentage drops to zero for dependence (but identical twins does not);
difference is similar for both groups between abuse and dependence;
sharper decrease between occasional and abuse for non-identical twins than identical twins/OWTTE;
Do not accept answers stating numerical values only
hypothesis supported as identical twins are more likely to behave the same for abuse and dependence than non-identical twins;
identical twins have the same genotype / OWTTE;
hypothesis not supported as environment is the major factor for trying cocaine;
not known if similar results may be due to similar environment;
not enough data for valid statistical analysis/OWTTE;
Question
Define the term stimulus.
Outline the functions of the following parts of the brain.
Medulla oblongata:
Outline the functions of the following parts of the brain.
Hypothalamus:
Explain the effects of psychoactive drugs on synaptic transmission.
Outline how endorphins act as painkillers.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
stimulus is a change in the (internal/external) environment that can be detected
medulla oblongata: controls autonomic functions of the body such as heart rate/blood pressure/ventilation/swallowing/vomiting/digestion/cranial reflexes
hypothalamus: links nervous and endocrine systems/produces hormones secreted by posterior pituitary/controls hormonal secretion by pituitary/maintains homeostasis such as control of body temperature/hunger/thirst/fatigue/circadian cycles
psychoactive drugs may increase or decrease transmission (to the post-synaptic membrane);
may increase the release/delay the breakdown/interfere with storage/uptake/reabsorption of neurotransmitters;
may mimic the action of neurotransmitters;
inhibitory drugs may reduce the effect of excitatory neurotransmitters/increase the effect/release of inhibitory neurotransmitters;
inhibitory drugs can hyperpolarize the post-synaptic neuron;
endorphins released by pituitary gland (during stress, injury or exercise);
endorphins block transmission of impulses at synapses involved in pain perception;
bind to receptors in the membrane neurons (involved in) sending pain signal;
block release of neurotransmitters;
Question
Explain the effects of cocaine in terms of its action at synapses in the brain and its social consequences.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
excitatory (psychoactive) drug;
cocaine attaches to dopamine pumps/transporters (on presynaptic membrane);
blocks uptake/recycling / causes dopamine to persist in the synaptic cleft;
amplifies synaptic transmission / causes constant stimulation of postsynaptic neuron;
causes euphoria/feelings of happiness/pleasurable effects;
causes feelings of great energy/alertness/talkativeness;
addictive / causes addiction;
changes in personality / problems with family/friends/work;
crimes to pay for cost of drug/crime associated with the production/distribution;
Question
Outline the effects of cocaine at synapses in the brain.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
excitatory (psychoactive) drug;
effect at synapses in brain that use dopamine as transmitter;
inhibits receptors / binds to membrane proteins that pump dopamine / inhibits reuptake of dopamine;
causes build-up of dopamine in synaptic cleft/synapse;
causes continuous transmission at these synapses;
Question
Cocaine is considered an excitatory drug. State one other example of an excitatory drug and one example of an inhibitory drug.
Excitatory drug: ………………………………………………..
Inhibitory drug: ………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Excitatory drug: amphetamines/nicotine/caffeine;
Inhibitory drug: alcohol/benzodiazepines/THC;
(no brand names accepted, do not accept marijuana / heroin/other opiates)
Question
The following diagram shows a section through the spinal cord.
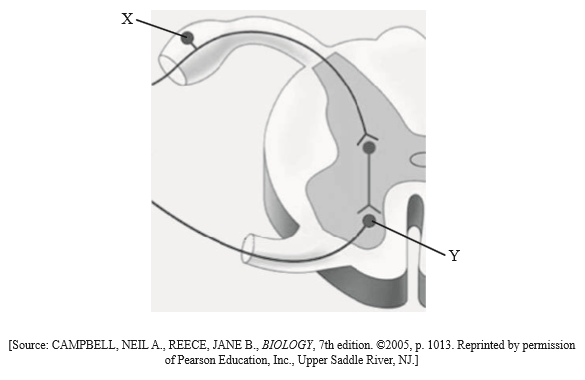
Outline one function for each of the following parts of the brain.

Label cells X and Y.
X: …………………………………………………….
Y: …………………………………………………….
Outline the direction of nerve impulses through the cells labelled X and Y.
Define the term reflex.
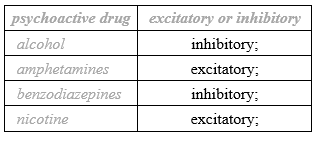
State whether the following psychoactive drugs are excitatory or inhibitory, using the table below.
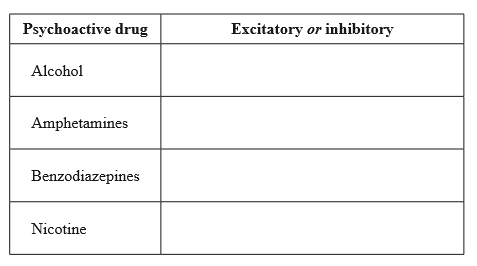
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme

X: (cell body of) sensory neuron;
Y: (cell body of) motor neuron;
(both needed)
from the sensory neuron/X to the motor neuron/Y
a rapid and unconscious response (to a stimulus / of the nervous system)
Award [1] for every two correct responses.
Question
Explain the role of the neurons used in the pain withdrawal reflex.
State one effect of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) on brain function.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
sensory neurons receive information from receptors;
transmit nervous impulses to the central nervous system;
relay neurons in the central nervous system transmit the information from sensory neurons to motor neurons;
motor neurons send impulse to effector;
inhibition of nervous impulses / binding to cannabinoid receptors / blocking of release of excitatory neurotransmitter
Question
List two stimuli and the receptors that detect them.
Outline how pain is perceived and the role of endorphins in this process.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. pressure/movement/sound (detected by) mechanoreceptors;
b. chemicals (detected by) chemoreceptors;
c. temperature (detected by) thermoreceptors;
d. light (detected by) photoreceptors;
e. pain (detected by) nocireceptors;
f. stretch/orientation/movement (detected by) proprioreceptors;
a. impulses passed from pain receptors to sensory areas;
b. of the cerebral cortex where pain is perceived / feelings of pain in the areas of the cerebral cortex;
c. endorphins act as painkillers;
d. which block transmission of impulses at the synapses involved in pain transmission;
Question
Discuss the causes of addiction, including genetic predisposition, social factors and dopamine secretion.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
social and genetic: [3 max]
genetic:
a. genetic link found for (cocaine) addiction;
b. difficult to prove / multifactorial;
social:
c. alcohol/other drug problems among family members;
d. poor school performance;
e. poverty / family conflicts / chaos / stress;
f. having friends who drink/use other drugs;
g. not fitting in socially / being excluded because of race/ability/ethnicity/gender/age/sexual orientation / other factors;
dopamine and addiction: [3 max]
h. substances with addictive potential stimulate the release of dopamine;
i. dopamine is a chemical in the brain that is associated with reward and pleasure;
j. substance use brings a flood of dopamine, which alters the chemistry of the brain;