Question
This light micrograph shows skeletal muscle
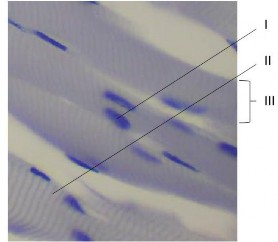
Identify
the dark structure indicated by I [1]
the protein producing the thick filament in the dark band indicated by II. [1]
the structure indicated by III [1]
Discuss whether the tissue shown in the micrograph consists of cells or not [2]
Explain how calcium is involved in muscle contraction [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a i nucleus
a ii myosin
a iii muscle fibre/muscle cell Reject myofibril because it would be much narrower – diameter 1 to 2 μm.
b
a «muscle fibres are» multinucleate/contain many nuclei «whereas cells are expected to have only one/so muscle fibers are an exception to the cell theory»
b one cell membrane/sarcolemma enclosing a whole muscle fibre «as expected for cells»
c very large/much larger/longer/than most cells
d muscle fibres formed by fusion of cells/are syncytia
c
a action potential/nerve impulse causes release of calcium
b from sarcoplasmic reticulum/specialized endoplasmic reticulum
c binds to troponin
d causes tropomyosin to move/be removed «from binding sites»
e exposes myosin-binding sites on actin/allows myosin «heads» to bind to actin
Question
Defence occurs on the micro and macro levels.
Describe the functioning of immunoglobulins.
Outline how antibiotics offer protection from certain forms of infectious disease.
Coughing to clear the airways is accomplished by muscle contractions. Explain muscle contraction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «immumoglobulins are/function as» antibodies
b. variety of binding sites / variable regions for binding
c. specific to antigens on bacteria/viruses/pathogens
d. constant region aids destruction of the bacteria/virus/pathogen
e. attracts phagocytes/macrophages to engulf pathogen
f. bursting pathogen cells/agglutination/neutralizing toxins/other example of the action of antibodies
Award marks for an annotated diagram.
a. protect against/kill/inhibit growth of microorganisms/bacteria/prokaryotes
b. bacteria/prokaryote processes blocked but not processes in eukaryotes/other organisms
c. block metabolic pathways/DNA replication/DNA transcription/translation/ribosome functioning/cell wall formation
d. do not protect against viruses as they have no metabolism/are non-living
e. antibiotics fail to protect if bacteria have resistance
f. can be used in humans/animals because antibiotics do not affect eukaryotic cells/bacterial metabolism is different
a. myofibrils «in muscle fibers/cells»
b. sarcomeres «are the repeating units in muscle/myofibrils»
c. sarcomeres arranged end to end / sarcomeres shorten during muscle contraction
d. actin and myosin/overlapping protein filaments/diagram to show sarcomere with actin and myosin overlapping
e. dark and light bands «in sarcomeres»/diagram to show this/light bands narrower when muscle is contracted
f. thick filament is myosin and thin filament is actin/diagram to show this
g. nerve impulses stimulate contraction/cause depolarization of sarcolemma/T-tubules/trigger release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum
h. calcium ions released from sarcoplasmic reticulum/bind to troponin
i. troponin causes tropomyosin to move/exposes binding sites on actin
j. myosin «heads» form cross bridges with/bind to actin
k. myosin heads move/change angle/swivel/cock / myosin heads cause the power stroke
l. myosin filaments pull actin towards center of sarcomere/more overlap between actin and myosin/Z-lines move closer
m. ATP is used «to provide energy»/cause cross-bridges to break/cause movement of myosin heads/cause filaments to slide/cause muscle contraction
n. intercostal/abdominal/diaphragm muscles contract «to cough»
Marks can be awarded for any point made clearly on an annotated diagram.
Question
Explain how skeletal muscle contracts.
Active skeletal muscle requires a good supply of oxygen. Outline the mechanism of ventilation in the lungs.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. sliding filament model / filaments/actin and myosin slide past each other;
b. action potential/depolarisation/nerve impulse arrives at end of motor neurone;
c. neurotransmitter/acetylcholine released causing action potential (in muscle fibre);
d. sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions;
e. calcium ions cause binding sites on actin/for myosin to be exposed;
f. myosin heads bind to sites on actin/form cross-bridges;
g. myosin (head) moves actin filament using energy from ATP;
h. actin moved towards the centre of sarcomere/M line/M band;
i. sarcomeres shortened;
j. (binding of) ATP causes release of myosin head from actin;
k. conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi causes myosin heads to change angle;
l. cycle (of events) repeated (during muscle contraction);
Accept the above points in annotated diagrams.
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
during inhalation:
a. external intercostal muscles contract moving rib cage up and out;
b. diaphragm contracts becoming lower/flatter;
c. increase in volume and decrease in pressure (of thorax);
d. air flows into lungs as atmospheric pressure is higher;
during exhalation:
e. internal intercostal muscles contract so ribs move in and down;
f. diaphragm relaxes and returns to domed shape;
g. decrease in volume and (therefore) increase in pressure (of thorax);
h. air moves out until pressure in lungs falls/is equal to atmospheric pressure;
i. abdominal muscles can be used to make a stronger/forced exhalation;
Question
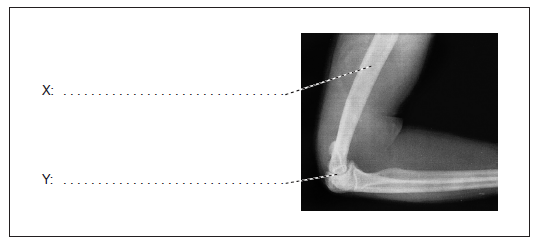
Label the structures indicated on the X-ray of a human elbow.
Explain the role of calcium in muscle contraction.
One of the stages of aerobic respiration is called the link reaction.
Label the diagram to indicate where the link reaction occurs.
Outline the role of coenzyme A in aerobic respiration.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
X: humerus;
Y: synovial fluid / cartilage / joint capsule / elbow joint;
action potential/nerve impulse/motor neuron causes release of calcium;
calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum;
calcium causes binding sites on actin to be exposed;
myosin heads bind to binding sites/to actin and push actin (inwards);
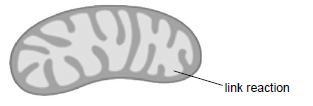
Accept a line or arrow pointing to any part of the matrix, or a circle in it. It is not necessary to state link reaction unless more than one area is indicated.
accept/bind acetyl group/acetate / acetyl coenzyme A/acetyl CoA formed;
passes acetyl group/acetate to Krebs cycle;