IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 3.5 Genetic modification and biotechnology
Topic 3 Weightage : 23%
All Questions for Topic 3.5 – polymerase chain reaction, Gel Electrophoresis, DNA Profiling, Gene Transfer, GMO Debate, Clones, Natural Cloning, Artificial Cloning, Stem Cuttings, Vector Delivery, Examples of GMOs, cDNA and Microarrays, Gene Therapy, Gene Silencing
Question
What benefit is derived from the use of Bt crops?
It can lead to an increase in genetic diversity of crop species.
Genetically modified species can interbreed with native species.
The numbers of monarch butterflies can be permanently reduced.
It can lead to a reduction in the use of pesticides.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
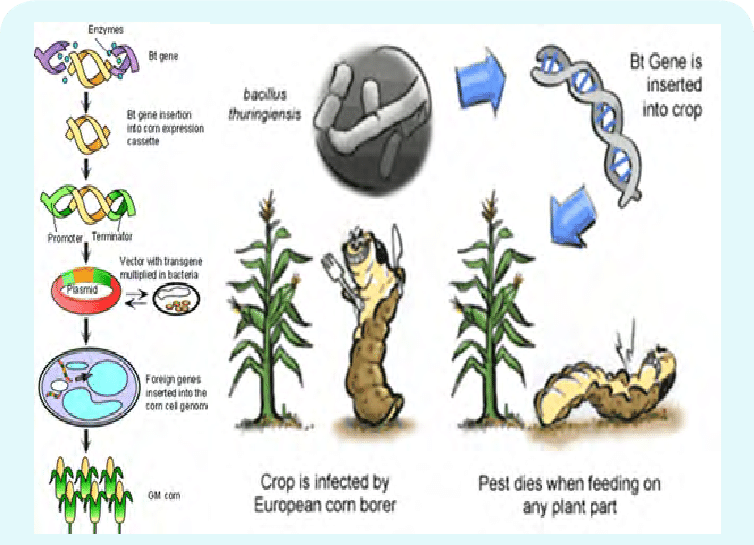
Bt crops are genetically modified crops that produce their own insecticides. As a result, they use significantly less pesticides than their conventional/organic counterparts. Non-GMO crops are frequently sprayed with insecticides; whereas the Bt GMOs produce their own insecticides, which greatly reduces the need for spraying pesticides. This reduction in pesticide use improves crop yield, reduces fungal toxins in the food supply, and improves the livelihood of farmers. Replacing toxic chemical pesticides with Bt has reduced hazards to the environment and farm workers.
Question
A two-cell sea urchin (Echinoidea) embryo was physically separated by scientists into two cells.
Each cell, through further embryonic development, became an adult sea urchin.
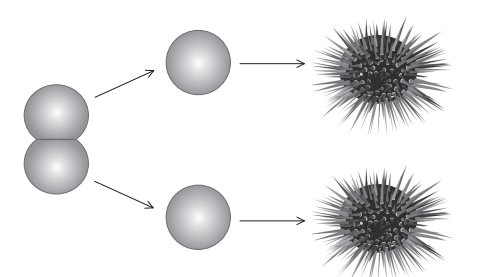
What is the relationship between the two adult sea urchins?
They are equivalent to non-identical twins.
Half of the genes would be the same.
Both adults would have haploid cells.
They are clones.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
When a cell is separated into two cells by scientists, each cell will develop into a separate embryo. If the two embryos are implanted into the uterus of a female animal and carried to term, they will be genetically identical clones.
Hind III is an endonuclease that recognizes the sequence A A G C T T, cutting between the two adenines.

Into how many DNA fragments would the strand shown be cut by HindIII?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Ans:B
- AAGCTT is the restriction site of the enzyme Hind III.
- It is palindromic in nature.
- It cleaves the sequence AAGCTT between the AA in presence of Mg+2 to give 5‘ overhangs, also called sticky ends.
- This enzyme is present in Haemophilus influenza hence the name Hind III
NOTE: In given fragment of DNA there are only two restriction site of the enzyme Hind III are clearly visible, so answer will be “A”
What is produced by somatic-cell nuclear transfer?
A. Adult sheep
B. Cloned embryos
C. Rooted stem-cuttings
D. Genetically modified food
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
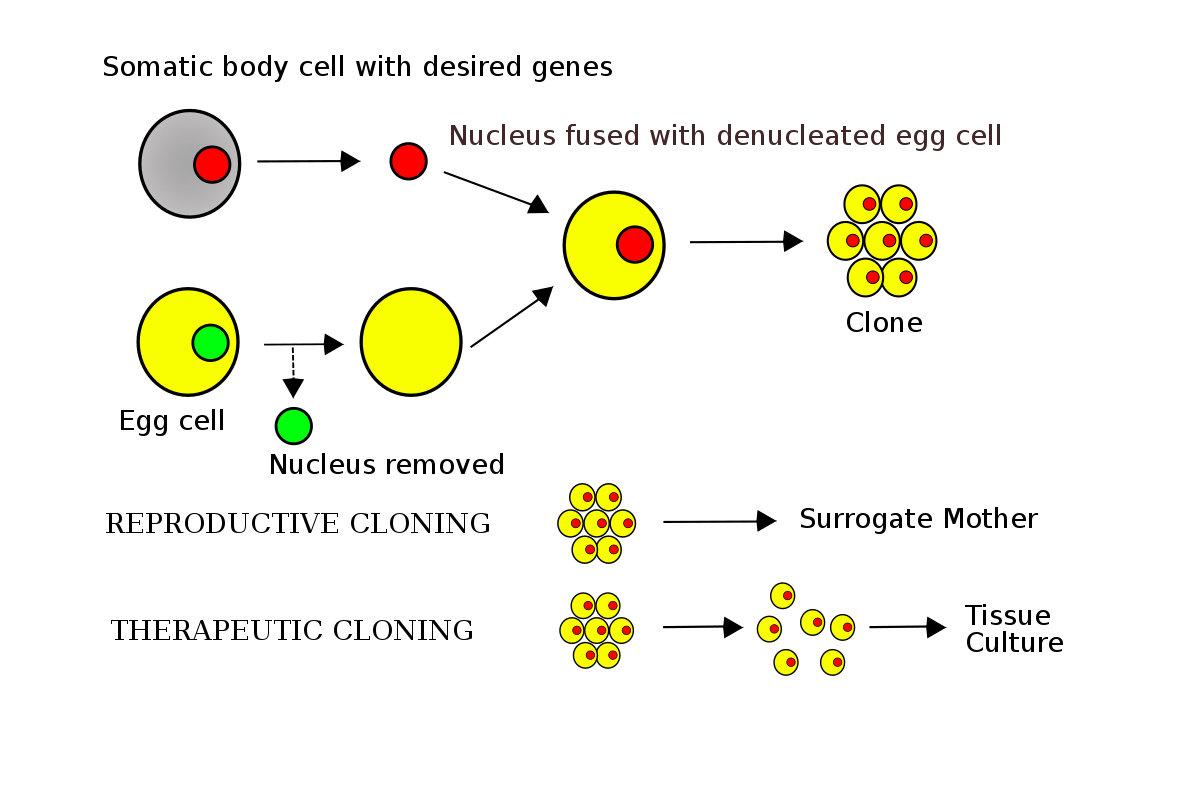
Somatic cell nuclear transfer is a laboratory strategy for creating a viable embryo from a body cell and an egg cell. Embryos produced by nuclear transfer from a patient’s somatic cell offer one potential source of embryonic stem cells for treatment of human degenerative diseases. The technique consists of taking an enucleated oocyte (egg cell) and implanting a donor nucleus from a somatic (body) cell. It is used in both therapeutic and reproductive cloning.
Which technique separates proteins according to size?
A. Treatment with restriction endonucleases
B. PCR
C. Gel electrophoresis
D. DNA profiling
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
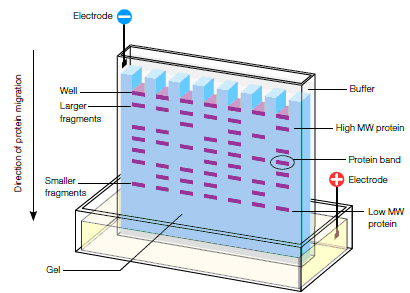
Gel electrophoresis of proteins is a technique that separates proteins based on their size or charge by applying an electric field to a gel matrix. The gel matrix is usually made of polyacrylamide, which has pores that affect the frictional coefficient of the proteins. Smaller proteins move faster through the gel matrix than larger proteins.
Question
A process for genetically modifying a plant is shown.
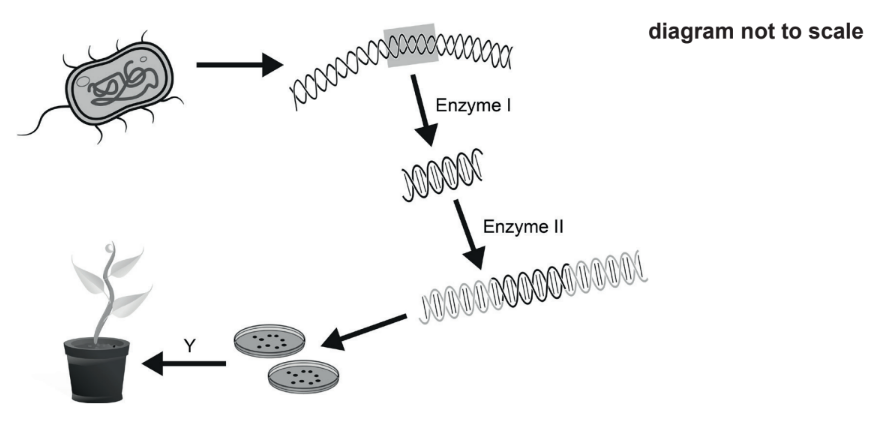
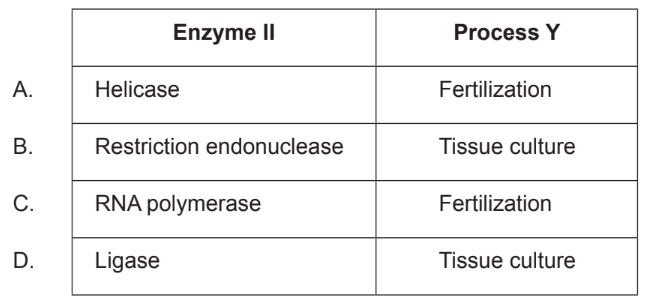
What is the name of enzyme II and the name of process Y?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Ligase is an enzyme that is used to join two DNA fragments together. In tissue culture, ligase is used to insert a gene of interest into a plasmid vector. The plasmid vector is then introduced into the plant cells using a variety of methods such as Agrobacterium-mediated transformation or biolistic transformation.