IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
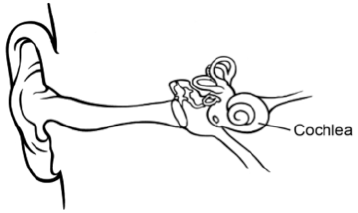
The image shows a human ear.
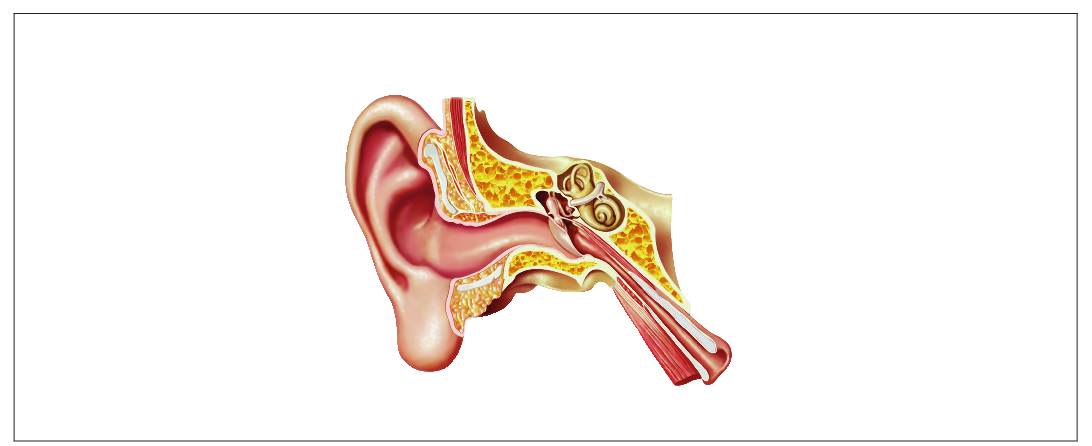
[Source: Leonello/iStock]
Using the letter M, label the structures which detect movement of the head.
Using the letter A, label where sound is amplified.
Explain the function of the cochlea in hearing.
Outline how the hearing of a deaf or partially deaf person could be improved.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Example of answer for part (a)(i)
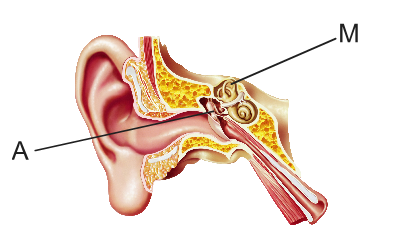
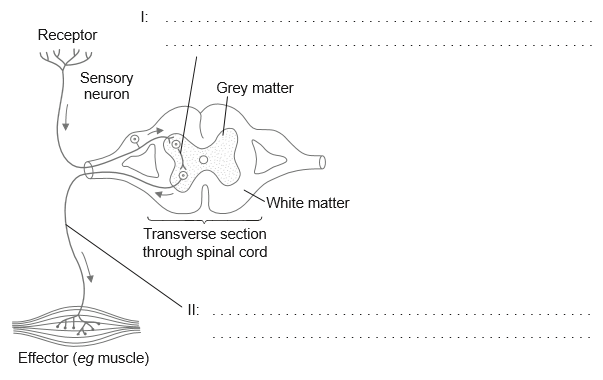
The candidate should label the semicircular canals
Line with the letter M is expected but accept the letter M on diagram if clearly indicating the correct structure
Example of answer for part (a)(ii)
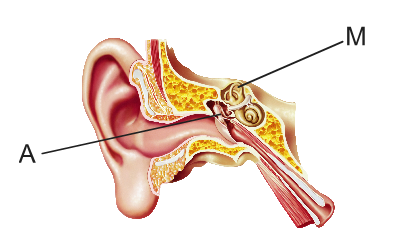
The candidate should label the bones/ossicles in middle ear
Line with the letter A is expected but accept the letter A on diagram if clearly indicating the correct location
a. sound «waves» enters the ear causing fluid in the cochlea to move/vibrate
b. «movement of fluid in cochlea» causes the hair cells to move
c. «details of hair cell movement» is transmitted to brain via the auditory nerve
[Max 2 Marks]
hearing aid/cochlear implant
Answer must refer to ear, not for example just “operation”
Accept other valid answers
Question
The diagram shows part of a retina.
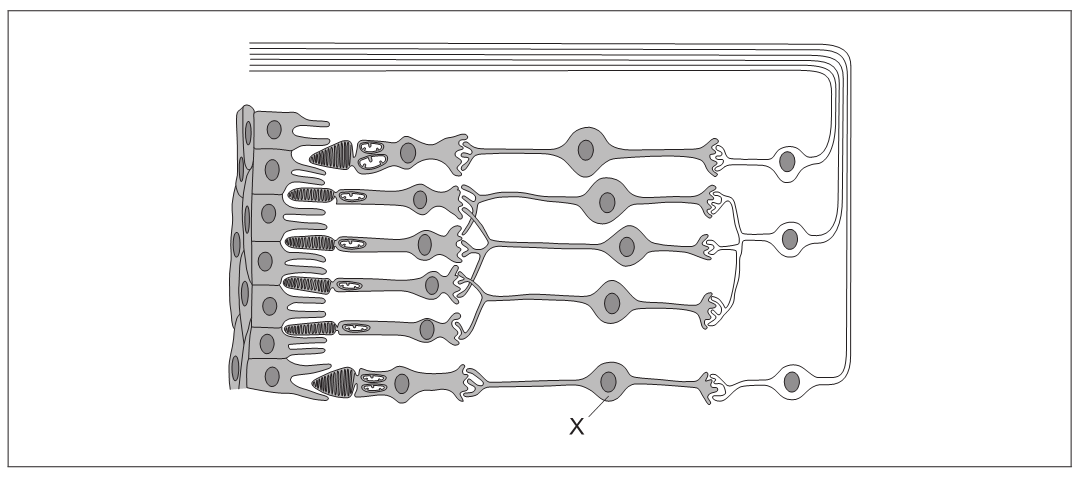
[Source: C. J. Clegg, Introduction to Advanced Biology, 2000, p. 285. Reproduced by permission of Hodder Education.]
Identify the cell labelled X.
Draw an arrow to show the direction of light through the retina.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
bipolar «cell»
arrow pointing from right to left
Question
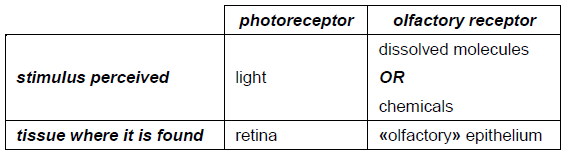
The diagram shows a photoreceptor and an olfactory receptor. The arrows show the direction of the stimulus.
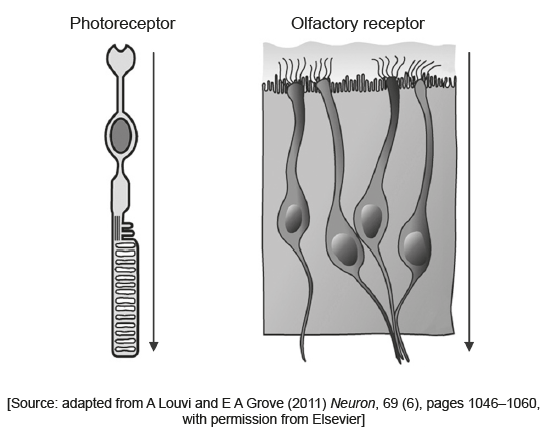
State the name of the photoreceptor shown.
Distinguish between a photoreceptor and an olfactory receptor.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
rod
Question
The diagram shows the anatomy of the human ear.
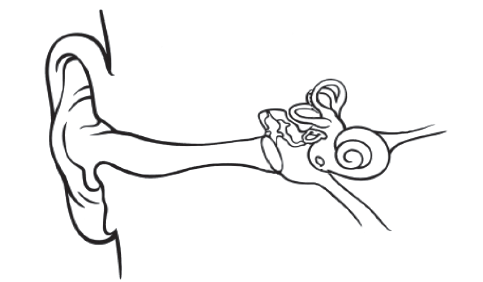
Label the cochlea on the diagram.
Explain the structure of the semicircular canals in relation to their functions.
Explain the role of ganglion cells in the eye.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. there are three semi-circular canals set perpendicular to one another /orientated in three planes of space / the direction of movement of the head in any direction is sensed
b. each canal is filled with liquid/perilymph
c. each canal contains «sensory» hairs
d. when the head moves the liquid in the canal moves more slowly/lags behind
e. this causes the sensory hairs to bend
f. send impulses to the brain «via the vestibular nerve»
a. ganglion cells transfer information to the brain
b. they receive visual information from photoreceptors/rod and cone cells/bipolar cells
c. their long axon extends to the brain «in the optic nerve»
d. they detect/process movement/colour
Question
The image shows a human eye.
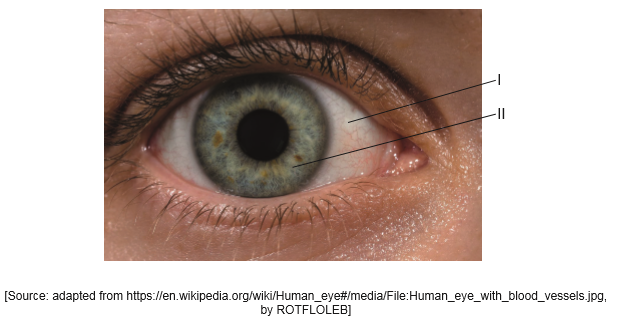
Identify the structures labelled I and II
Explain how the pupil of the eye can be used to assess brain damage.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: conjunctiva/sclera
AND
II: iris/cornea
To award [1] both answers are needed.
a. bright lights causes the pupil to constrict/iris to increase in size
b. low light causes the pupil to dilate/iris decrease in size
c. these are reflex actions
d. the test for brain damage is to (briefly) shine a bright light in the eyes
e. slow or unresponsive change in pupil size indicates brain damage/concussion
f. different response of each eye indicates brain damage/concussion
Question
To test hearing, sounds are played at very low volume levels and gradually increased until the patient can hear the sound. This is repeated with different frequencies which correspond to low or high pitch sounds. The results are marked on an audiogram. This audiogram is from a 60-year-old woman.
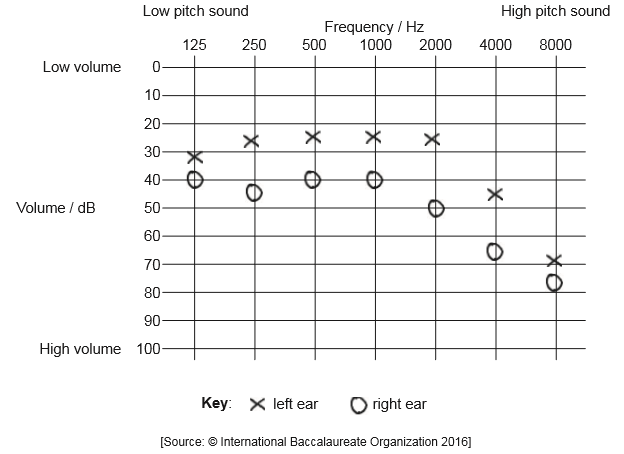
Human speech occurs at a volume of approximately 60 dB and at frequencies between 125 Hz and 4000 Hz. Outline whether the woman would hear all conversations with both ears.
The woman suffers from otosclerosis in the right ear, a condition where the bones of the middle ear do not function properly. Describe how this is consistent with the hearing test result shown in the audiogram.
Explain the role of the hair cells in the cochlea.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
left ear would hear everything but the right ear would not «at higher frequencies»
OR
cannot hear all high frequencies of speech (with both ears)
Allow numerical responses in support of the answer.
a. the bones in the middle ear amplify/make sounds louder
b. the audiogram shows the woman needs louder sounds to hear with her right ear
Allow vice versa.
Could use data to support answer.
a. sounds/vibrations make the fluid/liquid in the cochlea move/vibrate
b. amount of movement is proportional to the amplitude /loudness/ of the sound OWTTE.
c. amount of movement is proportional to the frequency/wavelength/pitch
d. hair cells located within organ of Corti
e. (hair cells have) nerve cells connected to auditory nerve
OR
nerve cells transmit impulses to brain
Question
Outline the nervous system processes involved in reading and responding to this question.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Photoreceptors in the retina detect reflected light/stimulus «from the page» (Accept rods and cones in place of photoreceptors).
Transmitted via the optic nerve to the visual cortex/brain/occipital lobe
Interpreting occurs in the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex involved in thinking
Cerebral cortex involved in memory
Motor/cerebral cortex involved in motor control
OR
motor neurons send impulses to muscle to move
Broca’s area is a region in the cortex linked to speech production
Question
Explain the functioning of hair cells in the semicircular canals of the inner ear.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«Sensory hair cells found in semicircular canals» detect movement of the head
Fluid in the canals lags behind movement of head
OR
inertia of fluid makes it move more slowly than head
Fluid movement causes “hairs” of hair cells to bend
Bending of hairs causes nearby sensory neuron to conduct signal
Hairs in all three semicircular canals «which are at right angles so» detect head movement in any direction
Signals passed on to the nerve/brain
Question
State the type of receptors that detect smell and temperature.
Smell: …………………………………………………
Temperature: …………………………………………………
Annotate the diagram of the reflex arc to show the name and function of the neurons labelled I and II.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. smell: chemoreceptor; (do not accept olfactory)
b. temperature: thermoreceptors;

Question
Lizards living in the Kalahari Desert of southern Africa are diurnal (active in daylight). Scientists studied this rhythmical behaviour during different seasons of the year. Observations were made of the number of lizards active each hour and this was recorded as a percentage of the total number of lizards that were active. The graph shows the results for the Southern Spiny Agama (Agama hispida) lizard. Between the hours of 19:00 and 7:00 the lizards were inactive.

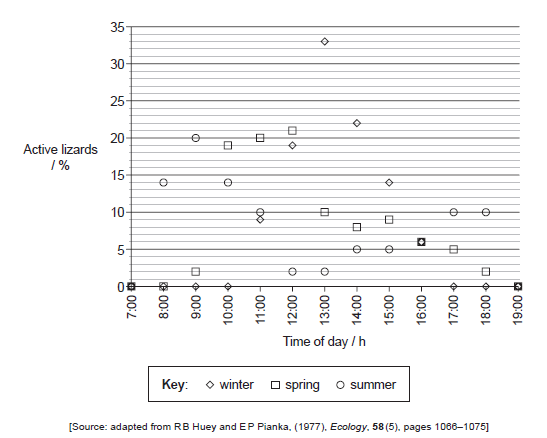
State one time in spring when 5 % of the lizards were active.
Winter and summer weather conditions differ in the Kalahari Desert. Compare the results for summer and winter.
The temperatures differ in summer and winter. Suggest one other possible reason why the lizard activity differs in summer and winter.
The body temperature of the lizard is similar to environmental temperature. State the type of receptors that could detect changes in external temperature.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
17:00
a. change in behaviour/availability of their prey/food sources;
b. changes in presence of predators;
c. protection from sun (in the middle of the day in summer);
d. amount of daylight hours (is reduced in winter);
Do not accept answers related to temperature eg: cold blooded or poikilothermic.
thermoreceptors/thermo
Question
Identify the type of retinal cells that function best in dim light.
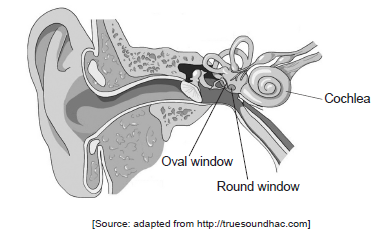
The image shows the human ear.
Outline the role of the round window in the perception of sound.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
rods
a. allows fluid in the cochlea to move;
b. as oval window moves in, round window moves out / vice versa;
Question
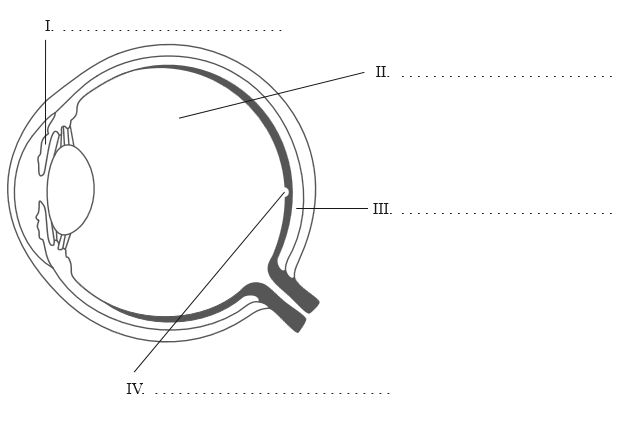
Label the following diagram of the eye.
Outline the diversity of stimuli that can be detected by human chemoreceptors.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I iris
II vitreous humour
III choroid
IV fovea (do not accept yellow spot)
Award [1] for every two correct answers.
a. (dissolved) chemicals detected by taste buds (in the tongue and mouth);
b. (airborne) chemicals detected by (olfactory) receptors;
c. chemicals/ions/pH in blood (for example CO2/glucose) detected by chemoreceptors (in carotid artery/medulla oblongata);
d. neuroreceptors detect neurotransmitters;
Question
State the missing cell type in the sequence encountered as light enters the retina.

Answer/Explanation
Markscheme

Question
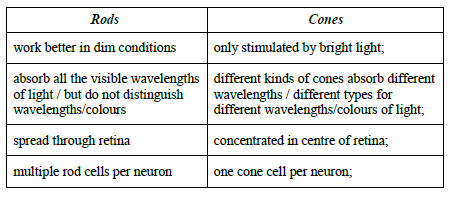
Using the table below, distinguish between rod cells and cone cells.
Outline how sound is perceived in the ear.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
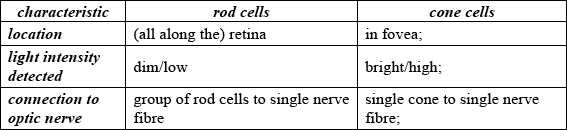
Award [1] for each correct row.
sound waves make eardrum/tympanic membrane vibrate;
vibration passes along the bones of middle ear/ossicles/malleus, incus and stapes making oval window vibrate;
vibration passed to fluid in cochlea;
vibration in cochlea stimulate hair cells/mechanoreceptors;
nerve impulse passed to auditory nerve;
Question
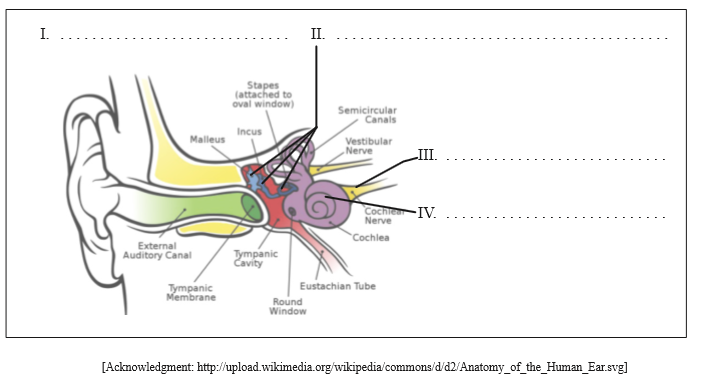
Label the diagram of the ear.
Explain how the cochlea functions during hearing.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Award [1] for any two of the following correctly identified.
I. pinna;
II. bones of the middle ear/ossicles/malleus, incus and stapes;
III. auditory nerve;
IV. cochlea;
bone/ossicle/stapes contacts oval window of cochlea;
ossicle vibrations are transmitted to cochlear fluid via the oval window;
cochlear fluid vibrations cause movement of (basilar) membrane (in precise areas);
movement depends on membrane width and thickness in specific area;
movement causes shearing motion of hair bundles projecting from hair cells attached to membrane;
stimulated hair cells generate action potential that arrive in the brain via auditory nerve;
Question
Compare rod and cone cells.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
rods and cones are both light-sensitive cells;
rods are far more numerous than cones;
rods are distributed evenly throughout the retina while cones are particularly concentrated at and around the fovea;
rod cells are all the same/black and white vision but there are three types of cone cells (absorb red, blue and green colour)/colour vision;
rod cells absorb all the visible wavelengths but each type of cone cell absorbs a different range;
rods are longer and thinner, cones have cone shape;
rod cells are principally used for dim light and night vision while cone cells require bright light / rods give poor visual acuity while cones give good visual acuity;
the pigment in rod cells is rhodopsin while in cone cells is iodopsin;
each individual cone cell is fed to a single (bipolar) neuron, whereas many rod cells synapse with a single (bipolar) neuron;
Question
List two dietary sources of vitamin D.
State an example of these receptors in humans.
Discuss exposure to sunlight as a source of vitamin D.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
e.g. cod liver oil / fish liver oil / oily fish (accept correctly named example) / egg yolk / fortified cereal / ONE named dairy product (i.e. milk/cheese/ yoghurt)
Allow any two sources for the mark. Reject fish alone.
hair cells of cochlea
UV light/sunlight on skin causes chemical production of vitamin D;
UV too low in winter in high latitudes;
vitamin D stored in liver so can make enough to last several months/through winter;
UV light can damage skin and cause skin cancer so exposure needs to be limited;
use of sun-block will inhibit vitamin D production;
covering skin with clothing prevents UV reaching skin; Accept reference to cultural/religious customs
Question
State the type of receptor cells that detect sound.
Outline the role of inheritance and learning in the development of birdsong in young birds.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
mechanoreceptor
inheritance plays role as basic song is the same for all members of a species;
birds raised in isolation still sing but song lacks complexity/sounds different from song heard in the wild / more complex songs develop when there is social interaction;
young birds learn details of songs/dialects from fathers/other birds;
(development of birdsong) is a form of motor learning/ability to learn is genetic/inherited;
Question
List two groups of sensory receptors, giving the stimulus each perceives.
Explain the processing of visual stimuli.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
mechanoreceptors – pressure;
chemoreceptors – chemical substances/pH;
thermoreceptors – temperature;
photoreceptors – light;
mechanoreceptors/proprioceptors – stretching/pressure;
hydroreceptors – humidity;
Accept other appropriate receptors with a stimulus.
retina/rod/cone cells convert light into impulses;
impulses pass to bipolar cells;
bipolar cells pass impulses to (sensory neurons of) the optic nerve;
at the optic chiasma, impulses cross over to the opposite optic nerve;
impulses continue to the thalamus where optical information is processed;
images form in the visual cortex;
Question
The diagram below shows a reflex arc.
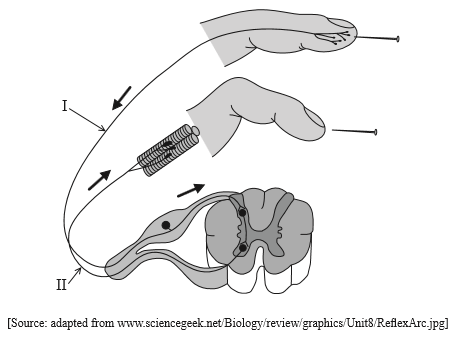
Label I and II.
I. …………………………………………………………
II. …………………………………………………………
Outline how stimuli can be detected by human sensory receptors.
Explain how sound is perceived by the ear.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
I: sensory neuron
II: motor neuron
(both needed)
sensory receptors transfer stimulus energy into electrochemical energy;
mechanoreceptors respond to touch/pressure/movement/sound waves;
thermoreceptors respond to temperature changes;
chemoreceptors detect chemicals/molecules;
photoreceptors respond to electromagnetic stimulation/light;
sound waves are (funneled through the ear canal) causing ear drum to vibrate;
vibrations of ear drum cause the bones of the middle ear/ossicles/malleus, incus and stapes/hammer, anvil and stirrup to move;
lever system of middle ear bones increases pressure on the oval window;
vibrations are transmitted from oval window through (fluid-filled) cochlea;
stimulation of hair cells/mechanoreceptors in cochlea;
vibrations are transformed into nerve impulses/action potentials;
impulse sent to brain along auditory nerve;
Question
Explain how sound is perceived by the ear.
Hearing is a result of the stimulation of mechanoreceptors. List three other main types of receptors.
1. …………………………………………………………
2. …………………………………………………………
3. …………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
sound (waves) vibrate eardrum/tympanic membrane;
movement is magnified by ossicles/middle ear bones;
oval window vibrates / fluid in cochlea moves and moves hairs in cochlea;
different frequencies detected by different parts of cochlea membrane and hair cells;
these are connected to the auditory nerve;
chemoreceptors / photoreceptors / thermoreceptors / baroreceptors
Award [1] for three correct receptors.
Question
Outline Pavlov’s experiments into the conditioning of dogs.
Outline how sound stimuli are detected in the ear.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. classical conditioning;
b. Pavlov sounded a bell before food / conditioned stimulus;
c. dogs salivated when they heard the bell / conditioned response;
d. the amount of salivation after the bell was as great as when the food alone was presented;
e. dogs had learnt to associate the two external stimuli;
a. sound waves reaching eardrum cause it to vibrate;
b. vibrations passed to bones of middle ear/oval window/fluid in cochlea;
c. detected by mechanoreceptors/hair cells (in cochlea of ear);
Question
Compare rods and cones.
Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons and motor neurons in the response of animals to stimuli.
List four general kinds of sensory receptor.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
receptors detect stimuli;
transmit information regarding stimuli to the central nervous system;
via sensory neurons;
central nervous system sends impulse to effector;
via motor neuron;
Award [1] for every two correct answers.
thermoreceptor / chemoreceptor / photoreceptor / mechanoreceptor / baroreceptor / propioceptor