IB Biology HL (HIGHER level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 4.2 Energy flow
Topic 4 Weightage : 8%
All Questions for Topic 4.2 – Energy Source, Energy Flow, Energy Loss, Energy Efficiency, Pyramids of Energy, Ecological Productivity, Food Webs, Ecological Pyramids, Biomagnification
Question
The diagram shows the energy flow between five “sinks” in a terrestrial ecosystem.
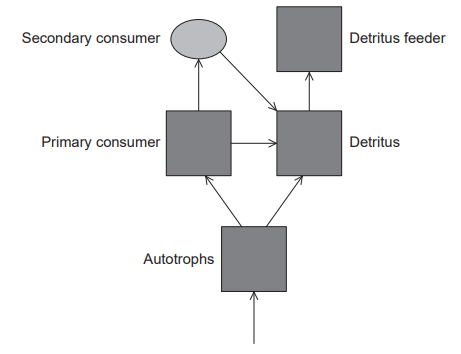
In a typical terrestrial ecosystem, which trophic level would have the highest biomass?
Autotrophs
Primary consumers
Secondary consumers
Detritus feeders
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Autotrophs are organisms that can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Because they are able to produce their own food, autotrophs are at the base of the food chain and are the primary producers of organic matter. As a result, they have the highest biomass of any trophic level. This is because they are able to convert energy from the sun or chemicals into organic matter, which can then be used by other organisms in higher trophic levels. As energy is transferred up the food chain, some of it is lost as heat, so there is less energy available to organisms at higher trophic levels. This means that the biomass of organisms at higher trophic levels is typically lower than that of autotrophs.
The diagram represents a pyramid of energy.
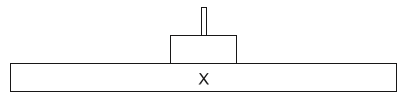
What level does the letter X represent?
A. Light
B. Primary consumers
C. Abiotic environment
D. Producers
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
X represents producer and are used as a source of energy and as building blocks for growth and development. Because producers are able to produce their own food, they form the base of the food chain in most ecosystems. Other organisms, such as herbivores and carnivores, rely on producers for their energy needs, since they are not capable of producing their own food. Without producers, most ecosystems would not be able to support life, since there would be no source of energy for other organisms to consume. Producers are typically plants or algae that use energy from the sun or from chemical reactions to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds such as sugars and starches.
The statement is about the role of some bacteria in ecosystems.

What is the mode of nutrition of these bacteria?
A. They are autotrophs.
B. They are consumers.
C. They are saprotrophs.
D. They are detritivores.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C
Saprotrophic bacteria play an important role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil. These bacteria are responsible for the process of decomposition, which is the breakdown of dead plants and animals into their component parts. As the bacteria break down the organic matter, they release nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the soil, where they can be taken up by plants and used to support new growth. This process is essential for the health of the ecosystem, since it helps to recycle nutrients and keep the soil fertile. In addition, saprotrophic bacteria can help to break down pollutants and other harmful substances in the environment, making them less toxic and easier to remove. Overall, saprotrophic bacteria are an essential part of the ecosystem, helping to maintain the balance of nutrients and supporting the growth of new life.
The following shows an energy pyramid.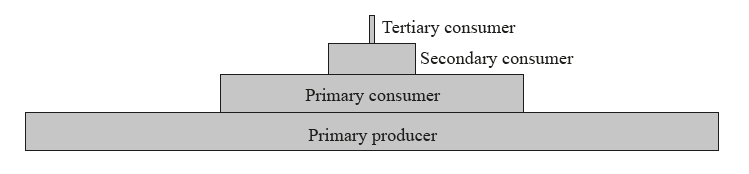
How is energy lost between the trophic levels?
A. photosynthesis, birth of an organism and digestion
B. respiration, death of an organism and egestion
C. recycling of nutrients, death of an organism and egestion
D. respiration, birth of an organism and digestion
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Energy is lost between trophic levels because organisms use some of the energy they consume for their own metabolic processes, such as respiration. Additionally, not all of the energy in the food that an organism consumes is assimilated into its body; some of it is egested as waste. When organisms die, their biomass is decomposed by microorganisms, which also require energy to carry out their metabolic processes. All of these factors contribute to the loss of energy between trophic levels.
This question refers to the following food web.
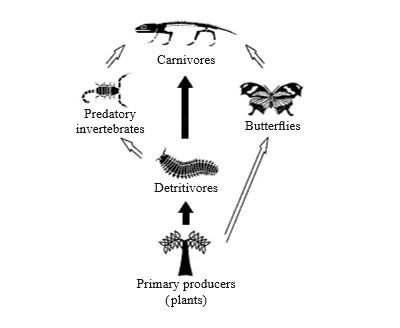
The energy passing from the detritivores to the predatory invertebrates in this food web is 14 000 kJ m–2 year–1. Approximately how much energy (in kJ m–2 year–1) passes from the predatory invertebrates to the carnivores?
A. 140
B. 1400
C. 14 000
D. 140 000
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The energy passing from the detritivores to the predatory invertebrates in this food web is 14 000 kJ m–2 year–1, generally on average, 90% of an organism’s energy is used for its life processes and only 10% is passed on to its predator in the next trophic level. So 10% of energy (1400 kJ m–2 year–1) will pass from the predatory invertebrates to the carnivores.
Question
What is a difference between detritivores and saprotrophs?
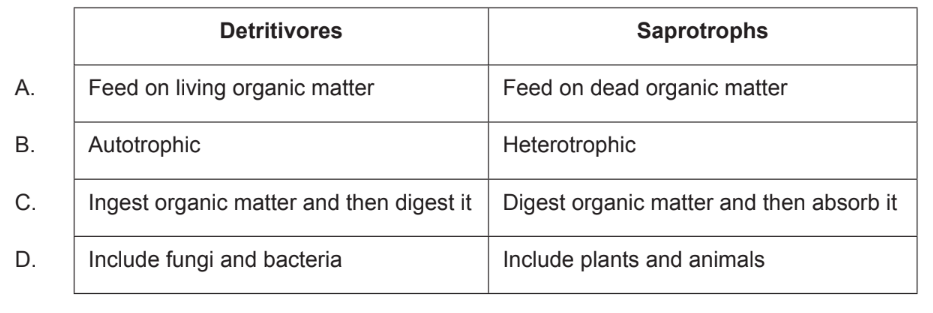
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
A key difference between detritivores and saprotrophs is that detritivores are organisms that consume dead and decaying organic matter, while saprotrophs are organisms that break down dead and decaying organic matter externally, through the use of enzymes. Detritivores, such as earthworms and woodlice, feed on dead organic matter, breaking it down internally and extracting nutrients from it. In contrast, saprotrophs, such as fungi and bacteria, release enzymes that break down organic matter outside of their bodies, and then absorb the resulting nutrients. Another difference is that detritivores are typically larger organisms, while saprotrophs are typically microscopic. Detritivores play an important role in breaking down organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil, while saprotrophs are important decomposers that help to break down dead organic matter in a wide range of environments.
Question
A self-sustaining system is set up in a sterile, sealed, transparent glass bottle with damp, sterilized soil and a small garden plant. If the system remains sterile, what could be the reason that the plant fails to grow and dies?
A. Lack of soil nutrients
B. Lack of oxygen
C. Lack of space
D. Lack of water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The lack of soil nutrients can impact the growth of a plant in a self-sustaining system set up in a sterile, sealed, transparent glass bottle with damp, sterilized soil because plants require a variety of nutrients to grow and thrive. Without these nutrients, the plant may be stunted or may not grow at all. In a self-sustaining system, the nutrients that are present in the soil are the only source of nutrition for the plant, so if these nutrients are not present in sufficient quantities, the plant will suffer. In addition, the sealed nature of the system means that there is no way for new nutrients to enter the system, so the plant is entirely dependent on the nutrients that are already present in the soil. Over time, these nutrients may be depleted, which can further impact the growth of the plant. To prevent this, it is important to carefully monitor the nutrient levels in the soil and to add additional nutrients as needed to ensure that the plant has the resources it needs to grow.
Question
A self-sustaining system is set up in a sterile, sealed, transparent glass bottle with damp, sterilized soil and a small garden plant. If the system remains sterile, what could be the reason that the plant fails to grow and dies?
A. Lack of soil nutrients
B. Lack of oxygen
C. Lack of space
D. Lack of water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The lack of soil nutrients can impact the growth of a plant in a self-sustaining system set up in a sterile, sealed, transparent glass bottle with damp, sterilized soil because plants require a variety of nutrients to grow and thrive. Without these nutrients, the plant may be stunted or may not grow at all. In a self-sustaining system, the nutrients that are present in the soil are the only source of nutrition for the plant, so if these nutrients are not present in sufficient quantities, the plant will suffer. In addition, the sealed nature of the system means that there is no way for new nutrients to enter the system, so the plant is entirely dependent on the nutrients that are already present in the soil. Over time, these nutrients may be depleted, which can further impact the growth of the plant. To prevent this, it is important to carefully monitor the nutrient levels in the soil and to add additional nutrients as needed to ensure that the plant has the resources it needs to grow.