IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
The diagram shows the human brain.
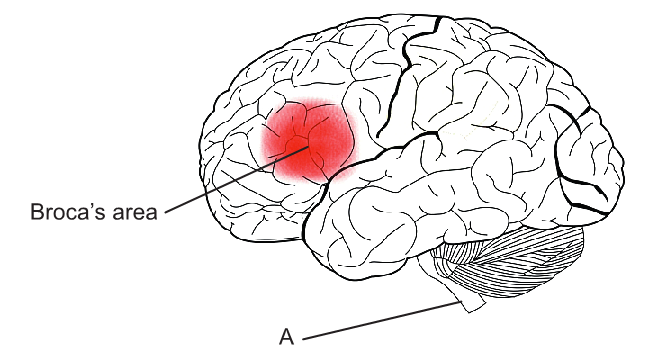
[Source: By charlyzon (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 ]
Identify the structure labelled A.
List two functions of the structure labelled A.
Outline the reason that Broca’s area is more developed in humans than other primates.
Suggest how an injury to the brain can help in understanding brain function.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
medulla «oblongata»
OR
brain stem
a. breathing «rate»
b. heart function
c. digestion/saliva production
d. swallowing reflex
e. coughing
f. vomiting
g. blood pressure
h. state of consciousness/sleep
Allow any two functions.
No ECF
[Max 2 Marks]
«controls motor functions involved with speech and» speech is more developed in humans
observe any changes in the person
Question
Explain how information from the left and right sides of the visual field is processed.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. information from the left-half of the visual field is detected by the right-half of the retina
OR
information from the right-half of the visual field is detected by the left-half of the retina
b. information from left-half of visual field is processed by the right hemisphere
OR
information from right-half of visual field is processed by the left hemisphere
c. impulses travel through optic nerve
d. optic nerves from each eye meet at the «optic» chiasma
e. information from inner fields «closer to the nose» cross at the «optic» chiasma OWTTE
f. impulses continue to the brain
g. an image forms in the visual cortex
Accept answer in a clearly annotated diagram.
Question
The graph shows the relationship between body mass and brain volume in three groups of primates.
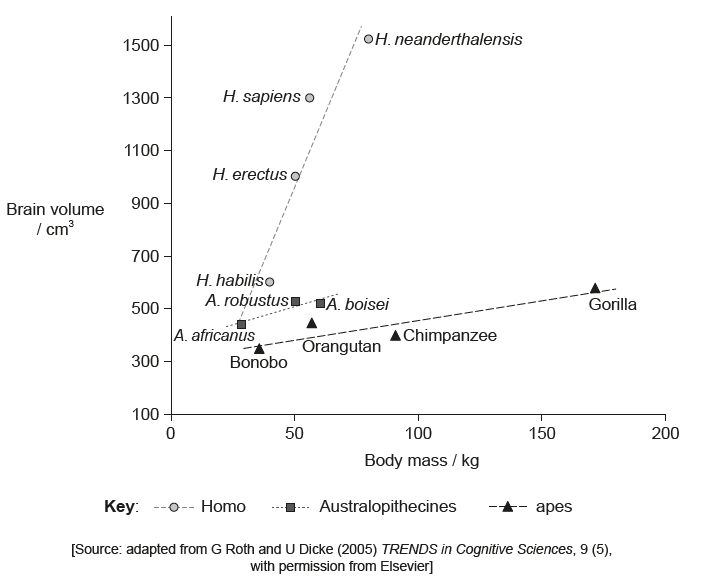
Analyse the relationship between body mass and brain volume in these primates.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. in all groups an increase in body mass means an increase in brain volume
b. in the apes, brain volume has increased only slightly with body mass
c. in the Homo group brain volume increases steeply with body mass
d. in Australopithecines brain volume has increased only slightly with body mass
OR
in Australopithecines fewer species were studied
e. at a small mass the brain volumes are more similar
Question
Outline the function of the autonomic nervous system in the human body.
Evaluate the use of the pupil reflex to test for brain damage.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. controls involuntary processes in the body
b. «uses centres located» in the brain stem/medulla
c. example of action of autonomic nervous system eg: the regulation of heart rate
a. a light is shone in the eye
b. «when light shone in eyes» if pupil does not constrict then there is some brain damage
c. if the pupil constricts it rules out certain types of brain damage
d. different response from each eye could indicate brain damage
e. more testing is needed to determine area/extent of brain damage OWTTE
Question
The cortex of the brain consists of several regions.
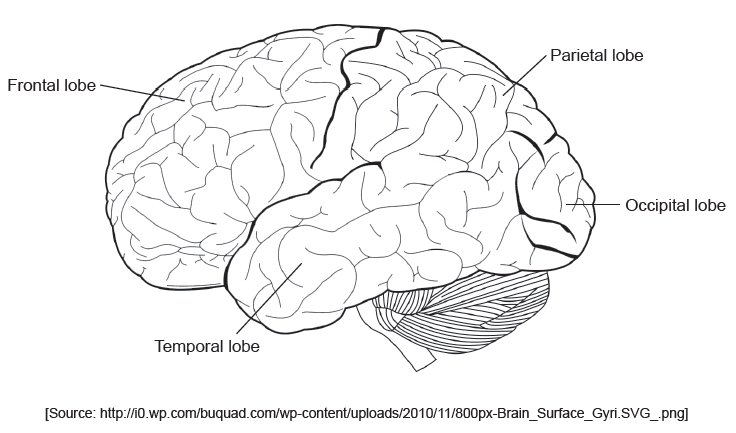
State whether this view of the brain shows the left side or the right side.
Outline the function of Broca’s area.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
left «side»
a. speech production
b. language comprehension/processing
c. damage leads to difficulty in verbalising thoughts
Question
In a study of brain organization, several factors were investigated. The relationship between the volumes of grey and white matter across mammalian species was compared.
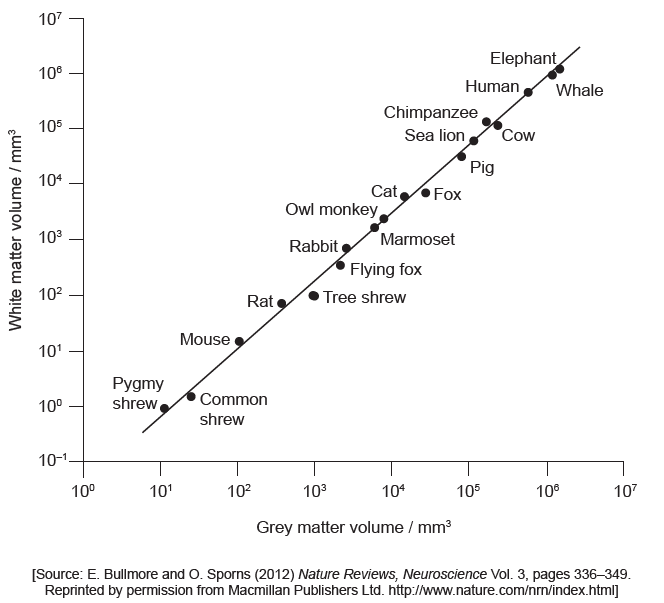
Describe the relationship between the volume of white matter and grey matter.
Outline the organization of the human cerebral cortex with regard to structure and function.
Outline one reason for the large energy requirement of the brain.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. positive correlation «between grey matter volume and white matter volume»
OR
as white matter «volume» increases so does grey matter «volume»
b. As animal/brain size increase the volume of grey and white matter are «approaching» equal
OR
as volume of grey matter increases, the ratio grey : white becomes closer to 1
Structure:
a. divided into left and right hemisphere
b. has extensive folding
c. has a large surface area : volume ratio
Function:
d. responsible for higher order functions/thinking/learning/memory/language
e. functions are located in specific areas of the cortex/lobes
f. sensory/motor functions of the left hemisphere correspond to the right side of the body
a. «brain» cells/neurons carry out large amount of respiration/metabolic activity
b. maintenance of resting potential requires energy/ATP
OR
functioning of Na-K pumps requires energy/ATP
OR
nerve impulse requires energy/ATP
Question
The image shows a human eye.
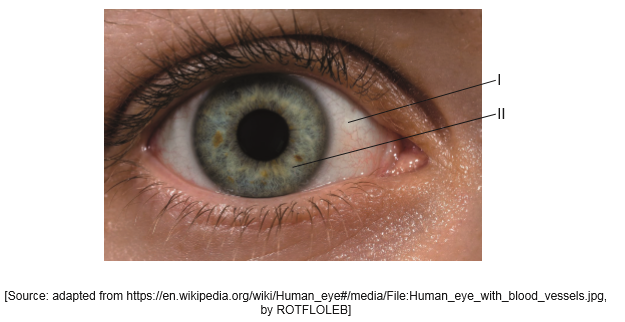
Identify the structures labelled I and II
Explain how the pupil of the eye can be used to assess brain damage.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: conjunctiva/sclera
AND
II: iris/cornea
To award [1] both answers are needed.
a. bright lights causes the pupil to constrict/iris to increase in size
b. low light causes the pupil to dilate/iris decrease in size
c. these are reflex actions
d. the test for brain damage is to (briefly) shine a bright light in the eyes
e. slow or unresponsive change in pupil size indicates brain damage/concussion
f. different response of each eye indicates brain damage/concussion
Question
The images show the brains of human (Homo sapiens) and baboon (Papio hamadryas). The images are not drawn to scale.
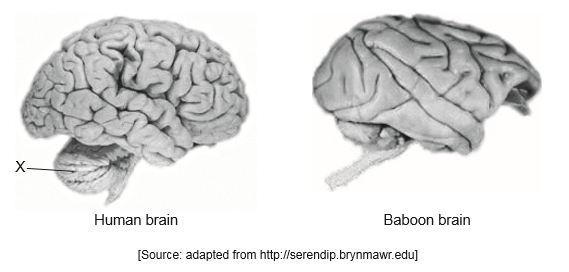
(i) Identify the structure labelled X.
(ii) Outline the function of X in the human brain
With reference to structures visible in the diagrams, explain how the human brain is more evolved for higher order functions than the baboon brain.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) cerebellum
(ii)
a. coordinates the actions of muscles
OR
motor control
b. important in balance/movement/muscle tone/posture
Do not allow ECF.
a. «higher order functions are» controlled by the cerebral hemispheres
b. the human brain has more folding of the (cerebral) cortex than the baboon brain
c. «folding» allows for more surface area / more synapses
d. «more cerebral cortex» without increasing cranium size
e. frontal lobe is larger proportion in the human brain than in the baboon brain
Do not allow answers relating to size as diagrams are not to scale and size is not “visible”.
Do not accept cerebellum unless a higher order function is given.
Question
This image shows an MRI (magnetic resonance image) human brain scan.
Identify the parts labelled I and II.
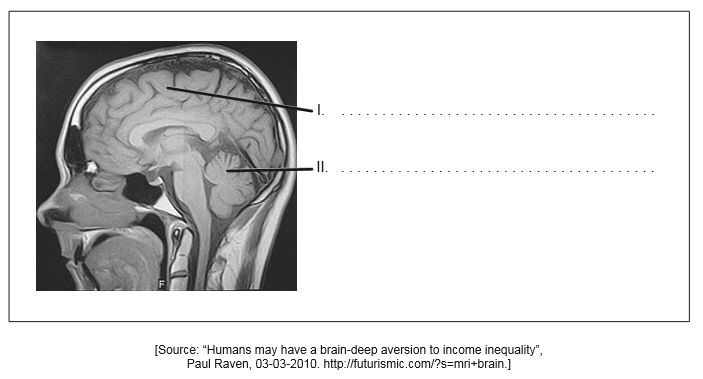
Outline the source of visual sensory input to the right cerebral hemisphere.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: cerebral cortex/hemisphere
OR
cerebrum
II: cerebellum
The left side of visual field in both eyes
Reference to both left and right eyes is required
Question
The hippocampus plays an important role in memory and spatial navigation. A larger hippocampus relative to brain volume has been associated with better spatial memory in birds. Two subspecies of the white-crowned sparrow, Zonotrichia leucophrys gambelii (migratory) and Zonotrichia leucophrys nuttalli (non-migratory) were compared. The graph shows the relationship between the volumes of the hippocampus and the brain in adult and young sparrows.

Relative hippocampal volume is the ratio between the volume of the hippocampus and the volume of the whole brain (hippocampus/brain).
State the relationship between brain volume and hippocampal volume in the non-migratory sparrows.
Compare the hippocampal volume in migratory and non-migratory young and adult sparrows.
Analyse the data in the scattergraph to find which of the four groups of birds has the highest relative hippocampal volume.
Suggest a reason why this group needs the largest relative hippocampal volume.
It is possible that non-migratory species possess more advanced cognitive skills other than spatial memory. Use the data to evaluate this hypothesis.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
as brain volume increases so does hippocampus volume / positive correlation
hippocampus volumes are larger in adults than in young birds;
larger range for migratory;
young non-migratory show wider range of hippocampus volumes than young migratory;
some overlap for non-migratory / none for migratory;
adult migratory (as for any brain volume this group has the largest hippocampal volume) } (allow mathematical explanation)
needed for migration / only adults migrate/remember flight paths
(Do not accept spatial navigation on its own without reference to migration)
Hypothesis supported:
non-migratory have larger brain volume;
larger brain implies more thinking skills;
hippocampus in non-migratory is approx same size as in migratory;
Hypothesis not supported:
only two species/small sample studied so over generalization;
similar hippocampus volume in both migratory and non-migratory birds;
Question
Discuss the correlation between diet and brain size.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
improved diet quality correlated (positively) with hominid skull development/size;
improved diet quality provides energy to support a greater brain function;
change of habitat (in Africa) 2.5 mya may have prompted emergence of Homo sp;
change in diet to include meat increased brain size (of hominids);
cooking food enabled hominids to eat a wider variety of food;